NCERT Summary: Synthetic Fibres and Plastics | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fibres and Fabrics |

|
| Synthetic Fibres |

|
| Plastics |

|
| Plastic & the Environment |

|
Fibres and Fabrics
The clothes are made of fabrics. Fabrics are made from fibres obtained from natural or artificial sources.
Type of Fibres
There are two types of fibre:
- Fibres that are obtained from natural sources are called natural fibres.
Example: Cotton, Silk, Wool, etc.

- Fibres that are man-made are called man-made or synthetic fibres.
Example: Rayon, Nylon, Acrylic, etc.
Synthetic Fibres
- Synthetic fibres are small units of chemicals joined together in the form of a chain. The chain so formed is called a polymer.
- The polymer is a Greek work in which ‘poly’ means many and ‘mer’ means units. Thus, polymer means ‘made of many units joined together.
Types of Synthetic Fibres
1. Rayon
- Rayon is synthesised from wood pulp. Rayon resembles silk, so it is also known as artificial silk.
 Products made from Rayon
Products made from Rayon
- Rayon fibre can be dyed in different colours. Rayon is very cheap compared to silk.
- Bedsheets, shirts, sarees, and many other clothes are made from rayon.
2. Nylon
- Nylon was first commercially synthesized fibre. The production of nylon was started almost simultaneously in New York and London, thus it got its name (NY for New York and Lon for London) as nylon.

- Nylon is synthesized from coal, water and air. The fibre of nylon is very strong and it also resembles silk.
- For the first time, nylon was used in making bristle of toothbrush commercially. After that, it was started used as fabrics.
- Nylon is used in making different types of clothes, ropes, socks, curtains, sleeping bags, parachutes, etc. The fibre of nylon is stronger than a steel wire of the same thickness.
3. Polyester
- Polyester is one of the most popular man-made fibres which are used in making clothes. It is made of repeating unit of a chemical called ester. Terylene is one of the most famous types of polyester.
- Polyester is used in making different types of apparel; such as shirts, pants, jacket, bedsheets, curtains, sarees, mouse-pad, etc. Polyester is used in making ropes, fabrics for conveyor belt, cushioning and insulating material in a pillow, etc.
- Fabrics made from polyester fibre are almost wrinkle-free, easy to wash and have a shiny appearance.
- It is the polyester which made the fabric cheaper in India as well as in the whole world.
- Terrycot is a fabric made after mixing of terylene and cotton. Polycot, poly-wool, etc. are other fabrics which are made by the mixing of polyester with other natural fibres.
- PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) is a very famous term for polyester. Water bottles and many containers (used in the kitchen), films, wires, and many other useful products are made using PET (polyester).
4. Acrylic
- Acrylic is man-made fibre. Since acrylic resembles wool, so it is also known as artificial wool or synthetic wool.
- Acrylic is cheaper than natural wool and can be dyed in various colours. Thus acrylic is very popular and taking the place of wool today.
- Acrylic is used in making sweaters, blanket, and many other clothes.
Characteristics of Synthetic Fibre
- Synthetic fibres are cheaper than natural fibre.
- Synthetic fibres are stronger than natural fibre.
- Synthetic fibres are more durable than natural fibre.
- It is easy to maintain synthetic fibres.
- It is easy to wash synthetic fabrics.
- Synthetic fabrics are dried up in less time.
- Synthetic fibres are readily available.
Plastics
- Plastic is also a polymer. Units of some plastics have linear arrangement while some plastics are formed by the cross-linked arrangement of their units.
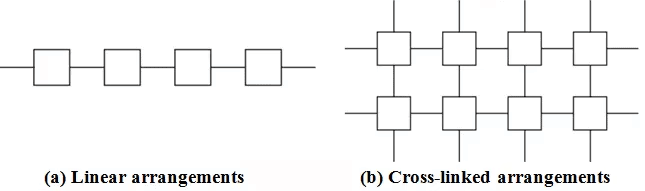
- Plastic can be moulded in all types of possible shapes.
- Plastic can be recycled, coloured, reused, mould or drawn into wires.
- Thus, plastic is used in making toys, suitcases, bags, cabinets, brush, chairs, tables, and many other countless items.
- Polythene is one of the most famous types of plastic, which is used in the manufacturing of carrying bags.
Types of Plastic
Plastic can be divided into two main types:
1. Thermoplastic
- Plastics that can be easily bent or deform on heating are known as thermoplastics.
Examples: PVC and Polythene.

- Thermoplastics are used in making toys, bottles, combs, containers, etc.
2. Thermosetting Plastic
- Plastics that do not get deformed or softened on heating when mould once, are called thermosetting plastics.
Example: Bakelite and melamine.
- Thermosetting plastics are used in making hardboard, electric switch handles of electrical appliances, handles of kitchen utensils, floor tiles, etc.
- Melamine is a poor conductor of heat and resists fire, thus it is used in making floor tiles, kitchen materials, etc.
- Bakelite is a poor conductor of electricity and heat, thus it is used in making electrical switches, and other electrical appliances.
Plastic as a Material of Choice
- Plastic has lightweight, lower price, good strength, and easy handling.
- Being lighter as compared to metals, plastics are used in cars, aircraft, and spacecraft too.
Characteristics of Plastic
- Poor Conductor: Plastic is a poor conductor of heat and electricity.
This makes it suitable to make the covering of electric wires, handles of electrical appliances, handles of utensils, kitchenware, floor tiles, etc. - Plastic is Non-Reactive: Plastic does not react with air and water and with many of the chemicals. Hence it does not get rusted like iron.
This character makes plastic suitable for making the container, water tank, water bottle, plastic pipes, taps, chair, table, and other many types of furniture. - Plastic is Strong and Durable: Plastics are lightweight, durable, cheap, and very strong. These qualities of plastic made it the need of today.
Whether it is polythene bags or pencil boxes, water bottles or umbrellas, furniture or aircraft, the use of plastics can be seen everywhere.
Biodegradable & Non-biodegradable
- Substances that get decomposed through the natural processes, such as the action of bacteria, etc. are called biodegradable substances.
Example: Potato peels, peels of other vegetables, foodstuffs, fruit, paper, cotton cloth, wood, etc. - Substances that either do not decompose or take many years to get decomposed through the natural process are called non-biodegradable substances.
Example: Tin, Aluminium, Plastics, etc.
Plastic & the Environment
- Plastic is a non-biodegradable substance. If it is left or thrown, it takes many years to get decomposed or either does not get decomposed.
- The non-biodegradable nature of plastic has made it a very major problem for the environment.
 Dumping of Plastic Waste
Dumping of Plastic Waste
Problems
- Plastic has become very popular and is being used for many purposes. As a result, we are generating a large amount of plastic waste. Since plastic is non-biodegradable, so plastic waste is getting accumulated around us.
- The disposal of plastic waste is a major concern as it cannot be even burnt. Burning plastic can result in the release of many harmful gases into the atmosphere. This can lead to air pollution.
Preventive Measures
- We should avoid the use of plastics things as far as possible.
- Do not throw plastic bags in the water bodies or on the road.
- The biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes should be collected separately and disposed off separately.
For dealing with plastic waste, we should follow the three Rs:

- Reduce: We should reduce the use of plastic.
Examples: We should use cloth or jute bag for purchasing any things instead of using plastic bags. - Reuse: We should reuse some plastic things and containers in our homes and offices.
Example: Empty plastic bottles and containers should be used for keeping other items in the home and kitchen. - Recycle: Thermoplastic can be recycled. So, items made of thermoplastic should be sent to the recycling industry.
Example: Toys, buckets, mugs etc.
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Synthetic Fibres and Plastics - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are synthetic fibres and how are they made? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of using synthetic fibres over natural fibres? |  |
| 3. How do plastics impact the environment? |  |
| 4. What measures can be taken to reduce plastic waste? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of recycling synthetic fibres and plastics? |  |















