Non-Metals | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Properties of Non-Metals |

|
| Physical Properties of Non-Metals |

|
| List of Non-Metals |

|
| Chemical Properties of Non-Metals |

|
Introduction
Non-metals are elements that do not possess the typical characteristics associated with metals. They exhibit excellent insulating properties for both heat and electricity. While most non-metals are in the form of gases, there are instances where they exist as liquids. Surprisingly, certain non-metals like carbon, sulphur, and phosphorus can even be found in solid states at room temperature.
Properties of Non-Metals
Non-metals possess characteristic properties such as high ionization energies and high electronegativity. As a result, non-metals tend to gain electrons when they react with other compounds, forming covalent bonds.
Here are the general properties of non-metals:
- Atomic Size: Non-metal atoms are typically smaller than metal atoms, and many of the properties of non-metals can be attributed to their atomic sizes.
- Electronegativity: Non-metals exhibit high electronegativity, meaning their atoms have a strong tendency to attract additional electrons. They also have a strong tendency to hold on to the electrons they already possess. In contrast, metals easily give up electrons to non-metals, forming positively charged ions. This difference in electron behavior distinguishes non-metals from metals, which readily conduct electricity.
Physical Properties of Non-Metals
Under normal temperature and pressure conditions, non-metals can exist as gases, solids, or liquids. In contrast, with the exception of mercury, metals are typically solid at room temperature. The presence of numerous non-metals in gaseous or liquid states indicates that non-metals generally have relatively low melting and boiling points under normal atmospheric conditions.
- In their solid state, non-metals tend to be brittle, lacking the malleability and ductility observed in metals. Ductility, the ability to be stretched into wires, is generally absent in non-metals, except for carbon, which can form carbon fibers used in various industries such as sports and music equipment.
- Non-metals also exhibit very low electrical conductivity, which is a crucial property distinguishing them from metals. They are not sonorous and do not produce a deep ringing sound when struck. Furthermore, non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity, except for graphite, which has some conductivity properties.
- By understanding these distinct physical properties of non-metals, we gain valuable insights into their behavior and applications in various fields.
List of Non-Metals
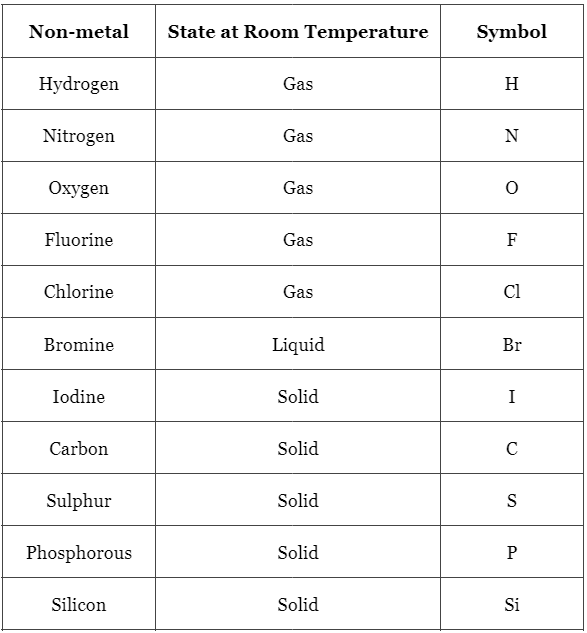
Chemical Properties of Non-Metals

Non-metals possess distinctive chemical properties that influence their reactions and bonding behavior. Let's explore some of these key chemical properties:
- Reaction with Water: Non-metals generally do not react with water, but they can exhibit high reactivity in the presence of air. For instance, phosphorus is a highly reactive non-metal that ignites upon exposure to atmospheric oxygen. To prevent this reaction, phosphorus is often stored in water.
- Reaction with Acids: Non-metals typically do not react with acids.
- Reaction with Bases: The interaction between non-metals and bases is complex. For example, when chlorine reacts with bases like sodium hydroxide, it produces products such as sodium hypochlorite, sodium chloride, and water.
- Reaction with Oxygen: Non-metals react with oxygen to form oxides. These oxides can be acidic or neutral. For instance, when sulfur reacts with oxygen, it forms sulfur dioxide (SO2), which further reacts with water to create sulfurous acid (H2SO3).
- Reaction with Metals: Non-metals often form ionic compounds when they react with metals. This results in the transfer of electrons from the metal to the non-metal, leading to the formation of charged ions.
Uses of Non-Metals
Non-metals find numerous applications in various fields due to their distinct properties. Let's explore some of the common uses of non-metals:
- Nitrogen (N) is widely used in the production of ammonia, nitric acid, and fertilizers.
- Chlorine (Cl) is employed in water purification processes.
- Hydrogen (H) is an essential component of rocket fuel.
- Carbon (C), specifically in its graphite form, is utilized to create pencils.
- Sulphur (S) is used in the preparation of sulfuric acid, an important chemical in various industries.
|
744 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|















