PIB Summary - 26th April, 2025 | PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC PDF Download
DRDO achieves significant milestone in Scramjet Engine Development
Context: Technical Achievement
- Milestone: DRDL (a lab in Hyderabad under DRDO) successfully tested the Active Cooled Scramjet Subscale Combustor on the ground for over 1,000 seconds.
- Location: Scramjet Connect Test Facility, Hyderabad.
- Date of Test: April 25, 2025.
- Significance: This test builds on a previous one (120 seconds) conducted in January 2025, demonstrating significant progress.
- Relevance: GS 3 (Science and Technology)
About Scramjet and Hypersonic Technology
Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet):
- Operates effectively at hypersonic speeds (Mach 5 and above).
- Air-breathing engine that uses atmospheric oxygen, minimizing the need to carry oxidizers onboard, unlike rockets.
- Requires supersonic combustion, which is extremely challenging due to the high temperatures and pressures involved.
Hypersonic Cruise Missiles:
- Capable of traveling over 6,100 kmph (Mach 5+).
- Maintain sustained cruise capabilities at extreme speeds.
- Ideal for penetrating enemy air defenses due to low reaction times and high kinetic energy.
What Was Tested
- Active Cooled Combustor:
- Utilizes cooling mechanisms to endure the intense heat generated from supersonic combustion.
- Ensures thermal stability during prolonged duration tests.
- Subscale Combustor Test:
- Validates the design before full-scale integration.
- Demonstrates the feasibility of sustained combustion and the durability of components.
Technological Significance
- Validates the design of the long-duration scramjet combustor and the capabilities of the new Scramjet Connect Test Facility.
- Represents a crucial step towards integrating flight-worthy scramjets for missile systems.
Collaborative Effort
- Developed through the combined efforts of multiple DRDO laboratories, Indian industry partners, and academic institutions.
- Symbolizes India’s advancing defense R&D ecosystem and commitment to technological self-reliance (Atmanirbharta).
Strategic & Defence Relevance
- Fundamental to India’s Hypersonic Cruise Missile Programme.
- Enhances next-generation missile capabilities with improved speed, reach, and survivability.
- Aligns with the global competition in hypersonic weapons among countries like the USA, Russia, and China.
What’s Next
- Preparation for full-scale combustor testing under flight conditions.
- Developing a roadmap for the operational deployment of indigenous hypersonic cruise missiles.
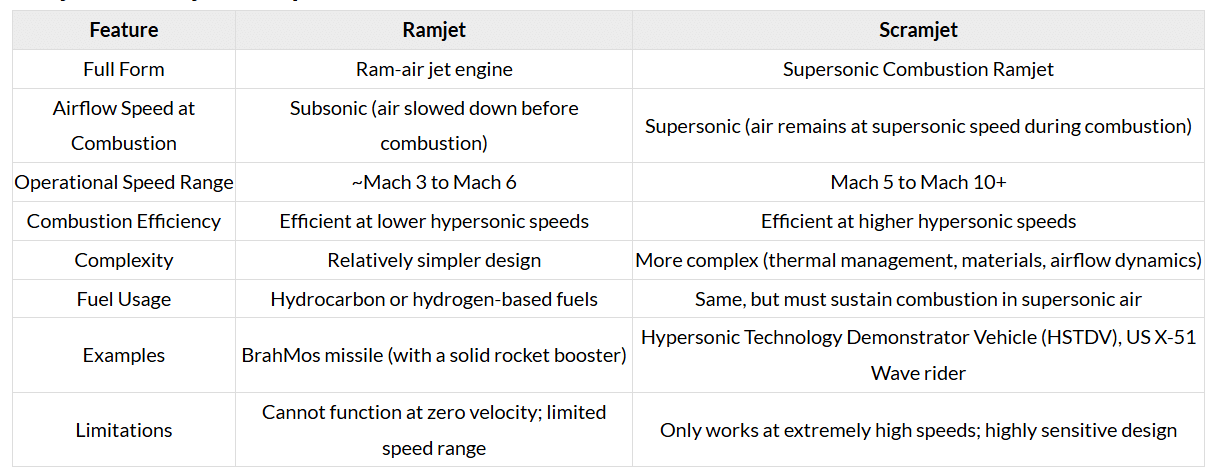
Ramjet vs Scramjet - Comparative Value Addition
World Malaria Day – 2025

Context and Background
- World Malaria Day is celebrated every year on April 25th, a tradition started by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2007.
- The day aims to raise awareness, promote global investment, and encourage partnerships to eradicate malaria.
- Malaria is an ancient disease that has affected humans for over 4,000 years and was a significant health issue in India after its independence.
India’s Progress and Global Recognition
- Between 2015 and 2023, malaria cases in India decreased by 80.5%, and deaths decreased by 78.38%.
- In 2024, India was removed from the WHO’s High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) group, marking a significant recognition of its progress.
- In 2023, 122 districts reported no malaria cases, highlighting the effectiveness of elimination efforts.
- This transition represents a major shift in India’s malaria control efforts and health governance.
India’s Elimination Targets
- Zero indigenous malaria cases by 2027, aiming for full malaria elimination by 2030.
- These targets align with the WHO Global Technical Strategy (2016–2030).
- India’s national roadmap includes:
- National Framework for Malaria Elimination (NFME) 2016–2030
- National Strategic Plan 2023–2027
Malaria - Disease Overview
- Cause: Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites, which are transmitted through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Transmission: While malaria is not spread directly from person to person, it can be transmitted through infected blood or contaminated needles.
- Symptoms:The symptoms of malaria include:
- Early Symptoms: Fever, headache, chills
- Severe Symptoms: Confusion, seizures, jaundice, difficulty breathing
- Treatment:The treatment for malaria depends on the type of Plasmodium parasite causing the infection:
- Plasmodium falciparum: Treated with Artemisinin-based Combination Therapies (ACTs).
- Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale: Treated with Chloroquine and Primaquine.
Global Burden
- Estimated 597,000 malaria-related deaths worldwide in 2023, a slight decrease from 600,000 in 2022.
- 11 High Burden High Impact (HBHI) countries accounted for 66% of malaria cases and 68% of deaths.
- Despite improvements, malaria remains a leading cause of illness and death in tropical regions.
India’s Key Strategies & Interventions
Core Interventions
- Test, Treat, Track Strategy: Implementing widespread surveillance, rapid diagnosis, and treatment to control malaria effectively.
- Vector Control: Utilizing Long-Lasting Insecticidal Nets (LLIN), insecticide sprays, and larval source management to reduce mosquito populations.
- Data-driven Governance: Employing real-time surveillance and digital tracking systems for effective monitoring and governance.
Focus Projects
- Intensified Malaria Elimination Project – 3 (IMEP-3): Aiming at 159 high-burden districts across 12 states with customized strategies for vulnerable populations and regional challenges.
Behaviour Change & Awareness
- Behaviour Change Communication (BCC): Utilizing local influencers, media campaigns, and community engagement to raise awareness and change behaviour regarding malaria prevention.
- Community Participation: Recognized by the Prime Minister as a key to success, highlighting the importance of community involvement in malaria elimination efforts.
Inter-sectoral & Capacity Building
- Collaboration Across Ministries: Working with various ministries such as health, environment, and housing to address the determinants of malaria.
- Training of Health Professionals: Over 850 health professionals trained in 2024 to enhance capacity in malaria management.
- Research Emphasis: Focusing on research related to insecticide resistance and therapeutic efficacy to adapt and improve malaria control strategies.
Integration with Ayushman Bharat
- Malaria Services Integration: Integrating malaria services with Ayushman Arogya Mandirs and Community Health Officers to ensure last-mile delivery and universal health access.
District-Level Differentiation
- NFME District Categorization: Districts are categorized into different phases, such as Category 3 (Intensified Control Phase) for high-transmission areas, to encourage district-specific planning and interventions.
Lessons from India’s Approach
- Planning and Execution: Combining top-down planning with bottom-up execution for effective malaria control.
- Community Ownership: Engaging communities in ownership of malaria elimination efforts.
- Tech-enabled Governance: Utilizing technology for governance and monitoring.
- Public-Private Coordination: Ensuring coordination between public and private sectors for comprehensive malaria control.
Theme 2025 – “Malaria Ends With Us”
- Collective Responsibility: Emphasizing the need for ownership and responsibility at all levels to combat malaria.
- Call for Reinvestment: Urging the world to reinvest in innovation, reimagine public health systems, and reignite momentum for malaria eradication.
Conclusion
- India is poised to set a global example in disease elimination, showcasing the effectiveness of science-led health policy, strong institutions, and active citizen engagement.
- Achieving a malaria-free India by 2030 represents not just a health objective but also a symbol of inclusive development and leadership in public health.
UDAN Scheme – Connecting India, One Flight at a Time.

Introduction
Launched in 2016, the UDAN (“Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik”) scheme aims to make air travel affordable and accessible, especially for people in smaller cities and remote areas. Over the years, this initiative has significantly improved regional connectivity, boosted socio-economic development, and democratized air travel in India.
Key Achievements
- Launch and Impact: UDAN was launched on October 21, 2016, and the first flight under the scheme took off from Shimla to Delhi on April 27, 2017. Since then, 625 routes have been operationalized, connecting 90 airports, including water aerodromes and heliports.
- Passenger Benefits: Over 1.49 crore passengers have benefited from affordable regional air travel, making air travel more accessible to the general public.
- Infrastructure Development: The number of airports in India has more than doubled, from 74 in 2014 to 159 in 2024, reflecting significant infrastructure growth.
- Financial Support: The government has disbursed ₹4,023.37 crore as Viability Gap Funding (VGF) to airlines, ensuring the commercial viability of flights on underserved routes.
Key Components of the Scheme
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF): This financial aid is crucial for making flights commercially viable on routes that are otherwise underserved.
- Airfare Cap: To ensure that air travel remains affordable for citizens, an airfare cap is implemented.
- Collaborative Governance: The scheme is managed collaboratively by the Central Government, State Governments, the Airport Authority of India (AAI), and private operators, ensuring effective implementation and management.
- Stakeholder Incentives:Various incentives are provided to stakeholders, such as:
- Airport Operators: Waiving landing and parking fees.
- AAI: Exempting Terminal Navigation Landing Charges (TNLC).
- Central Government: Capping excise duty on Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) at 2% at RCS airports.
- States: Reducing VAT on ATF to 1% or lower for 10 years.
Evolution Phases of UDAN
| UDAN Phase | Key Features |
|---|---|
| UDAN 1.0 (2017) | 128 routes awarded; 36 new airports. |
| UDAN 2.0 (2018) | Inclusion of 73 underserved airports; heliports introduced. |
| UDAN 3.0 (2019) | Tourism routes and seaplane operations initiated. |
| UDAN 4.0 (2020) | Focus on hilly, NE states, and island territories. |
| UDAN 5.5 (2024) | Expansion to 50+ water bodies for seaplanes. |
Recent Innovations and Future Vision
- UDAN Yatri Cafes: Affordable food outlets have been launched at various airports to enhance passenger experience.
- Seaplane Operations: Guidelines have been issued for seaplane operations in 50+ water bodies, focusing on boosting last-mile connectivity.
- Revamped UDAN Scheme: The scheme aims to connect 120 new destinations and enable affordable travel for 4 crore additional passengers over the next decade.
- Krishi UDAN: This initiative facilitates air cargo for agricultural produce from remote areas, involving 58 airports.
- Airport Infrastructure Push: Plans are underway to build 50 new airports in the next five years, with major expansions planned in Bihar.
Socio-Economic Impact
- Boost to Regional Tourism: Enhanced air access has significantly boosted tourism in hill states, coastal towns, and other remote regions, contributing to local economies.
- Healthcare Accessibility: Improved connectivity has facilitated faster medical emergencies and patient travel to metro cities, enhancing healthcare access for remote populations.
- Trade and Agriculture: Initiatives like Krishi UDAN have expedited the movement of goods and perishable agricultural products, benefiting farmers and traders.
- Employment Generation: The growth of airports and ancillary services in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities has created numerous job opportunities, contributing to local employment.
Conclusion
The UDAN Scheme has transformed India’s aviation landscape by making air travel affordable and accessible to a broader section of the population. It reflects inclusive governance, regional empowerment, and significant infrastructural advancements. The future expansion into hilly terrains, North-East India, and seaplane connectivity underlines India’s commitment to holistic and equitable national growth.





















