NCERT Summary: International Trade | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Changing Patterns of the Composition of India’s Exports |

|
| Changing Patterns of the Composition of India’s Import |

|
| Sea ports as Gateways of International Trade |

|
| Airports |

|
Introduction
 International Trade
International Trade
- Mutual Benefits: International trade is essential as no country can achieve self-sufficiency.
- Recent Changes: India’s international trade has significantly evolved in volume, composition, and direction over recent years. Despite contributing only about 1% to global trade, India plays a vital role in the world economy.
- Growth in Trade Volume: In 1950-51, India’s external trade was valued at Rs. 1,214 crore, increasing dramatically to Rs. 77,19,796 crore by 2020-21, indicating substantial growth.
- Factors for Growth: Key reasons for the rise in trade include:
1. Growth in manufacturing sectors
2. Liberal government policies
3. Diversification of markets - Import-Export Dynamics: While the total volume of imports and exports has increased, imports consistently exceed exports in value.
Changing Patterns of the Composition of India’s Exports
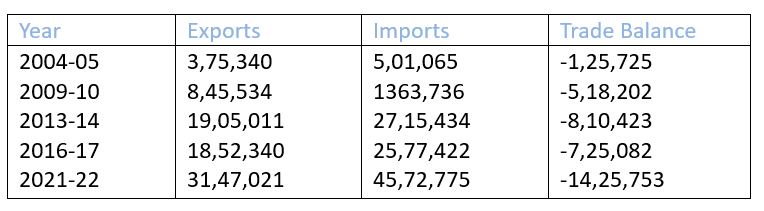 India's Foreign Trade (values in crores)
India's Foreign Trade (values in crores)
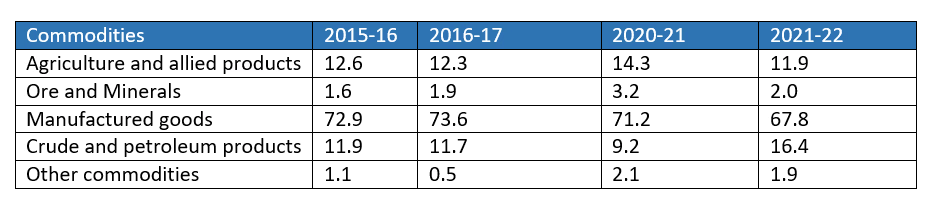 Composition of India’s Export, 2015-2022 (Percentage share in Exports)
Composition of India’s Export, 2015-2022 (Percentage share in Exports)
Changing Commodity Composition
- The makeup of India’s international trade has shifted over the years.
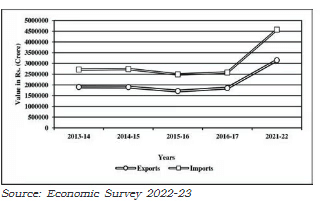 Extent of gap between Exports and Imports in India's Foreign Trade during 2013-14 to 2021-22
Extent of gap between Exports and Imports in India's Foreign Trade during 2013-14 to 2021-22
Export Trends
- Decreased Share: Exports of agriculture and allied products, as well as manufactured goods, have declined.
- Increased Share: Crude petroleum, petroleum products, and other commodities have seen an increase in export share.
- Stable Share: The share of ores and minerals has remained largely constant from 2015-16 to 2021-22.
Impact of Competition
- The decline in traditional agricultural exports, such as cashew, is attributed to intense international competition. However, exports of floricultural products, fresh fruits, marine products, and sugar have increased.
Manufacturing Sector Contribution
- In 2021-22, the manufacturing sector accounted for 67.8% of India’s total export value, with engineering goods experiencing significant growth.
Key Competitors
- China and other East Asian countries are major competitors in the manufacturing sector.
Gems and Jewellery
- This sector contributes significantly to India’s foreign trade.
Changing Patterns of the Composition of India’s Import
Food Shortages in the 1950s and 1960s
- India faced significant food shortages, leading to heavy imports of food grains, capital goods, machinery, and equipment.
Adverse Balance of Payments
- During this period, imports exceeded exports despite efforts at import substitution.
Post-1970 Changes
- Following the success of the Green Revolution, food grain imports ceased after the 1970s.
- The 1973 energy crisis led to rising petroleum prices, increasing import costs.
- Food grain imports were replaced by fertilizers and petroleum.
Current Import Composition
- The main components of India's import basket now include:
1. Machinery and equipment
2. Special steel
3. Edible oil
4. Chemicals
Trends in Imports
- Rising Petroleum Imports: There has been an increase in petroleum product imports, used both as fuel and industrial raw materials, reflecting industrialization and improved living standards.
- Decline in Capital Goods: Imports of capital goods have steadily decreased.
- Decline in Food Imports: The import of food and allied products has also declined.
Other Major Imports: Key imported items now include pearls, precious and semi-precious stones, gold, silver, and non-ferrous metals.
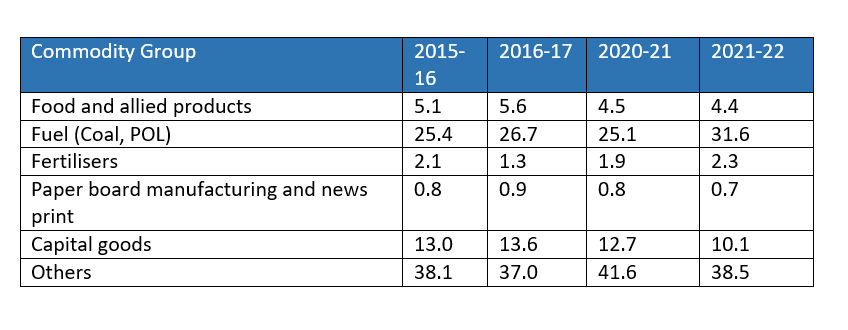 India Composition of Import 2015-22 (In percentage)
India Composition of Import 2015-22 (In percentage)
Direction of Trade
Global Trade Relations
- India engages in trade with a majority of countries and major trading blocs worldwide.
2021-22 Trade Data
- Trade statistics by region and sub-region for the period 2021-22 are presented in the table below.
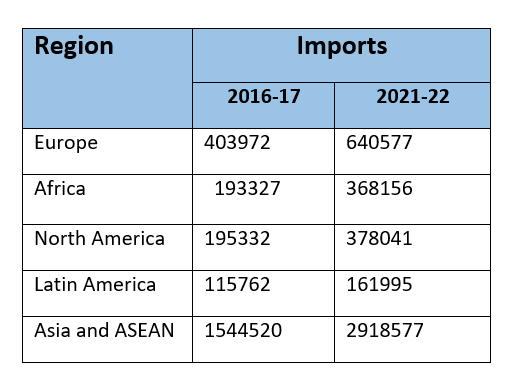 Direction of India’s Import trade (in crore rupees)
Direction of India’s Import trade (in crore rupees)
Future Trade Goals
- India aims to doubleits share in international trade over the next five years.
Strategic Measures
- To achieve this goal, India is implementing several strategies:
1. Import liberalization
2. Reduction of import duties
3. Delicensing
4. Transition from process to product patents
Trade Routes
- Most of India’s foreign trade is conducted via sea and air routes, with a smaller portion transported through land routes to neighboring countries like Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Pakistan.
Sea ports as Gateways of International Trade
 Unloading of goods on portGeographical Advantage
Unloading of goods on portGeographical Advantage
- India is bordered by sea on three sides and has a lengthy coastline, making water transport efficient and cost-effective when conditions are favorable.
Historical Significance
- India has a rich tradition of seafaring, with many ports historically identified by names ending in "pattan," meaning port. The west coast has a greater number of ports compared to the east.
Impact of European Traders
- The arrival of European traders and British colonization highlighted the importance of ports as gateways for international trade, leading to variations in port size and quality.
Current Port Infrastructure
- India has 12 major ports and 200 minor or intermediate ports.
- Major ports are regulated by the central government, while minor ports fall under state government oversight.
- Major ports handle a larger share of total trade traffic.
Historical Context
- The British utilized ports to extract resources from inland areas, with railways connecting local markets to international trade networks. This pattern persisted until 1947.
Post-Independence Developments
- The partition of India resulted in the loss of key ports like Karachi and Chittagong.
- To compensate, new ports such as Kandla and Diamond Harbour were developed.
- Despite setbacks, Indian ports continued to expand and modernize after independence.
Modern Infrastructure
- Today, Indian ports manage significant volumes of domestic and international trade, with many equipped with modern facilities.
- The modernization efforts have shifted from solely government-led initiatives to include private sector involvement.
Cargo Capacity Growth
- The handling capacity of Indian ports increased dramatically from 20 million tonnes in 1951 to over 837 million tonnes in 2016.
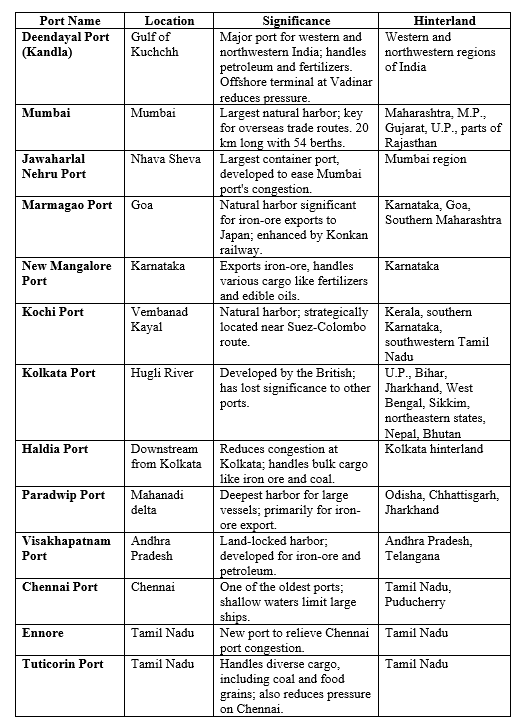
Here are some Indian ports along with their respective hinterlands:
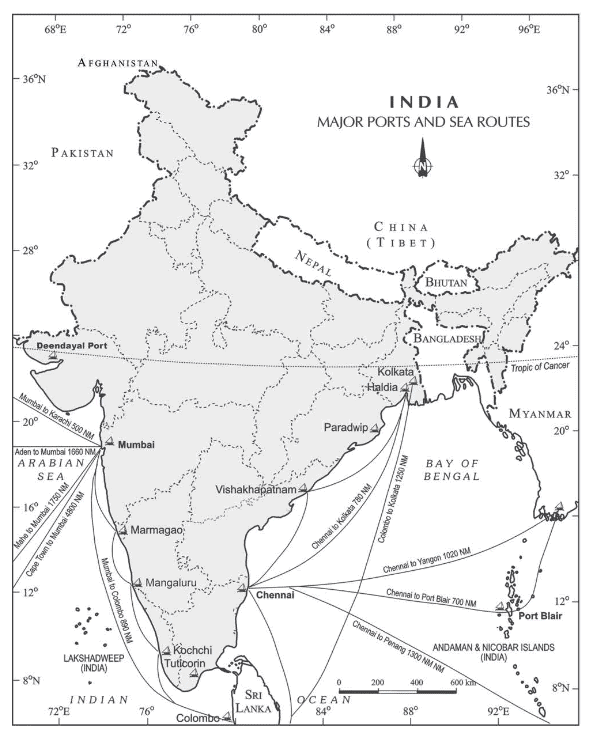 India – Major Ports and Sea Routes
India – Major Ports and Sea Routes
Airports
Significance in Trade
- Air transport is crucial for international trade, particularly for:
1. Speed: It allows for rapid transportation of goods.
2. High-Value and Perishable Goods: Ideal for transporting items that require quick delivery over long distances.
Limitations
- Cost: Air transport is expensive and not suitable for heavy or bulky items.
- Market Participation: Due to its cost and limitations, air transport has a smaller role in international trade compared to ocean shipping.
- Major Airports in India: As of 2016-17, India has 25 major airports, including, Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Delhi, Goa, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Mumbai, Thiruvananthapuram, Srinagar, Jaipur, Calicut, Nagpur, Coimbatore, Cochin, Lucknow, Pune, Chandigarh, Mangaluru, Vishakhapatnam, Indore, Patna, Bhubaneswar, and Kannur.
UDAN Scheme
- Since 2017, the UDAN scheme has operationalized 73 unserved/underserved airports, including, 9 heliports and 2 water aerodromes.
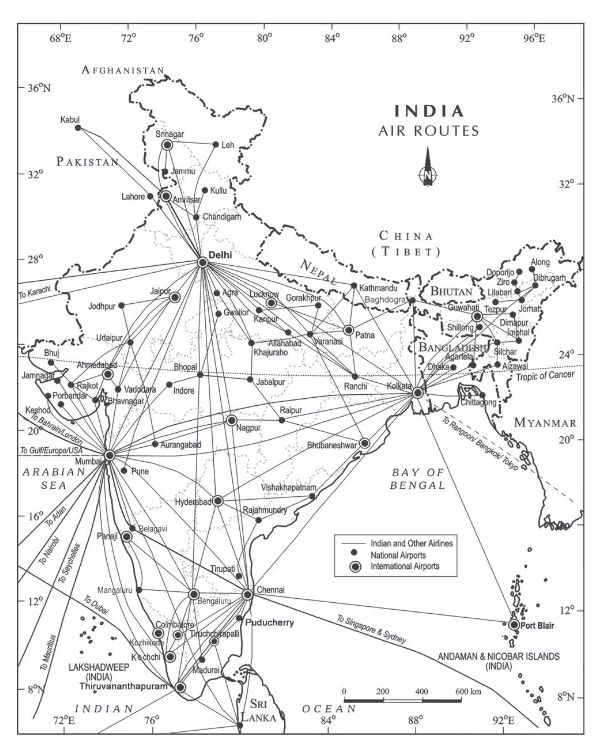 India – Air Routes
India – Air Routes
|
175 videos|619 docs|192 tests
|















