Nitin Singhania Summary: UNESCO’S List of Intangible Cultural Heritage | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
UNESCO recognizes that cultural heritage extends beyond monuments and objects to include living expressions inherited from ancestors, like oral traditions, performing arts, and social practices. To safeguard these vital elements, UNESCO established lists of Intangible Cultural Heritage. This program aims to protect and raise awareness about the significance of intangible heritage worldwide, emphasizing traditions, rituals, knowledge, and skills passed down through generations. Through a global compendium, UNESCO highlights the importance of preserving intangible heritage for future generations.

Intangible Cultural Heritage refers to the practices, representations, expressions, knowledge, skills, instruments, objects, and artifacts that communities, groups, and sometimes individuals identify as part of their cultural heritage.
UNESCO has compiled two major lists:
- The Representative List of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity: This list showcases cultural practices and expressions that highlight the diversity and richness of global heritage.
- The List of Intangible Cultural Heritage in Need of Urgent Safeguarding: This list focuses on cultural elements that are at risk and require immediate attention to ensure their survival.
The representative list, in particular, is important for academic and exam purposes, as it emphasizes the cultural practices that demonstrate the diversity of humanity.
Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity
Koodiyattam (Sanskrit Theatre)
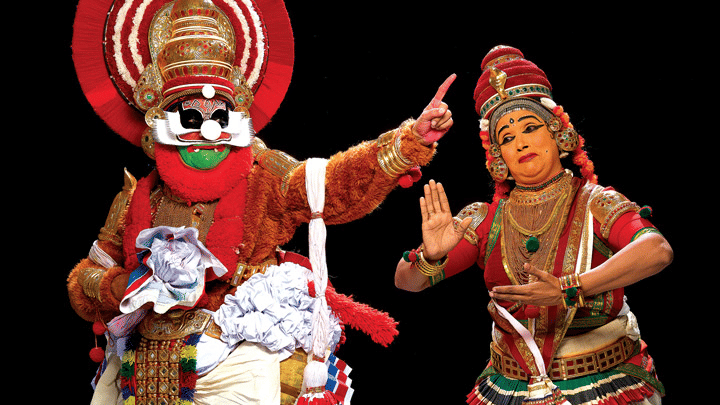

- Koodiyattam is a traditional dance theatre form from Kerala, India, which was included in the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity by UNESCO in 2008.
- It is performed by the Chakyars and the Ambalavasi Nambiar community, and the stories are drawn from Hindu mythology.
- The performances can last anywhere from 6 to 20 days and are primarily held in temples.
- A unique feature of Koodiyattam is the character known as the Vidushaka, who narrates in Malayalam, while other characters speak in Sanskrit.
Ramlila
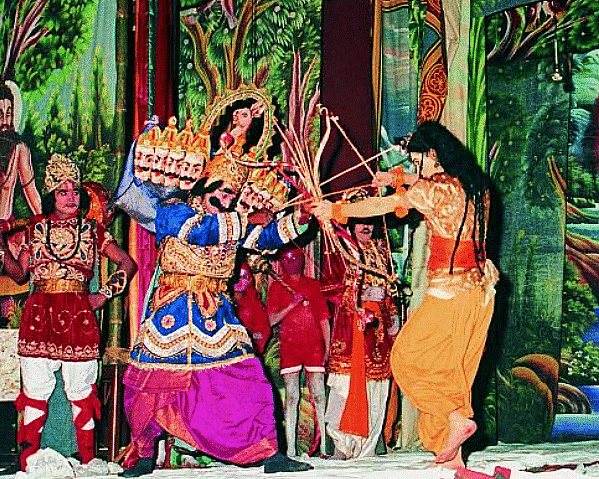
- Ramlila is a traditional form of theatre that depicts the Ramayana through songs, dances, and dialogues.
- It was started in 2008 in Uttar Pradesh and has since become a popular cultural event.
- Staged annually over 10 or more nights during 'Sharad Navaratras'.
- A special version of Ramlila at Bakshi ka Talab near Lucknow promotes community spirit and involvement.
The Tradition in Vedic Chanting

- Included in 2008, it is an oral tradition of reciting Vedic mantras, considered the oldest unbroken oral tradition.
- The recording of Vedic texts is believed to date back to the early Iron Age.
Ramman
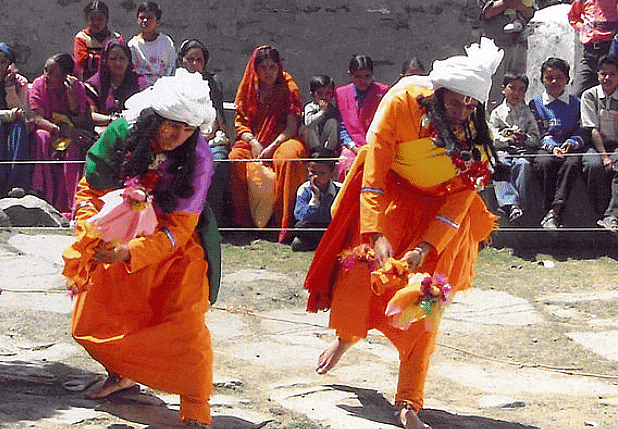

- Included in 2009, it is a religious festival and ritual theatre celebrated in the Garhwal region of Uttarakhand.
- Unique to Saloor-Dungra village, paying homage to the village deity, Bhumiyal Devta.
- A key feature of Ramman is the singing of Jagar, which involves musical renditions of local legends.
Mudiyettu
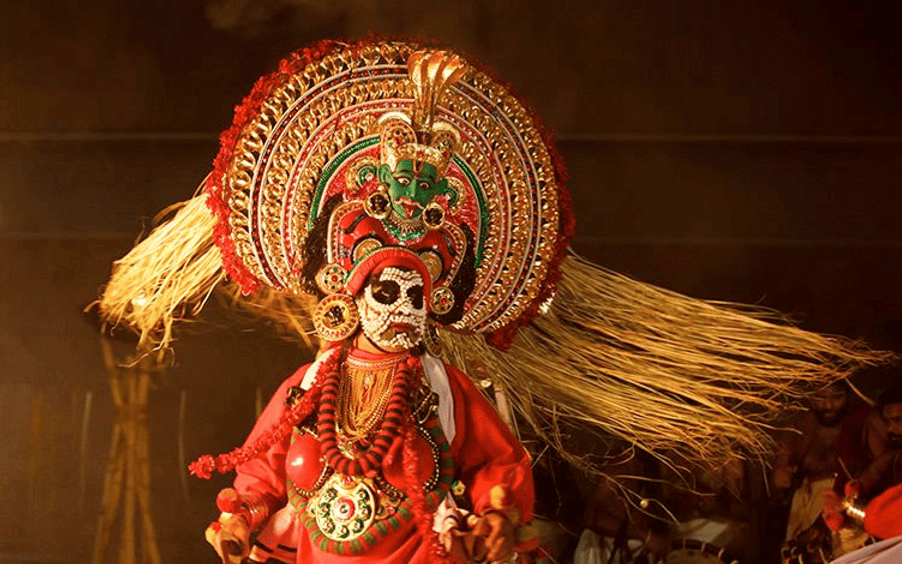

- Mudiyettu is a traditional form of ritual theatre from Kerala, India, which was recognized by UNESCO as part of the Intangible Cultural Heritage list in 2010.
- The performance depicts the mythological battle between Goddess Kali and the demon Darika.
- During the performance, artists wear intricate and elaborate costumes along with striking make-up to portray the characters.
Kalbelia
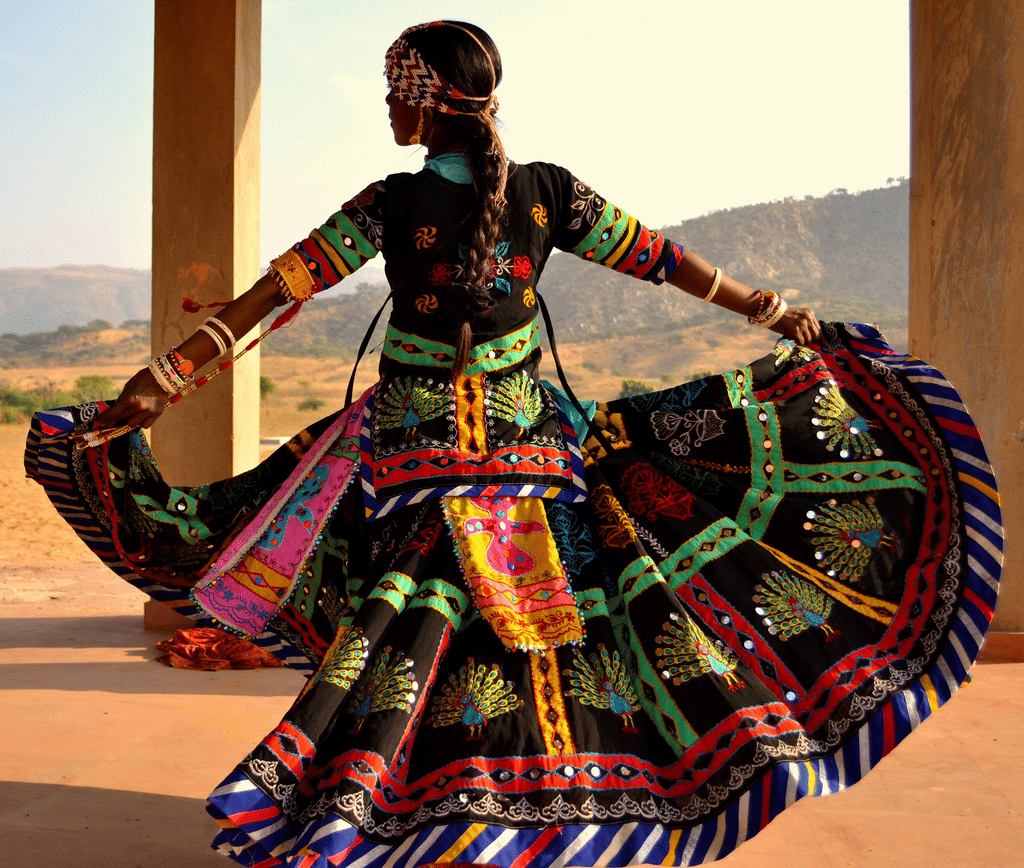

- Included in 2010, it is a dance performed by the Kalbelia tribe in Rajasthan resembling serpent movements.
- Songs based on mythology with spontaneous composition and improvisation during performances.
Chhau

- Chhau was added to the UNESCO list in 2010. It is a traditional martial dance originating from the regions of Odisha, Jharkhand, and West Bengal. This dance is celebrated during the spring festival.
- There are three distinct styles of Chhau: Purulia Chhau, Seraikella Chhau, and Mayurbhanj Chhau. Each style is unique to its region of origin and showcases different cultural elements.
- Chhau is a fascinating blend of dancing and martial arts. The performances often depict stories from Hindu mythology, with dancers wearing elaborate masks that add to the visual appeal and storytelling aspect of the dance.
Buddhist Chanting of Ladakh

- Included in 2012, it is a recitation of sacred Buddhist texts in the trans-Himalayan Ladakh region, relating to both Mahayana and Vajrayana sects.
Sankirtana

- Included in 2013, it is a ritual singing, drumming, and dancing art form in Manipur, narrating the life and deeds of Lord Krishna.
- Brings communities together on festive occasions, reinforcing communal relationships.
Traditional Brass and Copper Craft of Utensil Making among the Thathera Community of Jandiala Guru in Punjab

- Included in 2014, oral tradition passed down through generations, involving heating and molding metals intothin plates with curved shapes.
- Utensils serve functional and ritualistic purposes, using metals like brass, copper, and kansa.
Nowrouz

- Included in 2016, it is a New Year festival for Parsis, celebrated as the spring festival by the Kashmiri community.
- Customs include laying out symbolic items signifying prosperity, wealth, and happiness.
Yoga

- Included in 2016, it is a series of poses, meditation, controlled breathing, and chanting techniques to attain self-realization.
- Traditionally, yoga is taught through the Guru-Shishya parampara, which is a teacher-student tradition.
Kumbh Mela
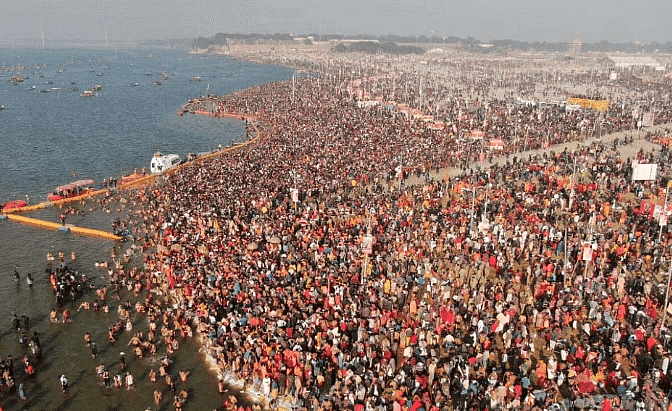

- Included in 2017, it is a mass Hindu pilgrimage to sacred rivers held at four places: Prayagraj, Haridwar, Nashik, and Ujjain.
- Held every 12 years, with variations in timing and names at different locations.
Durga Puja in Kolkata
- Included in 2021, it is an annual festival celebrated magnificently in West Bengal, marking the worship of the Hindu mother goddess Durga.
- Main attractions include pandals, decorations, sculptures, and communal gatherings.
UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN)
- The UNESCO Creative Cities Network was established in 2004 to promote cooperation among cities prioritizing creativity for sustainable urban development.
- The network encompasses seven creative fields: Crafts and Folk Arts, Media Arts, Film, Design, Gastronomy, Literature, and Music.
- As of March 2024, eight Indian cities—Srinagar, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Chennai, Jaipur, Varanasi, Gwalior, and Kozhikode—are part of the UCCN.
Recent Developments in UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage (Post-2021, India)
Garba of Gujarat (2023):- Description: Garba is a ritualistic and devotional folk dance performed during the nine-day Hindu festival of Navaratri, dedicated to the worship of feminine energy (Shakti). It features vibrant circular movements, singing, and traditional instruments like the dhol and mandolin, symbolizing Gujarat’s cultural vibrancy.
- Inscription Details: Added to the UNESCO Representative List on December 6, 2023, during the 18th session of the Intergovernmental Committee in Kasane, Botswana. It became India’s 15th ICH element on the list.
- Significance: Garba’s inclusion highlights its role as a community-driven event fostering social bonds and cultural continuity. It is performed in homes, temple courtyards, public spaces, and large open grounds, making it an inclusive cultural expression.
|
216 videos|855 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Nitin Singhania Summary: UNESCO’S List of Intangible Cultural Heritage - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the purpose of UNESCO's Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity? |  |
| 2. How are elements selected for inclusion in the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity? |  |
| 3. Can you give examples of some cultural practices included in the Representative List? |  |
| 4. What are some challenges faced in safeguarding intangible cultural heritage? |  |
| 5. How does the inclusion of an element in the Representative List benefit communities? |  |

















