Natural Hazards and Disasters- 2 | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
NDMA Guidelines for Crowd Management
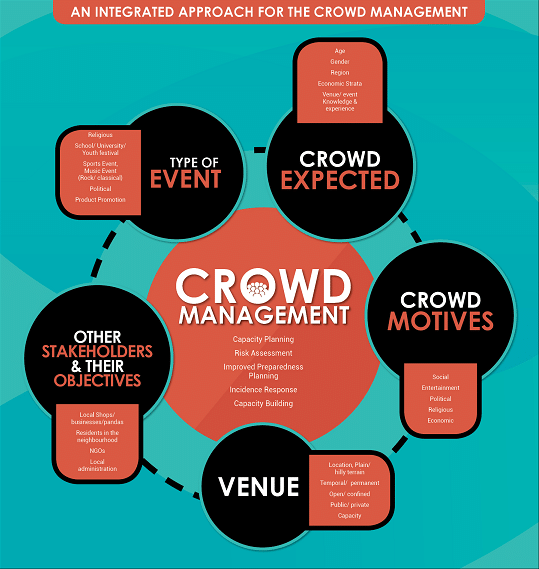
Planning the strategy for management
1. Understanding visitors
2. Understanding stakeholders
3. Crowd Management strategies
- Capacity planning
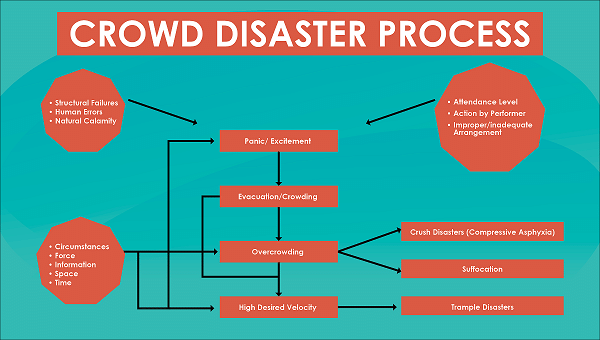
- Understanding Crowd behavior
- Crowd disaster process
- Crowd control
- Stakeholder approach
4. Risk analysis and preparedness
- Identify threats or causes
- Risk assessment
- Planning
- Develop a course of action
5. Information management and dissemination
6. Safety and security measures
7. Medical Emergency Services
Role of Media
Broadly we can categorize the role of media in the following way:
- Educational
- Critical
- Suggestive
Before a disaster:
- Bring to the attention of the authorities
- Prepare the community and making them aware of Do’s and Don’ts
- Keeping a watch on anti-social elements, thereby helping in maintaining the law and order situation
During a disaster:
- Broadcasting accurate information to stop rumors and hence reduce panic
- Make people aware of their Do’s and Don’ts to reduce further damage of a probable secondary risk
- Can assist the authorities in reaching out to the victims and their families
- Facilitate resource mobilization (funds) for relief operations
After a disaster:
- Informing the people about the post-disaster rehabilitation measures for putting pressure on the authorities
- Provide aid in investigating the causes of the disaster
- Can help generate expert opinion through debates/discussions for better preparedness levels in future
Role of Science and Technology Disaster Mitigation and Prevention
- Geographic information system
- Radiofrequency identification
- Radio, Television, SMS, etc.
These all including other technologies and methods help in creating early warning systems, information dissemination, search and rescue, insurance processing, etc.
Legal Provisions
- Disaster Management Act, 2005
- The Police Act, 1961
- Kerala Police Act, 2011
- UP Melas Act, 1938
- Cinematograph Act, 1952
- Delhi Cinematograph Rules, 1953
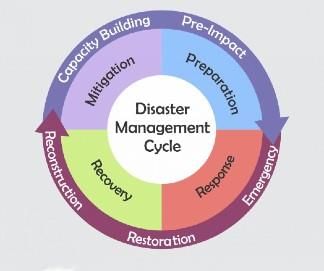
Disaster Prevention and Mitigation
Proper planning and mitigation measures can play a leading role in risk-prone areas to minimize the worst effects of hazards such as earthquakes, floods, and cyclones. These are the key areas which should be addressed to achieve this objective:
- Risk Assessment and Vulnerability Mapping: Mapping and vulnerability analysis in a multi-risk structure will be conducted utilizing Geographic Information System (GIS) based databases like the National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM) and National Spatial Data Infrastructure (NSDI).
- Increasing Trend of Disasters in Urban Areas:- Steps to prevent unplanned urbanization must be undertaken, with the plan of action formulated being given the highest priority. State Governments/UTs concerned on the other hand focus on urban drainage systems with special attention on non-obstruction of natural drainage systems.
- Critical Infrastructure:- Critical infrastructure like roads, dams, bridges, irrigation canals, bridges, power stations, railway lines, delta water distribution networks, ports and river, and coastal embankments should be continuously checked for safety standards concerning worldwide safety benchmarks and fortified if the current measures prove to be inadequate.
- Environmentally Sustainable Development:– Environmental considerations and developmental efforts, should be handled simultaneously for ensuring sustainability.
- Climate Change Adaptation:-. The challenges of the increase in the frequency and intensity of natural disasters like cyclones, floods, and droughts should be tackled in a sustained and effective manner with the promotion of strategies for climate change adaptation and disaster risk reduction.
|
175 videos|619 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Natural Hazards and Disasters- 2 - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are natural hazards and disasters? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of natural hazards? |  |
| 3. How can we prepare for natural hazards and disasters? |  |
| 4. What is the role of early warning systems in natural disaster management? |  |
| 5. What are the long-term effects of natural disasters? |  |
















