NEET Revised Syllabus 2025: Topic-wise Details & Important Chapters | Biology Class 11 PDF Download
The National Medical Commission (NMC) has announced the new syllabus for the NEET 2025 exam. The syllabus has been updated, with some topics removed and some new ones added to each subject.
The NMC NEET reduced syllabus 2025 PDF download is provided below.
NEET UG 2025 Reduced Syllabus (Official Notification)
Students should thoroughly review the complete NEET 2025 syllabus to prepare for the exam.
By going through this document we will be able to understand the topics added and reduced in NEET.

The NEET syllabus primarily consists of three core subjects: Biology, Physics, and Chemistry and the exam will consist of multiple-choice questions based on the topics mentioned in the syllabus.
The NEET exam will last for 3 hours and 20 minutes and will have 200 questions, out of which candidates need to answer 180. The scoring system remains the same, with four marks for correct answers and a deduction of one mark for wrong answers.
Below, you can find the syllabus for NEET 2025, organized by subject and based on the content from both 11th and 12th-grade classes.
NEET Biology 2025: Class 11 and Class 12 Syllabus
The NEET Biology 2025 syllabus is categorized into chapters. To achieve excellent scores in the NEET exam, candidates should thoroughly study all topics from both the 11th and 12th-grade Biology curriculum. The list of topics based on their respective chapters is provided below.
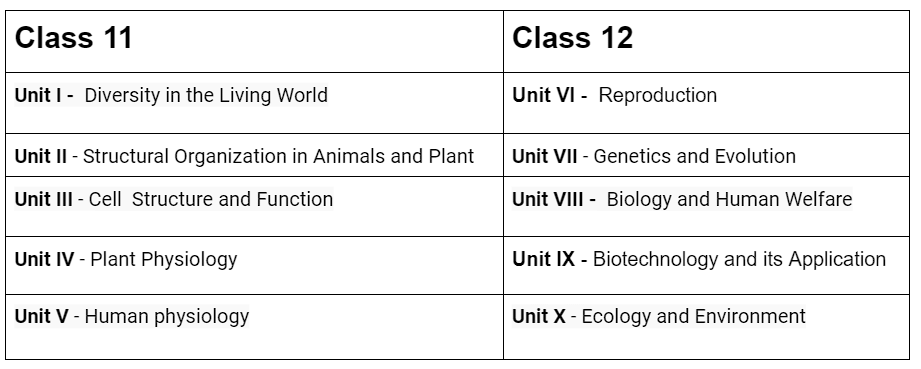
Detailed Biology Syllabus Class 11 and Class 12
The NEET Class 11 & 12 syllabus comprises five units each, containing various chapters. Below, you'll find the chapters and the specific topics that need to be studied in detail.
(a) Class 11 NEET Biology
Unit I: Diversity in the Living World
- What is living?
- Biodiversity: Need for classification, Taxonomy & Systematics.
- Concept of species and taxonomical hierarchy; Binomial nomenclature.
Chapter 2: Biological Classification
- Five kingdom classification: salient features.
- Classification of Monera; Protista and Fungi into major groups.
- Lichens Viruses and Viroid.
- Salient features and classification of plants into major groups.
- Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms (three to five salient and distinguishing features and at least two examples of each category).
- Salient features and classification of animals - non-chordate up to phyla level.
- Chordate up to class level (three to five salient features and at least two examples).
Unit II: Structural Organization in Animals and Plants
Chapter 5: Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Morphology and modifications: Tissues; Anatomy and functions of different parts of
flowering plants. - Root, stem, leaf, inflorescence- cymose and racemose, flower, fruit
and seed. - Floral Families: Family (Malvaceae, Cruciferae, Leguminoceae, compositae, graminae)
Chapter 6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy and functions of different parts of a flower
- Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Chapter 7: Structural Organization in Animals
- Animal tissues: Morphology, anatomy, and functions of different systems (digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous, and reproductive) of an insect (Frog) (Brief account only).
Unit III: Cell: Structure and Functions
Chapter 8: Cell: The Unit of Life
- Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life; Structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.
- Plant cell and animal cell; Cell envelope cell membrane, cell wall.
- Cell organelles- structure and function; Endomembrane system-endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies lysosomes, vacuoles; mitochondria, ribosomes, plastids, microbodies; Cytoskeleton cilia flagella centrioles (ultrastructure and function); Nucleus-nuclear membrane chromatin, nucleolus.
- Chemical constituents of living cells: Biomolecules-structure and function of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids.
- Enzymes-types, properties, enzyme action and classification and nomenclature of Enzymes.
Chapter10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis, and their significance.
Unit IV: Plant Physiology
Chapter 11: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Photosynthesis as a means of Autotrophic nutrition; Site of photosynthesis takes place; pigments involved in Photosynthesis (Elementary idea).
- Photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis; Cyclic and non-cyclic and photophosphorylation; chemiosmotic hypothesis; photorespiration c3 and c4 pathways; Factors affecting photosynthesis.
Chapter 12: Respiration in Plants
- Respiration: Exchange gases; cellular respiration-glycolysis. fermentation (anaerobic), TCA cycle and electron transport system (aerobic)
- Energy relations- Number of ATP molecules generated; Amphibolic pathways; Respiratory quotient.
Chapter 13: Plant Growth and Development
- Plant growth and development: Seed germination; phases of plant growth and plant growth rate; Conditions of growth; Differentiation, differentiation, and redifferentiation.
- The sequence of developmental process in a plant cell; Growth regulators- Auxin, Gibberellin, Cytokinin, Ethylene, ABA.
Unit V: Human Physiology
Chapter 14: Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Breathing and Respiration: Respiratory organs in animals; Respiratory system in humans.
- Mechanism of breathing and its regulation in humans-Exchange of gases, transport of gases, and regulation of respiration Respiratory volumes.
- Disorders related to respiration- asthma Emphysema, Occupational respiratory disorders.
Chapter 15: Body Fluids and Circulation
- Composition of blood, blood groups, coagulation of blood; composition of lymph and its function.
- Human circulatory system structure of human heart and blood vessels; cardiac cycle, cardiac output. ECG. Double circulation; Regulation of cardiac activity.
- Disorders of circulatory system-Hypertension, coronary artery disease, Angina pectoris, Heart failure.
Chapter 16: Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Excretory products and their elimination: Modes of excretion- Ammonotelism, ureotelism, uricotelism; Human excretory system structure and function; Urine formation, osmoregulation; Regulation of kidney function-Renin-angiotensin
- Atrial Natriuretic Factor ADH and Diabetes insipidus; Role of other organs in excretion; Disorders; Uremia, Renal failure, Renal calculi, Nephritis; Dialysis and artificial kidney.
Chapter 17: Locomotion and Movement
- Types of movement- ciliary, flagellar, muscular; Skeletal muscle- contractile proteins and muscle contraction.
- Skeletal system and its functions.
- Joints: Disorders of muscular and skeletal system- Myasthenia gravis, Tetany, Muscular Dystrophy, Arthritis, Osteoporosis, Gout.
Chapter 18: Neural Control and Coordination
- Neurons and nerves; Nervous system in humans central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, and visceral nervous system.
- Generation and conduction of nerve impulses.
Chapter 19: Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Endocrine glands and hormones; Human endocrine system-Hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal, Thyroid, parathyroid, Adrenal, Pancreas, Gonads.
- Mechanism of hormone action (Elementary idea); Role of hormones as messengers and regulators, Hypo-and hyperactivity and related disorders (common disorders e.g. Dwarfism, Acromegaly, Cretinism, goiter, exophthalmic goiter, diabetes, Addison's disease).
(b) Class 12 NEET Biology
The NEET syllabus for Class 12 is organized into five units (VI-X in NCERT), each comprising various chapters. Below, you will find information about the chapters and the specific topics that need to be studied.
Unit VI: Reproduction
Chapter 1: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Sexual reproduction in flowering plants: Flower structure; Development of male and female gametophytes; Pollination-types, agencies and examples.
- Outbreeding devices; Pollen-Pistil interaction; Double fertilization; Post fertilization events- Development of endosperm and embryo, Development of seed, and formation of fruit.
- Special modes- apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed and fruit formation.
- Male and female reproductive systems; Microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; Gametogenesis-spermatogenesis & oogenesis; Menstrual cycle.
- Fertilisation, embryo development upto blastocyst formation, implantation: Pregnancy and placenta formation (Elementary idea); Parturition (Elementary idea); Lactation (Elementary idea).
Chapter 3: Reproductive Health
- Need for reproductive health and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STD); Birth control and Methods, Contraception, and Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
- Amniocentesis, infertility and assisted reproductive technologies - IVF, ZIFT, GIFT (Elementary idea for general awareness).
Unit VII: Genetics and Evolution
Chapter 4: Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Heredity and variation: Mendelian inheritance; Deviations from Mendelism: Incomplete dominance, Co-dominance, Multiple alleles, and Inheritance of blood groups.
- Pleiotropy; Elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; Chromosome theory of inheritance; Chromosomes and genes; Sex determination in humans birds, honey bee; Linkage and crossing over.
- Sex-linked inheritance, Haemophilia colour blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans-Thalassemia; chromosomal disorders in humans; Down's syndrome, Turner's and Klinefelter's syndrome.
Chapter 5: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; Structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; DNA replication; Central dogma.
- Transcription, genetic code, translation; Gene expression and regulation- Lac Operon; Genome and human genome project; DNA finger printing, protein biosynthesis.
- Origin of life; Biological evolution and evidence for biological evolution from Paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology, and molecular evidence); Darwin's contribution, to the Modem Synthetic theory of Evolution.
- Mechanism of evolution: Variation (Mutation and Recombination) and Natural Selection with examples, types of natural selection; gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy-Weinberg principle; Adaptive Radiation; Human evolution.
Unit VIII: Biology in Human Welfare
Chapter 7: Human Health and Disease
- Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (Malaria, Filariasis, Ascariasis. Typhoid, Pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ringworm, dengue, chikungunya).
- Basic concepts of immunology-vaccines; Cancer, HIV, and AIDS; Adolescence, drug and alcohol abuse, Tobacco abuse.
Chapter 8: Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in human welfare: In household food processing, industrial production, sewage treatment, energy generation, and as biocontrol agents and biofertilizers.
Unit IX: Biotechnology
Chapter 9: Biotechnology: Principles and Processes
Principles and process of Biotechnology: Genetic engineering (Recombinant DNA technology).
Chapter 10: Biotechnology and its Applications
- Application of Biotechnology in health and agriculture: Human insulin and vaccine production, gene therapy genetically modified organisms-Bt crops: Transgenic Animals Biosafety issues-Biopiracy and patents
Unit X: Ecology
Chapter 11: Organisms and Populations
- Organisms and environment, Population interactions-mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism Population attributes-growth. birth rate ad death rate, age distibution.
- Ecosystem: Patterns, components; productivity and decomposition: Energy flow: Pyramids of number, biomass, and energy.
Chapter 13: Biodiversity and Conservation
- Concept of Biodiversity; Patterns of Biodiversity: Importance of Biodiversity; Loss of Biodiversity Biodiversity conservation; Hotspots, endangered organisms. extinction; Red Data Book. biosphere reserves, National parks and sanctuaries, and Sacred Groves.
NEET Biology Deleted Syllabus Class 11 & Class 12
Class 11 NEET Biology Deleted Chapters
As compared to NEET 2023, the following three (3) chapters have been completely omitted in the revised updated syllabus for NEET UG 2025, declared by the NMC:
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Digestion and Absorption
Class 12 NEET Biology Deleted Chapters
Similar to class 11, for class 12 three (3) chapters have been completely deleted in the latest syllabus for NEET UG 2025 by NMC, as per the details below::
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Strategies of Improvement on Food Production
- Environmental Issues
NEET Syllabus Biology Added Topics 2025
Few topics are added to the NEET 2025 syllabus and some topics exist in the NEET syllabus issued by NMC but are not given in NCERT Textbooks.
These topics are explained in the table below.
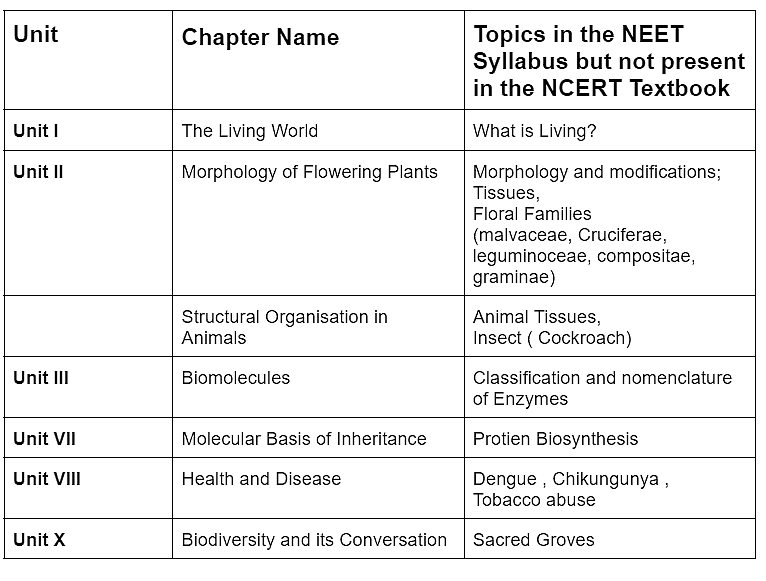 Topics Existing in NEET
Topics Existing in NEET
NEET Physics 2025: Class 11 and Class 12 Syllabus
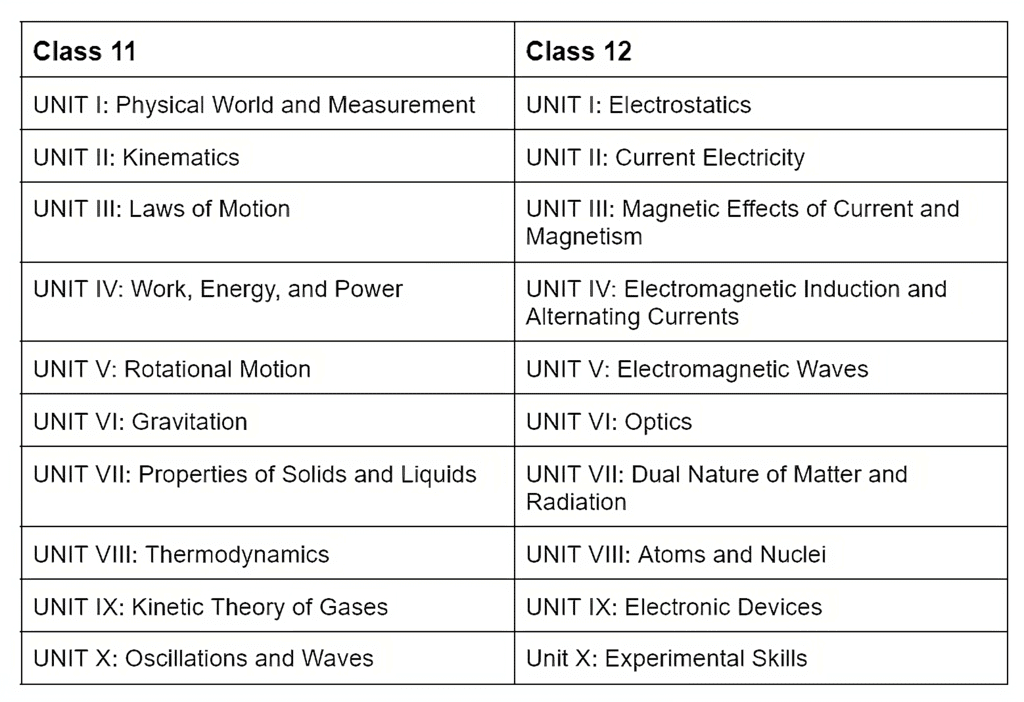
Class 11 and 12 NEET Physics Detailed Syllabus
The NEET syllabus for Class 11 & 12 is comprised of 20 units. Below, you will find information about the chapters and the details of topics that need to be studied.
(a) Class 11- NEET Physics
Unit I - Physical World and Measurement ( NCERT Textbook - Chapter 1)
- Units of measurements: System of Units, S I Units, fundamental and derived units, least count. significant figures, Errors in measurements
- Dimensions of Physics quantities, dimensional analysis, and its applications.
Unit II - Kinematics ( NCERT Textbook - Chapters 2 & 3)
- The frame of reference, motion in a straight line, Position-time graph, speed, and velocity
Uniform and non-uniform motion, average speed and instantaneous velocity, uniformly
accelerated motion, velocity-time, position-time graph, relations for uniformly accelerated
motion, Scalars, and Vectors. - Vector Addition and subtraction, scalar and vector products, Unit Vector, Resolution of a Vector.
- Relative Velocity, Motion in a plane, Projectile Motion. Uniform Circular Motion.
Unit III - Laws of Motion ( NCERT Textbook Chapter 4)
- Force and inertia, Newton's First law of motion: Momentum, Newton's Second Law of motion,
Impulses: Newton's Third Law of Motion. Law of conservation of linear momentum and its
applications. Equilibrium of concurrent forces. - Static and Kinetic friction, laws of friction, rolling friction.
- Dynamics of uniform circular motion: centripetal force and its applications: vehicle on a level circular road, vehicle on a banked road.
Unit IV - Work, Energy, and Power ( NCERT Textbook Chapter 5)
- Work done by a constant force and a variable force; kinetic and potential energies. work-energy theorem, power.
- The potential energy of spring conservation of mechanical energy. conservative and non - conservative forces; motion in a vertical circle: Elastic and inelastic collisions in one and two
dimensions.
Unit V - Rotational Motion (NCERT Textbook Chapter 6)
- Centre of the mass of a two-particle system, Centre of the mass of a rigid body: Basic concepts of rotational motion; moment of a force; torque, angular momentum, conservation of angular momentum and its applications.
- The moment of inertia, the radius of gyration, values of moments of inertia for simple geometrical objects, parallel and perpendicular axes theorems. and their applications. Equilibrium of rigid bodies. rigid body rotation and equations of rotational motion, comparison of linear and rotational motions.
Unit VI - Gravitation (NCERT Textbook Chapter 7)
- The universal law of gravitation. Acceleration due to gravity and its variation with altitude and depth. Kepler's law oi planetary motion. Gravitational potential energy; gravitational potential. Escape velocity, Motion of a satellite, orbital velocity, time period and energy of satellite.
Unit VII - Properties of Solids and Liquids ( NCERT Textbook Chapters 8,9 & 10)
- Elastic behavior, Stress-strain relationship, Hooke's Law. Young's modulus, bulk modulus, and modulus of rigidity. Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal's law and its applications. Effect of gravity on fluid pressure.
- Viscosity. Stokes' law. terminal velocity, streamline, and turbulent flow critical velocity Bernoulli's principle and its applications.
- Surface energy and surface tension, angle of contact, excess of pressure across a curved surface, application of surface tension - drops, bubbles, and capillary rise. Heat, temperature, thermal expansion; specific heat capacity, calorimetry; change of state, latent heat. Heat transfer- conduction, convection, and radiation.
Unit VIII - Thermodynamics (NCERT Textbook Chapter 11)
- Thermal equilibrium, zeroth law of thermodynamics, the concept of temperature. Heat, work, and internal energy. The first law of thermodynamics, isothermal and adiabatic processes.
- The second law of thermodynamics: reversible and irreversible processes.
Unit IX - Kinetic Theory of Gases (NCERT Textbook Chapter 12)
- Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done on compressing a gas, Kinetic theory of gases - assumptions, the concept of pressure. Kinetic interpretation of temperature: RMS speed of gas molecules: Degrees of freedom. Law of equipartition of energy and applications to specific heat capacities of gases; Mean free path. Avogadro's number.
Unit X - Oscillations and Waves ( NCERT Textbook Chapters 13 & 14)
- Oscillations and periodic motion - time period, frequency, displacement as a function of time. Periodic functions. Simple harmonic motion (S.H.M.) and its equation; phase: oscillations of a spring -restoring force and force constant: energy in S.H.M. - Kinetic and potential energies; Simple pendulum - derivation of expression for its time period.
- Wave motion: Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of traveling wave. Displacement relation for a progressive wave. Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves. Standing waves in strings and organ pipes, fundamental mode and harmonics- Beats.
(b) Class 12 NEET Physics
The NEET syllabus for Class 12 is organized into 10 units. Below, you will find information about the chapters and the details of topics that need to be studied.
Unit I - Electrostatics ( NCERT Textbook Chapters 1 & 2 )
- Electric charges: Conservation of charge. Coulomb's law forces between two point charges, forces between multiple charges: superposition principle and continuous charge distribution.
- Electric field: Electric field due to a point charge, Electric field lines. Electric dipole, Electric field due to a dipole. Torque on a dipole in a uniform electric field.
- Electric flux: Gauss's law and its applications to find field due to infinitely long uniformly charged straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet, and uniformly charged thin spherical shell. Electric potential and its calculation for a point charge, electric dipole and system of charges potential difference, Equipotential surfaces, Electrical potential energy of a system of two point charges, and of electric dipole in an electrostatic field.
- Conductors and insulators: Dielectrics and electric polarization, capacitors and capacitances,, the combination of capacitors in series and parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates. Energy is stored in a capacitor.
Unit II - Current Electricity ( NCERT Textbook Chapter 3)
- Electric current: Drift velocity, mobility, and their relation with electric current. Ohm's law. Electrical resistance, V-l characteristics of ohmic and non-ohmic conductors. Electrical energy and power Electrical resistivity and conductivity. Series and parallel combinations of resistors; Temperature dependence of resistance.
- Internal resistance, potential difference, and emf of a cell, a combination of cells in series and parallel. Kirchhoff's laws and their applications. Wheatstone bridge. Metre Bridge.
Unit III - Magnetic Effects of Current ( NCERT Textbook Chapters 4 & 5)
- Bio-Savart law and its application to the current carrying circular loop. Ampere's law and its applications to infinitely long current carrying straight wire and solenoid. Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields.
- Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field. The force between two parallel currents carrying conductors-definition of ampere. Torque experienced by a current loop in a uniform magnetic field: Moving coil galvanometer, its sensitivity, and conversion to ammeter and voltmeter.
- Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment. Bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid. magnetic field lines; Magnetic field due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) along its axis and perpendicular to its axis. Torque on a magnetic dipole in a uniform field. para, dia- and ferromagnetic substances with examples, the effect of temperature on magnetic properties.
Unit IV- Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current ( NCERT Textbook Chapters 6 & 7 )
- Electromagnetic induction: Faraday's law. Induced emf and current: Lenz's Law, Eddy currents. Self and mutual inductance. Alternating currents, peak and RMS value of alternating current/ voltage: reactance and impedance: LCR series circuit, , resonance: power in AC circuits, wattless current. AC generator and transformer.
Unit V - Electromagnetic Waves (NCERT Textbook Chapter 8)
- Displacement current: Electromagnetic waves and their characteristics, Transverse nature of electromagnetic waves, Electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet. X-rays. Gamma rays), Applications of e.m wave.
Unit VI - Optics ( NCERT Textbook Chapters 9 & 10)
- Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror formula. Refraction of right at plane and spherical surfaces, thin lens formula, and lens maker formula. Total internal reflection and its applications.
- Magnification, Power of a Lens. Combination of thin lenses in contact. Refraction of light through a prism. Microscope and Astronomical Telescope (reflecting and refracting ) and their magnifying powers.
- Wave optics: wavefront and Huygens' principle. Laws of reflection and refraction using Huygens principle. Interference, Young's double-slit experiment, and expression for fringe width, coherent sources, and sustained interference of light. Diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maximum. Polarization, plane-polarized light: Brewster's law, uses of plane-polarized light and Polaroid
Unit VII - Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation (NCERT Textbook Chapter 11)
- Dual nature of radiation. Photoelectric effect. Hertz and Lenard's observations; Einstein's photoelectric equation: particle nature of light. Matter waves-wave nature of particle, de Broglie relation.
Unit VIII - Atoms and Nuclei ( NCERT Textbook Chapters 12 & 13)
- Alpha-particle scattering experiment; Rutherford's model of atom; Bohr model, energy levels hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of nucleus, atomic masses, Mass-energy relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number, nuclear fission, and fusion.
Unit IX - Electronic Devices (NCERT Textbook Chapter 14)
- Semiconductors; semiconductor diode: I-V characteristics in forward and reverse bias; diode as a rectifier; I-V characteristics of LED. the photodiode, solar cell, and Zener diode; Zener diode as a voltage regulator.. Logic gates (OR. AND. NOT. NAND and NOR)
Unit X - Experimental skills
- Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities:
1. Vernier calipers are use to measure the internal and external diameter and depth of a vessel.
2. Screw gauge-its use to determine the thickness/ diameter of thin sheet/wire.
3. Simple pendulum-dissipation of energy by plotting a graph between the square of amplitude and time.
4. Metre Scale - the mass of a given object by the principle of moments.
5. Young's modulus of elasticity of the material of a metallic wire.
6. Surface tension of water by capillary rise and effect of detergents.
7. Co-efficient of Viscosity of a given viscous liquid by measuring the terminal velocity of a given spherical body.
8. Speed of sound in air at room temperature using a resonance tube.
9. Specific heat capacity of a given (i) solid and (ii) liquid by method of mixtures.
10. The resistivity of the material of a given wire using a meter bridge'.
11. The resistance of a given wire using Ohm's law.
12. Resistance and figure of merit of a galvanometer by half deflection method.
13. The focal length of: (i) Convex mirror (ii) Concave mirror, and Convex lens, using the parallax method.
14. The plot of the angle of deviation vs angle of incidence for a triangular prism.
15. Refractive index of a glass slab using a traveling microscope.
16. Characteristic curves of a p-n junction diode in forward and reverse bias.
17. Characteristic curves of a Zener diode and finding reverse breakdown voltage.
18. Identification of Diode. LED Resistor. A capacitor from a mixed collection of such items
NEET Chemistry 2025: Class 11 and Class 12 Syllabus
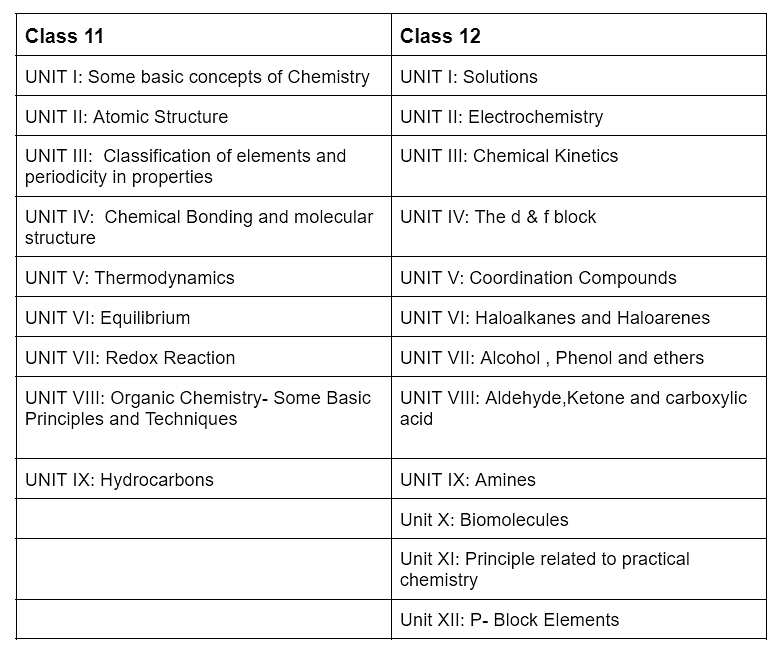
Class 11 and 12 NEET Chemistry Detailed Syllabus
The NEET syllabus for Class 11 & 12 is organized into 9 & 11 units respectively. Below, you will find information about the chapters and the specific topics that need to be studied while preparing for NEET
(a) Class 11 NEET Chemistry
Unit I – Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- General Introduction – Matter and its nature, Dalton's atomic theory: Concept of atom, molecule, element. and compound.
- Laws of chemical combination; Atomic and molecular masses, mole concept, molar mass, percentage composition, empirical and molecular formulae: Chemical equations and stoichiometry
- Nature of electromagnetic radiation, photoelectric effect; Spectrum of the hydrogen atom. Bohr model of a hydrogen atom - its postulates, derivation of the relations for the energy of the electron and radii of the different orbits, limitations of Bohr's model; Dual nature of matter, de Broglie's relationship. Heisenberg uncertainty principle. Elementary ideas of quantum mechanics, quantum mechanics, the quantum mechanical model of the atom, and its important features. Concept of atomic orbitals as one-electron wave functions: Variation of Ψ and Ψ2 with r for ls and 2s orbitals: Various
- Quantum numbers (principal, angular momentum, and magnetic quantum numbers) and their significance; shapes of s, p, and d - orbitals, electron spin, and spin quantum number: Rules for filling electrons in orbitals - Aufbau principle. Pauli's exclusion principle and Hund's rule, electronic configuration of elements, extra stability of half-filled and completely filled orbitals.
Unit III – Classification of elements and periodicity in properties
- Modern periodic law and present form of the periodic table. s, p. d and f block elements- periodic trends in properties of elements atomic and ionic radii. ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy) valence. oxidation states and chemical reactivity
Unit IV – Chemical Bonding and Molecular structure
- Kossel - Lewis approach to chemical bond formation, the concept of ionic and covalent bonds' Ionic Bonding: Formation of ionic bonds, factors affecting the formation of ionic bonds; calculation of lattice enthalpy, covalent Bonding: the concept of electronegativity. Fajan's rule, dipole moment:
- Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion(VSEPR)theory and shapes of simple molecules. Quantum mechanical approach to covalent bonding: Valence bond theory - its important features. the concept of hybridization involving s, p, and d orbitals; Resonance' Molecular orbital Theory - Its important features. LCAOs, 'types of molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding), sigma and pi-bonds, molecular orbital electronic configurations of homonuclear diatomic molecules, the concept ofbond order, bond length, and bond energy.
- Elementary idea of metallic bonding. Hydrogen bonding and its applications
- Fundamentals of thermodynamics: System and surroundings, extensive and intensive properties' state functions, types of processes: The first law of thermodynamics - the concept of work, heat internal energy and enthalpy, heat capacity, molar heat capacity and Hess law and heat dissociation, combustion, formation, atomization. sublimation. phase transition, hydration. ionization.
- The second law of thermodynamics - Spontaneity of processes: ΔS of the universe and ΔG of the system as criteria for spontaneity. ΔG" (Standard Gibbs energy change) and equilibrium constant.
- The meaning of equilibrium is the concept of dynamic equilibrium. Equilibria involving physical processes: Solid-liquid, Henry's liquid-gas and solid-gas equilibria, law. general characteristics of
- Equilibrium in Physical and chemical processes, dynamic nature of equilibrium, law of chemical equilibrium, equilibrium constant, factors affecting equilibrium Le Chatelier’s principle, ionic equilibrium – ionization of acids and bases, strong and weak electrolytes, degree of ionization, ionization of polybasic acids, acid strength, concept of pH., Hydrolysis of salts(elementary idea), buffer solutions, Henderson equation, solubility product, common ion effect (with illustrative examples)
- Concept of oxidation and oxidation and reduction, redox reactions oxidation number, rules of assigning oxidation number, balancing of redox reactions
Unit VIII – Organic Chemistry- Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- Methods of purification qualitative and quantitative analysis, classification and IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds, electronic displacements in a covalent bond, homolytic and heterolytic fission of a covalent bond
- Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, aromatic hydrocarbons.
- Aromatic hydrocarbons – introduction, IUPAC nomenclature, Benzene; resonance, aromaticity, chemical properties: mechanism of electrophilic substitution – Nitration sulphonation, halogenation, Friedel Craft’s alkylation and acylation, directive influence of functional group in mono-substituted benzene; carcinogenicity and toxicity.
Unit X - Purification and characterization of organic compounds
- Purification - Crystallization, sublimation, distillation, differential extraction, and , Chromatography and its principles and applications
- Qualitative analysis - Detection of nitrogen, sulfur' phosphorus' and halogens.
- Quantitative analysis (basic principles only) - Estimation of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and halogens. sulfur, phosphorus.
- Calculations of empirical formulae and molecular formulae: Numerical Problems in organic quantitative analysis.
(b) Class 12 NEET Chemistry
- Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids, the solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, colligative properties
- Redox reactions, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar conductivity variation of conductivity with concentration, lead accumulator, EMF of a cell, standard electrode potential, relation between Gibbs energy change and EMF of a cell, fuel cells; corrosion
- Electrolytic and metallic conduction, conductance and their in electrolytic solutions, molar conductivities variation with concentration: Kohlrausch laws and its applications.
- Electrochemical cells - Electrolytic and Galvanic cells, different potentials including types of electrodes, electrode standard- electrode.
- Potential Energy and Gibbs free energy.
- Dry cell and lead accumulator, Fuel cells.
- Rate of a reaction(average and instantaneous), factors affecting rates of reaction; concentration, temperature, catalyst; order and molecularity of a reaction; rate law and specific rate constant, activation energy, First order reaction and their characteristics,half live reactions Arrhenius equation
- Collision theory of Biomolecular gaseous reaction (no derivation)
Unit IV– d and f Block elements
- General introduction, electronic configuration, characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first-row transition metals, preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4, lanthanide, actinides
- Inner-transition Elements
(a) Lanthanoids-Electronic configuration, oxidation states, and lanthanoid contraction.
(b) Actinoids - Electronic configuration and oxidation states.
Unit V – Coordination Compounds
- Coordination compounds – Introduction, ligands, coordination number, color, magnetic properties and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds, isomerism (structural and stereo) bonding, Werner’s theory VBT, CFT; the importance of coordination compounds
- lmportance of co-ordination compounds (in qualitative analysis. extraction of metals and in biological systems).
Unit VI – Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Haloalkanes, haloarenes, dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, iodoform, freons, DDT - Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties
Unit VII– Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Alcohols – Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties (of primary alcohols only); identification of primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols, mechanism of dehydration, uses with special reference to methanol and ethanol, phenol, ethers
Unit VIII– Aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids
- Aldehydes and ketones, carboxylic acids - Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties
Unit IX – Amines (Organic compounds containing Nitrogen)
- Amines – nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses, identification of primary secondary and tertiary amines, cyanides and isocyanides, diazonium salts
- General introduction and importance of biomolecules.
- Carbohydrates - classification; aldoses and ketoses: monosaccharides (glucose and fructose) and constituent monosaccharides of oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, and maltose)'
- Proteins: Elementary Idea of amino acids, peptide bonds, polypeptides. Proteins: primary. secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure (qualitative idea)
- Vitamins: Classification and function
- Nucleic Acids- Chemical constitution of DNA and RNA, Biological functions of nucleic acids
- General introduction of Hormones.
Unit XI: Principle related to practical chemistry
- Detection of extra elements(Nitrogen, sulphur, halogens)inorganic compounds; Detection of
the following functional group, hydroxyl (alcoholic and phenolic), carbonyl (aldehyde and
ketones) carboxyl, and amino groups in organic compounds. The chemistry involved in the preparation of the following: Inorganic compounds: Mohr's salt. potash alum' Organic compounds: Acetanilide. p-nitro acetanilide' aniline yellow iodoform.
' The chemistry involved in the titrimetric exercises - Acids. bases and the use of indicators. oxalic acid vs KMnO4, Mohr's salt vs KMnO4.
Chemical principles involved in the qualitative salt analysis.
Chemical principles involved in the following experiments.
NEET Chemistry Deleted Syllabus 2025: Class 11 & 12
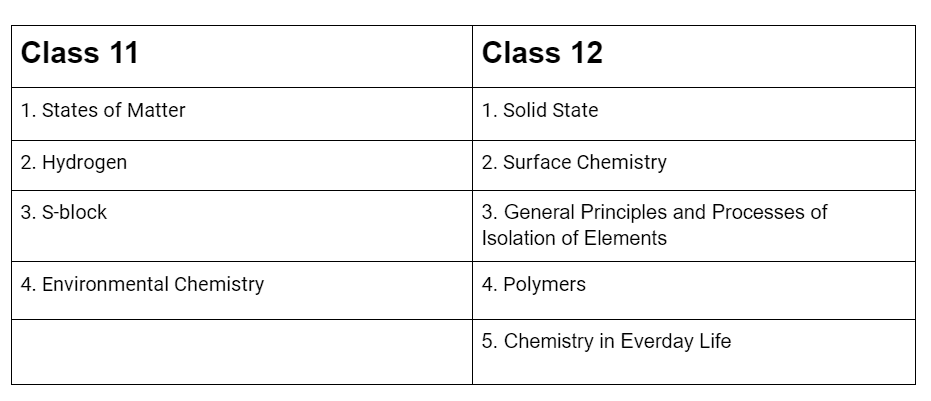
Chemistry NEET Syllabus Added Topics 2025
Most Important Chapters for NEET 2025
Some of the important topics from each section are listed in the table below.
Biology
- Diversity in the living world
- Genetics and Evolution
- Cell-The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals.
- Human physiology
- Reproduction
- Plant physiology
- Biotechnology
- Organisms and Populations
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and its Conservation
- Biology and Human welfare
Physics
Chemistry
|
181 videos|360 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Revised Syllabus 2025: Topic-wise Details & Important Chapters - Biology Class 11
| 1. What are the major changes in the NEET 2024 syllabus for Biology? |  |
| 2. Can you provide the list of important chapters for NEET 2024 preparation? |  |
| 3. What are the key additions in the NEET 2024 Chemistry syllabus? |  |
| 4. Are there any significant changes in the NEET 2025 syllabus compared to previous years? |  |
| 5. How can students effectively prepare for the NEET exam considering the changes in the syllabus? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















