Origin of Life | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding Evolution and the History of Life |

|
| Origin of Life |

|
| Theories on the Origin of Life |

|
| Evolution of Life Forms: A New Perspective |

|
Understanding Evolution and the History of Life
Evolutionary Biology looks at how life on Earth has changed over a long time. To understand this, we need to know what evolution really means. Evolution is about the changes that happen in plants and animals over millions of years. But before we dive into that, we should consider the big picture. the evolution of Earth, the stars, and even the universe.
The Beginning of Life
What we are going to explore is the story of how life began and developed on our planet, with the Earth's evolution and the unfolding of the universe as our background. This story involves enormous time spans and complex processes, and it is the basis for understanding the amazing variety of life we see today.
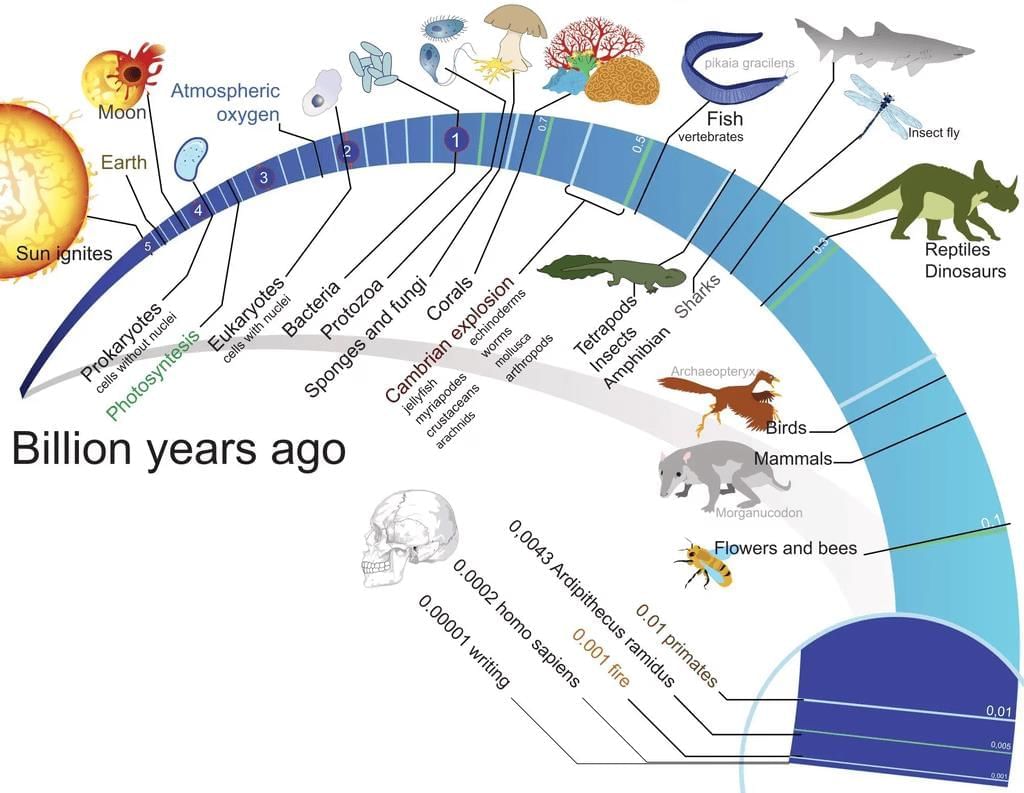
Origin of Life
Life on Earth and the Universe
- When we look at stars in the night sky, we're actually looking back in time. Stars are very far away, and their light takes a long time to reach us. What we see now is light that started its journey millions of years ago from trillions of kilometers away. In contrast, when we see things around us, we see them instantly, in the present. So, looking at stars is like peeking into the past.
- The origin of life is thought to be a special and unique event in the history of the universe. The universe is enormous, and Earth is just a tiny speck in it. The universe is also very old, about 13.8 billion years. It is made up of huge clusters of galaxies, and each galaxy contains stars, gas, and dust. Given the vastness of the universe, Earth is indeed a tiny part of it.
The Big Bang theory explains how the universe began. It describes a massive explosion that is hard to imagine in physical terms. After this explosion, the universe expanded and cooled down. Initially, only hydrogen and helium were formed. These gases eventually condensed under the force of gravity to form galaxies, including our Milky Way galaxy.
- Formation of Earth. Within the Milky Way galaxy, Earth is believed to have formed about 4.5 billion years ago. In the beginning, Earth had no atmosphere. As the planet cooled, water vapor, methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia were released from the molten interior, covering the surface.
- Role of UV Rays. Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun played a crucial role in breaking down water vapor into hydrogen and oxygen. The lighter hydrogen gas escaped into space, while oxygen reacted with ammonia and methane to form water, carbon dioxide, and other gases. This process also led to the formation of the ozone layer.
- Formation of Oceans. As Earth continued to cool, the water vapor eventually condensed and fell as rain, filling depressions on the surface and forming oceans. Life is believed to have appeared around 500 million years after the formation of Earth, which is approximately four billion years ago.
Theories on the Origin of Life
- Life from Outer Space. Some scientists propose that life may have come from outer space. Ancient Greek thinkers suggested that tiny units of life, called spores, were transferred to different planets, including Earth. This idea, known as "panspermia," is still considered by some astronomers.
- Spontaneous Generation. For a long time, it was believed that life could arise from decaying and rotting matter, such as straw and mud. This theory was known as spontaneous generation. However, Louis Pasteur conducted careful experiments that disproved this idea. He showed that life comes only from pre-existing life. In his experiments, he found that in sterilized flasks, life did not develop from killed yeast, while in flasks exposed to air, new living organisms could arise from killed yeast. This proved that spontaneous generation was not possible.
- Chemical Evolution. Pasteur's work did not explain how the first life form originated on Earth. Russian scientist Oparin and English scientist Haldane suggested that the first life form could have emerged from non-living organic molecules, such as RNA or proteins. They proposed that life began with chemical evolution, where diverse organic molecules formed from inorganic substances. The early conditions on Earth included high temperatures, volcanic activity, and a reducing atmosphere rich in methane and ammonia.
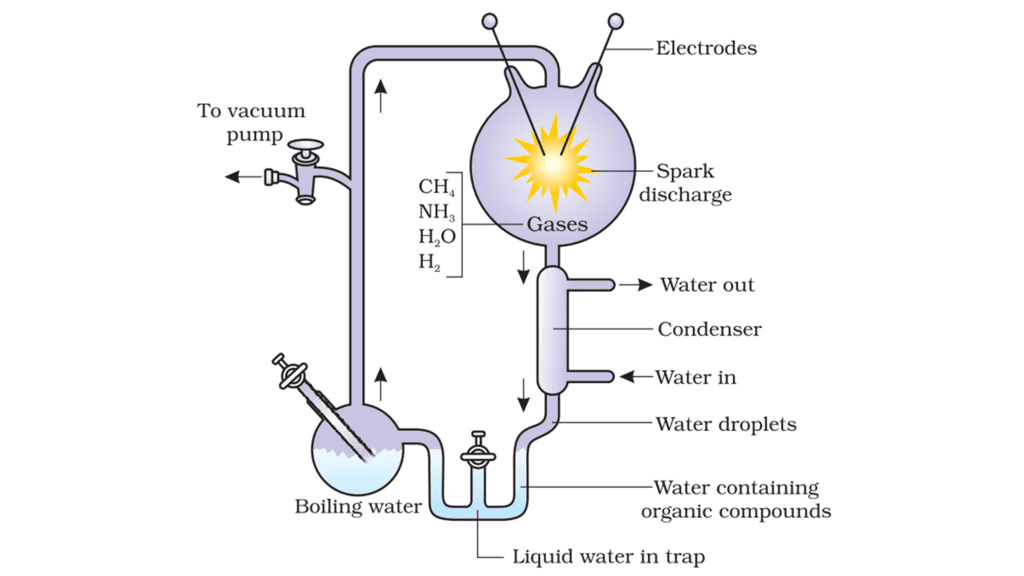
- Miller's Experiment. In 1953, American scientist S.L. Miller recreated similar conditions in a laboratory. He introduced electric sparks into a closed flask containing methane, hydrogen, ammonia, and water vapor at a high temperature of 800 degrees Celsius. Miller observed the formation of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Other experiments conducted by different scientists also resulted in the formation of sugars, nitrogen bases, pigments, and fats under similar conditions. The analysis of meteorites has revealed the presence of similar compounds, suggesting that similar processes may be happening in other parts of space. This limited evidence led to the acceptance of the idea of chemical evolution, although the exact process of how the first self-replicating metabolic capsule of life came into existence remains unknown.
- Early Life Forms. It is believed that the first non-cellular forms of life could have emerged around 3 billion years ago. These life forms were likely giant molecules, such as RNA, proteins, or polysaccharides, which reproduced their own molecules. The first cellular life forms probably did not appear until about 2 billion years ago and were likely single-celled organisms. All these early life forms existed in a watery environment. The prevailing view is that the first form of life arose gradually through evolutionary processes from non-living molecules. However, the story of how these first cellular life forms evolved into the complex diversity of life we see today is a fascinating and ongoing area of study.
Evolution of Life Forms: A New Perspective
Theory of Special Creation
- Traditional religious belief held that all living organisms were created as they are today, with no change in diversity over time.
- This theory also suggested that Earth is only about 4,000 years old.
Charles Darwin's Observations
- During his voyage on the H.M.S. Beagle, Darwin observed that current living forms share similarities with each other and with ancient life forms that no longer exist.
- He noted that different life forms have gone extinct over time, while new ones have emerged, indicating a gradual evolution of life.

Natural Selection
- Darwin proposed that within any population, there are variations in characteristics. Those individuals with traits that better suit their environment (such as climate, food, and physical conditions) are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- This process, called natural selection, means that the fittest individuals leave more offspring, ensuring their traits are passed on.
Alfred Wallace's Contribution
- Around the same time as Darwin, Alfred Wallace, a naturalist in the Malay Archipelago, reached similar conclusions about evolution and natural selection.
Common Ancestors and Geological History
- Over time, new types of organisms become recognizable, but all existing life forms share common ancestors that lived in different periods of Earth’s history.
- The geological history of Earth, which spans billions of years, closely aligns with its biological history, supporting the idea that Earth is very old, far older than the previously believed few thousand years.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Origin of Life - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the Panspermia hypothesis regarding the origin of life? |  |
| 2. How do scientists study the origins of life on Earth? |  |
| 3. What evidence supports the idea that life could exist elsewhere in the universe? |  |
| 4. What role did RNA play in the early evolution of life? |  |
| 5. How does evolution explain the diversity of life on Earth? |  |





















