UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography Optional for UPSC > National Airways
National Airways | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Historical Background
- On the occasion of the Kumbh Mela, the world's first airmail service was launched in India at Allahabad on February 18, 1911. As a result, India's civil aviation industry was born.
- However, it was during the post-independence period that it truly developed.
- In February 1929, JRD Tata received the first pilot license from Aeronautique International on behalf of the Aero Club of India and Burma.
- With the introduction of the first airline, Tata Air Services, Indian aviation emerged in 1932.
- The airline's first flight, from Karachi to Mumbai, took place in October 1932.
- Between 1933 and 1934, a number of other airlines emerged, including Indian Trans-Continental Airways, Madras Air Taxi Services, and Indian National Airlines.
- For the first time, the airline expanded worldwide in 1938.
- In addition to the dozen or so destinations in India, the carrier added Colombo, Sri Lanka (formerly Ceylon) to its route network.
- Air India and the government signed an agreement in 1948 to operate international flights under the name Air India International Ltd.
- AirIndia began international service on June 8, the same year, with a weekly route connecting Bombay and London via Cairo and Geneva.
- After the merger of the International Airport Authority of India and the National Airports Authority in 1995, the Airport Authority of India (AAI) was formed.
- In the Indian Air Space, the Airport Authority of India is responsible for delivering safe and efficient air traffic and aeronautical communication services. The agency is in charge of 125 airports.
- Some private businesses have also expanded their operations to other countries.
Need for Airways in India
- The importance of the aviation sector is growing by the day, owing to India's vastness, which makes it indispensable for faster communication.
- Aircraft are capable of gaining access to any location. It does not have any physical barriers, unlike other modes of transportation.
- The world's great mountain ranges can't be crossed by roads, trains, or ships.
- Airways provide easy access to inaccessible and isolated regions. For Example, Rajasthan's deserts, Leh's high altitude regions, and North East India's forested regions.
Favourable Factors for Indian Air Transport
- India's weather is quite conducive to air travel.
- Air travel is hampered by poor visibility caused by clouds, fog, and mist, although India is fortunate to have clear weather for the majority of the year, with the exception of a brief period during the rainy season.
- India's geographic center, with Europe and West Asia on one side and South East Asia and East Asia on the other.
- In India, there are vast plains that provide good landing locations.
- Due to India's huge size, there is a high demand for airlines.
Market Size of the Indian Aviation Industry
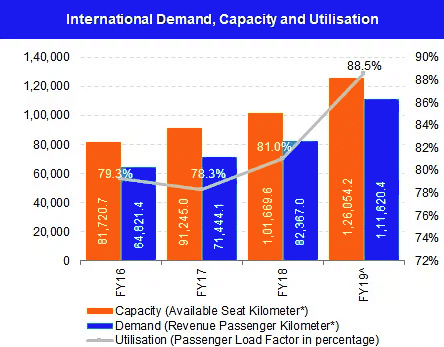
- In terms of handling domestic traffic, India's aviation sector has grown to become the world's third-largest domestic aviation market.
- According to the International Air Transport Association (IATA), India is predicted to overtake China and the United States as the world's third-largest air passenger market in the next ten years, by 2030.
- In FY21, India's passenger traffic was 115.37 million. The average daily domestic passenger flight departures were >2,300 in October 2021, with an average daily domestic traffic of >283,000 air passengers.
- India's airport freight traffic has the potential to reach 17 MT by FY40. Indian travelers' spending is estimated to increase to Rs. 9.5 lakh crore.
- The Indian government has been attempting to increase the number of airports to accommodate the growing aviation traffic.
- India had 153 operating airports as of 2020. By FY40, India plans to increase the number of operational airports to 190-200.
- Furthermore, the sector's growing demand has increased the number of planes in service.
Role of Airways in Regional Development
- According to the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO), investing one dollar in the aviation sector will yield a three-dollar return on the regional economy.
- The aviation industry serves as a crossroads for a variety of activities.
- Airports serve as a growth pole, propelling the region's growth through the overflow and trickle-down effects.
- Air services enhance tourism and the fundamental infrastructure needs of tourists.
- Markets, stores, restaurants, hotels, and other amenities are constructed to meet the desires of tourists.
- Furthermore, local skills are emphasized, and knowledge is disseminated through the exchange of viewpoints between tourists and residents, opening up new paths.
- Local handicrafts are encouraged, which benefits both the economy and the preservation of cultural heritage.
- With the development of tourism, there will be a dissemination of local ideas and creativity.
- Increased outsider contact with locals also aids in identifying local issues/problems, which are then brought to the attention of the national government, preventing extreme regionalism.
Challenges of Aviation Sector
Common Challenges
- Airline rates and fares are far greater than those charged by railways and highways.
- It is not mass transportation, but rather a form of class transportation.
- There is a difficulty with last-mile airway connectivity. Only railways and highways can deliver it.
- Heavyweight goods, which can only be delivered by railways, roads, or shipping, are not suitable for air transport.
- Storms, rain, and fog limit an aircraft's ability to fly.
- The majority of accidents are lethal, with little possibility of survival.
- Airports cannot be built everywhere; the geography of a location plays a vital role in the airport building.
India- specific Challenges
- Since India lacks a domestic base, it imports carrier aircraft.
- In India, the taxes on air turbine fuel are extremely expensive.
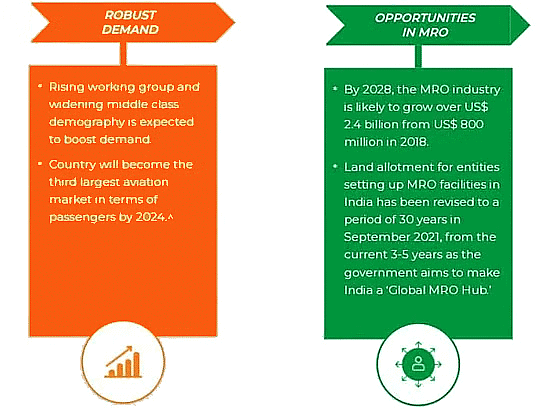
- In India, the maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) industry is underdeveloped.
- Air travel is less popular than other modes of transportation.
- The aviation industry is a high-capital-intensive industry. Airport expansion is likewise a difficult task.
- The entrance of low-cost carriers (LCCs) causes premium airlines' market share to dwindle.
- To counteract the loss of market share, premium airlines were obliged to lower their fares, which resulted in a pricing war among the airlines, potentially jeopardizing the carriers' financial sustainability.
- Despite the fact that India is one of the world's fastest-growing aviation markets, its airlines have been incurring losses.
- According to the Centre for Asia Pacific Aviation, India's unified airline industry will lose $1.65 billion to $2 billion this year.
Prospects in Indian Aviation Sector
- An increase in air traffic density is required.
- Rising GDP and per capita income, which have resulted in the rise of the middle class, are expected to boost the aviation industry's client base.
- The aviation sector's growth prospects are also improving as the urban population grows.
- The government's initiatives, which include the implementation of several schemes, are expected to provide Phillip to India's aviation sector.
- In comparison to luxury classes on trains, flights have grown more affordable.
- The modernization of airports by private companies under the PPP model (GMR for Delhi Airport) has boosted the aviation sector's prospects in India.
- Greenfield aviation projects in Hyderabad, Bangalore are increasing the world-class airport infrastructure in India.
Aviation Sector Under Make in India
- The aviation sector is one of the 25 sectors covered by the Make in India initiative.
- The following are some of the highlights for the aviation sector under the Make in India scheme:
- By 2032, freight traffic at Indian airports is estimated to reach 11.4 MT. India is the world's fastest-growing aviation market, with 520 million passengers predicted by 2037, according to IATA.
- Both greenfield and brownfield projects are eligible for 100 percent FDI under the automatic approach.
- According to Boeing, Indian carriers intend to increase their fleet size to roughly 1,200 aircraft by 2020.
- AAI intends to promote Guwahati as an inter-regional hub for the development of the aviation sector in the North-East States. It also intends to establish intra-regional centers in Agartala, Imphal, and Dibrugarh.
- To boost earnings, Indian airports are emulating the Special Economic Zone (SEZ) Aerotropolis model.
- The approach relies on retail, advertising, vehicle parking, security equipment, and services as sources of revenue.
Government Initiatives
Regional Connectivity Scheme (UDAN)
- This program is part of the National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP) and is jointly funded by the Indian government and state governments launched in June 2017.
- The scheme aims to improve connectivity to the country's remote and regional areas while also making air travel more affordable.
- This regional connectivity scheme (RCS) aims to improve air connectivity to tier-2 and tier-3 cities by revitalizing unused and underused airports.
- Nearly half of the seats on Udan flights are subsidized under the scheme, and participating carriers are given a certain amount of viability gap funding (VGF), which is split between the Centre and the affected states.
National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP)
- The National Civil Aviation Policy of 2016 calls for the creation of an ecosystem that allows for safe, sustainable, and affordable air travel as well as cost-effective cargo transportation.
- The Union Cabinet approved the National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP 2016) on June 15, 2016.
- Regional connectivity, safety, air transport operations, 5/20 requirement for international operations, bilateral traffic rights, fiscal support, maintenance, repair and overhaul, air cargo, and aeronautical 'Make in India' are all covered in the NCAP 2016.
- PM Narendra Modi launched the UDAN Scheme on April 27, 2017, as a key component of the National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP).
GPS-Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN)
- The GPS-aided GEO enhanced navigation is the Indian government's installation of a regional satellite-based augmentation system.
- The GAGAN satellite-based augmentation system is India's first of its kind.
- In civil aviation, it adds more accuracy for safety.
- This system may be expanded to provide seamless navigation services across many geographies.
No Objection Certificate Application System (NOCAS)
- NOCAS is the online application system for height clearance of buildings and structures in and near airports.
- It was implemented by the Airports Authority of India (AAI).
- On April 1, 2011, AAI made it operational for accepting online NOC applications.
e Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA)
- In India, the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is the regulatory authority in charge of civil aviation safety.
- The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) moved its functions and processes to an online platform in order to provide speedier service delivery and regulatory control.
- The e-GCA was launched on May 14, 2019.
- In November 2019, the first module on pilot licensing was released.
DigiSky
- To meet the standards for flying Civil Drones, the DigiSky internet platform has been developed.
- Based on the distinguishing qualities of No Permission No Takeoff, the Beta version of DigiSky is now available and captures the complete gamut of actions connected to drones, including registration of drones and pilots, approval of flight paths, post-flight analysis, and so on (NPNT).
- DigiSky also creates aerial ground monitoring systems for Earth observation, emergency response, environmental monitoring, forestry management, surveillance, and asset-intensive businesses.
e-sahaj
- The Sahaj portal's principal goal is to give security clearance.
- The Ministry of Civil Aviation was the one that introduced it.
- The Ministry of Civil Aviation and its associated offices, the Directorate General of Civil Aviation, and the Bureau of Civil Aviation Security use this portal to streamline the process of granting security clearance.
- This online platform has been used to process 100 percent of the Ministry's security clearances.
- The portal is ready to offer permissions in 24 different categories.
Significance of Aviation Sector
- International travel and transportation rely heavily on aviation.
- During times of conflict, disaster relief, and natural disasters, the importance of airways grows exponentially.
- Cargo (freight) services are mostly provided by the aviation industry.
- A region's modernity is measured by its airway.
- Airways are a free gift from nature, with no money spent on their creation or upkeep.
- The aviation industry, directly and indirectly, employs 7 million people.
- Air services enhance tourism, and fundamental infrastructure, such as roads and transit, is boosted to meet the needs of tourists.
Conclusion
In the following decade, India's aviation industry is predicted to rise by 10%. It has grown by 20.3 percent since 2015, the greatest rate of growth in any country's aviation industry. By 2026, the Indian government plans to invest US$ 1.83 billion in airport infrastructure as well as aviation navigation services. According to the most recent predictions, air travel demand will also grow at a rate of 4.3 percent per year over the next 20 years. If this rate of growth is maintained until 2036, the Indian air transportation industry will provide 15.5 million direct jobs and contribute $1.5 trillion in GDP to the global economy.
The document National Airways | Geography Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Geography Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
304 videos|718 docs|259 tests
|
Related Searches
















