NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Human Health & Disease | Biology Class 12 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Neoplastic characteristics of cells refer to: (NEET 2025)
A. A mass of proliferating cell
B. Rapid growth of cells
C. Invasion and damage to the surrounding tissue
D. Those confined to original location
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) A, B, D only
(b) B, C, D only
(c) A, B only
(d) A, B, C only
Ans: (d)
- Neoplastic characteristics of cells refer to the properties of cells that are involved in the formation of neoplasms or tumors.
- Neoplastic or tumor cells grow very rapidly, invading and damaging the surrounding normal tissues. As these cells actively divide and grow they also starve the normal cells by competing for vital nutrients.
- Cells sloughed from such tumors reach distant sites through blood, and wherever they get lodged in the body, they start a new tumor there.
- A. A mass of proliferating cells: Neoplastic cells form abnormal masses due to their unregulated growth and proliferation.
- B. Rapid growth of cells: Neoplastic cells exhibit rapid and uncontrolled growth, which is one of the hallmarks of cancer.
- C. Invasion and damage to the surrounding tissue: Neoplastic cells often have the ability to invade and damage surrounding tissues, leading to metastasis.
- D. Those confined to original location: This characteristic refers to benign tumors, which are not usually invasive and remain localized. However, this is not a defining characteristic of all neoplastic cells, particularly malignant ones.
Q2: Which are correct: (NEET 2025)
A. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging detect cancers of internal organs.
B. Chemotherapeutics drugs are used to kill non-cancerous cells.
C. α interferon activate the cancer patients' immune system and helps in destroying the tumour.
D. Chemotherapeutic drugs are biological response modifiers.
E. In the case of leukaemia blood cell counts are decreased.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C and D only
(b) A and C only
(c) B and D only
(d) D and E only
Ans: (b)
- Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) detect cancers of internal organs (A): CT and MRI are advanced imaging technologies used to visualize internal structures of the body. They are highly effective in detecting tumors and abnormalities within internal organs.
- α-interferon activates the cancer patients’ immune system and helps in destroying the tumor (C): α-interferon is a type of cytokine that boosts the immune system, enabling it to better target and destroy cancer cells.
Incorrect statements:
- Chemotherapeutic drugs are used to kill non-cancerous cells): Incorrect because chemotherapeutic drugs are designed to target and kill rapidly dividing cancer cells, although they can sometimes affect non-cancerous cells as well.
- Chemotherapeutic drugs are biological response modifiers: Incorrect because biological response modifiers are different types of therapies like α-interferon, used to enhance the body's immune response, not chemotherapeutic drugs.
- In the case of leukemia, blood cell counts are decreased: Incorrect because in leukemia, there is generally an abnormal increase in white blood cell counts, not a decrease.
Q3: After maturation, in primary lymphoid organs, the lymphocytes migrate for interaction with antigens to secondary lymphoid organ(s) / tissue(s) like: (NEET 2025)
A. thymus
B. bone marrow
C. spleen
D. lymph nodes
E. Peyer's patches
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) E, A, B only
(b) C, D, E only
(c) B, C, D only
(d) A, B, C only
Ans: (b)
- Spleen (C): The spleen filters blood and is a site where lymphocytes interact with blood-borne antigens. It plays a crucial role in immune responses to pathogens circulating in the bloodstream.
- Lymph Nodes (D): Lymph nodes are distributed throughout the body and filter lymph. They trap antigens from lymphatic fluid and allow interaction between lymphocytes and antigens, activating adaptive immune responses.
- Peyer’s Patches (E): Peyer’s patches are specialized mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues in the small intestine. They monitor intestinal contents for antigens and are essential for immune responses in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT).
Incorrect Options:
- Thymus (A): The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ responsible for the maturation of T cells.
- Bone Marrow (B): The bone marrow is another primary lymphoid organ responsible for the development and maturation of B cells.
Q4: Which of the following type of immunity is present at the time of birth and is a non-specific type of defence in the human body? (NEET 2025)
(a) Cell-mediated Immunity
(b) Humoral Immunity
(c) Acquired Immunity
(d) Innate Immunity
Ans: (d)
- Immunity refers to the ability of the body to resist harmful microorganisms or toxins and protect against diseases.
- There are two main types of immunity in the human body: innate immunity and acquired immunity.
- Innate immunity is present from birth and provides non-specific defense mechanisms against pathogens.
- Acquired immunity develops during an individual's lifetime and is specific to particular pathogens.
- Innate immunity is the body's first line of defense against infections and is present at the time of birth.
- It does not target specific pathogens; instead, it provides a general defense against all harmful microorganisms.
- Components:
- Physical barriers such as skin and mucous membranes prevent the entry of pathogens.
- Physiological barriers include acid in the stomach, saliva in the mouth, tears from eyes–all prevent microbial growth.
- Cellular components such as certain types of leukocytes (WBC) of our body like polymorpho-nuclear leukocytes (PMNL-neutrophils) and monocytes and natural killer (type of lymphocytes) in the blood as well as macrophages in tissues can phagocytose and destroy microbes.
- Cytokine barriers: Virus-infected cells secrete proteins called interferons which protect non-infected cells from further viral infection.
Other Options:
- Acquired Immunity:
- This type of immunity develops after exposure to specific pathogens.
- It involves the production of antibodies and memory cells, making it pathogen-specific.
- It is characterised by memory.
- Cell-Mediated Immunity:
- This is a type of acquired immunity where T-cells (a type of white blood cell) play a central role in defending against intracellular pathogens, such as viruses and some bacteria.
- Humoral Immunity:
- This is another type of acquired immunity where B-cells produce antibodies to target specific pathogens. Like cell-mediated immunity, it is specific and develops after exposure to pathogens
Q5: Identify the statement that is NOT correct. (NEET 2025)
(a) Antigen binding site is located at C-terminal region of antibody molecules.
(b) Constant region of heavy and light chains are located at C-terminus of antibody molecules.
(c) Each antibody has two light and two heavy chain.
(d) The heavy and light chains are held together by disulfide bonds.
Ans: (a)
- Option 1: "Each antibody has two light and two heavy chains" is correct. Each antibody molecule comprises two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains.
- Option 2: "The heavy and light chains are held together by disulfide bonds" is correct. Disulfide bonds between the chains provide structural integrity to the antibody molecule.
- Option 3: "Antigen binding site is located at C-terminal region of antibody molecules" is incorrect. The antigen binding site is located at the N-terminal region where the variable regions are present.
- Option 4: "Constant region of heavy and light chains are located at C-terminus of antibody molecules" is correct. The constant regions are situated at the C-terminal ends and are involved in effector functions of antibodies.
2024
Q1: Match List I with List II : (NEET 2024)
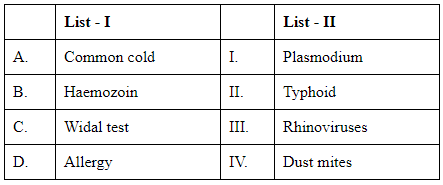 Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A-III, B-IV, C-III, D-I
(b) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
(c) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(d) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
Ans: (c)
To correctly match the items in List I with List II, we need to understand each term and its relationship:
Common Cold is primarily caused by Rhinoviruses. Hence, A is linked with III.
Haemozoin is a byproduct of the digestion of blood by parasites such as Plasmodium (which causes malaria). Therefore, B corresponds with I.
Widal test is a diagnostic test for Typhoid fever, caused by the bacterium Salmonella Typhi. Thus, C matches with II.
Allergy can be triggered by many allergens, including Dust Mites, which are a common cause of respiratory and dermatological allergies. Consequently, D aligns with IV.
Based on this, the matching should be:
A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
Therefore, the correct answer is: Option C: A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
Q2: Match List I with List II : (NEET 2024)
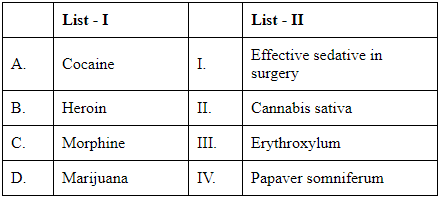
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(b) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
(c) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
Ans: (d)
To solve this matching problem, we need to identify which plant or application each substance in List I is correctly associated with in List II.
List I (Substances) and List II (their sources or uses):
Cocaine - Cocaine is derived from the coca plant, known scientifically as Erythroxylum. This matches with III in List II.
Heroin - Heroin is derived from the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. This corresponds to IV in List II.
Morphine - Like heroin, Morphine is also derived from the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. However, morphine is also directly associated with its use as a sedative in surgery, making I a valid association for its usage.
Marijuana - Marijuana is derived from Cannabis sativa, which corresponds to II in List II.
With this information:
A (Cocaine) matches with III (from Erythroxylum).
B (Heroin) matches with IV (Papaver somniferum).
C (Morphine) as an effective sedative in surgery matches with I.
D (Marijuana) matches with II (Cannabis sativa).
The correct matching based on the provided options is: Option D: A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
This option correctly matches the substance with their respective sources or primary uses.
Q3: Which of the following are Autoimmune disorders?
A. Myasthenia gravis
B. Rheumatoid arthritis
C. Gout
D. Muscular dystrophy
E. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below: (NEET 2024)
(a) A, B & D only
(b) A, B & E only
(c) B, C & E only
(d) C, D & E only
Ans: (b)
Autoimmune disorders are conditions in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues. Analysis of the given diseases in the context of autoimmune disorders includes:
Myasthenia gravis: This is an autoimmune disorder where antibodies interfere with the communication between nerves and muscles, leading to muscle weakness.
Rheumatoid arthritis: Another autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and potentially leading to joint deformity.
Gout: This is not an autoimmune disease; it's a form of arthritis caused by excess uric acid in the bloodstream, resulting in the formation of crystals in joints, not by immune system activity attacking body tissues.
Muscular dystrophy: This refers to a group of genetic diseases characterized by progressive weakness and loss of muscle mass, not caused by an autoimmune response.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): It is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks various body systems including skin, joints, and organs like kidneys and heart.
With this analysis, the correct diseases identified as autoimmune disorders are Myasthenia gravis, Rheumatoid arthritis, and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Therefore, among the provided options, the correct answer is: Option B: A, B & E only.
Q4: Given below are two statements :
Statement I : Bone marrow is the main lymphoid organ where all blood cells including lymphocytes are produced.
Statement II : Both bone marrow and thymus provide micro environments for the development and maturation of T-lymphocytes. In the light of above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below (NEET 2024)
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Ans: (a)
The correct answer is option no. (A) as both statements I and II are correct.
In humans, the bone marrow is the main lymphoid organ where all blood cells including lymphocytes are produced.
Both bone-marrow and thymus provide micro-environments for the development and maturation of T-lymphocytes.
Options (B), (C) and (D) are incorrect.
Q5: Match List I with List II: (NEET 2024)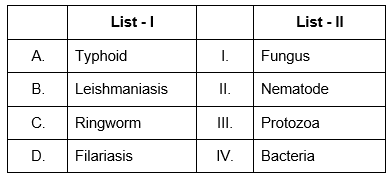 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
(b) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(c) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(d) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I
Ans: (b)
Sol: To correctly match List I (Diseases) with List II (Pathogen Types), we need to understand the causative agents for each disease listed in List I.
Details for each disease:
Typhoid: This is a bacterial infection caused by Salmonella typhi. Hence, it matches with "Bacteria".
Leishmaniasis: This disease is caused by parasitic protozoans of the genus Leishmania. Therefore, it corresponds to "Protozoa".
Ringworm: Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by a worm. It’s a fungal infection on the skin, caused by various types of fungi. So, Ringworm should be associated with "Fungus".
Filariasis: Also known as lymphatic filariasis, this condition is caused by infection with parasites classified as nematodes (roundworms) of the family Filarioidea. Thus, it matches with "Nematode".
With this understanding:
A should be paired with IV (Bacteria).
B should be paired with III (Protozoa).
C should be paired with I (Fungus).
D should be paired with II (Nematode).
Corresponding to the options provided:
Option A: A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV - Incorrect
Option B: A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II - Correct!
Option C: A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II - Incorrect
Option D: A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I - Incorrect
Therefore, the correct answer is Option B: A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II.
Q6: Given below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). (NEET 2024)
Assertion (A): Some human organs like the liver and kidney fail to function normally, and transplantation is the only remedy to enable the patient to live a normal life.
Reason (R): Tissue matching and blood group matching are essential before undertaking any transplant, and the patient has to take immunosuppressants thereafter.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are True, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are True, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is True, but (R) is False.
(d) (A) is False, but (R) is True.
Ans: (b)
Assertion (A): It is true that some human organs, such as the liver and kidney, can fail to function normally, and in such cases, organ transplantation is often the only remedy to restore normal life functions. Transplantation is a well-established medical procedure for organs like the kidney and liver when they fail due to disease or damage.
Reason (R): The statement is also true. Tissue matching and blood group matching are crucial before organ transplantation to reduce the risk of rejection. Additionally, immunosuppressive drugs are required post-transplantation to prevent the immune system from rejecting the transplanted organ.
However, (R) does not directly explain (A). While the necessity of tissue and blood group matching, along with immunosuppressants, is important for the success of transplants, (A) addresses the necessity of the transplant itself due to organ failure, which is not explained by (R). Therefore, (R) is not the direct explanation for why transplantation is needed, but it is still true.
Thus, both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Q7: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2024)
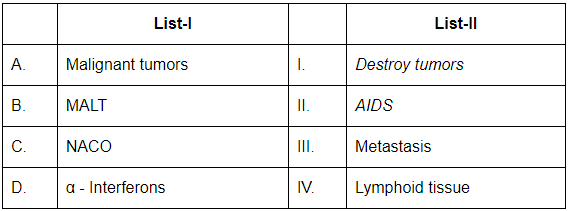 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(b) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
Ans: (a)
- A. Malignant tumors: These are characterized by metastasis (III), which is the spread of cancer cells from the primary site to other parts of the body.
- B. MALT (Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue): This is associated with lymphoid tissue (IV), as MALT is made up of lymphoid tissues found in mucosal linings, such as in the digestive and respiratory tracts.
- C. NACO (National AIDS Control Organization): This organization is involved in the fight against AIDS (II) in India and works on the prevention, treatment, and care of individuals affected by HIV/AIDS.
- D. α-Interferons: These are used in the treatment of various diseases, including cancer, as they destroy tumors (I) by enhancing the immune response and inhibiting the growth of tumor cells.
Thus, the correct matching is A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I.
Q8: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2024)
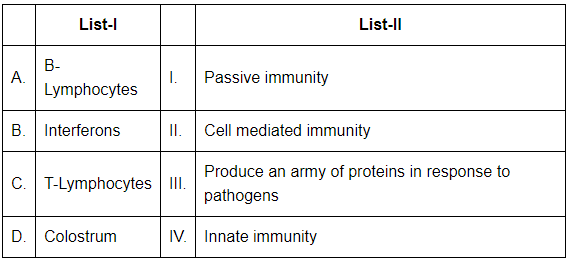 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
(b) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(d) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
Ans: (c)
- A. B-Lymphocytes: These are responsible for producing an army of antibodies (III) in response to pathogens, which help to neutralize or destroy the pathogens.
- B. Interferons: Interferons are part of the innate immunity (IV) system, as they are proteins produced by cells in response to viral infections and help to inhibit viral replication.
- C. T-Lymphocytes: T-Lymphocytes are involved in cell-mediated immunity (II), where they directly attack infected cells or help regulate the immune response.
- D. Colostrum: Colostrum, the first milk produced after birth, provides passive immunity (I) to the newborn by transferring antibodies from the mother to the baby.
Thus, the correct matching is A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I.
2023
Q1: Which one of the following common sexually transmitted diseases is completely curable when detected early and treated properly? (NEET 2023)
(a) Genital herpes
(b) Gonorrhoea
(c) Hepatitis-B
(d) HIV Infection
Ans: (b)
- Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It can be effectively treated with antibiotics, especially when detected early.
- Hepatitis B, HIV Infection, and Genital Herpes are caused by viruses. These viral infections can be managed with antiviral therapy but they are typically not completely curable.
Q2: In which blood corpuscles, the HIV undergoes replication and produces progeny viruses? (NEET 2023)
(a) TH cells
(b) B-lymphocytes
(c) Basophils
(d) Eosinophils
Ans: (a)
HIV, or the Human Immunodeficiency Virus, primarily infects CD4+ T cells, which are a type of T cell. In the context of the options given, TH cells, or T helper cells, are a subset of CD4+ T cells.
Q3: Match List I with List II. (NEET 2023)
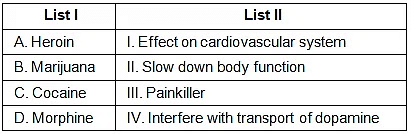
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(b) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
Ans: (a)
Solution.
- Heroin belongs to the category of opioids and it is a depressant that slows down body functions.
- Marijuana is known for its effect on the cardiovascular system of the body.
- Cocaine interferes with the transport of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
- Morphine is used is a sedative and painkiller.
Q4: Match List I with List II. (NEET 2023)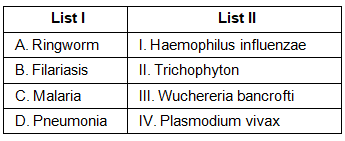
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(b) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(c) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
Ans: (a)
Option (a) is the correct answer because:
- Ringworm is a fungal infection of the skin, hair, or nails.It is caused by various species of dermatophyte fungi, including Trichophyton, Microsporum and Epidermophyton.
- Filariasis is a parasitic disease caused by several species of thread-like nematode worms (filarial worms). The most common filarial worms causing the disease include Wuchereria bancrofti. It is a causative agent of lymphatic filariasis, a type of filariasis that affects the lymphatic system.
- Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease caused by Plasmodium parasites.
- Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, and it can be caused by various infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms. Haemophilus influenzae is indeed one of the bacteria that can cause pneumonia, especially in certain populations, like children and older adults.
Q5: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2023)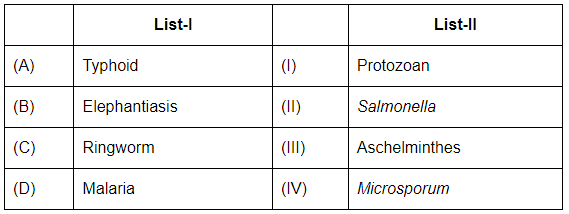 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A)-(I) (B)-(IV) (C)-(III) (D)-(II)
(b) (A)-(I) (B)-(III) (C)-(IV) (D)-(II)
(c) (A)-(II) (B)-(III) (C)-(IV) (D)-(I)
(d) (A)-(II) (B)-(IV) (C)-(III) (D)-(I)
Ans: (c)
- A. Typhoid: Caused by the bacterium Salmonella (II).
- B. Elephantiasis: Caused by Aschelminthes (III), specifically filarial worms.
- C. Ringworm: Caused by Microsporum (IV), a fungus.
- D. Malaria: Caused by a Protozoan (I), specifically the genus Plasmodium.
Thus, the correct matching is:
- A-II: Typhoid is caused by Salmonella.
- B-III: Elephantiasis is caused by Aschelminthes (filarial worms).
- C-IV: Ringworm is caused by Microsporum.
- D-I: Malaria is caused by a Protozoan.
Q6: Diacetyl morphine is also called as: (NEET 2023)
(a) Amphetamine
(b) Barbiturate
(c) Crack
(d) Smack
Ans: (d)
Diacetyl morphine is commonly known as heroin or smack in street slang. It is an opioid derived from morphine and is known for its potent effects as a painkiller and its high potential for abuse.
The other options are not related to diacetyl morphine:
- Amphetamine is a type of stimulant drug, not related to diacetyl morphine.
- Barbiturate refers to a class of drugs used as sedatives or anticonvulsants, which are also not related.
- Crack refers to a form of cocaine, not heroin.
Q7: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2023)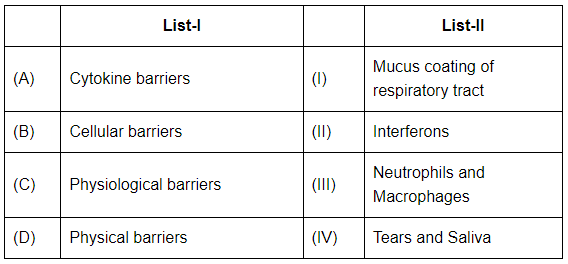 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A)-(II) (B)-(III) (C)-(IV) (D)-(I)
(b) (A)-(III) (B)-(I) (C)-(IV) (D)-(II)
(c) (A)-(III) (B)-(I) (C)-(II) (D)-(IV)
(d) (A)-(II) (B)-(III) (C)-(I) (D)-(IV)
Ans: (d)
- A. Cytokine barriers: Cytokines are proteins that help in immune responses and include interferons (II), which play a role in the defense against viral infections.
- B. Cellular barriers: These barriers involve neutrophils and macrophages (III), which are white blood cells that help to fight infections by engulfing pathogens.
- C. Physiological barriers: Mucus coating of the respiratory tract (I) is a physiological barrier that helps trap dust, microbes, and other particles in the air.
- D. Physical barriers: Tears and saliva (IV) act as physical barriers, helping to wash away pathogens from the eyes and mouth.
Thus, the correct matching is A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV.
2022
Q1: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2022)
Statement I: Autoimmune disorder is a condition where body defense mechanism recognises its own cells as foreign bodies.
Statement II: Rheumatoid arthritis is a condition where body does not attack self cells.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both statement I and statement II are incorrect
(b) Statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect
(c) Statement I is incorrect but statement II is correct
(d) Both statement I and statement II are correct
Ans: (b)
- Option (b) is the correct answer as autoimmune disorder is a condition where body defense mechanism recognises its own cells as foreign bodies. Sometimes, due to genetic and other unknown reasons, the body attacks self cells.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an example where body attacks self cells (synovial membrane).
So Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
Q2: Select the incorrect statement with respect to acquired immunity. (NEET 2022)
(a) Anamnestic response is elicited on subsequent encounters with the same pathogen
(b) Anamnestic response is due to memory of first encounter
(c) Acquired immunity is non-specific type of defense present at the time of birth
(d) Primary response is produced when our body encounters a pathogen for the first time
Ans: (c)
There are two main types of immunity in human body:
1. Innate immunity is the non-specific immunity present at the time of birth. This works on physical, physiological, cytological and chemical barriers.
2. Acquired immunity is the adaptive or specific immunity which a person develops during his/her lifetime. This works by B-cell and T-cells of the body.
Q3: Which of the following reasons is mainly responsible for graft rejection in transplantation of organs?
(a) Cell-mediated response
(b) Inability of recipient to differentiate between ‘self’ and ‘non-self’ tissues/cells
(c) Humoral immune response only
(d) Auto-immune response (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (a)
- Option (1) is the correct answer as the body is able to differentiate between ‘self’ and ‘non-self’ and the cell-mediated immune response is responsible for the graft rejection.
- Option (2) is incorrect as body of higher vertebrates have the ability to differentiate foreign organisms from self cells.
- Option (4) is incorrect as the autoimmune response occur when the body’s immune system fails to recognize ‘self’ from ‘non-self’ and starts destroying the body’s own cells.
Q4: Match List - I with List - II : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (a) - (iii), (b) - (i), (c) - (ii), (d) - (iv)
(b) (a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (iv), (d) - (i)
(c) (a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (i), (d) - (iv)
(d) a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
Ans: (a)
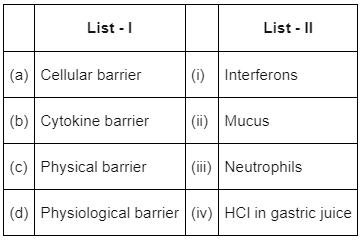
- Option (a) is the correct answer because cellular barriers include NK cells, macrophages (monocytes) and neutrophils (PMNL).
- Cytokine barriers include interferons.
- Physical barriers include mucus membranes and skin.
- Physiological barriers include HCl in gastric juice, saliva and tears etc.
2021
Q1: Identify the incorrect pair (NEET 2021)
(a) Drugs - Ricin
(b) Alkaloids - Codeine
(c) Toxin - Abrin
(d) Lectins - Concanavalin A
Ans: (a)
- Option (a) is incorrect because ricin is a toxin obtained from Ricinus plant. Vinblastin and curcumin are drugs.
- Morphine and codeine are alkaloids.
- Abrin is also a toxin obtained by plant Abrus.
- Concanavalin A is a lectin.
Q2: For effective treatment of the disease, early diagnosis and understanding its pathophysiology is very important. Which of the following molecular diagnostic techniques is very useful for early detection? (NEET 2021)
(a) Hybridization Technique
(b) Western Blotting Technique
(c) Southern Blotting Technique
(d) ELISA Technique
Ans: (d)
- Option A: Hybridization Technique - This technique, including Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH), involves the pairing of single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules with complementary sequences, allowing the detection of specific nucleic acids within a complex mixture. It's widely used for gene mapping, diagnosis of genetic disorders, and identification of infectious agents. However, its application is more towards locating specific sequences rather than early detection of diseases.
- Option B: Western Blotting Technique - This is a protein analysis method that involves the separation of proteins via gel electrophoresis, followed by their transfer to a membrane and detection using antibodies. It's used for identifying specific proteins in a sample and understanding protein size or abundance, but it is not primarily used for early disease detection.
- Option C: Southern Blotting Technique - This method involves the transfer of DNA fragments from an agarose gel to a membrane followed by hybridization with a labeled DNA probe to detect specific DNA sequences. It's widely used in molecular biology for gene detection and mapping but not necessarily for early disease detection.
- Option D: ELISA Technique - The Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a popular technique used for detecting and quantifying substances such as peptides, proteins, antibodies, and hormones. In the context of disease detection, ELISA is exceptionally valuable because it can be used to detect specific antigens or antibodies in blood samples, making it a crucial tool for early diagnosis of diseases. This might include viral infections (like HIV), bacterial infections, and autoimmune diseases. Its sensitivity and specificity make ELISA particularly useful for early detection, when the levels of the target molecule might be very low but detecting it is critical for effective treatment.
Therefore, for early detection of diseases, the ELISA Technique stands out among the options given for its ability to detect specific biomolecules related to diseases at an early stage, facilitating early diagnosis and treatment.
Q3: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2021)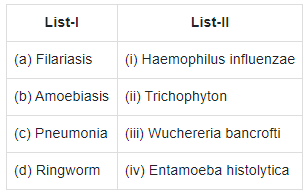 Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Ans: (d)
- Filariasis or elephantiasis is caused by filarial worm known as Wuchereria bancrofti. It affect the lymphatic vessels of lower limbs resulting in gross deformities.
- Amoebiasis/Amoebic dysentery is caused by a protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica in the large intestine of human.
- Penumonia is caused by bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae.
- Ringworm is caused by fungi belonging to genera Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton.
Q4: The Adenosine deaminase deficiency results into
(a) Addison's disease
(b) Dysfunction of immune system
(c) Parkinson's disease
(d) Digestive disorder (NEET 2021)
Ans: (b)
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) enzyme is crucial for the immune system to function. Hence, its deficiency results in the dysfunction of immune system.
- Hyposecretion of hormones of the adrenal cortex causes Addison's disease.
- Parkinson's disease is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system.
- Disorders which affect GIT & associated glands are called digestive disorders.
2020
Q1: Identify the wrong statement with reference to immunity (NEET 2020)
(a) Active immunity is quick and gives a full response
(b) Foetus receives some antibodies from mother, it is an example of passive immunity
(c) When exposed to antigen (living or dead) antibodies are produced in the host’s body. It is called “Active immunity”
(d) When ready-made antibodies are directly given, it i
s called “Passive immunity”.
Ans: (a)
Active immunity is slow and takes time to give its full effective response in comparison to passive immunity where pre-formed antibodies are administered.
Q2: Match the following diseases with the causative organism and select the correct option. (NEET 2020)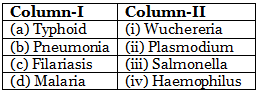
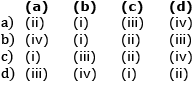
Ans: (d)
Typhoid fever in humans is caused by pathogenic bacterium Salmonella typhi. Pneumonia is caused by Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. Filariasis or elephantiasis is caused by the filarial worm, Wuchereria bancrofti and Wuchereria malayi. Malaria is caused by different species of Plasmodium.
Q3: The infectious stage of plasmodium that enters the human body is : (NEET 2020)
(a) Female gametocytes
(b) Male gametocytes
(c) Trophozoites
(d) Sporozoites
Ans: (d)
Plasmodium enters the human body as sporozoites (Infectious stage) through the bite of Infected Female Anopheles mosquito.
2019
Q1: Which of the following immune response is responsible for the rejection of kidney grafts? (NEET 2019)
(a) Cell-mediated immune response
(b) Auto-immune response
(c) Humoral immune response
(d) Inflammatory immune response
Ans: (a)
Cell-mediated immune response (CMI) causes rejection of graft. Immune response by T-lymphocytes (T-cells) is by activation of cytotoxic killer cells which detects and destroys the foreign cells and also a cancerous cell is called cell mediated immune response.
Q2: Colostrum, the yellowish fluid, secreted by mother during the initial days of lactation is very essential to impart immunity to the newborn infants because it contains (NEET 2019)
(a) Immunoglobulin A
(b) Natural killer cells
(c) Monocytes
(d) Macrophages
Ans: (a)
The yellowish milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is called colostrum. It contains several antibodies especially immunoglobulin A, which imparts naturally acquired passive immunity to the newborn.
Q3: Identify the correct pair representing the causative agent of typhoid fever and the confirmatory test for typhoid. (NEET 2019)
(a) Salmonella typhi / Widal test
(b) Plasmodium vivax / UTI test
(c) Streptococcus pneumoniae / Widal test
(d) Salmonella typhi / Anthrone test
Ans: (a)
Typhoid fever is caused by salmonella typhi which is diagnosed through WIDAL TEST.
Q4: Which of the following sexually transmitted diseases is not completely curable ?
(a) Genital herpes
(b) Chlamydiasis
(c) Gonorrhoea
(d) Genital warts (NEET 2019)
Ans: (a)
HIV and Genital Herpes is not completely curable.
Q5: The drug called ‘Heroin’ is synthesized by (NEET 2019)
(a) Nitration of morphine
(b) Methylation of morphine
(c) Acetylation of morphine
(d) Glycosylation of morphine
Ans: (c)
Heroine is formed by acetylation of morphine.
2018
Q1: Which part of poppy plant is used to obtain the drug “smack”? (NEET 2018)
(a) Flowers
(b) Latex
(c) Roots
(d) Leaves
Ans: (b)
 Poppy Plant'Smack' also called as brown sugar/Heroin is formed by acetylation of morphine. It is obtained from the latex of unripe capsule of Poppy plant (Papaver somniferum).
Poppy Plant'Smack' also called as brown sugar/Heroin is formed by acetylation of morphine. It is obtained from the latex of unripe capsule of Poppy plant (Papaver somniferum).
Q2: Which of the following is not an autoimmune disease? (NEET 2018)
(a) Psoriasis
(b) Rheumatoid arthritis
(c) Alzheimer’s disease
(d) Vitiligo
Ans: (c) Alzheimer's disease is due to deficiency of neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Alzheimer's disease is due to deficiency of neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Q3: In which disease does mosquito-transmitted pathogen cause chronic inflammation of lymphatic vessels? (NEET 2018)
(a) Elephantiasis
(b) Ascariasis
(c) Ringworm disease
(d) Amoebiasis
Ans: (a)
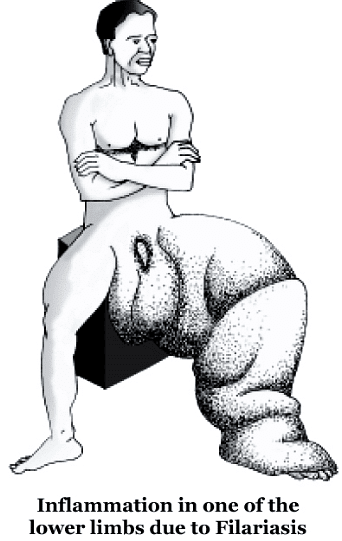
Lymphatic filariasis, also known as elephantiasis, is a human disease caused by parasitic worms known as filarial worms. It is caused by roundworm, Wuchereria bancrofti and it is transmitted by culex mosquito.
2017
Q1: Transplantation of tissues/organs fails often due to non-acceptance by the patient’s body. Which type of immune response is responsible for such rejections? (NEET 2017)
(a) Cell-mediated immune response
(b) Hormonal immune response
(c) Physiological immune response
(d) Autoimmune response
Ans: (a)
Cell mediated immune response causes non-acceptance or rejection of graft or transplanted tissues/organs.
Q2: MALT constitutes about_________ percent of the lymphoid tissue in human body. (NEET 2017)
(a) 20%
(b) 70%
(c) 10%
(d) 50%
Ans: (d)
MALT or Mucosa Associated Lymphoid Tissue constitutes about 50 percent of the lymphoid tissue in human body. It is scattered along mucosal lining in the human body
2016
Q1: Which of the following sets of diseases is caused by bacteria? (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Cholera and tetanus
(b) Typhoid and smallpox
(c) Tetanus and mumps
(d) Herpes and influenza
Ans: (a)
Cholera is caused by bacterium Vibrio cholerae, tetanus is caused by bacterium Clostridium tetani, typhoid is caused by bacterium Salmonella typhi, small pox is caused by Variola virus, mumps is caused by Paramyxo virus, Herpes is caused by Herpis simplex virus and influenza is caused by Orthomyxovirus.
Q2: Which of the following is correct regarding AIDS causative agent HIV? (NEET 2016)
(a) HIV is enveloped virus containing one molecule of single-stranded RNA and one molecule of reverse transcriptase.
(b) HIV is enveloped virus that contains two identical molecules of single-stranded RNA and two molecules of reverse transcriptase.
(c) HIV is an unenveloped retrovirus.
(d) HIV does not escape but attacks the acquired immune response.
Ans: (b)
The correct option is b HIV is enveloped virus that contains two identical molecules of single-stranded RNA and two molecules of reverse transcriptase.
Statement b is correct. The correct form of other statements are a HIV is a virus containing ssRNA and reverse transcriptase enzyme enveloped by protein coat. c HIV rs enveloped retrovirus. d HIV escapes the immune cells and attacks helper T-cells of immune system.
Q3: Antivenom injection contains preformed antibodies while polio drops that are administered into the body contain (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Gamma globulin
(b) Attenuated pathogens
(c) Activated pathogens
(d) Harvested antibodies
Ans: (b)
Oral Polio Vaccine consists of a mixture of attenuated (weakened) poliovirus strains of all three poliovirus types.
Q4: In higher vertebrates, the immune system can distinguish self-cells and non-self. If this property is lost line to a genetic abnormality and it attacks self-cells, then it leads to (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Autoimmune disease
(b) Active immunity
(c) Allergic response
(d) Graft rejection
Ans: (a)
Autoimmunity is a disorder of the body’s defence mechanisms in which an immune response is elicited against its own tissues, which are thereby damaged or destroyed. Autoimmunity may be caused due to genetic or environmental factors.
Q4: Which of the following statements is not true for cancer cells in relation to mutations? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Mutations inactivate cell control.
(b) Mutations inhibit the production of telomerase.
(c) Mutations in proto-oncogenes accelerate the cell cycle.
(d) Mutations destroy telomerase inhibitors.
Ans: (b)
Telomerase production is increased in cancer. Telomerase has been examined in hundreds of studies as a potentially sensitive biomarker for screening, early cancer detection, prognosis or in monitoring as an indication of residual disease.
|
65 videos|390 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Human Health & Disease - Biology Class 12
| 1. What are the common diseases that affect the human population? |  |
| 2. How does the immune system protect the body from diseases? |  |
| 3. What are the risk factors for developing chronic diseases? |  |
| 4. How do infectious diseases spread in human populations? |  |
| 5. How can individuals prevent the spread of diseases in communities? |  |

















