NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Wave Optics | Physics Class 12 PDF Download
2025
Q1: The intensity of transmitted light when a polaroid sheet, placed between two crossed polaroids at 22.5° from the polarization axis of one of the polaroids, is (Io is the intensity of polarised light after passing through the first polaroid): (NEET 2025)
(a) 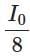
(b) 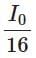
(c) 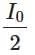
(d) 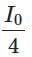
Ans: (a)
When light passes through a polaroid at an angle θ from the original polarization direction, the transmitted intensity is given by:
I = I0 × cos²θ
Since there are two polaroids with one in between at 22.5°, the intensity after the first polaroid becomes I0.
After the second polaroid (placed at 22.5° to the first):
I1 = I0 × cos²(22.5°)
After the third polaroid (crossed with the first, i.e., 90° apart, and thus 67.5° from the middle one):
I2 = I1 × cos²(67.5°)
So final intensity = I0 × cos²(22.5°) × cos²(67.5°)
cos(22.5°) ≈ 0.924, cos²(22.5°) ≈ 0.853
cos(67.5°) ≈ 0.383, cos²(67.5°) ≈ 0.146
Final intensity ≈ I0 × 0.853 × 0.146 ≈ I0 × 0.124 ≈ I0 / 8
Q2: An unpolarized light beam travelling in air is incident on a medium of refractive index 1.73 at Brewster's angle. Then: (NEET 2025)
(a) both reflected and transmitted light are perfectly polarized with angles of reflection and refraction close to 60° and 30°, respectively.
(b) transmitted light is completely polarized with angle of refraction close to 30°
(c) reflected light is completely polarized and the angle of reflection is close to 60°
(d) reflected light is partially polarized and the angle of reflection is close to 30°
Ans: (c)
Using Brewster's law
μ = tan θp
⇒ 1.73 = tan θp
⇒ √3 = tan θp
⇒ θp = 60°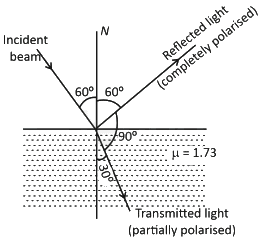
2024
Q1: If the monochromatic source in Young's double slit experiment is replaced by white light, then (NEET 2024)(a) Interference pattern will disappear
(b) There will be a central dark fringe surrounded by a few coloured fringes
(c) There will be a central bright white fringe surrounded by a few coloured fringes
(d) All bright fringes will be of equal width
Ans: (c)
In Young’s double-slit experiment, if a monochromatic source is replaced by white light, which contains multiple wavelengths, the patterns observed on the screen will differ significantly.
First, remember that the pattern formed in the double-slit experiment consists of both bright and dark fringes due to constructive and destructive interference, respectively. The position and intensity of these fringes depend on the wavelength of the light used. For monochromatic light (light of a single wavelength), the interference pattern is stable, with bright and dark fringes evenly spaced. Each fringe is uniformly bright or dark.
When using white light, which is a combination of various wavelengths of light, each color, or each wavelength, forms its own interference pattern with slightly different fringe spacing. This occurs because the separation between fringes Δy is given by the formula:
Δy = λL / d
Where:
λ is the wavelength of light
L is the distance from the slits to the screen
d is the separation between the slits
Since different wavelengths have different values for λ, each color’s fringes will be at slightly different positions. The result is that near the center of the pattern, where there is the least path difference, all wavelengths constructively interfere to form a bright white central fringe. However, moving away from the center, the fringes start to show different colors as the path difference between the light from the two slits increases. This causes a dispersion of colors with different orders of fringes dominated by different colors. The constructive and destructive interference patterns of different wavelengths slightly offset one another.
Thus:
- Option A - "Interference pattern will disappear" is incorrect because the interference pattern does not disappear but changes due to the dispersion of colors.
- Option B - "There will be a central dark fringe surrounded by a few coloured fringes" is incorrect as the central fringe in the presence of white light is bright, not dark.
- Option C - "There will be a central bright white fringe surrounded by a few coloured fringes" is correct. This is because all the wavelengths interfere constructively at the center, creating a bright white fringe, succeeded by colored fringes due to the varying interference conditions for each wavelength.
- Option D - "All bright fringes will be of equal width" is incorrect. The width and spacing of the fringes vary by wavelength, so the interference pattern will not have uniform fringe widths.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option C: "There will be a central bright white fringe surrounded by a few coloured fringes."
Q2: An unpolarised light beam strikes a glass surface at Brewster's angle. Then (NEET 2024)
(a) The reflected light will be partially polarised.
(b) The refracted light will be completely polarised.
(c) Both the reflected and refracted light will be completely polarised.
(d) The reflected light will be completely polarised but the refracted light will be partially polarised.
Ans: (d)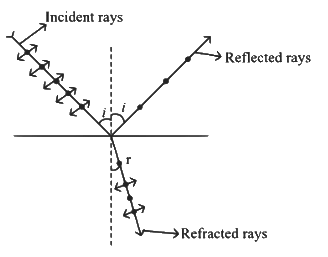 According to Brewster's law, reflected rays are completely polarized and refracted rays are partially polarized.
According to Brewster's law, reflected rays are completely polarized and refracted rays are partially polarized.
Q3: In Young's double slit experiment, if the wavelength of light used is increased (say from violet to red), then the: (NEET 2024)
(a) fringe width decreases.
(b) fringe width increases.
(c) central bright fringe becomes dark.
(d) fringe width remains unaltered.
Ans: (b)
In Young's double slit experiment, the fringe width (β) is given by the formula:
β = λL / d
Where:
- λ is the wavelength of light,
- L is the distance between the slits and the screen,
- d is the distance between the slits.
If the wavelength of light is increased (say from violet to red), then λ increases. Since the fringe width is directly proportional to the wavelength, the fringe width will increase as well.
Correct Answer: (b) fringe width increases.
Q4: If an unpolarised light is incident on a plane surface of refractive index √3 at Brewster's angle, then the angle of refraction is: (NEET 2024)
(a) 0°
(b) 30°
(c) 60°
(d) 90°
Ans: (b)
When unpolarised light is incident on a plane surface at Brewster's angle, the angle of refraction can be determined using Brewster's Law, which states that at Brewster's angle (θᵦ), the angle of incidence (θᵦ) and the angle of refraction (θᵣ) are related by the refractive index (n) of the medium.
Brewster's angle is given by the formula:
tan(θᵦ) = n₂ / n₁
Where:
- n₁ is the refractive index of the medium from which the light is coming (usually air, where n₁ ≈ 1),
- n₂ is the refractive index of the medium the light is entering (given as √3).
Now, applying Brewster's law:
tan(θᵦ) = √3
So,
θᵦ = tan⁻¹(√3) = 60°
At Brewster's angle, the light is partially reflected and refracted. The angle of refraction (θᵣ) is related to the angle of incidence (θᵦ) using Snell's law:
n₁ * sin(θᵦ) = n₂ * sin(θᵣ)
Substituting the values:
sin(60°) = √3 * sin(θᵣ)
Since sin(60°) = √3 / 2, we solve for θᵣ:
(1) * (√3 / 2) = (√3) * sin(θᵣ)
sin(θᵣ) = 1 / 2
θᵣ = 30°
Correct Answer: (b) 30°
Q5: Two slits in Young's double slit experiment are 1.5 mm apart, and the screen is placed at a distance of 1 m from the slits. If the wavelength of light used is 600 × 10⁻⁹ m, then the fringe separation is: (NEET 2024)
(a) 4 × 10⁻⁵ m
(b) 9 × 10⁻⁸ m
(c) 4 × 10⁻⁷ m
(d) 4 × 10⁻⁴ m
Ans: (d)
The formula for fringe separation in Young's double-slit experiment is:
β = λL / d
Where:
- λ is the wavelength of light,
- L is the distance from the slits to the screen,
- d is the distance between the slits.
Given:
- d = 1.5 mm = 1.5 × 10⁻³ m (distance between the slits),
- L = 1 m (distance from the slits to the screen),
- λ = 600 × 10⁻⁹ m (wavelength of the light).
Substituting the values into the formula:
β = (600 × 10⁻⁹ m) × (1 m) / (1.5 × 10⁻³ m)
β = (600 × 10⁻⁹) / (1.5 × 10⁻³)
β = 4 × 10⁻⁴ m
Correct Answer: (d) 4 × 10⁻⁴ m
Q6: An interference pattern can be observed due to the superposition of more than one of the following waves: (NEET 2024)
(A) y = a sin(ωt)
(B) y = a sin(2ωt)
(C) y = a sin(ωt − ϕ)
(D) y = a sin(3ωt)
Identify the waves from the options given below:
(a) (B) and (C) only
(b) (B) and (D) only
(c) (A) and (C) only
(d) (A) and (B) only
Ans: (c)
For interference to occur, the waves must have a constant phase relationship.
(A) y = a sin(ωt): A simple harmonic wave with a sinusoidal form.
(C) y = a sin(ωt − ϕ): This represents a wave with a phase shift, and interference is possible between waves that have a phase difference.
In the case of (B) y = a sin(2ωt) and (D) y = a sin(3ωt), these are waves of different frequencies (ω and 2ω, or 3ω), which typically do not produce a simple interference pattern.
Thus, interference is possible between waves (A) and (C).
Correct Answer: (c) (A) and (C) only
Q7: A beam of unpolarised light of intensity I₀ is passed through a polaroid A, through another polaroid B, oriented at 60°, and finally through another polaroid C, oriented at 45° relative to B as shown in the figure. The intensity of the emergent light is: (NEET 2024)
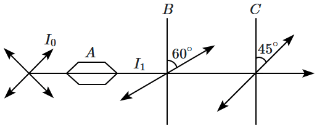
(a) I₀ / 16
(b) I₀ / 4
(c) I₀ / 2
(d) I₀ / 32
Ans: (a)
First Polaroid (A): When unpolarised light passes through the first polaroid, the intensity is reduced by half:
I₁ = I₀ / 2
Second Polaroid (B):
The light passing through polaroid B, which is oriented at 60° to the initial polarisation, will have its intensity reduced according to Malus' Law:
I₂ = I₁ × cos²(60°) = (I₀ / 2) × (1/2)² = I₀ / 8
Third Polaroid (C):
The light passing through polaroid C, which is oriented at 45° to polaroid B, will again be reduced by Malus' Law:
I₃ = I₂ × cos²(45°) = (I₀ / 8) × (√2/2)² = (I₀ / 8) × (1/2) = I₀ / 16
Correct Answer: (a) I₀ / 16
2023
Q1: For Young's double-slit experiment, two statements are given below: (NEET 2023)
Statement I: If the screen is moved away from the plane of slits, angular separation of the fringes remains constant.
Statement II: If the monochromatic source is replaced by another monochromatic source of larger wavelength, the angular separation of fringes decreases.
Which of the following is correct?
(a) Statement I is False but Statement II is True.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are True.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are False.
(d) Statement I is True but Statement II is False.
Ans: (d)
Statement I: If the screen is moved away from the slits, the fringe linear separation increases because the distance between the slits and the screen increases. However, the angular separation (θ = λ / d) of the fringes remains constant. So, Statement I is True.
Statement II: The angular separation of the fringes depends on the wavelength of the light. A larger wavelength (λ) leads to a larger angular separation because θ = λ / d. Therefore, Statement II is False, as the angular separation increases with a larger wavelength, not decreases.
Correct Answer: (d) Statement I is True but Statement II is False.
2022
Q.1. For Young’s double slit experiment, two statements are given below:Statement I: If screen is moved away from the plane of slits, angular separation of the fringes remains constant.
Statement II: If the monochromatic source is replaced by another monochromatic source of larger wavelength, the angular separation of fringes decreases.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below: (2022)
A: Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
B: Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
C: Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
D: Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
Ans: C
Solution: For YDSE, angular fringe width is given by α = λ/d
It does not depend on the distance of screen from the slit, so statement I is correct.
Angular fringe width ∝ λ
 angular separation of fringes increases
angular separation of fringes increasesSo, statement I is true and statement II is false.
Q.2. In a Young’s double slit experiment, a student observes 8 fringes in a certain segment of screen when a monochromatic light of 600 nm wavelength is used. If the wavelength of light is changed to 400 nm, then the number of fringes he would observe in the same region of the screen is (2022)
A: 8
B: 9
C: 12
D: 6
Ans: C
Solution:
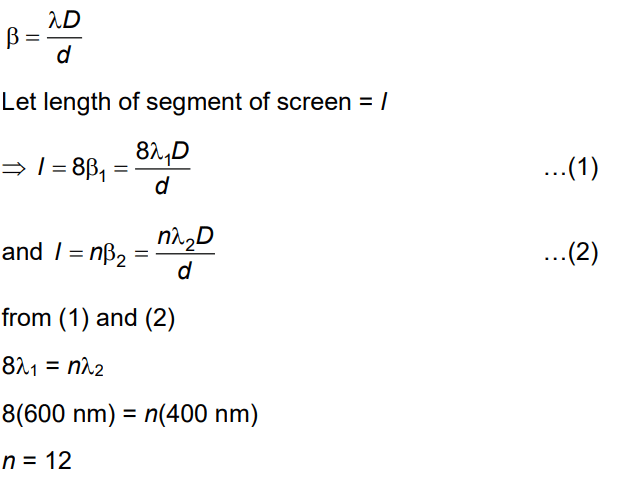
2020
Q.3. Assume that light of wavelength 600 nm is coming from a star. The limit of resolution of telescope whose objective has a diameter of 2m is: (2020)
A: 7.32 × 10–7 rad
B: 6.00 × 10–7 rad
C: 3.66 × 10–7 rad
D: 1.83 × 10–7 rad
Ans: C
Solution: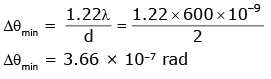
Q.4. The Brewster’s angle ib for an interface should be : (2020)
A: 45° < ib < 90°
B: ib = 90°
C: 0° < ib < 30°
D: 30° < ib < 45°
Ans: A
Solution: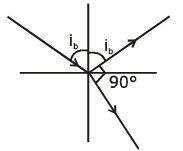
m = tan (ib)
ib = tan-1 (μ)
(μ > 1)
ib > 45
45 < ib < 90°
Q.5. In Young's double slit experiment, if the separation between coherent sources is halved and the distance of the screen from the coherent sources is doubled, then the fringe width becomes : (2020)
A: four times
B: one-fourth
C: double
D: half
Ans: A
Solution:
Fringewidth in YDSE is given by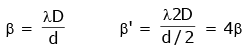
2019
Q.6. In a double slit experiment, when light of wavelength 400 nm was used, the angular width of the first minima formed on a screen placed 1 m away, was found to be 0.2°. What will be the angular width of the first minima, if the entire experimental apparatus is immersed in water? (μwater = 4/3) (2019)
A: 0.266°
B: 0.15°
C: 0.05°
D: 0.1°
Ans: B
Solution:
In air angular fringe width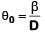
Angular fringe width in water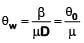
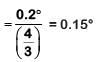
2018
Q.7. Unpolarised light is incident from air on a plane surface of a material of refractive index 'μ'. At a particular angle of incidence 'i', it is found that the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other. Which of the following options is correct for this situation ? (2018)
A: Reflected light is polarised with its electric vector parallel to the plane of incidence
B: Reflected light is polarised with its electric vector perpendicular to the plane of incidence
C: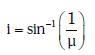
D: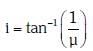
Ans: (b)
Solution:
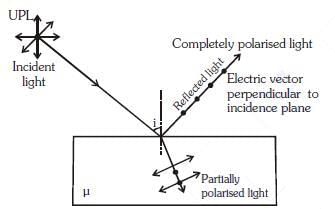
Q.8. In Young's double slit experiment the separation between the slits is 2 mm, the wavelength λ of the light used is 5896 Å and distance D between the screen and slits is 100 cm. It is found that the angular width of the fringes is 0.20°. To increase the fringe angular width to 0.21° (with same λ and D) the separation between the slits needs to be changed to :- (2018)
A: 1.8 mm
B: 1.9 mm
C: 2.1 mm
D: 1.7 mm
Ans: B
Solution: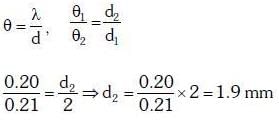
2017
Q.9. Young's double slit experiment is first performed in air and then in a medium other than air. It is found that 8th bright fringe in the medium lies where 5th dark fringe lies in air. The refractive index of the medium is nearly :- (2017)
A: 1.59
B: 1.69
C: 1.78
D: 1.25
Ans: C
Solution:
Fringe Width in a medium -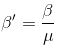
- where in
Since wavelength in a medium become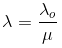
Fringe width in air 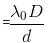
Fringe width in any other medium 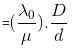
According to question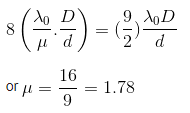
Q.10. Two Polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their axis perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light I0 is incident on P1 . A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its axis makes an angle 45° with that of P1. The intensity of transmitted light through P2 is :- (2017)
A:
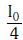
B:
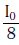
C:
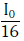
D:
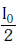
Ans: B
Solution:
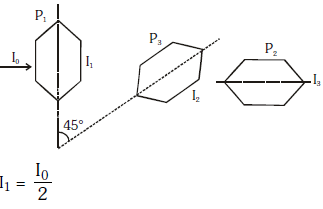
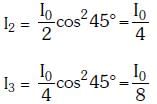
2016
Q.11. In a diffraction pattern due to a single slit of width 'a' the first minimum is observed at an angle 30º when light of wavelength 5000 Å is incident on the slit. The first secondary maximum is observed at an angle of : (2016)
A: sin-1 (3/4)
B: sin-1 (1/4)
C: sin-1 (2/3)
D: sin-1 (3/2)
Ans: A
Solution:
Given that, first minimum is observed at an angle of 30º in a diffraction pattern due to a single slit of width a.
i.e., n = 1, θ = 30º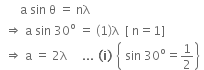
For 1st secondary maxima,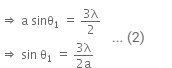
Putting the value of a from Eqn. (i) to Eqn. (ii), we get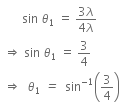
Q.12. The intensity at the maximum in Young's double slit experiment is I0. Distance between two slits is d = 5λ, where λ is the wavelength of light used is the experiment. What will be the intensity in front of one of the slits on the screen placed at a distance D = 10d ? (2016)
A: I0/2
B: I0
C: I0/4
D: 3I0/4
Ans: A
Solution:
Given,
Maximum intensity = Io
Distance between the slits, d = 5λ
Distance of screen from the slit, D = 10d
Using the formula,
Path difference, 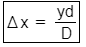
Here,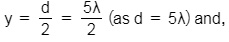
D = 10d = 50λ
So,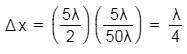
Corresponding phase difference will be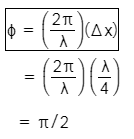
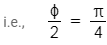

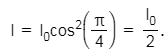
2015
Q.13. A radiation of energy = ‘E’ falls normally on a perfectly reflecting surface. The momentum transferred to the surface is (C = Velocity of light) : (2015)
A: E/C2
B: E/C
C: 2E/C
D: 2E/C2
Ans: C
Solution:
The radiation energy is given by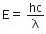
Initial momentum of the radiation is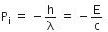
The reflected momentum is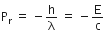
So, the change in momentum of light is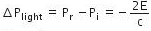
Thus, the momentum transferred to the surface is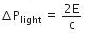
Q.14. In a double slit experiment, the 2 slits are 1 mm apart and the screen is placed 1 m away. A monochromatic light of wavelength 500 nm is used. What will be the width of each slit for obtaining ten maxima of double slit within the central maxima of single slit pattern ? (2015)
A: 0.02 mm
B: 0.2 mm
C: 0.1 mm
D: 0.5 mm
Ans: B
Solution:
In a double slit experiment, the two slits are 1 mm apart.
d = 1 mm = 10-3 m.
The screen is placed at a distance D = 1 m away. Monochromatic light of wave length
λ = 500 nm = 5 x 10-7 m is used.
The distance between two successive maxima or two successive minima is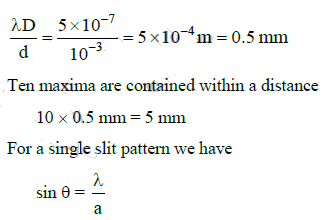
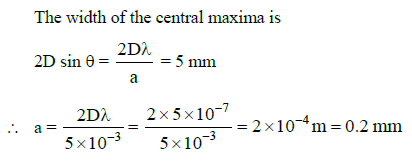
Q.15. For a parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength ‘λ’, diffraction is produced by a single slit whose width ‘a’ is of the order of the wavelength of the light. If ‘D’ is the distance of the screen from the slit, the width of the central maxima will be : (2015)
A: 2Da/λ
B: 2Dλ/a
C: Dλ/a
D: Da/λ
Ans: (b)
Solution:
For a parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength λ, diffraction is produced by a single slit whose width 'a' is of the order of the wavelength we have

where θ is the angle subtended by the first minima and the central maxima at the slit.

If x is the width of the central maxima, we have
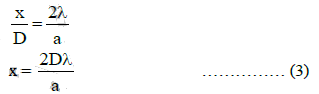
where D is the distance of the screen from the slit
2014
Q.16. A beam of light of λ = 600 nm from a distant source falls on a single slit 1mm wide and the resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 2m away. The distance between first dark fringes on either side of the central bright fringe is : (2014)
A: 2.4 cm
B: 2.4 mm
C: 1.2 cm
D: 1.2 mm
Ans: B
Solution: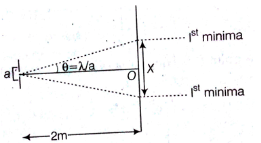
From the above figure,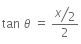
For small θ and when θ is counted in rad, tan ≈ θ
So,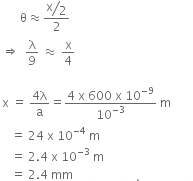
Q.17. In the Young’s double−slit experiment, the intensity of light at a point on the screen where the path difference is λ is K, (λ being the wave length of light used). The intensity at a point where the path difference is λ/4, will be : (2014)
A: K/2
B: Zero
C: K
D: K/4
Ans: A
Solution:
I = 4Io cos2(S/2)
4I0 = K
∵ δ = 2π if path different = λ
Phase difference when path difference = Δ/4 is equal to 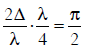
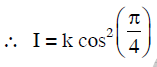
"There is no Question for NEET 2021"
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Wave Optics - Physics Class 12
| 1. What are the key concepts covered in Wave Optics for NEET? |  |
| 2. How does Young's double-slit experiment demonstrate the wave nature of light? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the diffraction pattern in Wave Optics? |  |
| 4. How is polarization of light explained in Wave Optics? |  |
| 5. What types of problems related to Wave Optics are commonly asked in the NEET exam? |  |






















