Nucleic Acids and Polysaccrides | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Polysaccharides? |

|
| Characterstics of Polysaccharides (Carbohydrates) |

|
| Types of Polysaccharides |

|
| What are Nucleic Acids? |

|
What is Polysaccharides?
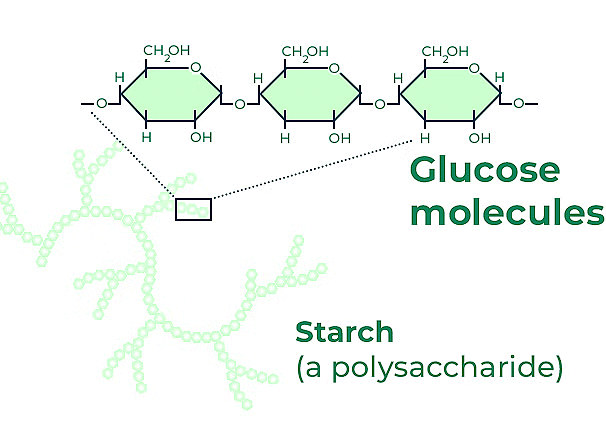
A polysaccharide is a type of carbohydrate, specifically a complex carbohydrate, that consists of multiple monosaccharide (simple sugar) units linked together. These long chains of sugar molecules can be quite large and complex. Polysaccharides serve various important functions in living organisms, such as energy storage, structural support, and cellular recognition.
Polysaccharides have diverse functions in living organisms, including energy storage, structural support, and as components of important molecules like DNA and RNA. They are made up of long chains of monosaccharides (simple sugars) linked together by glycosidic bonds, and the specific arrangement and type of monosaccharides determine the properties and functions of the polysaccharide.
Common examples of polysaccharides include starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin.
Characterstics of Polysaccharides (Carbohydrates)
- The acid insoluble pellet contains polysaccharides, which are long chains of sugars.
- Polysaccharides like cellulose, starch, glycogen, and inulin are examples of these macromolecules.
- Cellulose is a homopolymer made up of glucose units and is the main component of plant cell walls.
- Starch and glycogen serve as energy storage forms in plants and animals, respectively.
- In a polysaccharide chain like glycogen, the ends are termed as the reducing end and the non-reducing end.
- Cellulose forms plant cell walls and is the main material in products like paper and cotton fiber.
- Complex polysaccharides like chitin, found in arthropod exoskeletons, are mostly homopolymers with unique structures.
Types of Polysaccharides
Polysaccharide are categorized in two ways:
(a) Homopolysaccharides.
(b) Heteropolysaccharides.
Homopolysaccharides, are a type of polysaccharide where every unit within the structure is made up of the same kind of monosaccharide. Unlike heteropolysaccharides, which contain a variety of monosaccharide types, homopolysaccharides are characterized by their uniformity in monosaccharide composition throughout.
Heteropolysaccharides, or heteroglycans, are polysaccharides that consist of multiple types of monosaccharides, resulting in a wide array of sugar units within their structures. Unlike homopolysaccharides, where each monosaccharide unit is identical, heteropolysaccharides exhibit diversity in monosaccharide composition, featuring different structures and properties.
What are Nucleic Acids?
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules essential for life, found in all living organisms. They play crucial roles in storing, transmitting, and expressing genetic information. There are two main types of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
- Nucleic acids are polynucleotides, essential macromolecules in living tissues, along with polysaccharides and polypeptides.
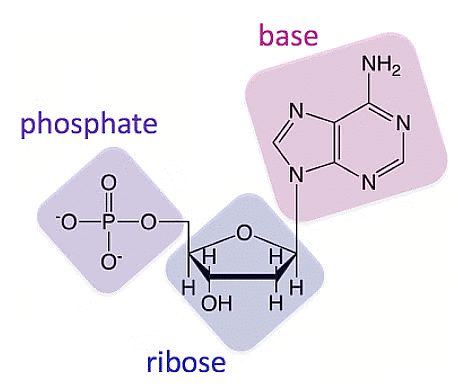
- A nucleotide, consisting of a heterocyclic compound, a monosaccharide, and a phosphate, is the basic unit of nucleic acids.
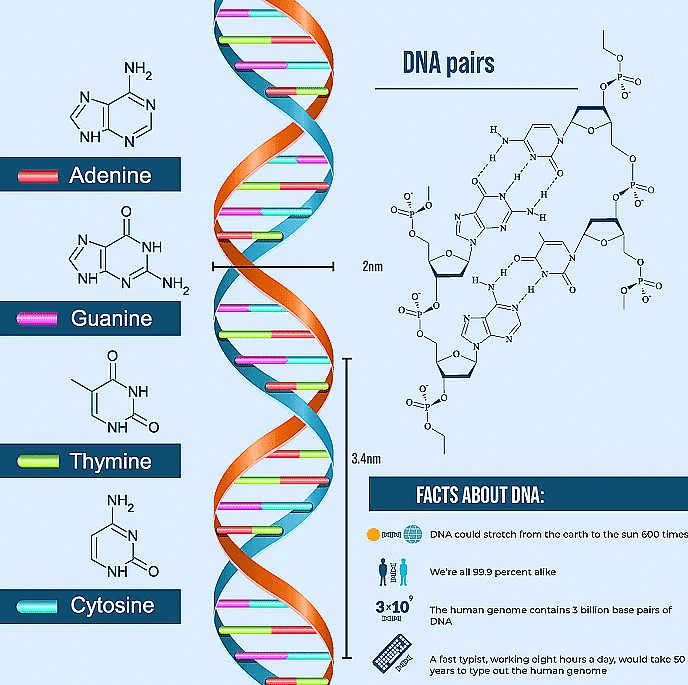
- Nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids include adenine, guanine, uracil, cytosine, and thymine.
- The sugar component in nucleotides is either ribose or 2’-deoxyribose, determining if it's DNA or RNA.
- DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are the two main types of nucleic acids.
Nucleotides
Nucleotides link together through phosphodiester bonds to form long chains, which constitute the backbone of DNA and RNA molecules. The sequence of nucleotides along these chains carries genetic information and plays a vital role in the functioning of cells.
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA. They are composed of three main components:
- Nitrogenous base: This is a heterocyclic compound that contains nitrogen atoms. In DNA, the nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil (U).
- Sugar molecule: In DNA, the sugar molecule is deoxyribose, hence the name deoxyribonucleic acid. In RNA, the sugar molecule is ribose, giving rise to ribonucleic acid.
- Phosphate group: This is a phosphoric acid or phosphate group attached to the sugar molecule.
|
179 videos|531 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Nucleic Acids and Polysaccrides - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are Polysaccharides? |  |
| 2. What are the characteristics of Polysaccharides (Carbohydrates)? |  |
| 3. What are the types of Polysaccharides? |  |
| 4. What are Nucleic Acids? |  |
| 5. How are Nucleic Acids and Polysaccharides related? |  |