NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Haloalkanes & Haloarenes | Chemistry Class 12 PDF Download
2024
Q1: The compound that will undergo SN1 reaction with the fastest rate is
(a) 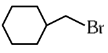
(b) 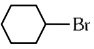
(c) 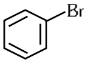
(d) 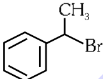 (2024)
(2024)
Ans: (d)
Reactivity towards ,SN1 depends upon stability of carbocation.
Order of stability is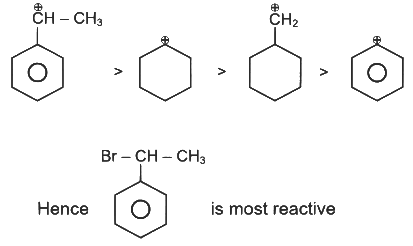
2023
Q1: The given compound (2023)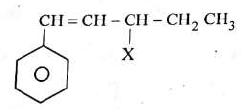 is an example of ______.
is an example of ______.
(a) Benzylic halide
(b) Aryl halide
(c) Allylic halide
(d) Vinylic halide
Ans: C
α-carbon is sp3 carbon which is right next to 
This a-position is known as allylic position
Hence, 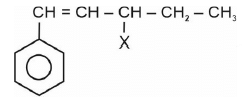
is allylic halide
2021
Q1: The major product of the following chemical reaction is : (NEET 2021)
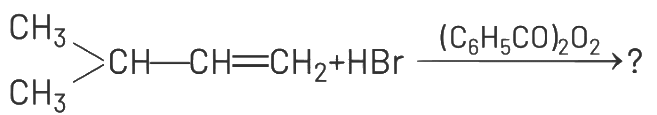 (a)
(a) 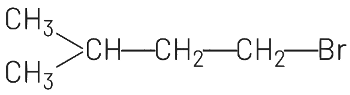
(b) 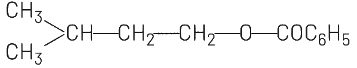
(c) 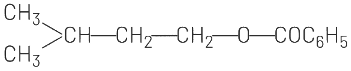
(d) 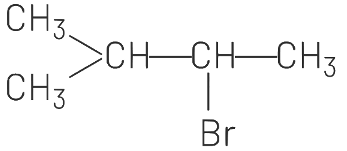
Ans: (d)
Addition of HBr to an alkene in presence of a peroxide (benzoyl peroxide [(C6H5CO)2O2] gives an anti Markownikoff’s product. Anti-Markownikoff’s rule states that hydrogen is added to a more substituted carbon atom of an unsymmetrical alkene.
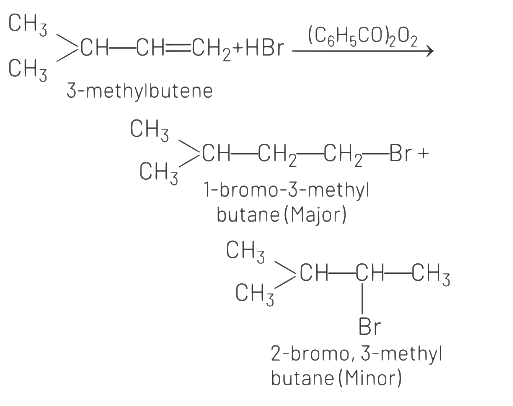
Q2: The major product formed in dehydrohalogenation reaction of 2-Bromo pentane is Pent-2-ene.This product formation is based on- (NEET 2021)
(a) Hofmann Rule
(b) Huckel's Rule
(c) Saytzeff's Rule
(d) Hund's Rule
Ans: (c)
Major product formed in dehydrohalogenation reaction of 2-bromopentane is pent-2-ene because according to Saytzeff's Rule, in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the preferred product is that alkene which has greater number of alkyl group(s) attached to the doubly bonded carbon atoms.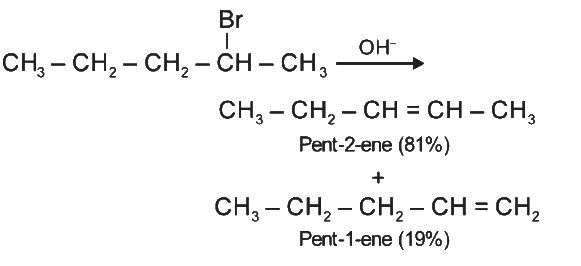
2020
Q1: Which of the following alkane cannot be made in good yield by Wurtz reaction? (NEET 2020)
(a) n-Heptane
(b) n-Butane
(c) n-Hexane
(d) 2,3-Dimethylbutane
Ans: A
Wurtz reaction is used to prepare symmetrical alkanes like
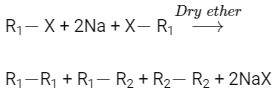
Using Wurtz reaction, n-Heptane can not be produced in good production because it is unsymmetrical alkane.
Q2: Elimination reaction of 2-Bromo-pentane to form pent-2-ene is: (NEET 2020)
(a) β-Elimination reaction
(b) Follows Zaitsev rule
(c) Dehydrohalogenation reaction
(d) Dehydration reaction
(a) (b), (c), (d)
(b) (a), (b), (d)
(c) (a), (b), (c)
(d) (a), (c), (d)
Ans: (c)
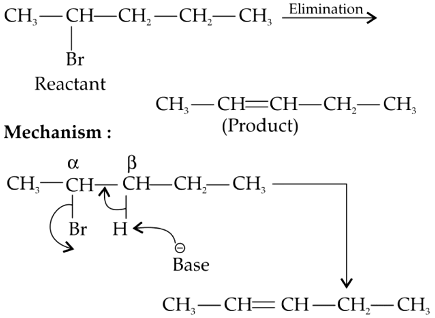
Since β-hydrogen is abstracted it is β-elimination.
Since more substituted alkene is formed (stable and major product), it follows Zaitsev's rule or Saytzev's rule.
Since H and Br are removed, it is dehydrohalogenation.
2018
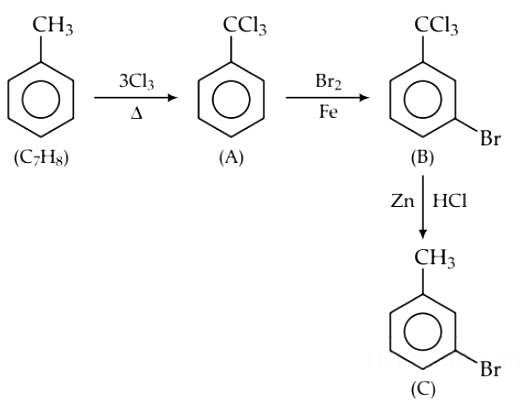
Q9. The compound C7H8 undergoes the following reactions : (NEET 2018)
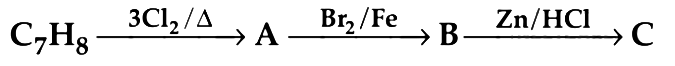
The product ‘C’ is
(a) m–bromotoluene
(b) o–bromotoluene
(c) 3–bromo–2,4,6–trichlorotoluene
(d) p–bromotoluene
Ans: (d)
2017
Q10. Identify A and predict the type of reaction (NEET 2017)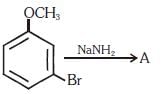
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Ans: (d)
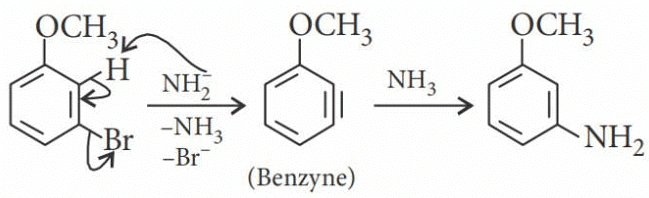
m-Bromoanisole gives only the respective meta substituted aniline. This is a substitution reaction which goes by an elimination-addition pathway.
2016
Q1: Consider the reaction, (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
CH3CH2CH2Br + NaCN
This reaction will be the fastest in
(a) ethanol
(b) methanol
(c) N, N' -dimethylformamide (DMF)
(d) Water
Ans: (c)
The reaction,
CH3CH2CH2Br + NaCN
follows SN2 mechanism which is favoured by polar aprotic solvent i.e., N, N'–dimethylformamide (DMF).
2015
Q1: In an SN1 reaction on chiral centers, there is (NEET / AIPMT 2015
(a) inversion more than retention leading to partial racemisation
(b) 100% retention
(c) 100% inversion
(d) 100% racemisation
Ans: (a)
- In case of optically active alkyl halides, SN1 reaction is accompanied by racemisation. The carbocation formed in the slow step being sp2 hybridised is planar and attack of nucleophile may take place from either side resulting in a mixture of products, one having the same configuration and other having inverted configuration.
- The isomer corresponding to inversion is present in slight excess because SN1 also depends upon the degree of shielding of the front side of the reacting carbon.
2014
Q1: Which of the following compounds will undergo racemisation when solution of KOH hydrolyses? (AIPMT 2014)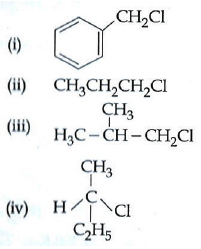
(a) (iii) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: (c)
Out of the given four compounds only (iv) compound is chiral and hence only this compound will undergo racemisation.
|
108 videos|287 docs|122 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Haloalkanes & Haloarenes - Chemistry Class 12
| 1. What are haloalkanes and haloarenes? |  |
| 2. What are some common uses of haloalkanes and haloarenes? |  |
| 3. How do haloalkanes and haloarenes differ in terms of reactivity? |  |
| 4. What are some environmental concerns associated with haloalkanes and haloarenes? |  |
| 5. How are haloalkanes and haloarenes named according to IUPAC nomenclature? |  |


















