NCERT Summary: Understanding Secularism | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction to Secularism |

|
| What is Secularism? |

|
| Why is it Important to Separate Religion from the State? |

|
| What is Indian Secularism? |

|
Introduction to Secularism
In a diverse country like India, where people follow different religions, secularism plays a crucial role in ensuring that everyone is treated equally, regardless of their faith. Imagine being a Hindu or a Muslim in a neighborhood where one religion is very dominant. Even though you are an Indian citizen, you might face difficulties finding a place to live simply because of your religion. If you raise this issue of discrimination and are told to go back to where your family originally came from, it could make you very upset. This feeling of anger could lead to two possible reactions.

- Retaliation: You might argue that Christians should be treated the same way in areas where Hindus or Muslims are in the majority. This response is about getting even.
- Fighting for Justice: Alternatively, you might believe that no one should be discriminated against based on their religion and work towards ending such discrimination. This approach aligns with the idea of secularism.
Secularism aims to prevent religious domination and ensure justice for everyone, regardless of their religion.
Historical Context of Discrimination
Throughout history, discrimination and persecution based on religion have been widespread:
- Nazi Germany: During Hitler’s regime, Jews were severely persecuted and killed.
- Modern Israel: The State of Israel has faced criticism for its treatment of Muslim and Christian minorities.
- Saudi Arabia: Non-Muslims in Saudi Arabia face restrictions on building places of worship and public religious gatherings.
These examples highlight how religious domination can lead to serious discrimination and persecution of minority groups.
What is Secularism?
Secularism refers to the separation of religion from State power. It means that the State does not officially recognize or support any religion.
 Secularism: Separation of Religion from State.
Secularism: Separation of Religion from State.
The separation of religion from state authority is crucial for several reasons:
- Preventing Religious Domination: Secularism ensures that no single religion can use state power to dominate others.
- Protecting Individual Freedom: It allows individuals the freedom to follow, change, or interpret their religion without interference from the state.
In India, the Constitution ensures that the State is secular, meaning it:
- Preventing Religious Domination: The state ensures that no religious community can dominate others or its own members.
- Avoiding Enforcing Religion: The state does not impose any religion nor restrict religious freedom.
- Preventing Discrimination: The state treats all individuals equally, regardless of their religion.
Why is it Important to Separate Religion from the State?
In a democratic society where multiple religions coexist, the separation of religion from the State is crucial to prevent the majority religion from using government power to discriminate against minority communities.
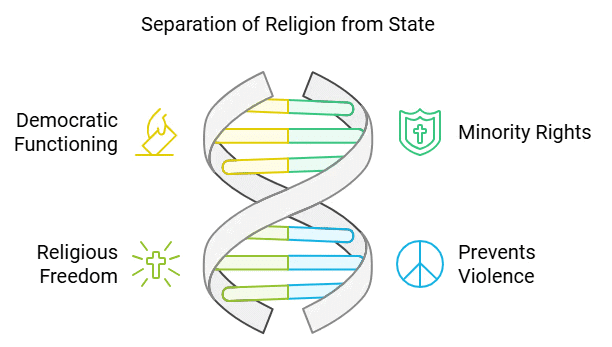
Here are key reasons why this separation is essential:
Ensures Democratic Functioning: It helps a country maintain its democratic principles by ensuring no religion dominates others through State support.
Protects Minority Rights: Separation safeguards minorities from the tyranny of the majority, preventing discrimination and protecting the Fundamental Rights of all citizens.
Promotes Religious Freedom: It allows individuals to freely practice, change, or reinterpret their religion without fear of State intervention or coercion.
Prevents Religious Violence: By keeping religion separate from governance, the State reduces the potential for religious violence and conflict.
In this context, the term "State" refers to the organized political community with authority over a territory, ensuring that governance remains neutral regarding religious matters.
Examples:
- Abolition of Untouchability: The Indian government intervened to abolish untouchability, a discriminatory practice within Hinduism, thereby ensuring equality for lower castes.
- Support for Religious Schools: The State permits religious communities to establish schools but does so without giving preferential treatment to any particular religion.
What is Indian Secularism?
The Indian Constitution mandates that the State must be secular to ensure the following:
- No religious community dominates another.
- Within a religion, no group dominates others.
- The State neither promotes nor restricts religious freedom.

Key Features of Indian Secularism:
- Non-alignment with Religion: The Indian State maintains a distance from religious practices. For instance, government institutions like courts, schools, and offices do not display or promote any religion.
- Religious Freedom in Schools: Government schools are prohibited from promoting any specific religion, including through prayers or celebrations. However, private schools are not bound by this rule.
- Example: In a government school, students cannot celebrate religious festivals as this violates the policy of equal treatment of all religions. Such celebrations can be done outside the school premises.
Strategies of Indian Secularism:
- Non-Interference: The State allows religious communities to follow their practices without interference. For example, Sikhs are exempted from wearing helmets as wearing a turban is an integral part of their faith.
- Intervention: The State can intervene in religious matters when necessary, such as banning untouchability within Hinduism, which discriminated against lower castes, to uphold Fundamental Rights.
- Example: The abolition of untouchability was an instance where the State intervened to prevent religious-based discrimination.
State Support: The Constitution allows religious communities to set up their schools and colleges, with the State offering financial aid on a non-preferential basis.
Comparison with Other Secular Democracies:
- In countries like the United States, the Constitution strictly separates religion from the State. For example, the U.S. First Amendment prevents the government from promoting any religion.
- Difference in Indian Secularism: Unlike the U.S., Indian secularism allows the State to intervene in religious matters, as long as it upholds Constitutional principles and aims to protect individual rights.
Importance of Secularism in India:
- The Indian Constitution upholds secularism to ensure equality, protect religious freedom, and prevent discrimination. While violations of these principles may occur, the Constitution provides a framework for addressing them. Awareness of these rights empowers citizens to take action against such violations.
These principles of secularism form the foundation of India's democratic structure and ensure the peaceful coexistence of diverse religious communities.
Some Important Terms
- Secularism: It refers to the separation of religion from the State.
- Coercion: Forcing someone to do something. In the chapter, the term refers to the force used by a legal authority such as the State.
- Freedom to interpret: It refers to the freedom that all persons shall have to understand things in their own way. In the chapter, it refers to individual liberty to develop their own understanding and meaning of the religion they practice.
- Intervene: In the chapter, the term refers to the State’s efforts to influence a particular matter by the principles of the Constitution.
|
151 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Understanding Secularism - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the core principles of secularism? |  |
| 2. How does secularism benefit society? |  |
| 3. In what ways is Indian secularism distinct from Western secularism? |  |
| 4. What role does the Constitution play in secularism in India? |  |
| 5. Why is the separation of religion from the state crucial in a democratic society? |  |




















