NCERT Summary: The Indian Constitution | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
What is the Meaning of The Indian Constitution?
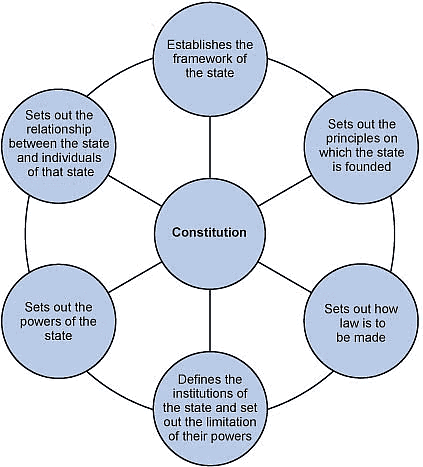
The Constitution of India is the supreme law of India.
It sets up the basic framework for how the country is governed, including the political system, the roles and powers of government bodies, and the rights and responsibilities of citizens.
The Constitution also guarantees fundamental rights to individuals and lays down the directive principles for the state, guiding the government in its actions.

Why Does a Country Need a Constitution?
Most countries have a constitution, but not all are democratic. A constitution defines the ideals and nature of the country, reflecting citizens' aspirations. It serves as a set of rules and principles agreed upon by all citizens for governing the country, outlining the type of government and shared ideals.
Example of Constitutional Change: Nepal
- In 2008, Nepal transitioned from a constitutional monarchy to a federal democratic republic, necessitating a new constitution that aligned with the people's aspirations.
- Changing political systems, like Nepal's move to democracy, necessitates revising fundamental rules, leading to the adoption of a new constitution in 2015.
- The previous constitution defined governance by the King and his council, highlighting the significance of constitutional change in political transitions.
Role of the Constitution in a Democracy
- A constitution outlines essential guidelines for decision-making, ensuring leaders exercise power responsibly on behalf of the people.
- Democratic constitutions incorporate safeguards to prevent the misuse of authority by political leaders.
- For example, the Indian Constitution guarantees fundamental rights, such as equality for all, prohibiting discrimination based on religion, race, caste, gender, or place of birth.
Protection Against Tyranny
- Constitutions prevent dominant groups from exploiting their power over weaker individuals or groups, ensuring fairness for all.
- They safeguard against both inter-community and intra-community domination, preserving equality and justice.
Safeguarding Rights and Freedoms
- The Constitution prevents individuals from making harmful decisions that undermine the country's core principles.
- It ensures that fleeting emotions, like the desire for a strong leader during times of political disillusionment, do not erode citizen rights.
- The Constitution maintains a stable framework that protects the rights and liberties of the people, ensuring long-term adherence to democratic values.
Upholding Democratic Values
- In democratic societies, constitutions uphold essential values and principles, ensuring stability and protection of rights.
- By examining the Indian Constitution, we see how these democratic ideals are translated into specific rules and safeguards for the people.
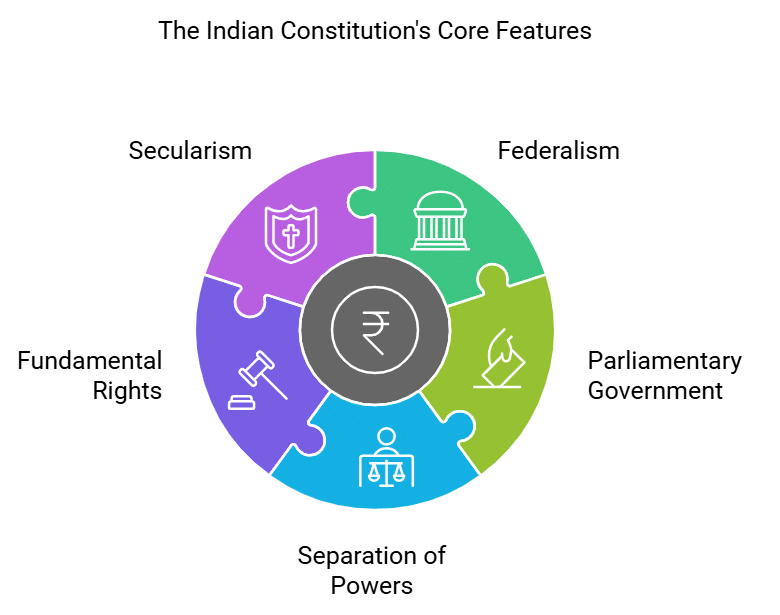
The Indian Constitution: Key Features
- By the beginning of the twentieth century, the Indian national movement was actively fighting for independence from British rule.
- During the freedom struggle, nationalists envisioned a free India as a democracy where everyone would be treated equally and have a say in governance.
- Around 300 individuals, members of the Constituent Assembly since 1946, worked together over three years to draft India's Constitution.
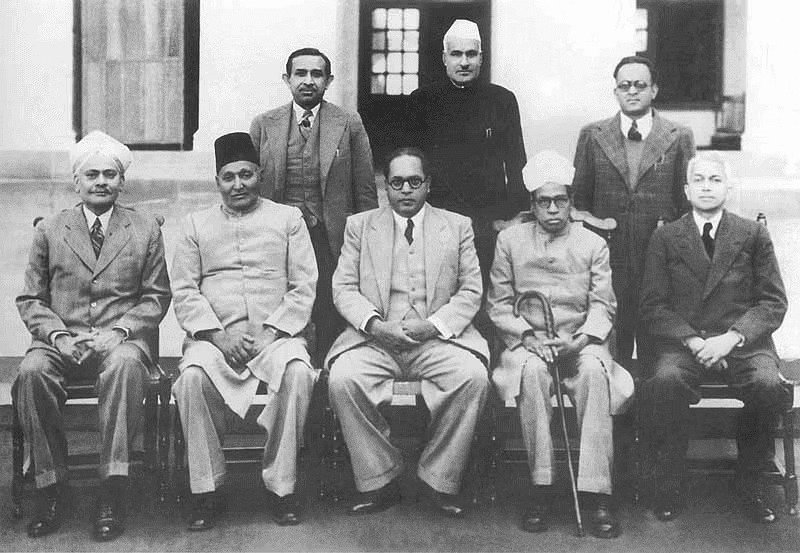 Drafting Committee of the Constituent Assembly of India
Drafting Committee of the Constituent Assembly of India
- The Constituent Assembly faced the challenge of uniting diverse communities with different languages, religions, and cultures.
- During the drafting of the Constitution, India was facing turmoil due to the imminent partition, undecided princely states, and widespread socio-economic challenges.
- The Constitution crafted by the Assembly members reflects a commitment to diversity alongside national unity, addressing poverty through socio-economic reforms, and highlighting the importance of people's participation in choosing their representatives.
Listed below are the key features of the Indian Constitution.
1. Federalism
- This concept entails the presence of multiple levels of government within the country. In India, we observe governments at both the state and central levels. Panchayati Raj represents the third tier of government.
- The vast diversity of communities in India necessitated a governmental system that did not solely concentrate power in individuals located in the national capital of New Delhi. Instead, it was crucial to establish an additional layer of government at the state level to address region-specific concerns.
- While each state in India enjoys autonomy in certain areas, matters of national significance require compliance with laws enacted by the central government.
- The Constitution delineates specific domains for each level of government to legislate upon and outlines their funding mechanisms.
- Under the federal system, states derive authority not just from the central government but also from the Constitution itself. Every individual in India is subject to regulations formulated by these distinct tiers of government.
2. Parliamentary Form of Government
- In the Parliamentary form of Government, there are different levels of government, and at each level, representatives are chosen by the people through elections.
- The Constitution of India, under Article 326, guarantees universal adult suffrage, which means that all adult citizens have the right to vote in elections.
- The members of the Constituent Assembly believed that allowing everyone to vote would strengthen democracy and help challenge traditional social hierarchies.
- In India, citizens have the power to directly elect their representatives, and any eligible citizen can contest in elections.
- Furthermore, every citizen, regardless of their social background, has the opportunity to stand for election.
3. Separation of Powers
- The Constitution outlines three government organs: legislature, executive, and judiciary.
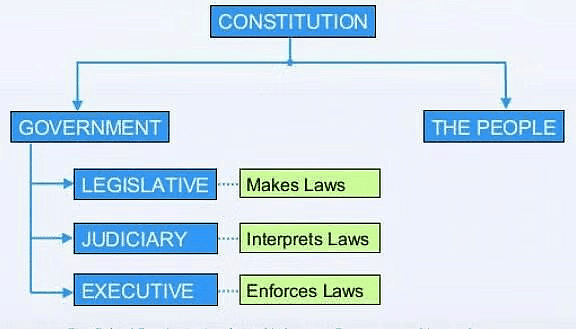
- Legislature consists of elected representatives, while the executive implements laws and governs.
- The judiciary system comprises the courts in the country.
- To prevent power abuse, each organ has distinct powers, acting as checks on one another for a balanced power structure.
4. Fundamental Rights
- Termed as the 'conscience' of the Indian Constitution due to historical suspicions of State power post-colonial rule.
- Aimed at safeguarding citizens from arbitrary State power, ensuring protection against misuse of authority.
- Guarantee rights of individuals against both the State and fellow citizens, addressing diverse community needs.
- Protect minority rights against potential majority dominance, reflecting Ambedkar's dual objectives for Fundamental Rights.
- Emphasize citizens' entitlement to claim rights and the obligation of all law-making authorities to adhere to these rights.
- Directive Principles of State Policy: Included in the Constitution to advocate for social and economic reforms, offering guidance to shape laws and policies for poverty alleviation.
Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution
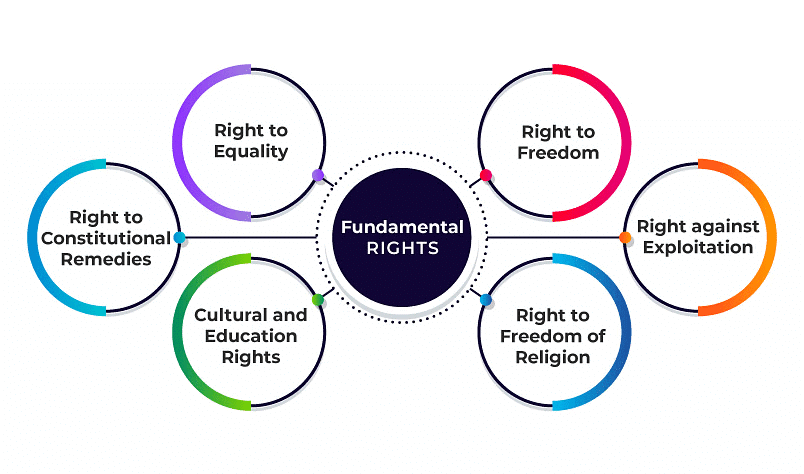 Fundamental Rights
Fundamental Rights
1. Right to Equality:
- All individuals are equal before the law, ensuring equal protection under the country's laws.
- No citizen can face discrimination based on religion, caste, or sex.
- Access to public places like playgrounds, hotels, and shops is guaranteed to everyone.
- The State cannot discriminate in employment matters, except for certain situations detailed in the Constitution.
- Untouchability practices have been abolished.
2. Right to Freedom: Encompasses freedom of speech and expression, forming associations, moving freely within the country, and choosing any profession.
3. Right against Exploitation: The Constitution prohibits human trafficking, forced labor, and employing children under 14 years old.
4. Right to Freedom of Religion: All citizens have the freedom to practice, profess, and propagate their chosen religion.
5. Cultural and Educational Rights: Minorities, whether religious or linguistic, can establish educational institutions to preserve and enhance their culture.
6. Right to Constitutional Remedies: Citizens have the right to seek legal recourse if they believe any of their Fundamental Rights have been violated by the State.
5. Secularism
- A secular state does not officially promote any one religion as the state religion.
- Further discussion on secularism will be provided in the upcoming chapter.
Influence of History on the Constitution:
- A country's history often shapes the type of Constitution it adopts.
- The Constitution plays a vital role in establishing the ideals for all citizens to follow, including elected representatives.
- Changes in constitutional rules can significantly impact the functioning of the government, similar to how rule changes affect a football game.
- The Indian Constitution has undergone amendments to address new political concerns, indicating the evolving nature of the country's governance.
- In certain cases, a substantial constitutional change can alter the fundamental essence of a nation, as observed in Nepal's transition to democracy and the subsequent adoption of a new Constitution.
|
142 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: The Indian Constitution - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the significance of the Indian Constitution in shaping the nation? |  |
| 2. Why is a constitution essential for a country? |  |
| 3. What are the key features of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. How does the Indian Constitution protect the rights of citizens? |  |
| 5. How has the Indian Constitution evolved over time? |  |
















