Package of Practices | Agriculture Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Primary Activities
Primary activities are the oldest form of economic activity where humans exploit natural resources for their needs. These activities are directly dependent on the environment and include gathering, hunting, nomadic herding, and various types of agriculture.Gathering and Hunting:
Gathering and hunting are the oldest economic activities known to humanity. Gathering is practiced in regions with harsh climatic conditions and involves primitive societies extracting both plants and animals to satisfy their needs for food, shelter, and clothing. The main features of gathering and hunting activities include:
- Low capital and skill investment
- Low yield per person
- No surplus in production
Gathering is practiced in various areas of the world, including:
- Northern Canada, northern Eurasia, and southern Chile (high altitude areas)
- Low latitude zones such as the Amazon Basin, tropical Africa, northern fringe of Australia, and interior parts of Southeast Asia
Nomadic Herding or Pastoral Nomadism:
- Nomadic herding, also known as pastoral nomadism, is a primitive subsistence activity where herders rely on animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools, and transport.
- Herders move from one place to another along with their livestock, depending on the availability and quality of pastures and water. This leads to an irregular pattern of movement.
- Nomadic pastoralism is different from transhumance, where there is a fixed seasonal pattern of movement.
- This type of pastoralism is commonly practiced in regions with little arable land, typically in the developing world.
- An estimated 30–40 million nomadic pastoralists worldwide, with most found in central Asia, northern and western regions of Africa, parts of southern Africa, and tundra regions.
- In the Himalayan region, communities such as Gujjars, Bakarwals, Gaddis, and Bhotiyas practice nomadic pastoralism and transhumance.
Commercial Livestock Rearing:
- Commercial livestock rearing is a more organized and capital-intensive activity compared to nomadic pastoralism.
- It is typically practiced in permanent ranches where animals are bred and reared on a large scale for products such as meat, wool, hides, and skin.
- Emphasis is placed on breeding, genetic improvement, disease control, and health care of animals.
- Countries known for commercial livestock rearing include New Zealand, Australia, Argentina, Uruguay, and the United States.
- Ranches, large stock farms where animals are bred and reared on a commercial scale, are a common feature of this type of farming, especially in the United States.
Types of Agriculture in Various Parts of the World
Primary Subsistence Agriculture:Subsistence agriculture is a type of farming where the produce is primarily meant for local consumption, with little surplus for sale. It is characterized by low levels of technology and inputs, and the primary goal is to meet the basic needs of the farmers and their families.
- Primitive Subsistence Agriculture: This includes practices like shifting cultivation, where land is cleared and cultivated for a short period before being left fallow. It is widely practiced by various tribes in tropical regions such as Africa, South and Central America, and Southeast Asia.
- Intensive Subsistence Agriculture: In this system, crops are grown mainly for local consumption, with surplus sold in the market. It is prevalent in densely populated areas of monsoon Asia. There are two sub-types: one dominated by wet paddy cultivation and the other by crops like sorghum, soybeans, sugarcane, maize, and vegetables.
Mediterranean Agriculture:
Mediterranean agriculture is characterized by its practice in regions with a Mediterranean climate, where winters are wet and summers are dry. This type of farming is intensive, highly specialized, and varied in the kinds of crops raised.
- Crop Variety: Farmers grow a mix of crops for both domestic consumption and export. Common crops include wheat, barley, and vegetables for local use, while citrus fruits, olives, and grapes are often grown for export.
- Specialization: The Mediterranean region is known as the "Orchard Lands of the World" and is a hub for the global wine industry. Viticulture, or grape cultivation, is a specialty, with high-quality wines produced from premium grapes. Inferior grapes are dried to make raisins and currants, and other crops like olives and figs are also produced.
- Seasonal Advantage: Mediterranean agriculture has the advantage of growing more valuable crops, such as fruits and vegetables, in winter when there is high demand in European and North American markets.
Plantation Agriculture:
Plantation agriculture is a type of farming that developed in parts of Asia, Africa, and Latin America, influenced by European practices during the colonial period. While it covers a relatively small area, it holds significant commercial value.
- Major Products: Plantation agriculture focuses on high-value tropical crops such as tea, coffee, rubber, and oil palm. These plantations were initially established to supply important tropical crops to European markets.
- Important Regions: Notable plantation regions include tea gardens in India and Sri Lanka, banana and sugar plantations in the West Indies, coffee plantations in Brazil, and rubber plantations in Malaysia.
- Capital Intensity: Plantation agriculture is highly capital-intensive, with most crops being tree crops that require significant investment in land, labor, and infrastructure.
Extensive Commercial Grain Cultivation
Extensive commercial grain cultivation is primarily practiced in regions with fertile soils, such as the Eurasian steppes with chernozem soil, the Canadian and American Prairies, the Pampas of Argentina, the Veld of South Africa, the Australian Downs, and the Canterbury Plain of New Zealand.- Mechanization: This type of agriculture is highly mechanized, with advanced machinery used for planting, harvesting, and processing grains.
- Farm Size: Farms are typically very large, covering extensive areas of land.
- Crop Focus: Wheat is the predominant crop, although other grains may also be grown.
- Yield Characteristics: While the yield per acre may be low, the yield per capita is high due to the large scale of production.
Mixed Farming:
Mixed farming is an agricultural system found in highly developed regions of the world, including northwestern Europe, eastern North America, Russia, Ukraine, and temperate parts of southern continents.
- Farming Practices: Farmers traditionally raise animals and grow crops on the same farm, creating a mixed economy. This system is characterized by high capital expenditure on machinery and buildings, extensive use of chemical fertilizers and green manures, and the skill and expertise of farmers.
- Intensive and Specialized Farming: In some cases, farming may be very intensive and highly specialized, focusing on specific crops or livestock.
Dairy Farming:
Dairy farming is a highly advanced and efficient method of rearing milch animals for milk production. It is characterized by high capital intensity due to the need for animal sheds, storage facilities for fodder, feeding and milking machines, and emphasis on cattle breeding, health care, and veterinary services.
- Capital and Labor Intensity: Dairy farming involves significant capital investment in infrastructure and technology. It is also labor-intensive, requiring rigorous care in feeding and milking the animals. Unlike crop farming, there is no off-season for dairy production.
- Location: Dairy farming is typically practiced near urban and industrial centers where there is a demand for fresh milk and dairy products. Improvements in transportation, refrigeration, pasteurization, and preservation processes have extended the shelf life of dairy products.
Market Gardening and Horticulture
Market gardening and horticulture are agricultural practices focused on the cultivation of vegetables, fruits, and flowers solely for urban markets. These practices are well-developed in densely populated industrial districts, particularly in northwestern Europe (including Britain, Denmark, Netherlands, Belgium, and Germany) and in the northeastern United States.- Truck Farming: In regions where farmers specialize in vegetable production, the practice is known as truck farming. The name "truck farming" comes from the distance a truck can cover overnight, which determines the market reach of the farm.
- Regional Specialization: Farmers in certain regions may focus solely on vegetable production, while others may include a wider variety of products such as fruits and flowers.
Factory Farming:
- Factory farming is a method of mass food production where animals are kept in very confined spaces to maximize profit. This type of farming is particularly concentrated in developed countries such as the United States, various European nations, and Australia.
Co-Operative Farming:
Co-operative farming involves a group of farmers forming a co-operative society to pool their resources for more efficient and profitable farming. Individual farms remain intact, and farming is a matter of cooperative initiative.
- Functions of Co-operative Societies: Co-operative societies help farmers procure essential inputs, sell products under favorable terms, and process quality products at lower costs.
- Origin and Success: The co-operative movement originated over a century ago and has been successful in many Western European countries such as Denmark, the Netherlands, Belgium, and Sweden. In Denmark, nearly every farmer is a member of a co-operative due to the movement's success.
Collective Farming:
Collective farming, also known as the Kolkhoz model, is based on social ownership of the means of production and collective labor. This model was introduced in the former Soviet Union to improve agricultural efficiency and boost production for self-sufficiency.
- Resource Pooling: Farmers pool their resources such as land, livestock, and labor. However, they are allowed to retain small plots for personal use to meet daily needs.
- Government Involvement: The government sets yearly targets, and produce is sold to the state at fixed prices. Excess produce can be distributed among members or sold in the market.
- Compensation and Rewards: Members are paid based on the work assigned to them, with exceptional work rewarded in cash or kind. This model was primarily adopted by socialist countries and has been modified in post-Soviet states after the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Indian Agriculture
- India is a nation where a significant portion of the population, about 49%, relies on agriculture for their livelihood, either directly or indirectly.
- The net sown area in India constitutes around 47% of the total land area.
- Agricultural activities consume more than 80% of the water in India, with nearly half of the net sown area, approximately 68.4 million hectares, being irrigated as of 2019.
- States like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Odisha continue to be heavily dependent on agriculture for their economies.
GDP Composition in 2018-19:
- Agriculture: 16.5%
- Services: 55.3%
- Industry: 28.6%
Facts and Data about the Agriculture Sector
- The share of agriculture and allied sectors in Gross Value Addition (GVA) decreased from 18.2% in 2014-15 to 16.5% in 2019-20.
- The Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishing sector is projected to grow by 2.8% in 2019-20, down from 2.9% in the previous year.
- According to the 2010-11 Agricultural Census, 47% of landholdings are less than half a hectare, which is insufficient to support a family of five. This has forced many farmers to seek alternative income sources.
- About 80% of farmers own less than two hectares of land.
Salient Features of Indian Agriculture
- Predominantly subsistence agriculture, where farmers grow enough to meet their own needs.
- Heavily reliant on the monsoon, which is erratic and unreliable, affecting about 60% of agricultural activities.
- India’s diverse relief, climate, and soil conditions allow for a wide variety of crops to be grown, including all types of tropical, subtropical, and temperate crops.
- Predominance of food crops, which occupy about two-thirds of the total cropped area.
- Agriculture is the backbone of the rural economy and plays a critical role in ensuring the country’s food security.
- The sector suffers from poor infrastructure in terms of electricity, storage, water, credit, and marketing.
- Agriculture also supports allied sectors and activities, such as cattle and poultry farming.
- There is a significant involvement of women in the agriculture sector.
- Indian agriculture is characterized by low mechanization, inadequate agricultural research, and extension services.
- The fragmented nature of agricultural holdings makes it challenging to achieve economies of scale.
Productivity of Agriculture
- Productivity of Agriculture refers to the number of crops produced per unit of land.
- In India, productivity levels are significantly lower compared to countries like China and the USA. For instance, in 2018, the average productivity in India was 3075 kg/ha, while the world average was 3200 kg/ha.
- Factors such as fertilizer use, irrigation, and rainfall cause substantial variations in productivity across different regions.
- Regions that experienced the Green Revolution, such as parts of Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh, show higher productivity levels. Other high productivity states include Tamil Nadu, Kerala, West Bengal, and Maharashtra.
- However, productivity in the Gangetic Plain is declining due to land bifurcation, which leads to smaller land holdings.
- Key issues affecting agricultural productivity include:
- Decreasing sizes of agricultural land holdings
- Dependence on the monsoon
- Inadequate access to irrigation
- Imbalanced use of soil nutrients
- Uneven access to modern technology
- Lack of access to formal agricultural credit
- Limited procurement of food grains by government agencies
- Failure to provide remunerative prices to farmers
Cropping Intensity
- Cropping intensity is the ratio of gross cropped area to net sown area.
- It measures how many times the land is cropped in a year.
- Factors affecting cropping intensity include climate, crop demand, and availability of irrigation and other inputs.
Boosting Productivity
To boost productivity in agriculture sustainably, we need to focus on:
Irrigation:
- Increase access to water for Rabi season crops through schemes like the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY).
Seeds and Fertilizer:
- Enhance seed research and increase seed replacement rates.
- Promote soil health cards to customize fertilizer use.
New Technology:
- Utilize genetically modified (GM) seeds for higher productivity and reduced input use.
- Implement precision farming and related technologies for efficient resource use.
Diversification:
- Encourage crop diversification to provide farmers with a wider range of crops to grow, reducing risks and expanding production opportunities.
Crops in India
Basic Facts about Crops in India:
- In 2018, India produced approximately 284.83 million tons of food grains.
- India is the world’s largest producer of milk, pulses, and jute.
- India plays a leading role in global agricultural trade, with its agricultural export basket accounting for just over 2.15% of world agricultural trade.
Crop Classification Based on Type of Produce: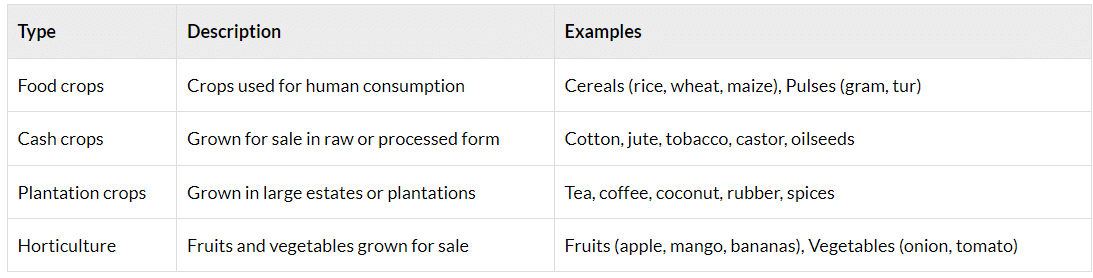
Crop Classification Based on Climate: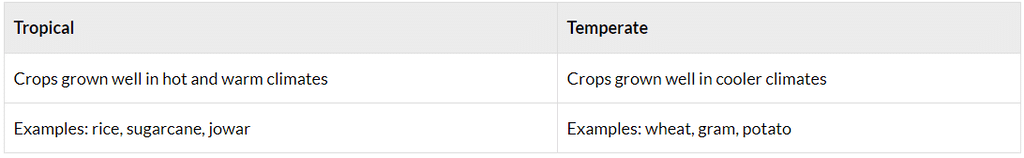
Crop Classification Based on Growing Season: 
Major Food Crops in India
Rice:
- Rice is the preferred staple food in southern and north-eastern India.
- In 2018-19, India produced 42 million metric tons (MMT) of rice, making it the second highest producer in the world, after China.
- India also had the highest export volume of rice worldwide, at 9.8 million metric tons in 2018/2019.
- West Bengal is the largest producer of rice in India, followed by Uttar Pradesh.
Favourable Conditions:
- Rice is a tropical and kharif crop, thriving in warm and wet conditions.
- Temperature: Ideally between 22-32°C with high humidity.
- Annual Rainfall: Above 150 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep clayey and loamy soil.
Geographical Distribution:
- Rice is a staple for the majority of India’s population and is grown on about one-fourth of the total cropped area.
- Despite being a crop of tropical humid areas, rice has around 3,000 varieties that can be grown in different agro-climatic regions, from sea level to about 2,000 m altitude.
- In southern states and West Bengal, conditions allow for the cultivation of two or three rice crops in a year.
- In the Himalayas and north-western India, rice is grown as a kharif crop during the southwest monsoon season.
Other Information:
- In West Bengal, farmers grow three crops of rice known as ‘aus’, ‘aman’, and ‘boro’.
- Farmers in West Bengal are experimenting with the Pokkali variety of rice, known for its saltwater resistance, to address seawater intrusion in paddy fields caused by Cyclone Amphan.
- The Kuttanad Below Sea Level Farming System in Kerala is recognized as a Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System (GIAHS) site in India.
Wheat
Overview- Wheat is the preferred staple food in northern and north-western parts of India.
- India’s wheat production reached a record 20 million tonnes (MT) in 2018-19, making it the third largest producer of wheat in the world, after the European Union and China.
- Uttar Pradesh is the largest producer of wheat in India, followed by Punjab and Haryana.
Favourable Conditions:
- Temperature: Between 10-15°C during sowing and 21-26°C during ripening and harvesting, with bright sunlight.
- Rainfall: Around 75-100 cm.
- Soil Type: Well-drained fertile loamy and clayey loamy soil, such as in the Ganga-Sutlej plains and black soil region of the Deccan.
- Light drizzles and cloudiness during ripening, often brought by Western Disturbances, can enhance yields.
Geographical Distribution:
- Wheat is the second most important cereal crop in India, producing about 12 percent of the world’s total wheat.
- Primarily a crop of temperate zones, wheat is cultivated during the rabi season (winter) in India.
- About 85 percent of wheat cultivation is concentrated in north and central India, including the Indo-Gangetic Plain, Malwa Plateau, and the Himalayas up to 2,700 m altitude.
- While mostly grown under irrigated conditions, wheat is rainfed in the Himalayan highlands and parts of the Malwa Plateau in Madhya Pradesh.
- Leading wheat-producing states include Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh.
Other Information:
- The rice-wheat cropping system is labor, water, capital, and energy-intensive, becoming less profitable as these resources diminish.
- Climate change further exacerbates the challenges of this cropping system.
Millets
Overview:- Millets are small-seeded grasses grown in a variety of climatic conditions.
- They are highly nutritious and are an important part of the diet in many regions of India.
- Millets include varieties such as jowar (sorghum), bajra (pearl millet), and ragi (finger millet).
Favourable Conditions:
- Temperature: Between 27-32°C.
- Rainfall: Around 50-100 cm.
- Soil Type: Millets can be grown in inferior alluvial or loamy soil, as they are less sensitive to soil deficiencies.
Geographical Distribution:
- India is the largest producer of millets, followed by Niger.
- Millets are grown entirely under subsistence farming and are often used as fodder crops.
- They are important for nutritional security, although they are less preferred by farmers due to lower remunerative outcomes.
- Major millet-producing states include Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Uttar Pradesh.
Other Information:
- Jowar (Sorghum)
- Grown in both Kharif and Rabi seasons, with variations in different regions.
- High nutritional value and suitable for rainfed areas of dryland farming.
- Major producers include Maharashtra, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Bajra (Pearl Millet)
- Grown in areas with 40-50 cm of annual rainfall, primarily in hot and dry climatic conditions.
- Cultivated alone or as part of mixed cropping.
- Leading producers include Maharashtra, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Haryana.
- Maize (Corn)
- Grown as a rainfed Kharif crop under semi-arid conditions and inferior soils.
- Leading producers include Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh.
Oilseeds
Overview:- Oilseeds are produced for extracting edible oils, with major crops including groundnut, rapeseed and mustard, soybean, and sunflower.
Favourable Conditions:
- Temperature: Between 15-30°C.
- Rainfall: Around 30-75 cm.
- Soil Type: Loam to clayey loam and well-drained sandy loams.
Geographical Distribution:
- Major oilseed-producing regions include the drylands of the Malwa plateau, Marathwada, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Telangana, Rayalaseema region of Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka plateau.
- Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, and Gujarat are the main producers, accounting for over two-thirds of the area and production.
- Oilseeds together occupy about 14 percent of the total cropped area in the country.
Groundnut:
- Largely a rainfed Kharif crop of drylands, but also cultivated during the Rabi season in southern India.
- Leading producers include Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Maharashtra.
Rapeseed and Mustard:
- Frost-sensitive crops cultivated during the Rabi season in north-western and central India.
- Leading producers include Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, West Bengal, and Madhya Pradesh.
Soybean:
- Mostly grown in Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, which together produce about 90 percent of the total output.
Sunflower:
- Cultivation is concentrated in Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and adjoining areas of Maharashtra.
Sesamum:
- India is the largest producer, accounting for one-third of global production.
- Rainfed Kharif crop with fluctuating production levels.
- Major producing states include West Bengal, Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Maharashtra.
Cash Crops
- Cash Crops are grown for sale in the market.
- They occupy only about 15 percent of cropped area but account for over 40 percent of agriculture production by value.
- Examples are Cotton, jute, tobacco, castor, oilseeds, sugarcane
Cotton
- Cotton is mainly grown in tropical and sub-tropical regions.
- It thrives in temperatures between 21-30°C and requires rainfall of around 50-100 cm.
- The best soil for cotton cultivation is well-drained, deep black soils, such as regur or lava soil, found in the Deccan Plateau, Malwa Plateau, and parts of Gujarat.
- Cotton is a kharif season crop, primarily in semi-arid areas. India produces both short staple (Indian) and long staple (American) cotton, with the latter known as ‘Narma’, mainly in the northwestern regions.
- Cotton covers about 4.7 percent of India’s total cropped area.
- India is the largest producer of cotton, with Gujarat and Maharashtra being the top states.
- Cotton cultivation faces challenges such as erratic rainfall and pest attacks.
Types of Cotton
1. Long Staple Cotton:
- Fiber Length: 24 to 27 mm.
- Characteristics: Fiber is fine, lustrous, and used for making superior quality cloth.
- Production: About 50% of total cotton production in India.
- Main Growing Areas: Punjab, Haryana, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh.
2. Medium Staple Cotton:
- Fiber Length: Between 20 mm and 24 mm.
- Production: About 44% of total cotton production in India.
- Main Growing Areas: Rajasthan, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, and Maharashtra.
3. Short Staple Cotton:
- Fiber Length: Less than 20 mm.
- Characteristics: Used for manufacturing inferior cloth and fetches lower prices.
- Production: About 6% of total cotton production.
- Main Growing Areas: Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Punjab.
Bt Cotton
- Bt Cotton is genetically modified to include a toxin from the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis, which is harmful to certain pests like bollworms.
- This modification helps protect the cotton crop from these pests.
- Bt Cotton was first tested in the United States in 1995, and later adopted in China (1997) and India (2002).
Jute
- Jute is the second most important fiber crop in India after cotton.
- It requires a humid climate with 120-150 cm of rainfall and 80-90 percent relative humidity during its growth period.
- Jute is a cash crop primarily grown in West Bengal and adjoining eastern parts of the country.
- After the partition, India lost significant jute-growing areas to East Pakistan (now Bangladesh ).
- Currently, India produces about three-fifths of the world’s jute.
- West Bengal accounts for about three-fourths of jute production in India, with Bihar and Assam also being notable jute-growing areas.
- Similar to cotton, jute depletes soil fertility quickly, so it is essential to replenish the soil annually with silt-laden floodwater from rivers.
- Post-harvest, jute fiber processing requires a large supply of cheap labor and abundant water.
Sugarcane
- Temperature: Sugarcane grows best in temperatures between 21-27°C, with a hot and humid climate.
- Rainfall: It requires around 75-100 cm of rainfall.
- Soil Type: Deep, rich loamy soil is ideal for sugarcane cultivation.
- Sugarcane is primarily a tropical crop. While it can be grown in rainfed conditions in sub-humid and humid climates, it is largely an irrigated crop in India.
- In 2018-19, India became the largest producer of sugarcane, surpassing Brazil for the first time in 16 years.
- In the Indo-Gangetic plain, sugarcane cultivation is concentrated in Uttar Pradesh. In western India, it is grown in Maharashtra and Gujarat.
Reasons for the Shift of Sugar Industry from Northern to Peninsular India
- Higher Yields: Peninsular India’s tropical climate results in higher sugarcane yields per hectare.
- Sucrose Content: Sugarcane in Peninsular India has higher sucrose content due to the predominance of tropical varieties, whereas the northern plains grow sub-tropical varieties with lower sugar content.
- Crushing Season: Sugar factories in Peninsular India have a longer crushing season.
- Cooperative Management: Cooperative sugar mills in South India are more successful in management compared to those in the north.
- Factory Relocation: Sugar factories have relocated from the northern plains to regions like Punjab, Haryana, South India, and Western India.
Plantation Crops
A plantation refers to a large-scale farm focused on cultivating cash crops. These include cotton, coffee, tea, cocoa, sugar cane, sisal, oilseeds, oil palms, fruits, rubber trees, and forest trees.Tea
Favourable Conditions for Cultivation:- Temperature: Ideally between 20-30°C.
- Rainfall: Requires about 150-300 cm of rainfall.
- Soil Type: Prefers deep, fertile, and well-drained soil rich in humus and organic matter.
Characteristics:
- Tea leaves are rich in caffeine and tannin.
- Indigenous to the hills of northern China.
- Grown in undulating topography of hilly areas with humid and sub-humid conditions.
Geographic Distribution in India:
- Assam: Major tea-growing area; plantations started in the 1840s.
- West Bengal: Tea cultivation in sub-Himalayan region (Darjeeling, Jalpaiguri, Cooch Bihar).
- Western Ghats: Cultivation on lower slopes of Nilgiris and Cardamom hills.
Other Information:
- Labour Requirements: Abundant supply of cheap and skilled labour needed at all stages.
- Employment: One of the largest employers of women in organized industries.
- Production: India is the second largest producer of tea globally (2019), with Assam as the largest producer.
- Exports: India is the fourth largest exporter, accounting for 14% of global tea exports.
- Declining Exports: Facing competition from Kenya (CTC tea) and Sri Lanka and Mozambique (orthodox tea).
Issues in the Industry:
- Lack of Innovation: Stagnation in tea plant quality and agricultural practices.
- Rising Input Prices: Making tea farming less profitable.
- Small Farmers: Large share of production from small farmers facing sustainability issues.
- Monsoon Dependence: Heavy reliance on monsoon for rainfall.
- Trade Barriers: Phyto-sanitary objections by the EU affecting exports.
- Trade Policy: Reduction of export concessions under FTP 2015.
- Labour Issues: Strikes and unrest in tea farms.
- Social Unrest: Areas like Assam and Darjeeling facing insurgency and extortion, deterring investment.
Coffee
Favourable Conditions for Cultivation:- Temperature: Ideal range is between 15-28°C.
- Rainfall: Requires approximately 150-250 cm of rainfall.
- Soil Type: Well-drained, deep, and friable loam soil is preferred.
Geographic Distribution in India:
- Karnataka: Accounts for over two-thirds of coffee production in India.
- Kerala: Contributes about 22% of the production.
- Tamil Nadu: Accounts for approximately 6.5% of production.
Other Information:
- Varieties of Coffee: India mainly grows Arabica coffee, which is of superior quality and in high demand internationally. Robusta and Liberia varieties are also grown but in smaller quantities.
- Labour Requirements: Coffee cultivation requires a significant amount of cheap and skilled labor.
- Ideal Slopes: Northern and eastern aspects of slopes are preferred for cultivation as they are less exposed to strong afternoon sun and southwest monsoon winds.
Rubber
Rubber is primarily obtained from the latex of the Hevea brasiliensis tree, along with several other tropical tree species. The latex production begins approximately 5-7 years after planting the tree.Climatic Requirements:
- Temperature: Rubber trees thrive in hot climates, with optimal temperatures ranging from 25°C to 35°C.
- Humidity:. humid environment is crucial, with annual rainfall requirements around 200 cm, well-distributed throughout the year.
Soil Requirements:
- Rubber plantations prefer deep, well-drained loamy soils. These soils should have good drainage capacity to prevent waterlogging, which can adversely affect the trees.
Geographic Distribution in India:
- Kerala: The state is the largest producer, contributing about 92% of the total rubber production in India.
- Tamil Nadu: Accounts for approximately 3% of rubber production.
- Karnataka: Contributes around 2% of the rubber produced.
- Tripura: The state is the fourth largest producer of rubber in India, contributing about 2% of the total production.
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: Small quantities of rubber are also produced in these islands.
Cultivation and Harvesting:
- Initial Growth: After planting, it takes around 5-7 years for the rubber trees to mature and start yielding latex. The growth period is crucial for the development of the tree and its root system.
- Latex Tapping: Once the trees reach maturity, latex is harvested by making incisions in the bark of the tree. The latex is collected and processed to produce natural rubber.
Conclusion:
- Rubber cultivation is a significant agricultural activity in India, particularly in states like Kerala, where the climatic and soil conditions are ideal for rubber tree growth.
- The industry plays a vital role in the economy, providing employment and contributing to the production of natural rubber used in various industries.
Spices
Spices are essential for flavoring food and are cultivated in specific regions of India where the soil and climatic conditions are suitable. Here’s a detailed overview:1. Pepper:
- Major Producing States: Kerala (94% of production), Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Soil Requirements: Well-drained sandy, clayey, or red loam soils are ideal.
- Climatic Conditions: Requires humid and warm conditions for optimal growth.
2. Cardamom:
- Major Producing States: Kerala (53% of production), Karnataka (42%), and Tamil Nadu.
- Uses: Known as the “queen of aromatic spices,” cardamom is used in medicinal preparations and as a flavoring agent.
3. Chillies:
- Major Producing States: Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- Key Districts in Andhra Pradesh: Guntur, East Godavari, and West Godavari are the leading districts for chili production.
4. Ginger:
- Major Producing States: India is the largest producer, with significant contributions from Meghalaya, Andhra Pradesh, and Kerala.
- Uses: Widely used for its flavor and medicinal properties.
5. Turmeric:
- Major Producing States: India is a leading producer, with Andhra Pradesh being the largest producer (more than half of the total production).
- Uses: Used for its flavor, color, and medicinal properties. Native to tropical South-East Asia.
India is a significant exporter of spices, with a continuous increase in the area under cultivation and production. The hilly regions of Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu provide the best soil conditions for growing most spices, contributing to India’s reputation as a major spice producer and exporter.
Horticulture
- India ranks second globally in the production of fruits and vegetables, following China.
- The horticulture sector contributes approximately 25-30% to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) from agriculture.
- India is the leading producer of bananas and mangoes in the world.
Fruits and Nuts in India
Cashew Nut
- The cashew nut is used as a dry fruit.
- India is the world leader in cashew production.
- Major producing states include:
- Maharashtra (29.9%)
- Andhra Pradesh (15.7%)
- Odisha
- Kerala
- Karnataka
- Tamil Nadu
Mango
- The mango is native to the Indian monsoon regions.
- India produces more than half of the world’s mangoes and is the largest exporter.
- The Alfonso mango is a significant export variety.
- Major producing states include:
- Uttar Pradesh
- Bihar
- Andhra Pradesh
- West Bengal
- Odisha
Apple
- The apple is a temperate fruit that requires a sunny climate with gentle winds.
- Optimal growth conditions include an average temperature of around 22°C during the growing season and low temperatures during the non-growing season.
- Poor conditions such as low temperatures, rain, fog, and cloudy weather can hinder growth during maturation.
- Apples require well-distributed rainfall of 100-125 cm throughout the growing season.
- Apple orchards should be free from hailstorms and frost.
- Important apple-growing regions include:
- Kullu and Shimla districts in Himachal Pradesh
- Kashmir Valley
- Hilly areas of Uttarakhand
Banana
- Bananas are grown in tropical and subtropical regions.
- While cultivation occurs throughout India, peninsular India offers ideal conditions for banana production.
- Major producing states include:
- Tamil Nadu
- Maharashtra
Orange
- Most orange orchards rely on rainfed irrigation.
- Orange cultivation is widespread but is particularly concentrated in the hilly regions of Uttarakhand.
- Important orange-growing regions include:
- Kangra Valley in Himachal Pradesh
- Darjeeling in West Bengal
- Khasi and Jaintia Hills in Meghalaya
- Kodagu district in Karnataka
Peach
- The peach is a temperate fruit that is highly perishable, even more so than apples.
Crop Diversification
Crop diversification refers to the shift from the dominance of a single crop in a region to the production of a variety of crops. This practice is essential for several reasons:- Maintaining Soil Fertility: Growing a diverse range of crops suitable to a particular agro-climatic zone helps in maintaining soil fertility. It prevents the excessive use of nutrients and reduces the need for extensive irrigation.
- Arresting Groundwater Depletion: Diversifying cropping patterns from water-intensive crops like paddy to less water-consuming crops such as pulses, oilseeds, and maize can help tackle the issue of depleting groundwater tables.
- Beneficial Insects and Pest Control: Crop diversification can provide habitats for beneficial insects while reducing the colonization by pests.
- Additional Employment Opportunities: It can create more job opportunities in the agricultural sector.
- Reducing Agricultural Risks: Diversification acts as a safeguard against the risks associated with agriculture, such as natural calamities and pest attacks.
- Increasing Income Levels and Reducing Poverty: Crop diversification can lead to higher income levels for farmers, contributing to poverty reduction (Sustainable Development Goal 1).
Meaning and Reasons for Diversification of Agricultural Activities
Diversification of agricultural activities refers to the process of reducing the share of the labor force in the agriculture sector and finding employment in non-farm activities. This shift is necessary for several reasons:
- Reducing Risk: Earning from the agriculture sector can be risky due to factors like unpredictable weather, fluctuating prices, and pest attacks. Diversification reduces this risk by providing alternative sources of income.
- Offering Wider Choices: Diversifying agricultural activities gives people a wider choice of employment opportunities, making the job market more flexible.
Types of Farming
Farming can be classified based on the main source of moisture for crops into irrigated and rainfed farming.Irrigated Farming:
- Protective Irrigation: This type of irrigation aims to protect crops from soil moisture deficiency. It acts as a supplementary source of water, in addition to rainfall.
- Productive Irrigation: This type of irrigation provides sufficient soil moisture during the cropping season to achieve high productivity.
Rainfed Farming:
- Dryland Farming: This is practiced in regions with annual rainfall less than 75 cm. Crops grown include ragi, bajra, moong, gram, and guar. Various soil moisture conservation and rainwater harvesting measures are practiced.
- Wetland Farming: This is practiced in areas where rainfall exceeds the soil moisture requirement during the rainy season, leading to potential flood and soil erosion hazards. Crops grown include rice, jute, sugarcane, and aquaculture in freshwater bodies.
Climate Smart Agriculture
Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) is an approach to managing agricultural systems in a way that addresses the challenges of food security and climate change simultaneously. It focuses on increasing productivity, enhancing resilience, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Here are the key aspects of Climate Smart Agriculture:
- Triple Win: CSA aims to increase yields, make them resilient to climate impacts, and transform farms into solutions for climate change.
- Greenhouse Gas Reduction: CSA seeks to reduce and remove greenhouse gases where possible.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): CSA contributes to achieving SDGs and ensuring food security.
- Resilience Building: CSA helps farmers adapt to and build resilience against climate change impacts.
Practices Under Climate Smart Agriculture
- Minimum Soil Disturbance: This involves practices like zero tillage or controlled tillage, where only a small percentage of the soil surface is disturbed.
- Retention of Crop Residues: Keeping crop residues or other soil surface covers helps improve soil health.
- Crop Rotations: Rotating crops helps reduce the build-up of weeds, pests, and diseases. If land is limited, intercropping can be used, with legumes recommended for their nitrogen-fixing abilities.
- Increasing Soil Organic Content: Enhancing the organic content of soil is crucial for soil health and productivity.
- Promoting Carbon Soil Capture: Practices that capture and store carbon in the soil contribute to climate mitigation.
Key Initiatives:
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana: This initiative promotes organic farming and traditional agricultural practices.
- Soil Health Cards: These cards provide farmers with information about the health of their soil, helping them make informed decisions about soil management.
- PM Fasal Bima Yojana:. scheme that provides insurance coverage and financial support to farmers in the event of crop failure.
- PM Krishi Sinchai Yojana: This initiative focuses on improving irrigation facilities and water management in agriculture.
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture:. mission aimed at promoting sustainable agricultural practices and enhancing productivity.
- National Initiative on Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA): This initiative focuses on enhancing the resilience of Indian agriculture to climate change.
- National Adaptation Fund:. fund aimed at supporting projects that enhance climate resilience in various sectors, including agriculture.
- National and State Action Plan on Climate Change: These plans outline strategies and actions to address climate change at the national and state levels.
Integrated Farming System
Integrated Farming System (IFS) is an agricultural approach that combines crop production, livestock rearing, aquaculture, horticulture, agro-industry, and allied activities into a single, efficient, and sustainable system. It aims to optimize resource use, increase productivity, and ensure food security while reducing poverty and enhancing farmers' livelihoods. Here are the key aspects of Integrated Farming System:
- Resource Management: IFS focuses on the efficient and sustainable management of resources such as land, water, and organic waste. This includes practices like vermicomposting and organic farming.
- Sustainability: The system aims to achieve multiple objectives, including sustainability, food security, and poverty reduction. By involving livestock and other activities, IFS promotes a circular economy where waste from one component becomes input for another.
- Climate Smart Agriculture: IFS is aligned with the principles of Climate Smart Agriculture, as it enhances resilience to climate change, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and contributes to national development goals.
- Doubling Farmers' Income: The approach is seen as a pathway to achieving the government’s goal of doubling farmers’ income by 2022, as recommended by the Ashok Dalwai Committee.
- Diversification: IFS encourages diversification of income sources for farmers, reducing their dependence on a single crop or activity and spreading risk.
Overall, Integrated Farming System represents a holistic and inclusive approach to agriculture that can help address the challenges of food security, climate change, and rural poverty in India.
Irrigation Methods in India
Irrigation refers to the artificial application of water to land or soil to assist in the growth of crops. It supplements or substitutes rainwater with water from various sources. Here are the main methods of irrigation practiced in India:
1. Well and Tube Well Irrigation: Wells are a common source of irrigation in states like Punjab, Bihar, Tamil Nadu, and others. There are different types of wells:
- Shallow Wells: These are not always reliable as water levels can drop during dry months.
- Deep Wells: These are more suitable for irrigation as they provide a consistent water supply throughout the year.
- Tube Wells: These are installed where groundwater is available and are often powered by electricity for larger irrigation.
Merits:
- Wells are simple, cheap, and can be used as needed.
- Well water can enhance soil fertility due to beneficial chemicals.
- Wells provide reliable water during droughts when surface water is scarce.
Demerits:
- Limited irrigation area per well.
- Tube wells can deplete groundwater, making it unfit for agriculture.
- Groundwater depletion can occur, especially in regions with subsidized electricity for irrigation.
2. Canal Irrigation: Canals are effective in areas with low relief, deep fertile soils, a perennial water source, and extensive command areas. They are primarily found in the northern plains of India, such as Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, and Punjab.
Merits:
- Provides perennial irrigation, helping to increase farm production.
- Saves crops from drought conditions.
- Initial costs are high, but it is economical in the long run.
Demerits:
- Can overflow during the rainy season, causing floods.
- Suitable mainly for plain areas.
- Canal water can lead to water-logging and salinity issues.
- Initial costs are high, and it can be uneconomical in rocky areas.
Types of Canals:
- Inundation Canals: These are taken from rivers without regulation and provide irrigation mainly during the rainy season.
- Perennial Canals: These are constructed by creating barrages across perennial rivers and are more common in India.
3. Tank Irrigation: Tanks are created by building a bund across a stream to impound water for irrigation. They are found in regions like the Karnataka Plateau, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Kerala, Bundelkhand, Rajasthan, and Gujarat.
Merits:
- Most tanks are natural and low-cost.
- Tanks have a long lifespan.
- Fishing in tanks can supplement farmers' income.
Demerits:
- Tanks can dry up during dry seasons.
- Water evaporation from shallow tanks can reduce availability.
- Lifting and transporting water from tanks can be labor-intensive and costly.
4. Drip Irrigation: Drip irrigation involves applying water near the plant roots through emitters at a low rate. It is suitable for a variety of crops, especially vegetables, orchard crops, flowers, and plantation crops.
Merits:
- Reduces fertilizer and nutrient loss.
- Field leveling is not necessary.
- Recycled non-potable water can be used.
- Increases water application efficiency.
- Reduces soil erosion and weed growth.
Demerits:
- Higher initial costs.
- Risk of clogging and wastage if not installed properly.
- Requires skilled labor for installation and maintenance.
5. Sprinkler Irrigation: Water is sprayed into the air and allowed to fall on the ground, resembling rainfall. This method is suitable for uneven lands and shallow soils.
Merits:
- Suitable for all soil types except heavy clay.
- Water saving of 30-50%.
- Increases yield.
- Saves land as no bunds are required.
Demerits:
- Requires skilled labor for management.
- Higher initial costs.
- Efficiency is poor under high wind and temperature conditions.
- Can reduce soil productivity in the long term.
6. Fertigation: Fertigation involves applying fertilizers within irrigation water through the drip system. It improves nutrient availability and efficiency.
Advantages:
- Greater absorption of nutrients and water by crops.
- Potential for 25-50% higher yields.
- Saves nutrients and reduces labor and energy use.
|
52 videos|224 docs
|
FAQs on Package of Practices - Agriculture Optional for UPSC
| 1. What are the primary types of agriculture practiced in different regions of the world? |  |
| 2. What are the salient features of Indian agriculture? |  |
| 3. How can productivity be boosted in Indian agriculture? |  |
| 4. What are the major food crops cultivated in India? |  |
| 5. What are cash crops, and which ones are significant in India? |  |





















