PIB Summary- 4th February, 2025 | PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Nuclear Power in Union Budget 2025-26 |

|
| Benefits Accorded to Classical Language |

|
| Ranbhoomi App |

|
| Measures by Government for Promoting Biofuel |

|
Nuclear Power in Union Budget 2025-26
Context
The Union Budget 2025-26 emphasizes nuclear energy as a key element of India’s energy transition strategy, with a focus on innovation, capacity building, and private sector participation.

Introduction to Nuclear Energy in India
- India has set a target of achieving 100 GW of nuclear power capacity by 2047, which aligns with the broader goals of Viksit Bharat, ensuring energy reliability and reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
- The government is focusing on indigenous nuclear technology and public-private collaborations to achieve this target.
Nuclear Energy Mission for Viksit Bharat
- The government has launched the Nuclear Energy Mission to enhance domestic nuclear capabilities, promote private sector involvement, and speed up the development of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs).
- The initiative has allocated ₹20,000 crore for research and development (R&D) of SMRs, with the goal of developing at least five indigenously designed SMRs by 2033.
- To implement this mission, amendments to the Atomic Energy Act and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act will be made to encourage private sector investments in nuclear power.
Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs) and SMRs
- Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs), a key part of the government’s nuclear energy plan, are 220 MW Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) known for their safety and performance.
- The government plans to upgrade BSRs to make them suitable for deployment near industries like steel and aluminum, serving as captive power plants.
- Private companies will be involved in providing land, cooling water, and capital, while the Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) will manage the design, quality assurance, and operations.
- The Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) is also developing SMRs, which will be used for repurposing coal-based plants and providing power to remote areas.
Government Initiatives to Enhance Nuclear Capacity
- India is focused on expanding its nuclear capacity from 8,180 MW to 22,480 MW by 2031-32, with ten reactors under construction and ten more in pre-project stages.
- The government has given in-principle approval for a 6 x 1208 MW nuclear power plant in collaboration with the USA at Kovvada in Andhra Pradesh.
- A significant milestone was achieved with the criticality of Unit-7 of the Rajasthan Atomic Power Project, marking the country’s growing capability in building and operating indigenous nuclear reactors.
Safety and Regulatory Framework
- Safety remains a top priority in India’s nuclear energy policy, with strict protocols ensuring that radiation levels in Indian nuclear plants are well below global standards.
- The government’s efforts to promote nuclear energy align with the goal of providing clean, reliable, and sustainable energy for the country.
Recent Developments in Nuclear Energy
- India has discovered new uranium deposits in the Jaduguda Mines, extending the life of the mine by over 50 years.
- The first two units of the indigenous 700 MWe PHWR at Kakrapar, Gujarat, began commercial operations in 2023-24.
- The country’s first Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR) achieved key milestones, and the government has signed a joint venture with NTPC to develop new nuclear power plants.
Conclusion
- The Union Budget 2025-26 marks a transformative shift towards nuclear energy, aiming to enhance India’s energy security and meet long-term economic and environmental goals.
- With the Nuclear Energy Mission for Viksit Bharat, India is poised to become a global leader in advanced nuclear technology by 2047.
Benefits Accorded to Classical Language
Context
The news discusses the Government of India’s support for classical languages, including recognition, establishment of Centers of Excellence, and the recent addition of five new classical languages.
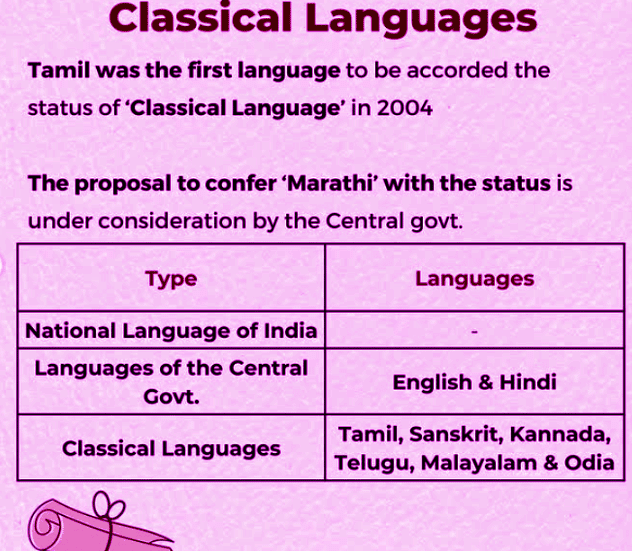
Support for Classical Languages
- The Government of India provides various forms of support to languages notified as classical languages, such as awards, centers of excellence, and professional chairs in central universities.
- This initiative aims to preserve and promote India’s rich linguistic heritage.
Languages Recognized as Classical
The following languages have been notified as classical languages by the Government of India:
- Tamil (2004)
- Sanskrit (2005)
- Telugu (2008)
- Kannada (2008)
- Malayalam (2013)
- Odia (2014)
Institutions and Centers of Excellence
The Ministry of Education, through the Central Institute of Indian Languages (CIIL), Mysuru, is actively promoting these languages. Various Centers of Excellence have been established to support research and scholarly activities:
- Tamil: Central Institute of Classical Tamil (CICT), Chennai (established in 2008).
- Sanskrit: Central Sanskrit University, Shri Lal Bahadur Shastri National Sanskrit University, and National Sanskrit University.
- Telugu: Centre of Excellence for Studies in Classical Telugu, Nellore.
- Kannada: Centre of Excellence for Studies in Classical Kannada, Mysuru.
- Malayalam: Centre of Excellence for Studies in Classical Malayalam, Tirur.
- Odia: Centre of Excellence for Studies in Classical Odia, Bhubaneswar.
Recent Additions
In October 2024, the Government notified five more languages as classical languages:
- Marathi
- Pali
- Prakrit
- Assamese
- Bengali
Ranbhoomi App
Context
The Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan Initiative and Ranbhoomi App, launched by the Ministry of Defence in collaboration with the Ministry of Tourism and State Governments, aim to open historically significant battle sites to citizens.
These locations commemorate the sacrifices of the Indian Armed Forces and foster a sense of nationalism and awareness about India’s military history.
State-Wise Coverage of Shaurya Gantavya Sites
- A total of 77 sites spanning Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Rajasthan, and Gujarat.
- These sites include locations of past military engagements, border posts, and high-altitude strategic regions.
- Areas like Galwan Valley, Kargil, Longewala, Doklam, and Tawang hold deep historical and military significance.
Enhanced Safety & Risk Mitigation Measures
- Military Assistance: Visitors in high-risk zones must coordinate with Army units via a single-window system.
- Regulated Access & Permits: High-altitude sensitive zones require special permits to ensure security.
- Emergency Response: Evacuation and medical aid protocols are in place, backed by Army support.
- Weather Advisories: Real-time updates to prevent risks associated with extreme climatic conditions.
Infrastructure & Sustainable Tourism
- Existing infrastructure includes war memorials, museums, and refreshment facilities.
- State-led schemes are improving amenities for visitors.
- Promotion of eco-friendly tourism practices to safeguard fragile ecosystems.
Digital Integration via Ranbhoomi App
- Aims to digitally engage citizens by providing detailed information on these locations.
- Enhances awareness about India’s military history.
- Likely includes historical narratives, visitor guidelines, and interactive features.
Potential Impact
National Integration & Patriotism
- Strengthens civic awareness about India’s defense history.
- Instills national pride by showcasing valour and sacrifice.
Strategic Soft Power & Tourism Boost
- Encourages border tourism, aiding local economies.
- Enhances India’s soft power by showcasing its military legacy.
Security Concerns & Geopolitical Implications
- Increased civilian footfall near border areas like Galwan, Doklam, and Tawang could lead to diplomatic sensitivities.
- Need for strict visitor management to avoid unintended security risks.
Conclusion
The Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan Initiative and Ranbhoomi App mark a significant step in connecting citizens with India’s military history and heritage. While they offer patriotic engagement and economic benefits through tourism, ensuring security and sustainable access remains crucial for their long-term success.
Measures by Government for Promoting Biofuel
Context
The government is promoting biofuels through policy support, fiscal incentives, and investment in advanced biofuel projects to enhance energy security and sustainability.
National Policy on Biofuels (2018, Amended in 2022)
Identifies diverse feedstocks for biofuel production, including:
- Sugar-based sources: C & B-heavy molasses, sugarcane juice, sugar syrup, sugar beet, sweet sorghum.
- Starch-based sources: Corn, cassava, rotten potatoes, broken rice, surplus food grains.
- Biomass & Agricultural Residues: Rice straw, cotton stalk, corn cobs, sawdust, bagasse.
- Industrial & Municipal Waste: Agro-food industry waste, plastic waste, industrial off-gases, municipal solid waste.
- Non-edible oil sources: Used cooking oil, animal tallow, acid oil, algae, seaweed, short-gestation oil-rich crops.
Policy & Fiscal Measures to Promote Biofuels
Blending Targets:
- Indicative targets for biodiesel blending in diesel and direct biodiesel sales under the National Policy on Biofuels.
Tax Incentives:
- Reduction of GST on biodiesel procurement for blending programs from 12% to 5%.
Regulatory Framework:
- Notification of 2019 guidelines for the sale of biodiesel for blending with High-Speed Diesel (HSD).
Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN Yojana (2019, Amended 2024)
Objective:
- Supports the establishment of Advanced Biofuel Projects with financial assistance.
Scope Expansion (2024 Amendment):
- More inclusive support for setting up 2G ethanol plants, CBG (Compressed Bio-Gas) units, and advanced bio-refineries.
Expected Benefits of These Measures
Energy Security:
- Reduces dependency on crude oil imports and strengthens domestic fuel production.
Rural Economy Boost:
- Encourages farmers to utilize agricultural residues, generating additional income.
Environmental Sustainability:
- Helps in waste management (municipal solid waste, plastic waste, agro-industrial residues).
- Reduces air pollution by promoting biofuels over fossil fuels.
Circular Economy Approach:
- Efficient resource utilization by converting waste into energy.
Challenges & Way Forward
Feedstock Availability & Supply Chain Issues:
- Ensuring a steady supply of diverse raw materials for biofuel production.
Infrastructure Development:
- Need for more bio-refineries and blending facilities to meet future demand.
Investment & Financial Viability:
- Attracting private sector participation through viable incentives.
Technology Adoption:
- Promoting advanced biofuel technologies to enhance efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
The government’s multi-pronged approach—policy support, fiscal incentives, and investment promotion—is shaping India’s biofuel sector. While challenges persist, continued focus on infrastructure, innovation, and sustainable feedstock sourcing will be key to achieving energy self-sufficiency and a cleaner environment.




















