PIB Summary- 13th March, 2025 | PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC PDF Download
PMVIKAS FOCUSES ON UPLIFTMENT OF MINORITY COMMUNITIES
Context
The Ministry of Minority Affairs launched PM VIKAS to empower six notified minority communities through skill development, entrepreneurship, and educational support programs.
Pradhan Mantri Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PM VIKAS)
- Flagship Scheme: PM VIKAS is a major initiative by the Ministry of Minority Affairs, launched to support six notified minority communities.
- Scheme Convergence: It merges five previous schemes—‘Seekho Aur Kamao’, ‘Nai Manzil’, ‘Nai Roshni’, ‘Hamari Dharohar’, and ‘USTTAD’—to provide a comprehensive support system.
- Focus Areas: The scheme emphasizes skill development, entrepreneurship, leadership training for minority women, and education support for school dropouts.
- Awareness Campaign: Awareness is created through multimedia campaigns, including print and electronic media, FM radio, pocket booklets, and pamphlets in multiple languages.
- Public Engagement: Events such as ‘Hunar Haats’ and ‘Lok Samvardhan Parvs’ are organized to connect with minority communities.
- Inclusivity: The scheme aims to empower minorities economically and socially through structured government interventions.
White Revolution 2.0
Launch & Objective
Initiated by the Ministry of Cooperation on September 19, 2024.
Aims to boost milk production and expand dairy cooperatives.
Implementing Body
Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD).
Key Schemes
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission – Enhances indigenous bovine breeds & milk productivity.
- National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD) – Strengthens procurement & processing infrastructure.
- Supporting Dairy Cooperatives & Farmer Producer Organisations (SDCFPO) – Aids dairy cooperatives.
- Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) – Funds infrastructure growth.
Goals & Progress
- Target: Increase cooperative milk procurement to 1,007 lakh kg/day by 2028-29.
- Progress (as of March 12, 2025):
- 2.35 lakh dairy cooperative societies established/strengthened.
- Milk production (2023-24): 239.30 million tonnes (63.56% increase in a decade).
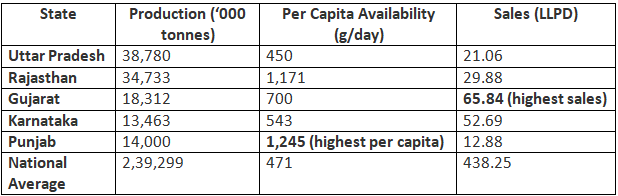
State-wise Data (2023-24)
Karnataka’s Dairy Growth
- Milk Procurement Growth: 51.61 LKgPD (2013-14) → 82.98 LKgPD (2023-24).
- KMF Network: 15,888 societies across 24,000 villages (2024-25).
- Quality Improvement: Training programs in northern Karnataka.
- Consumption Data Issue: 2019 estimate: 162.4 million tonnes, but lacks updated figures.
Key Insights
- Karnataka ranks 7th in production but 2nd in sales (52.69 LLPD) – strong market penetration.
- Punjab has the highest per capita availability (1,245 g/day), while Bihar lags (277 g/day).
- Uttar Pradesh leads in production but lacks sales efficiency.
Implications & Challenges
Positive Outcomes
- Expansion of cooperatives and genetic upgradation for sustainability.
- Infrastructure schemes aim to reduce wastage & boost farmer income.
Challenges
- Lack of consumption data complicates demand-supply balance.
- Production-sales mismatch (e.g., UP) indicates distribution inefficiencies.
Conclusion
White Revolution 2.0 strengthens India’s dairy industry, with Karnataka as a success model. To meet 2028-29 targets, bridging regional disparities and aligning production with demand are crucial.
White Revolution 1.0 – Operation Flood
- Launched in 1970 by NDDB under Dr. Verghese Kurien.
- Objective: Transform India into the world’s largest milk producer.
- Phases: Implemented in three stages (1970-1996).
Key Strategies
- Establishment of dairy cooperatives.
- Improvement of cattle breeds.
- Creation of a National Milk Grid.
Achievements
- Milk Production Surge: 21.2 million tonnes (1970) → 69.1 million tonnes (1996) (226% increase).
- Farmers Empowered, import dependency reduced, India became self-sufficient in dairy.
MEASURES TO CURB DRUG TRAFFICKING
Drug trafficking poses a serious threat to national security, public health, and socio-economic stability. To combat this menace, the government has adopted a multi-faceted approach, integrating structural reforms, enforcement measures, technology, and international cooperation.
Structural Measures
- Narco-Coordination Centre (NCORD): A 4-tier system ensuring coordination between Central and State drug enforcement agencies, supported by the NCORD portal for data sharing.
- Anti-Narcotics Task Force (ANTF): Present in each State/UT, led by an ADG/IG-level officer, serving as the NCORD Secretariat to enforce decisions.
- Joint Coordination Committee (JCC): Chaired by the NCB Director General, overseeing investigations of major drug seizures.
Enforcement Enhancements
Empowered Forces:
- BSF, Assam Rifles, SSB, and RPF authorized under the NDPS Act, 1985, for search, seizure, and arrests at borders and railways.
Joint Operations:
- NCB collaborates with the Navy, Coast Guard, BSF, and State ANTFs for coordinated anti-trafficking efforts.
NCB Expansion:
- Regional Offices: Increased from 3 to 7 (new: Amritsar, Guwahati, Chennai, Ahmedabad).
- Zonal Units: Expanded from 13 to 30 (new: Gorakhpur, Siliguri, Agartala, Itanagar, Raipur; 12 sub-zones upgraded).
- Staff Strength: Increased to 1,496 with 536 new posts, focusing on cyber, legal, and enforcement roles.
- Narco-Canine Pool: Established at 10 NCB Zonal Offices to aid drug detection.
Technological and Public Engagement
- Darknet & Crypto Task Force: Under the Multi-Agency Centre, monitors digital platforms, tracks trends, and updates databases to disrupt online trafficking.
- MANAS Helpline (1933): A 24/7 toll-free helpline enabling citizens to report drug issues via calls, SMS, chatbots, emails, and web-links.
- Forensic Upgrades: Central Government supports states in enhancing forensic labs for better investigations.
International and Maritime Focus
- Maritime Security Group (NSCS): Established in November 2022 under the National Security Council Secretariat to counter maritime drug trafficking.
- Global Cooperation: NCB holds DG-level talks with Myanmar, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and other nations to tackle cross-border and maritime drug trafficking.
Capacity Building
- Training Programs: NCB conducts continuous training for drug law enforcement officers to improve skills and coordination.
Strengths:
- Robust Coordination: NCORD, ANTF, and JCC ensure seamless inter-agency collaboration.
- Expanded NCB Reach: Increased regional presence and staffing boost operational capacity.
- Tech-Driven Initiatives: Darknet Task Force and MANAS Helpline modernize drug enforcement efforts.
Challenges:
- Implementation Gaps: Requires consistent funding and inter-agency synergy.
- Local Loopholes: Corruption and enforcement bottlenecks may hinder effectiveness.
Impact Potential:
A well-executed combination of enforcement, technology, and public reporting could significantly disrupt trafficking networks.
FAQs on PIB Summary- 13th March, 2025 - PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC
| 1. What is PMVIKAS and how does it aim to uplift minority communities? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of White Revolution 2.0 in India? |  |
| 3. What measures are being implemented to curb drug trafficking in India? |  |
| 4. How does the PMVIKAS initiative collaborate with other government schemes? |  |
| 5. What role does community participation play in the success of PMVIKAS and White Revolution 2.0? |  |





















