NCERT Summary: Understanding Marginalisation | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
What does it mean to be Socially Marginalised?
Being socially marginalized means being pushed to the edges or sidelines and not being included in the main parts of society.

- Marginalisation can be felt in everyday situations, such as in the classroom or playground, where differences in taste, accent, or behavior can lead to exclusion.
- Social Marginalisation: Groups or communities may be excluded due to differences in language, customs, religion, poverty, or social status.
- Exclusion Impact: Marginalised groups often lack access to resources and opportunities, experience a sense of powerlessness, and are viewed with hostility or fear.
- Factors of Marginalisation: Economic, social, cultural, and political factors contribute to the marginalisation of certain groups.
- The chapter will discuss two communities in India that are considered socially marginalised.
Who are Adivasis?
The term ‘Adivasis’ refers to the original inhabitants. Adivasis are communities that lived and often continue to live in close association with forests.
 Adivasis
Adivasis
(i) Population: They make up about 8% of India’s population and are prominent in mining and industrial areas like Jamshedpur and Rourkela.
(ii) Diversity: India has over 500 Adivasi groups, with significant populations in states such as Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and various northeastern states.
(iii) Geographic Distribution: States like Odisha have over 60 different tribal groups. 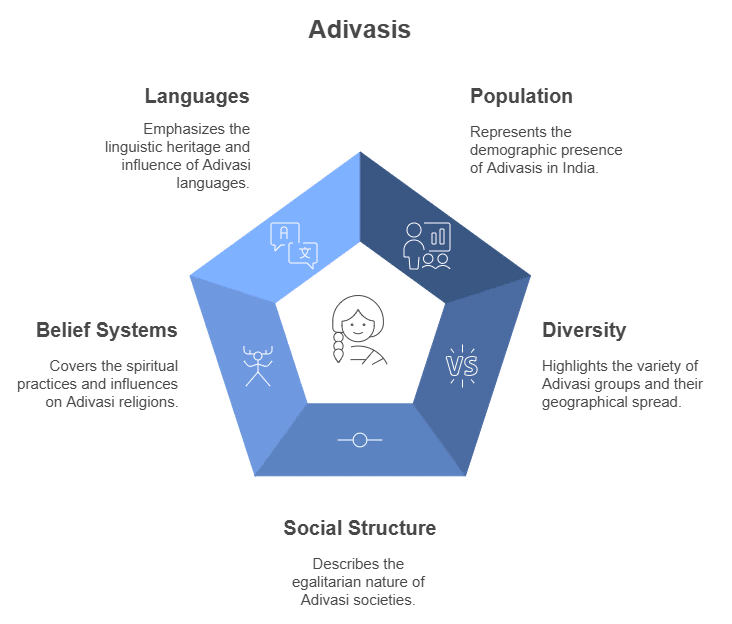
(iv) Social Structure: Adivasi societies are distinctive for their lack of hierarchy, unlike caste-based or monarchy-based communities.
(v) Belief Systems: They practice diverse belief systems, including ancestor worship, and nature spirits, and have been influenced by surrounding religions such as Shakta, Buddhist, and Christian traditions.
(vi) Religious Influence: Adivasi religions have influenced dominant religions and cults like Jagannath in Odisha and Shakti traditions in Bengal and Assam.
(vii) Christianity: Many Adivasis converted to Christianity during the 19th century, which remains a significant religion among them.
(viii) Languages: Adivasis speak their own languages, some older than Sanskrit, influencing mainstream Indian languages. Santhali is notable for its large number of speakers and published works.
Adivasis and Stereotyping
(i) Stereotypical Portrayal: Adivasis are often depicted in colorful costumes, headgear, and dancing in school events, books, and movies.
(ii) Lack of Awareness: There is limited understanding of the actual lives and realities of Adivasis.
(iii) Misconceptions: They are frequently viewed as exotic, primitive, and backward due to these stereotypes.
(iv) Adivasis are sometimes unfairly blamed for their lack of advancement, with the belief that they resist change and new ideas.
(v) Such stereotypes can lead to discrimination and reinforce negative perceptions about Adivasi communities.
Adivasis and Development
Forests play a crucial role in the development of all empires and settled civilization in India. Adivasis had deep knowledge of forest. Often empires heavily depended on Adivasis for the crucial access to forest resources.

Historical Significance of Forests:
- Forests provided metal ores (iron, copper, gold, silver), coal, diamonds, timber, medicinal herbs, and animal products (wax, lac, honey).
- Essential for life support: recharging rivers, affecting air and water quality.
Adivasi Control Over Forests:
- Extensive knowledge and control over forests until mid-19th century.
- Not governed by large states; empires depended on Adivasis for forest resources.
Changes in Adivasi Life:
- Traditionally hunter-gatherers, nomads, and engaged in shifting agriculture.
- Over the past 200 years, economic changes, forest policies, and political forces have displaced them.
- Shift to working in plantations, construction sites, industries, and domestic work.
Impact of Development Projects:
- Forest lands cleared for timber, agriculture, and industrial use.
- Areas rich in minerals taken over for mining; land acquisition often forceful.
- Over 50% of displaced people from mining projects are tribals; 79% from Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Jharkhand.
Environmental and Social Impact:
- Lands submerged by dams; militarized areas in the Northeast.
- 106 national parks (44,402.9 sq km) and 573 wildlife sanctuaries (123,762.56 sq km) established on lands originally occupied by tribals.
- Tribals living in these areas are labeled as encroachers.
Economic Consequences:
- Loss of traditional livelihoods and food sources.
- Migration to cities leads to low-wage jobs, contributing to poverty; 45% in rural areas and 35% in urban areas live below the poverty line.
- High malnutrition rates and low literacy among tribal children.
Cultural Loss:
- Displacement results in loss of traditions, customs, and community structures.
- Example: Gobindha Maran’s loss of essential community spaces (cremation ground, temple, well, pond) due to a refinery project in Odisha.
Interconnected Issues:
- Economic dispossession impacts social and cultural dimensions.
- Displacement often involves violence and has deep effects on traditional ways of life.
Minorities and Marginalisation
The term minority is most commonly used to refer to communities that are numerically small in relation to the rest of the population.
Safeguards for Minorities:
- Purpose: To protect minority groups from being culturally dominated by the majority.
- Prevention of Discrimination: Ensures protection against discrimination and disadvantage.
- Cultural Diversity: Safeguards uphold India’s cultural diversity and promote equality and justice.
Role of the Constitution:
- Provides constitutional safeguards to religious and linguistic minorities.
- Courts uphold the law and enforce Fundamental Rights, allowing citizens to seek justice if their rights are violated.
Insecurity and Relations: Small communities may feel insecure about their lives, assets, and well-being. Tensions between minority and majority communities can increase this sense of insecurity.
Muslims and Marginalisation
Muslims are 14.2% of India’s population and are considered to be a marginalized community in India
Muslim Population: As per the 2011 Census, Muslims constitute 14.2% of India's total population. This significant proportion highlights their presence as a major minority group within the country.
Socio-Economic Marginalization: Muslims are considered marginalized due to comparatively lower socio-economic development. This marginalization is reflected in various indicators such as basic amenities, literacy, and public employment, demonstrating that the community lags behind in these critical areas.
Sachar Committee Report (2005):
- Chair: Justice Rajindar Sachar.
- Objective: To investigate the social, economic, and educational status of Muslims in India.
- Key Findings: The report identified that Muslims faced marginalization similar to Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs). It highlighted issues such as lower average years of schooling for Muslim children aged 7-16 compared to other socio-religious communities.- Economic and Social Dimensions:
- Distinctive Customs: Certain practices among Muslims, such as wearing the burqa, sporting a long beard, or wearing a fez, can set them apart from the mainstream. This visible difference sometimes leads to discrimination and negative stereotyping.
- Impact of Discrimination: These distinct customs can cause Muslims to be viewed as different, which may lead to unfair treatment, social exclusion, and, in some cases, migration from their original places of residence. This migration often results in the ghettoization of the community.
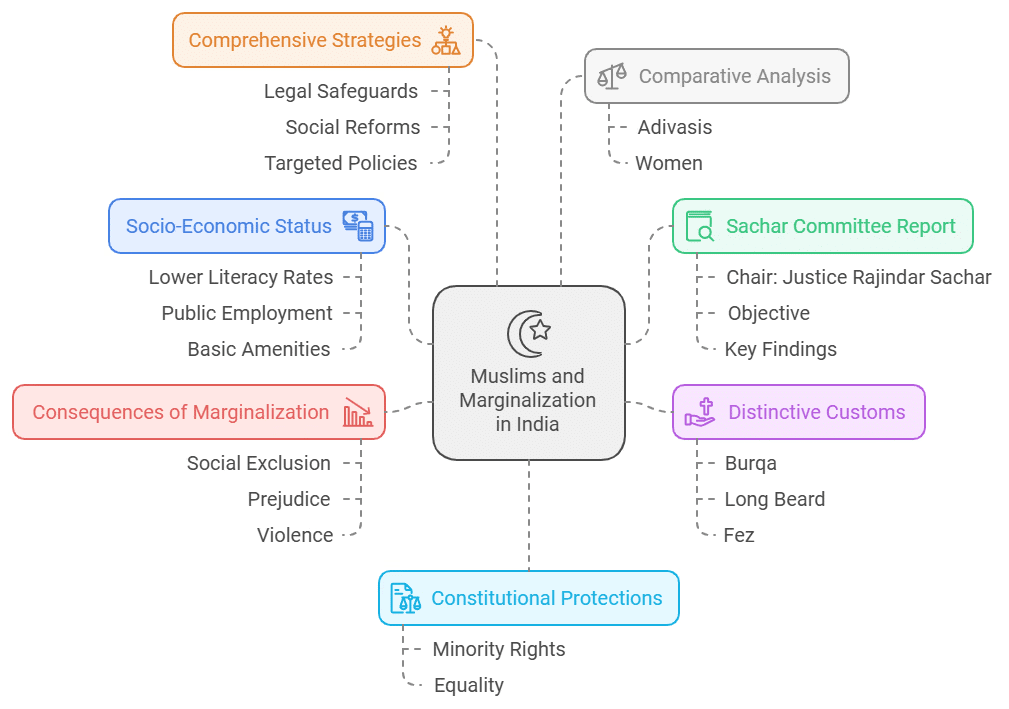
- Consequences of Marginalization:
- Social Exclusion: The marginalization of Muslims sometimes results in their communities being isolated, leading to socio-economic disadvantages and perpetuating cycles of poverty.
- Prejudice and Violence: The social marginalization and stereotyping of Muslims can lead to increased hostility, prejudice, and even violence against them. Comparative Analysis: The marginalization of Muslims shares similarities with that of other marginalized groups such as Adivasis and women, as observed in various chapters and studies. This indicates that marginalization is a multifaceted issue affecting various communities in different ways.
Need for Comprehensive Strategies: Addressing marginalization requires a multi-dimensional approach, including legal safeguards, social reforms, and targeted policies. The Constitution and associated laws are crucial in protecting minority rights and promoting equality.
Constitutional Protections: The Indian Constitution provides safeguards for minorities to ensure their cultural, social, and economic rights are protected. This is essential to preserving India's diversity and ensuring equitable treatment for all citizens.
Conclusion
- Concept of Marginalisation: Examined through the experiences of various communities.
- Causes and Variations: Different reasons and ways in which communities face marginalisation.
- Linked Issues: Marginalisation often involves disadvantage, prejudice, and powerlessness.

- Examples in India: Dalits and other marginalised groups experience low social status and unequal access to resources.
- Possibility of Change: Marginalised communities can change their circumstances over time.
- History of Struggle: Groups have a history of resistance and efforts to overcome marginalisation.
- Goals of Marginalised Groups: Desire to maintain cultural identity while accessing rights and development opportunities.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) Related to Understanding Marginalisation
1. What is marginalization?
Ans. Marginalization refers to the social, economic, and political exclusion of certain groups of people from mainstream society. This exclusion can be due to various factors, including race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and disability. It often leads to discrimination, lack of access to resources and opportunities, and lower social mobility. Marginalization is a form of social inequality and can have long-lasting effects on individuals and communities.
2. What are the different types of marginalization?
Ans. There are several types of marginalization, including economic marginalisation, political marginalisation, social marginalisation, and cultural marginalisation. Economic marginalisation occurs when individuals or groups lack access to economic resources, such as education, employment, and healthcare. Political marginalisation occurs when individuals or groups are excluded from political decision-making processes and lack representation in government. Social marginalisation occurs when individuals or groups are excluded from social institutions and networks, such as schools, clubs, and religious organizations. Cultural marginalisation occurs when individuals or groups are excluded from cultural practices and traditions.
3. How does marginalisation affect mental health?
Ans. Marginalisation can have a significant impact on mental health. Individuals who experience marginalisation may be more likely to experience depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions. They may also face stigma and discrimination related to their mental health, which can further exacerbate their symptoms. Marginalisation can also lead to social isolation, which can contribute to poor mental health outcomes. It is important to address the root causes of marginalisation in order to promote mental health and well-being for all individuals.
4. What are some strategies for addressing marginalisation?
Ans. There are several strategies for addressing marginalisation, including promoting diversity and inclusion, providing education and training on cultural competency, advocating for policies and laws that promote social justice and equality, and providing resources and support to marginalized communities. It is also important to listen to the voices of marginalized communities and involve them in decision-making processes. By working together, we can create a more equitable and inclusive society.
5. How can individuals support those who are experiencing marginalisation?
Ans. Individuals can support those who are experiencing marginalisation by educating themselves on the issues and challenges faced by marginalized communities, speaking out against discrimination and injustice, and advocating for policies and laws that promote equality and social justice. They can also support marginalized communities through volunteering, donating to organizations that work to support these communities, and participating in community events and activities. It is important to listen to the experiences and perspectives of marginalized individuals and communities and to support them in their efforts to create positive change.
Key Terminologies
1. Hierarchy: A graded system or arrangement of persons or things. Usually persons at the bottom of the hierarchy are those who have the least power. The caste system is a hierarchical system and Dalits are considered to be at the lowest end.
2. Ghettoisation: A ghetto is an area or locality that is populated largely by members of a particular community. Ghettoisation refers to the process that leads to such a situation. This may occur due to various social, cultural and economic reasons. Fear or hostility may also compel a community to group together as they feel more secure living amongst their own. Often a ‘ghettoised’ community has few options of moving out, which may lead to them becoming alienated from the rest of the society.
3. Mainstream: Literally this refers to the main current of a river or stream. It is used to refer to a cultural context in which the customs and practices that are followed are those of the dominant community. In connection with this, mainstream is also used to refer to those people or communities that are considered to be at the centre of a society, i.e. often the powerful or dominant group.
4. Displaced: In the context of this chapter this refers to people who are forced or compelled to move from their homes for big development projects including dams, mining etc.
5. Militarised: An area where the presence of the armed forces is considerable.
6. Malnourished: A person who does not get adequate nutrition or food.
|
147 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
















