Overview: Chemical Reactions & Equations - 2 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Types of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions involve breaking and making of bonds between atoms to produce new substances.
(i) Combination Reactions
A reaction in which a single product is formed from two or more reactants is called a combination reaction.
Example:
(i) Burning of coal C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
(ii) Formation of water from H2 and O2. 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (I)
Now, let's do an activity to understand the combination reaction a little more.
Activity 3
Aim: Perform an activity to illustrate a combination reaction.
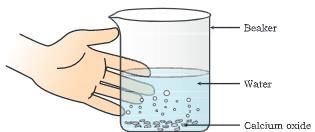
Materials required: Beaker (500 mL ), water, calcium oxide ( quick lime).
Procedure:(i) Take a clean 500 mL Pyrex glass beaker.
(ii) Take about 50 g of quick lime in it.
(iii) Add about 100 ml water to it carefully.
(iv) Quick lime (calcium oxide) reacts vigorously with water to form a single product slaked lime Ca(OH)2 and a large amount of heat is evoked.
CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + Heat
Some more examples of a combination reaction are: Burning of coal
C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
Formation of water from H2 (g) and O2 (g)
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
Observations:
- When water is added to quick lime, a suspension of slaked lime is formed.
- On touching the beaker we feel it is hot.
- A clear solution appears as the suspension of slaked lime settles down to the bottom of the beaker.
- On blowing exhaled air that contains sufficient carbon dioxide, lime water turns milky.
Result:
- Quick lime reacts vigorously with water to produce slaked lime releasing a large amount of heat. So the reaction is highly exothermic.
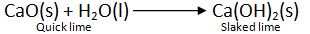
- Slaked lime is only slightly soluble in water, so it forms a suspension of slaked lime in water.
- The clear solution obtained after the suspension settles is called lime water.
- Exhaled air contains CO2 which turns lime water milky.
- Calcium oxide and water react to form only a single product, calcium hydroxide. So the reaction is a combination reaction.
Interesting Fact:
White Washing of Buildings
A solution of slaked lime Ca(OH)2 is applied on the walls and roofs. After 2 or 3 days, slaked lime reacts with atmospheric carbon dioxide and it changes into calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
Calcium carbonate gives a shiny white finish to the walls.
(ii) Exothermic Reactions
Reactions which take place with the evolution of heat (increase of temperature) are called exothermic reactions.
 Evolution of heat in Exothermic reaction
Evolution of heat in Exothermic reaction
Example: Burning of natural gas and respiration are exothermic reactions.
- CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) (Burning of natural gas)
- C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) (Respiration)
- The decomposition of vegetable matter into compost is also an exothermic reaction.
(iii) Endothermic Reactions
Reactions which take place with absorption of heat (lowering of temperature) are called endothermic reactions.
 Absorption of heat in Endothermic reaction
Absorption of heat in Endothermic reaction
Example:
- Melting of ice cubes.

- Evaporating liquid water.
(iv) Decomposition Reactions
When a single reactant breaks down to give simpler products, it is called a decomposition reaction. For example:
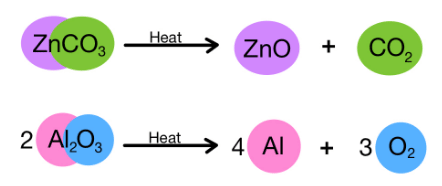
Let's do an activity to understand the decomposition reaction more.
Activity 4
Aim: Perform an activity to illustrate the decomposition reaction.
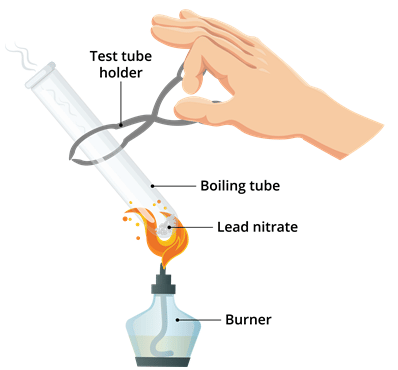
Materials required: Lead nitrate powder, boiling tube, test tube holder, burner.
Procedure:
(i) Take a clean Pyrex glass boiling tube.
(ii) Add to it about 2 g powdered lead nitrate.
(iii) Using a test tube holder or pair of tongs, heat the test tube on a Bunsen burner.
(iv) Note the change that takes place.
Observation: We observe that brown fumes are emitted from the test tube.
The following reaction takes place in this activity:
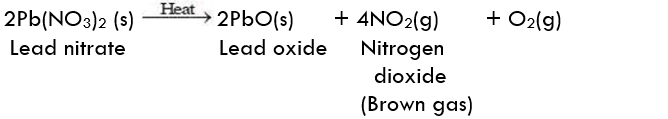
Result:
In the above reaction, lead nitrate breaks down into simpler products proving that this is the decomposition reaction.
Similarly, we can perform the activities of heating ferrous sulphate crystals and calcium carbonate to illustrate decomposition reactions.
Activity 5
Aim: Perform the electrolysis of water experiment to illustrate the decomposition reaction.
Materials required: A plastic mug, two graphite rods, two test tubes, a 6 V battery, a switch, two rubber stoppers, and sulphuric acid.
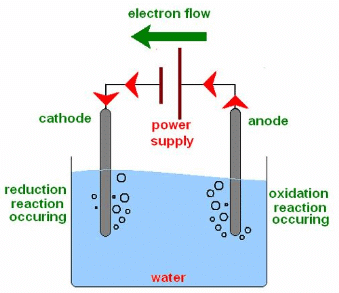 Electrolysis of Water
Electrolysis of Water
Procedure:
(i) Set up the apparatus as shown in Fig. above.
(ii) Fill the mug with water such that graphite rods are immersed. Add a few drops of sulphuric acid.
(iii) Connect the electrodes to a 6 V battery and switch on the current. Leave the apparatus undisturbed for some time.
(iv) Formation of bubbles at both electrodes will take place.
(v) The reaction that takes place is as follows:
2H2O (l) → 2H2 (g) + O2 (g)
Observation:
- Hydrogen gas is collected in the test tube over the cathode while oxygen gas is collected in the test tube over the anode.
- It is interesting to note that the volume of hydrogen collected is twice the volume of oxygen as explained by the above chemical equation.
- Hydrogen and oxygen gases can be identified as under: Bring a burning candle near the tube placed over the cathode. A pop sound is produced (hydrogen is a combustible gas).
- Again, bring the burning candle near the tube placed over the anode. The flame gets brighter (oxygen is a supporter of combustion).
Result: As we have seen in the reaction that water is converted into very simple products like hydrogen and oxygen hence it is a decomposition reaction.
Activity 6
Aim: Perform an activity (decomposition of silver salt) to illustrate the decomposition reaction.
Materials required: China dish, silver chloride.
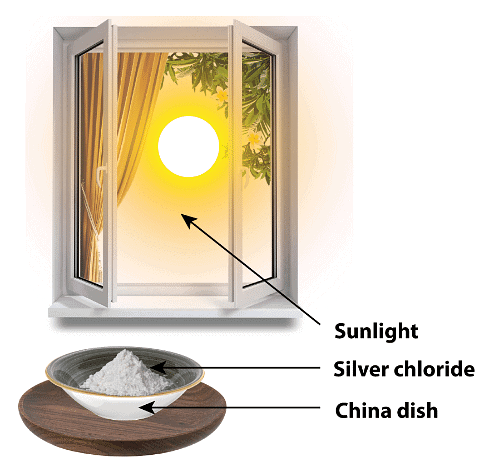
Procedure
(i) Take about 2 g silver chloride in a china dish (Fig. 1.6).
(ii) Place the china dish in sunlight for some time.
(iii) You will observe that silver chloride becomes grey after some time.
Observation:
Silver chloride becomes grey after some time because silver chloride undergoes decomposition by the action of sunlight (sunlight is also a form of energy).
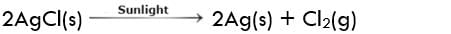
Result:
As we have seen in the above reaction Silver chloride breaks down into simpler products like Silver and chlorine gas, hence proving that this is a decomposition reaction.
(v) Displacement Reaction
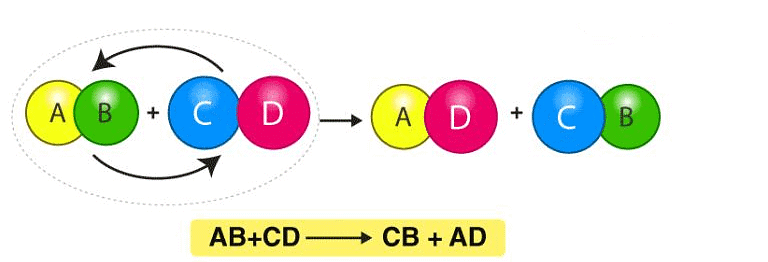
A reaction in which one substance displaces another from the aqueous solution is called displacement reaction.
A general reaction of this type may be represented as: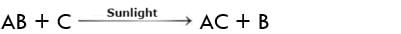
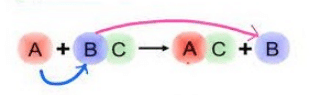
Thus C has displaced B in the above reaction.
Activity 7
Aim: Perform an activity to illustrate displacement reaction.
Materials required: Test tube, thread, stand with clamp, copper sulphate solution, iron nails.
Procedure:
(i) Take three iron nails and clean them by rubbing them with sandpaper.
(ii) Take two test tubes. Mark them A and B. In each test tube take about 10 mL of copper sulphate solution.
(iii) Tie two nails with a thread and immerse them in the copper sulphate solution in test tube B for about 20 minutes Fig. 1.7(a).
Keep one nail aside for comparison.
(iv) Take out the iron nails from the copper sulphate solution in test tube B.
(v) Compare the colour of the copper sulphate solution in the two test tubes.
Observation:
- It will be observed that the intensity of the blue colour has decreased in test tube B compared to that in test tube A.
- Also, compare the colours on the nails. It will be seen that the nail removed from the copper sulphate solution has a brown coating of Cu on it.
- The following reaction takes place in the above experiment:

- Iron is more reactive than copper. It displaces copper from the solution of copper salt.
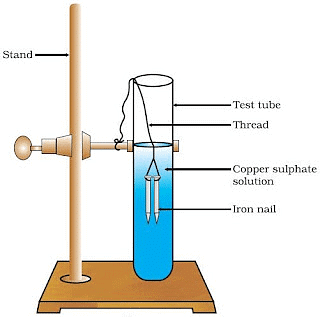 Iron nails dipped in copper sulphate solution
Iron nails dipped in copper sulphate solution
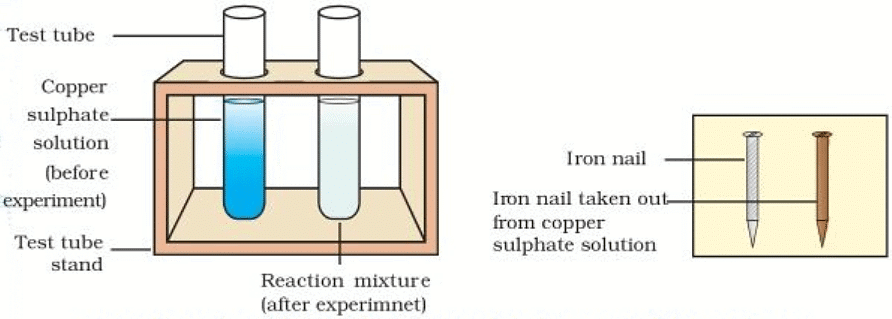 Iron nails and copper sulphate solutions compared before and after the experiment
Iron nails and copper sulphate solutions compared before and after the experiment
- Similarly, we can experiment using zinc or lead in place of Cu. Both Zn and Pb are more reactive than Cu.
- Zinc and lead displace copper from the solution of CuSO4 as per the following equations:
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Pb(s) + CuSO4(aq) → PbSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Copper which is displaced gets deposited on zinc or lead as the brown coating.
(vi) Double Displacement Reaction
Reactions in which there is an exchange of ions between the reactants are called double displacement reactions.
Activity 8
Aim: Perform an activity to illustrate a double displacement reaction.
Materials required: Two test tubes, sodium sulphate solution, and barium chloride solution.
Procedure:
(i) Take two 20 mL clean test tubes.
(ii) Take 5 mL barium chloride solution in one test tube and 5 mL sodium sulphate solution in the other test tube.
(iii) Add sodium sulphate solution to the test tube containing barium chloride solution as shown in Fig. 1.8.
Observation:
- It will be observed that a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed as a result of the exchange of ions between the two substances.
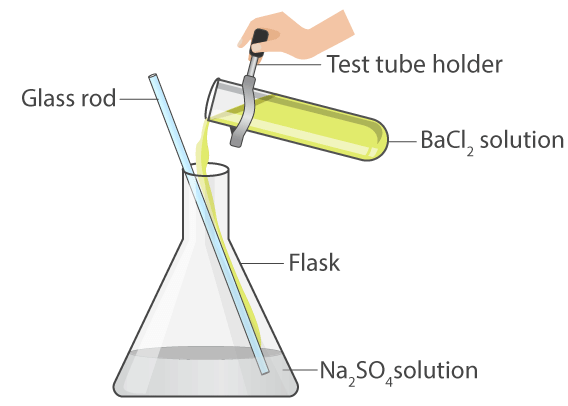
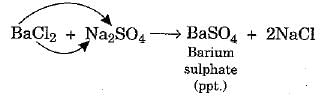
- Any reaction that produces a precipitate can be called a precipitation reaction.
- Similarly, we can carry out the reaction between lead nitrate and potassium iodide by mixing their aqueous solutions to illustrate a double decomposition reaction.
(vii) Oxidation and Reduction
Reactions in which a substance gains oxygen or loses hydrogen is called an oxidation reaction.
Similarly, a reaction in which a substance loses oxygen or gains hydrogen is called a reduction reaction.
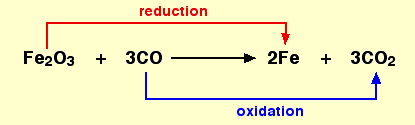
- If a substance gains oxygen during a reaction, it is said to be oxidised. Similarly, if a substance loses oxygen during a reaction, it is said to be reduced.
- One reactant gets oxidised while the other gets reduced during a reaction. Such reactions are called reduction-oxidation reactions or redox reactions.
Activity 9
Aim: Perform an activity to illustrate oxidation.
Materials required: China dish, copper powder, wire gauze, tripod stand, burner.
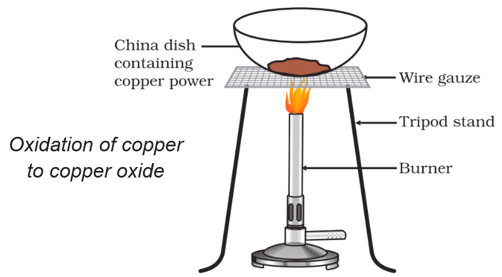
Procedure:
(i) Take about 2 g copper powder in a clean china dish (Fig.1.9)
(ii) Place it on a wire gauze supported on a tripod stand.
(iii) Heat it for about 15 minutes.
Observation:
- It will be observed that copper powder becomes black because of the formation of copper oxide (oxidation).

- We say that copper has been oxidised to copper oxide. Now, if we pass hydrogen gas over heated CuO, we obtain Cu (Brown colour) back. This is because CuO has been reduced to Cu.
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O - It may be schematically represented as under:
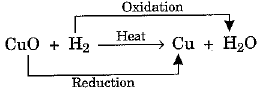
- Some other examples of redox reactions are:
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
The Effects of Oxidation and Reduction Reaction in Everyday Life
(i) CorrosionWhen a metal is attacked by substances around it such as moisture, acids, etc., it is said to corrode and this process is known as corrosion.
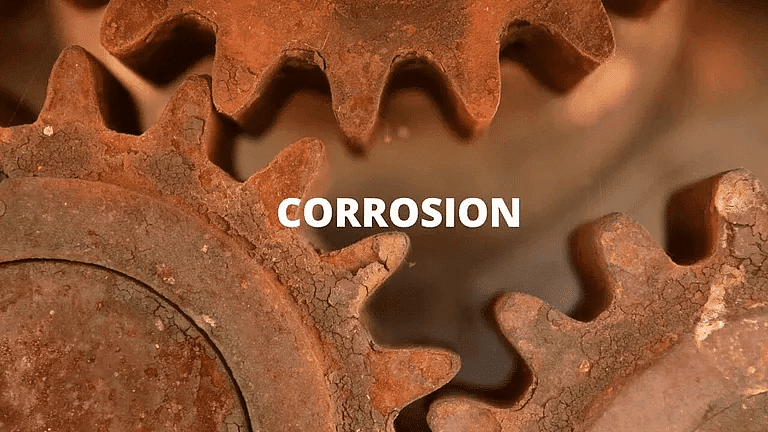
- Iron articles are shiny when new. But with time, they get coated with a reddish-brown powder called rust. Silver articles become black and copper articles become green on the surface due to corrosion.
- Corrosion causes damage to car bodies, bridges, iron railings, ships, etc.
(ii) Rancidity
When fats and oils are oxidised (or kept in open for some days), their smell and taste changes. We say that they have gone rancid. This phenomenon is called rancidity.
 Rancidity
Rancidity
- Antioxidants are added to foods containing oils and fats to prevent rancidity. The antioxidant substances that are added to food are preferentially oxidised and thus they prevent the oxidation of foods.
- Keeping food in air-tight containers helps to slow down oxidation. Chips manufacturers flush bags of chips with nitrogen to prevent chips from getting oxidised.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Chemical Reactions & Equations - 2 - Science Class 10
| 1. What are exothermic reactions and can you provide an example? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions? |  |
| 3. Can you explain what a displacement reaction is with an example? |  |
| 4. What are oxidation and reduction reactions, and why are they important? |  |
| 5. How do oxidation-reduction reactions affect everyday life? |  |






















