UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary > PIB Summary - 12th May, 2025
PIB Summary - 12th May, 2025 | PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC PDF Download
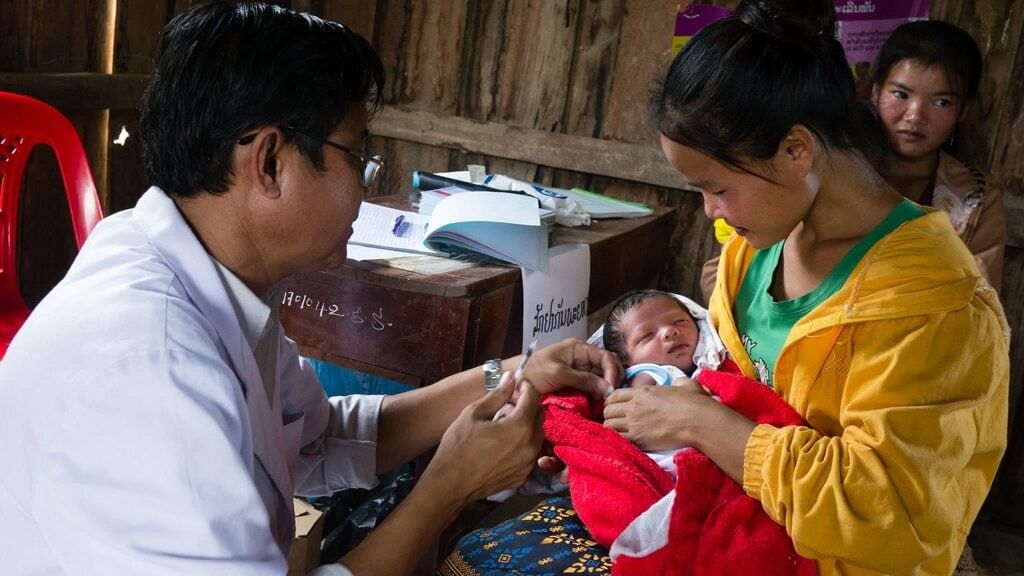
India witnesses a steady downward trend in maternal and child mortality towards achievement of SDG 2030 targets
Introduction
- India has made significant progress in reducing maternal and child mortality rates from 2014 to 2021, moving closer to the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) targets for 2030.
- This improvement is attributed to strong policy measures, better health infrastructure, and governance based on data.
Progress in Key Indicators (2014–2021)
Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR)
- MMR has decreased from 130 (2014–16) to 93 (2019–21) per lakh live births.
- This is a 37-point reduction and a significant move towards the SDG target of ≤70 by 2030.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
- IMR has declined from 39 to 27 per 1,000 live births.
Neonatal Mortality Rate (NMR)
- NMR has decreased from 26 to 19 per 1,000 live births.
Under-Five Mortality Rate (U5MR)
- U5MR has fallen from 45 to 31 per 1,000 live births.
Fertility Rate
- The fertility rate has stabilized at 2.0 (down from 2.3 in 2014), nearing the replacement level.
Sex Ratio at Birth
- The sex ratio at birth has improved from 899 to 913 females per 1,000 males.
State-wise SDG Target Achievement (as per SRS 2021)
Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR)
- Target Achieved (≤70) in 8 States: Kerala, Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Jharkhand, Gujarat, Karnataka.
Under-Five Mortality Rate (U5MR)
- Target Achieved (≤25) in 12 States/UTs: Includes Kerala (8), Delhi (14), Tamil Nadu (14), Maharashtra (16), Gujarat (24), etc.
Neonatal Mortality Rate (NMR)
- Target Achieved (≤12) in 6 States/UTs: Kerala (4), Delhi (8), Tamil Nadu (9), Maharashtra (11), J&K (12), Himachal Pradesh (12).
India’s Global Outperformance (1990–2023)
- MMR Reduction: India saw an 86% decline compared to the global average of 48%.
- U5MR Reduction: India achieved a 78% reduction, while the global rate was 61%.
- NMR Reduction: India’s reduction was 70%, surpassing the global rate of 54%.
- IMR Reduction: India experienced a 71% reduction, compared to the global rate of 58%.
Policy Interventions Driving Change
- Ayushman Bharat: The world’s largest health assurance scheme providing ₹5 lakh per family.
- Free Institutional Deliveries: Covering C-sections, transport, medicines, diagnostics, and nutrition support.
- Infrastructure Strengthening: Enhancements in Maternal and Child Health (MCH) Wings, Special Newborn Care Units (SNCUs), High Dependency Units (HDU)/Intensive Care Units (ICU), Neonatal B edside Units (NBSU), and Mother-Newborn Care Units.
- Clinical Protocols: Implementation of antenatal corticosteroids, Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP), and early screening protocols.
- Human Resource Development: Skill development for birth attendants, midwives, Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs), and community workers.
- Data-Driven Governance: Utilization of real-time digital health monitoring for evidence-based decision-making.
Scale of Impact
- The initiatives support approximately 300 lakh safe pregnancies and 260 lakh healthy live births annually.
- Emphasis is placed on equitable access, quality assurance, and dignified care for all.
Capacity Building Enhanced Through Interactive Training Under the “Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Program”
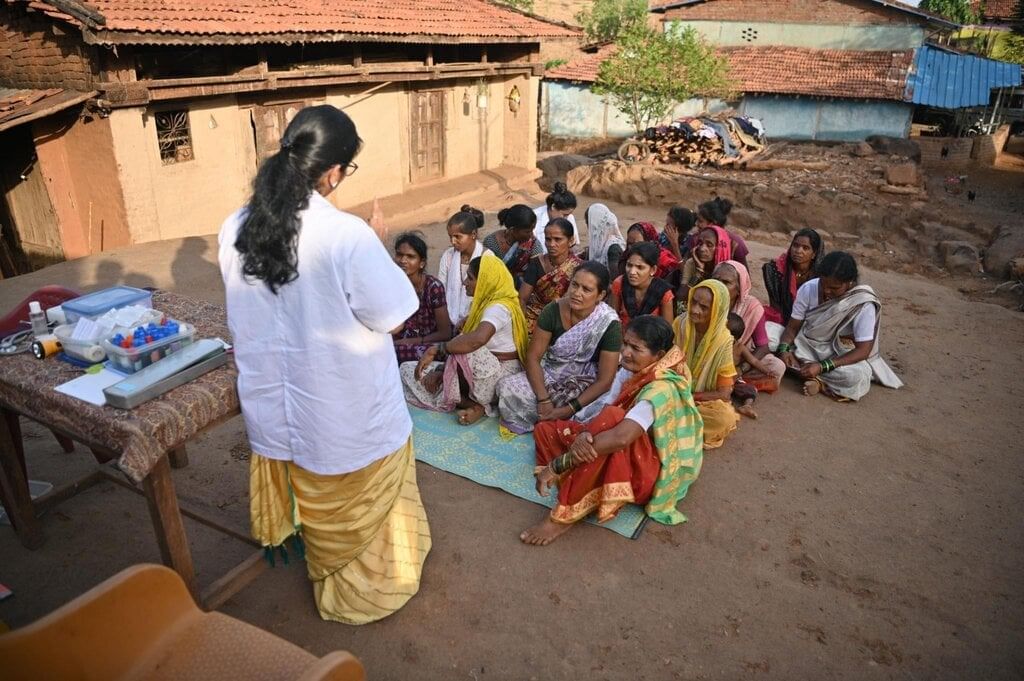

Program Overview
- Organizing Body: The program is organized by the Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) in collaboration with the Capacity Building Commission.
- Target Group: The program is aimed at officers ranging from Assistant Section Officers to Under Secretaries.
- Relevance: The program is relevant to General Studies Paper 2 (Governance) and General Studies Paper 4 (Ethics & Capacity Building).
Objectives and Significance
- To strengthen the competency, accountability, and responsiveness of public servants.
- To promote a collaborative work culture, interpersonal bonding, and enhanced administrative effectiveness among officers.
- To align with the broader vision of Mission Karmayogi, which aims to reform India’s national civil services.
Training Modules Covered
The training includes several modules designed to inspire and transform the mindset of officers:
- Who is a Rashtriya Karmayogi? This module defines the role and qualities of a Rashtriya Karmayogi.
- Expanding Our Vision of Success and Fulfillment: This module encourages officers to broaden their perspective on success and fulfillment in their roles.
- Creating a Karmayogi: This module focuses on the attributes and values needed to be a Karmayogi.
- Rashtriya Karmayogi as a Nation-Builder: This module emphasizes the role of Karmayogis in nation-building.
Integration with Mission Karmayogi
- Launched in 2020: Mission Karmayogi is a National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB) aimed at reforming civil services in India.
- Shift from Rule-Based to Role-Based Performance: The mission aims to transition civil services from a rule-based framework to a role-based performance system.
- Continuous Learning: Mission Karmayogi ensures continuous learning through competency frameworks, online self-learning on the iGOT Karmayogi platform, and role-specific digital content and certification.
Ethical & Behavioral Capacity (GS 4 Link)
- Competency Building: The program builds competencies in emotional intelligence, ethical decision-making, service motivation, and empathy.
- Reinforcing Governance Values: It reinforces values of integrity, non-partisanship, dedication, and transparency in governance.
- Inspirational Quote: The program is guided by the principle expressed by Mahatma Gandhi: “The best way to find yourself is to lose yourself in the service of others.”
Impact and Strategic Relevance
- Citizen-Centric Bureaucracy: The program promotes a citizen-centric and performance-oriented bureaucracy.
- Culture of Excellence: It cultivates a culture of excellence, innovation, and adaptive leadership within the public administration.
- Capacity-Building and Digital Governance: The program reinforces the government’s focus on capacity-building, digital governance, and responsive public administration.
Challenges and Way Forward
- Regular Evaluation: There is a need for regular evaluation of training outcomes and officer performance to ensure effectiveness.
- Customization: The training approach should avoid a one-size-fits-all model and be customized according to the specific roles and ministries of the officers.
- Behavioral Transformation: The focus should be on behavioral transformation rather than just delivering knowledge, to bring about meaningful change in public administration.
The document PIB Summary - 12th May, 2025 | PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on PIB Summary - 12th May, 2025 - PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC
| 1. What is the current trend in maternal and child mortality rates in India? |  |
Ans. India is witnessing a steady downward trend in maternal and child mortality rates, which is a positive indicator towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) targets set for 2030.
| 2. How does the Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Program contribute to capacity building? |  |
Ans. The Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Program enhances capacity building through interactive training sessions that equip participants with essential skills and knowledge, ultimately improving public service delivery.
| 3. What are the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) related to maternal and child health? |  |
Ans. The Sustainable Development Goals related to maternal and child health primarily include Goal 3, which aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages, with specific targets to reduce maternal and child mortality rates.
| 4. What measures are being taken to achieve the SDG targets for maternal and child health in India? |  |
Ans. India is implementing various health initiatives, enhancing healthcare infrastructure, promoting awareness, and providing training programs like the Rashtriya Karmayogi Jan Seva Program to ensure that maternal and child health services are accessible and effective.
| 5. Why is the reduction of maternal and child mortality important for India? |  |
Ans. Reducing maternal and child mortality is crucial for India as it not only improves the health and well-being of mothers and children but also contributes to overall societal development, economic growth, and the achievement of national and international health goals.
Related Searches





















