UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary > PIB Summary - 9th July 2025
PIB Summary - 9th July 2025 | PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC PDF Download
India’s Healthcare Transformation (2014–2025)
Context and Vision
- Policy Commitment as Catalyst: India's healthcare reforms in the past decade have focused on making healthcare accessible, affordable, equitable, and of high quality.
- 2014 Baseline: In 2014, India faced significant challenges in healthcare infrastructure, human resources, diagnostics, availability of medicines, and public trust in the healthcare system.
Foundations of Reform
National Health Mission (NHM)
- The NHM has been the core vehicle for systemic reform in India’s healthcare sector.
- It has led to improved outcomes in maternal and child health, better control of communicable diseases, and overall strengthening of the healthcare system.
Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AB-HWCs)
- A total of 1.77 lakh Ayushman Arogya Mandirs have been operationalised, providing doorstep primary care services.
- Data shows 427.57 crore visits, 36.64 crore teleconsultations, and 5.5 crore wellness sessions conducted through these centres.
Telemedicine Push
- Initiatives like eSanjeevani and TeleMANAS have created a pan-India digital health bridge.
- This has significantly improved access to specialists in remote areas and mainstreamed mental health services.
Maternal & Child Health Revolution
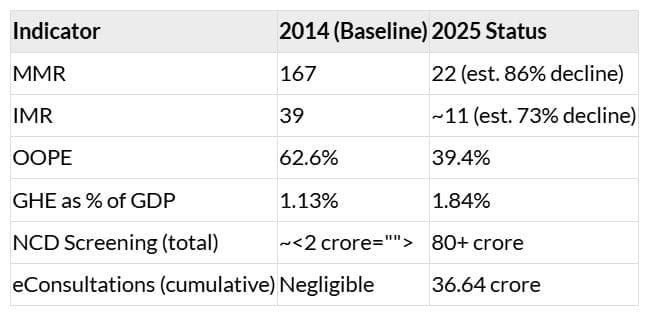
- Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR): Declined by 86%, compared to the global average decline of 48% (UN-MMEIG).
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR): Declined by 73%, while the global average decline is 58%.
- Global Recognition: India has been recognized as an “exemplar” in reducing child mortality on the global stage.
- Initiatives: Targeted interventions under the National Health Mission (NHM) and the Mission Indradhanush, which includes 6 new vaccines.
- U-WIN Portal:. total of 42.75 crore doses have been administered, and 10.68 crore beneficiaries have been digitized through this portal.
Preventive Care over Curative Care
- Cancer Screening: Arogya Mandirs are conducting screenings for breast, cervical, and oral cancers.
- NCD Screenings: As of May 2025, screenings for Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) include 28 crore for hypertension, 27 crore for diabetes, and 27 crore for oral cancer.
- Shift in Focus: The emphasis on early diagnosis is aimed at reducing the overall disease burden and associated costs.
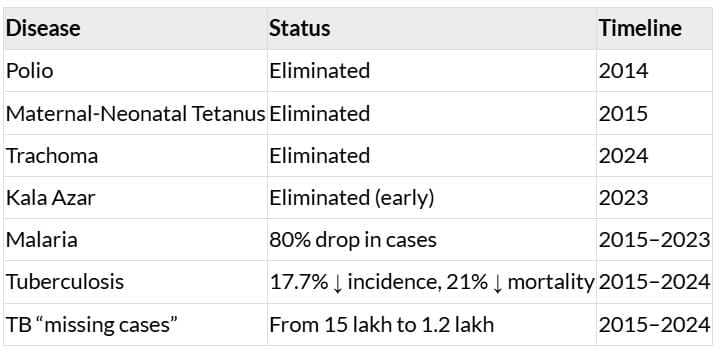
Communicable Disease Milestones
Financial Protection & Affordability
- Government Health Expenditure (GHE): Increased from 1.13% to 1.84% of GDP.
- Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE): Decreased from 62.6% to 39.4%.
- Key Schemes: Implementation of free drugs and diagnostics programs, with CT and lab services in over 30 states.
- Dialysis Program: Benefited 28 lakh individuals and saved ₹8,725 crore.
- Ambulance Network: Expanded to over 28,000 vehicles and 1,498 Mobile Medical Units (MMUs), including services for tribal areas under PM-JANMAN.
Infrastructure & Human Resources
PM-ABHIM (since 2021):
- 18,802 Ayushman Arogya Mandirs established.
- 602 Critical Care Blocks set up.
- 730 Public Health Labs inaugurated.
Human Resource Surge:
- 5.23 lakh recruits under NHM, including 1.18 lakh Community Health Officers (CHOs) to bridge gaps between community and Primary Health Centres (PHCs).
- Over 34,000 facilities certified under National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS) for quality and patient safety.
Digital & Data-Driven Systems
- U-WIN:. system for vaccine logistics and tracking at a population scale.
- eSanjeevani: Recognized as one of the world’s largest teleconsultation platforms.
- Digitization of Health Records: Under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
Outcome Metrics: A Scorecard
Critical Reflections & Challenges Ahead
- Sustainability: The challenge of maintaining funding levels to match the ambitious healthcare goals.
- Quality Gaps: Assessing whether the quality of secondary and tertiary care units is improving at an adequate pace, despite the increase in quantity.
- Urban-Rural Equity: Addressing the potential disparity where urban areas may advance more rapidly in digital health, while rural regions require enhanced connectivity and resources.
- NCD Burden: The need to accelerate preventive measures to counterbalance the rising incidence of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs).
Conclusion: The Road to Universal Health Coverage (UHC)
- India’s healthcare transformation over the past 11 years is among the most ambitious and extensive globally, reflecting a strong commitment to health equity.
- The journey illustrates the effectiveness of political will, digital advancements, expansion of human resources, and financial reallocation in achieving health goals.
- The vision of “ Swasth Bharat ”—healthcare accessible to all—has become increasingly achievable, marking a significant step towards Universal Health Coverage.
Digital Employment & Welfare Ecosystem in India (2015–2025)
The Digital Governance Framework
- Vision: Utilize digital tools for the efficient and citizen-centric delivery of employment services and social security.
Transformation Pillars:
- Interlinked platforms (NCS, e-Shram, EPFO)
- Aadhaar-based targeting
- Real-time data flow
- Integrated service delivery
- Crisis-resilient infrastructure
Relevance: GS 2 (Labour welfare, Governance, Social Issues)
Digital Public Infrastructure for Jobs & Skills
1. National Career Service (NCS) Portal
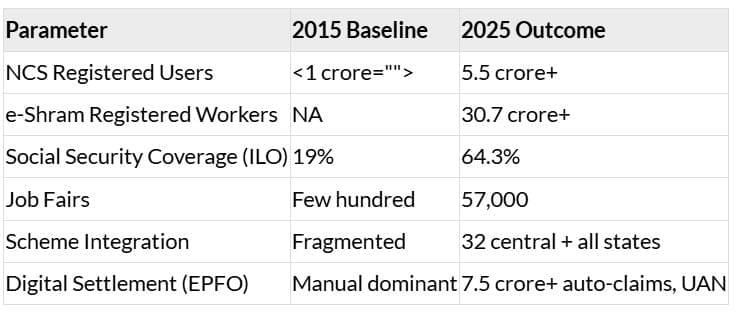
- Launch: 2015, by the Ministry of Labour & Employment
- Scale: 5.5 crore+ job seekers, 57,000 job fairs
- Integrated With: SID, Udyam, e-Shram, EPFO, ESIC, DigiLocker, PM GatiShakti
- Features: Career counseling, job search by skill/location, internship/apprenticeship listings
- Impact: Democratized job access via phone; links job seekers with 30+ state/private job portals
2. Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH)
- Enables skill tracking, upskilling, certifications
- Integrated with NCS for seamless training-to-employment mapping
Compliance, Grievance & Transparency Portals
- Shram Suvidha: One-stop portal for labour law compliance
- Samadhan: Worker grievance redressal and settlement of claims
- ESIC Dhanwantari Module: Digitised patient records for better hospital care
- UMANG App: Access point for EPFO, e-Shram, ESIC
Social Security for the Unorganised Sector
1. e-Shram Portal
- Launch: 2021; Registrations: 30.7 crore+
- Integrated Schemes: 13+ Central + 32 State schemes
- Features: Unique ID card for each unorganised worker, 22-language multilingual access (via MEITY’s Bhashini), State Microsites, Mobile Apps for ease
- Union Budget 2025-26: Extended e-Shram to gig/platform workers, Coverage under PM Jan Arogya Yojana enabled
2. Interlinkages
- Connected to PM-SYM, myScheme, DISHA, NCS, SIDH
- Workers can register once and access pensions, insurance, jobs, skills
3. Global Recognition
- ILO Social Protection Data (2025): Coverage jumped from 19% (2015) to 64.3% (2025)
- India ranks 2nd globally in beneficiary count: 94.13 crore
- Recognised in WSPR 2026: First country to report comprehensive central + state scheme data
EPFO 2.0: Digitisation & Pension Reforms
- Members: 34.6 crore+
- Pensioners under CPP System: 77 lakh
- Auto-settlement limit raised: ₹1 lakh
- Members benefitting (auto-claims): 7.5 crore
- Yearly fund transfer: ₹90,000 crore
- E-passbook, UAN, Digital Life Cert: Enhance ease & transparency
- Centralised pension disbursement: Improves accessibility
- Fund transfer process simplified: 1.25 crore+ members benefit
Benefits of Interlinked Portals

Crisis-Responsive Infrastructure
- Pandemic Preparedness: e-Shram and NCS databases facilitate quick identification of distressed workers
- Resilience in Real Time: Portals can deliver benefits directly, even during lockdowns or disasters
Summary Scorecard: Key Achievements
Challenges and Way Forward
Challenges:
- Fragmentation still exists in regional portals.
- Gig/platform workers’ contributions to funds remain unstructured.
- Awareness and digital literacy gaps, especially in tribal and remote areas.
Recommendations:
- Encourage private-sector data sharing with e-Shram.
- Incentivize gig platforms to co-contribute to workers’ welfare.
- Expand digital training for workers on using scheme portals.
- Create portable, stackable benefits across state boundaries.
Conclusion: Tech-Driven Welfare State
- India’s digital welfare architecture represents a new model of inclusive, responsive governance. With real-time databases, interoperable portals, and universal access frameworks.
- India is now closer than ever to ensuring every citizen is not only employed but also protected.
The document PIB Summary - 9th July 2025 | PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on PIB Summary - 9th July 2025 - PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC
| 1. What are the key components of India's healthcare transformation plan? |  |
Ans. India's healthcare transformation plan encompasses several key components, including a focus on maternal and child health, a shift from curative to preventive care, milestones in managing communicable diseases, financial protection and affordability for healthcare access, improvements in infrastructure and human resources, and the adoption of digital and data-driven systems to enhance health outcomes.
| 2. How has India approached maternal and child health in its healthcare reforms? |  |
Ans. India has initiated a maternal and child health revolution by implementing targeted programs aimed at reducing maternal and infant mortality rates. These programs prioritize prenatal care, skilled birth attendance, and postnatal support, alongside community engagement and education to improve health outcomes for mothers and children.
| 3. Why is preventive care emphasized over curative care in India's healthcare strategy? |  |
Ans. Preventive care is emphasized over curative care in India's healthcare strategy to reduce the burden of diseases and improve overall health outcomes. By focusing on prevention, such as vaccination, health education, and early detection of diseases, the aim is to reduce healthcare costs, enhance quality of life, and promote a healthier population.
| 4. What measures have been taken to ensure financial protection and affordability in healthcare? |  |
Ans. To ensure financial protection and affordability, India has introduced various health insurance schemes and financial assistance programs aimed at vulnerable populations. These measures are designed to reduce out-of-pocket expenses for healthcare and increase access to essential medical services, thereby mitigating the economic impact of health-related expenditures on families.
| 5. How is digital technology being integrated into India's healthcare system? |  |
Ans. Digital technology is being integrated into India's healthcare system through the development of digital health platforms, electronic health records, telemedicine services, and data analytics. These innovations aim to streamline healthcare delivery, improve patient management, enhance access to services, and facilitate data-driven decision-making to optimize health outcomes.
Related Searches
















