Plant Kingdom | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
Introduction
The plant kingdom consists of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms capable of producing their own food primarily through photosynthesis. These organisms, which contain chlorophyll, include a wide range of familiar types such as trees, flowers, grasses, ferns, and mosses. There are over 390,000 species of plants that thrive in almost every land environment.
Plants play a crucial role in ecosystems as primary producers. They convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy through photosynthesis, which then gets transferred through the food chain, supporting nearly all life forms on Earth, either directly or indirectly. In addition to this, plants also:
Plants also provide oxygen, stabilize soil, cycle nutrients, regulate climate, and offer habitat for animals.
Evolution of Biological Classification Systems
The classification of living organisms has evolved over time through the contributions of various scientists. Initially, organisms were broadly categorized based on external features, but later systems included deeper biological traits.
1. Two-Kingdom Classification (Carolus Linnaeus):
In 1735, Carolus Linnaeus introduced the Two-Kingdom system in his work Systema Naturae. He divided all living organisms into two kingdoms: Plantae and Animalia. This classification was primarily based on visible characteristics such as movement and mode of nutrition.
2. Evolution of Plant Kingdom Classification:
In early systems, plants were categorized based on external growth forms — as trees, shrubs, and herbs. As scientific understanding progressed, internal structures and reproductive features were used for more accurate classification.
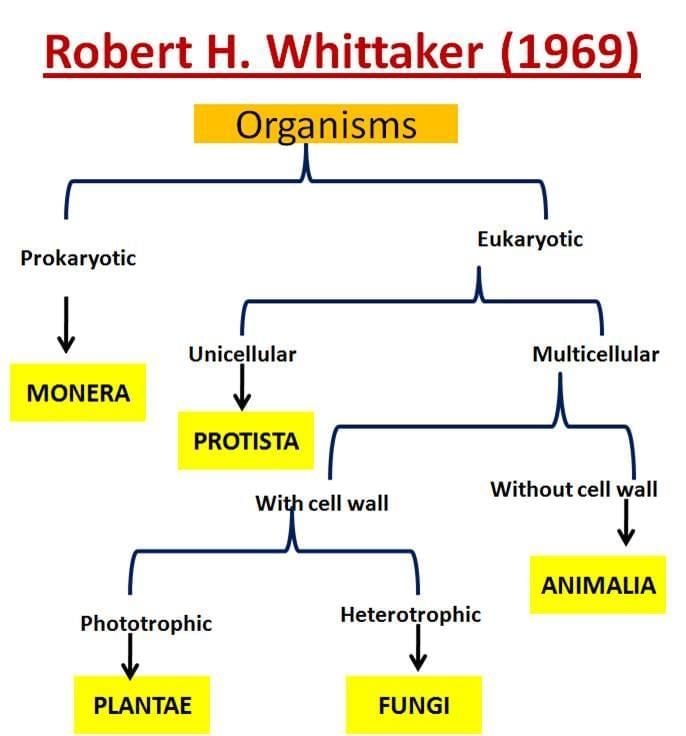
3. Five-Kingdom Classification (R.H. Whittaker):
In 1969, R.H. Whittaker proposed the Five Kingdom classification system. He considered multiple criteria like:
- Cellular structure (prokaryotic or eukaryotic
- Body organization (unicellular or multicellular)
- Mode of nutrition (autotrophic or heterotrophic)
- Reproduction Methods
- Phylogenetic relationships.
The five kingdoms he proposed were:
- Monera (prokaryotes like bacteria)
- Protista (unicellular eukaryotes)
- Fungi (saprophytic organisms)
- Plantae (photosynthetic autotrophs)
- Animalia (heterotrophic multicellular organisms)
Plant Classification Systems
Botanists classify plants based on shared evolutionary history and characteristics. Classification helps understand relationships and origins.
Linnaean System
- The Linnaean system classifies plants in a hierarchical order: kingdom, division, class, order, family, genus, and species, from the broadest category to the most specific.
- Taxonomic names are derived from the Latinized names of the genus and species.
Phylogenetic System
- This system groups plants based on their evolutionary relationships and DNA evidence.
- Plants that are closely related share a common ancestor.
- Common phylogenetic groups include Bryophytes (such as mosses and liverworts) and Tracheophytes (which include ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms).
Plant Kingdom: Plantae
Kingdom Plantae includes all the plants. They are eukaryotic, multicellular and autotrophic organisms. The plant cell contains a rigid cell wall. Plants have chloroplast and chlorophyll pigment, which is required for photosynthesis.

Characteristics of Kingdom Plantae
- Plants are non-motile, meaning they do not move from one place to another.
- They are autotrophs, capable of producing their own food.
- Plants can reproduce asexually through methods like vegetative propagation or sexually.
- They are multicellular eukaryotic organisms, with cells that have an outer cell wall and a large central vacuole.
- Plants contain chlorophyll, a pigment located in chloroplasts that plays a vital role in photosynthesis.
- They possess various organelles responsible for anchorage, reproduction, support, and photosynthesis.
Classification of Kingdom Plantae
A plant kingdom is further classified into subgroups. Classification is based on the following criteria:
- Plant body: Presence or absence of a well-differentiated plant body. E.g. Root, Stem and Leaves.
- Vascular system: Presence or absence of a vascular system for the transportation of water and other substances. E.g. Phloem and Xylem.
- Seed formation: Presence or absence of flowers and seeds and if the seeds are naked or enclosed in a fruit.
The plant kingdom has been classified into five subgroups according to the above-mentioned criteria:
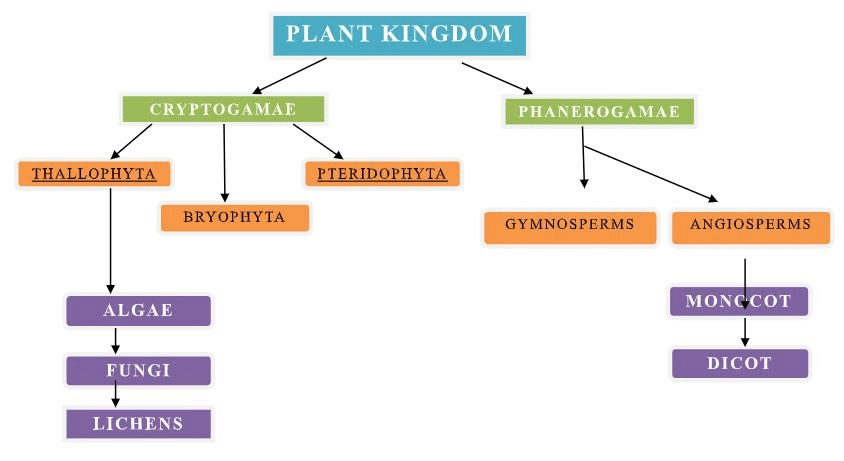
Cryptogams
- Cryptogams are a group of plants or plant-like organisms that do not produce seeds.
- They are classified within a sub-kingdom of the Plantae kingdom called Cryptogams, which encompasses algae, fungi, and bryophytes.
- Reproduction in cryptogams occurs through spores, and their reproductive organs are not visible, as they are hidden.
- These organisms are considered to be less evolved in comparison to other types of plants.
Thallophyta (Algae)
- Thallophyta includes plants with a simple body structure known as a thallus, which can take various forms such as filamentous, colonial, branched, or unbranched.
- These plants do not have specialized organs like stems, roots, or leaves.
- Some common examples of Thallophyta are Volvox, Fucus, Spirogyra, Chara, Polysiphonia, and Ulothrix.

Bryophyta
Bryophytes do not have vascular tissues. The plant body has root-like, stem-like and leaf-like structures. Bryophytes are terrestrial plants but known as “amphibians of the plant kingdom” as they require water for sexual reproduction. They are present in moist and shady places. Bryophyta includes mosses, hornworts and liverworts. Some of the common examples are Marchantia, Funaria, Sphagnum, Antheoceros, etc.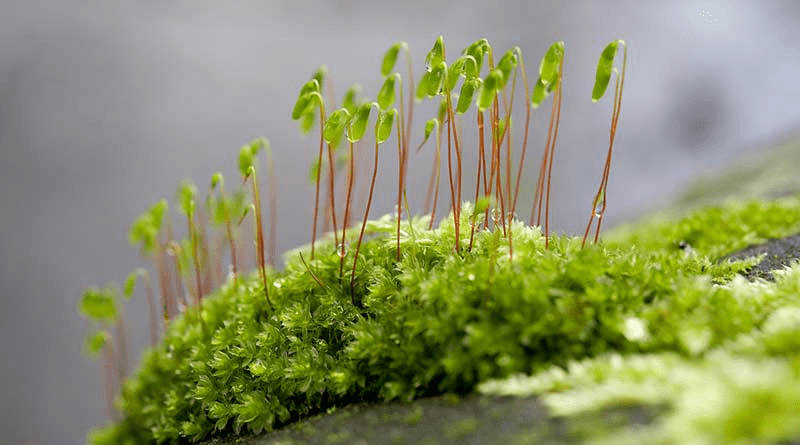 Bryophyta
BryophytaPteridophyta
Pteridophytes have a well-differentiated plant body into root, stem and leaves. They have a vascular system for conduction of water and other substances. Some of the common examples are Selaginella, Equisetum, Pteris, etc.
 Pteridophyta
Pteridophyta
Phanerogams
- Phanerogams are a group of plants known for bearing seeds.
- They are classified within a sub-kingdom of the kingdom Plantae, which includes Angiosperms and Gymnosperms.
- These plants reproduce through seeds, and their reproductive organs are exposed.
- Phanerogams are considered to be highly evolved plants.

Gymnosperms
Gymnosperms have a well-differentiated plant body and vascular tissues. They bear naked seeds, i.e. seeds are not enclosed within a fruit. Some of the common examples of gymnosperms are Cycas, Pinus, Ephedra, etc.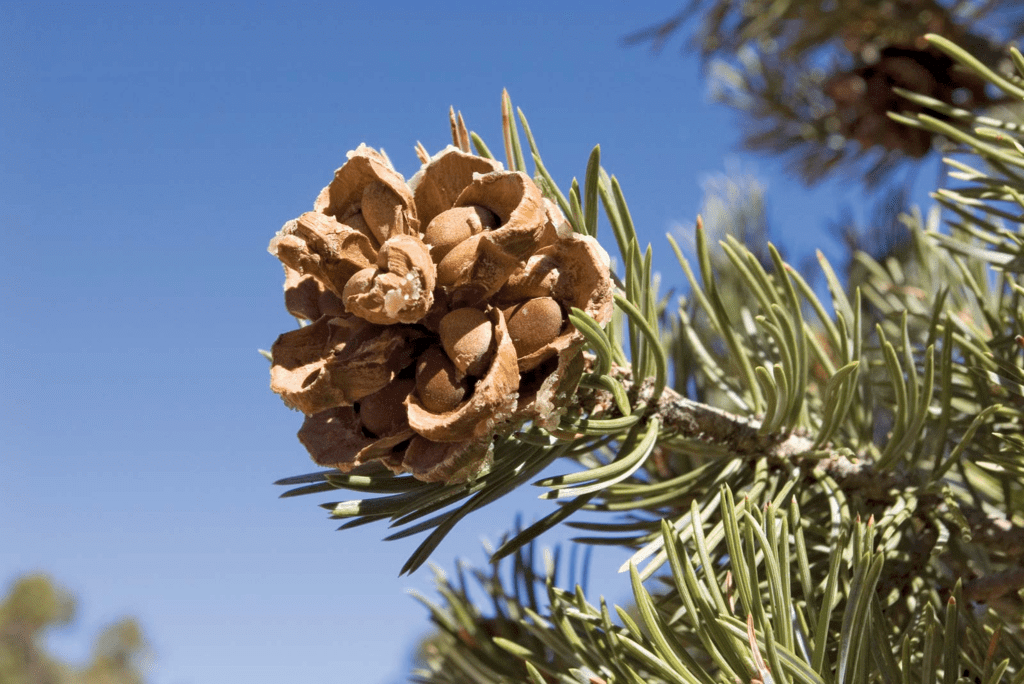 Gymnosperms
GymnospermsAngiosperms
Angiosperms are seed-bearing vascular plants with a well-differentiated plant body. The seeds of angiosperms are enclosed within the fruits. Angiosperms are widely distributed and vary greatly in size, e.g. Wolffia is small measuring about 0.1 cm and Eucalyptus trees are around 100 m tall. Angiosperms are further divided into monocotyledons and dicotyledons according to the number of cotyledons present in the seeds. Some of the common examples are mango, rose, tomato, onion, wheat, maize, etc.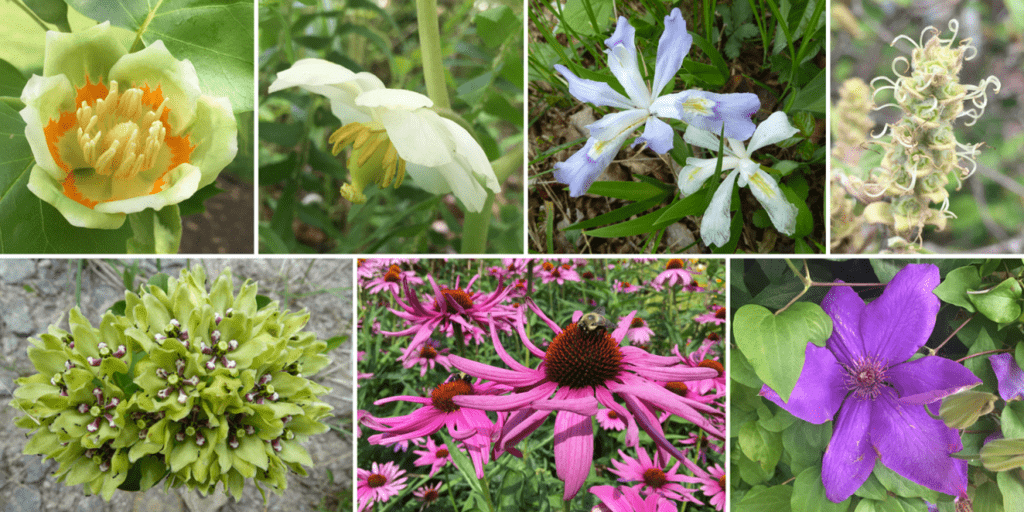 Angiosperms
AngiospermsPlant Structure and Function
Plants, despite their diverse shapes and sizes, share some crucial structural and functional characteristics. Let's explore these features in detail.
 Plant Structure
Plant Structure
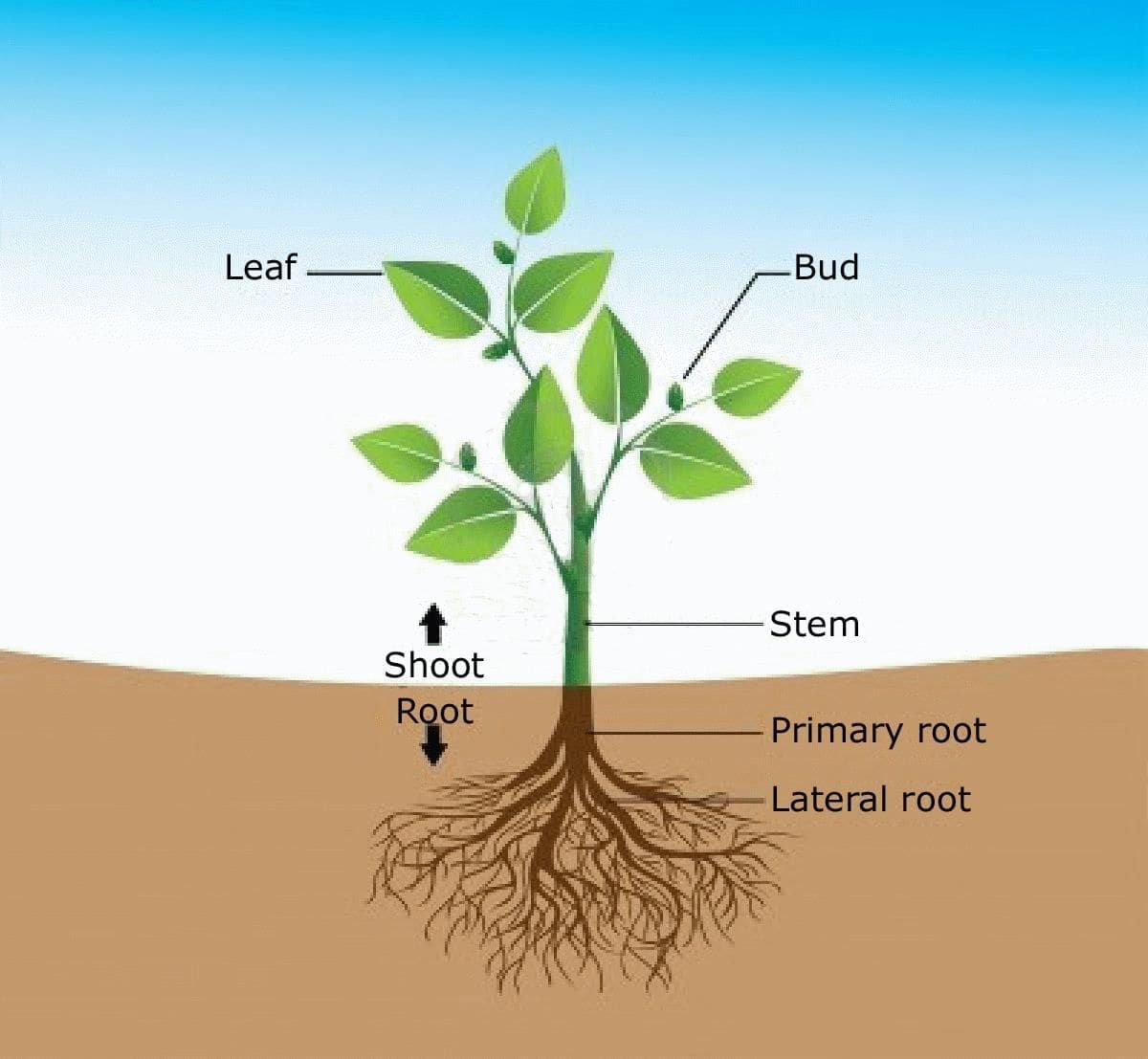
Roots
- Roots serve as the foundation of the plant, anchoring it securely in the soil. They are also responsible for absorbing essential water and minerals from the ground.
- There are two main types of root systems: fibrous roots, which spread out in all directions, and taproots, which have a single, deep root.
- Some specialized roots have unique functions, such as storing food or aiding in vegetative propagation, where new plants grow from parts of the parent plant.
Stems
- Stems play a vital role in providing support to the plant and facilitating the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant.
- Herbaceous plants have soft, green stems that are flexible, while woody plants develop hard stems covered with protective bark as they mature.
- Stems can also be modified into various forms, such as rhizomes (underground stems), corms (swollen underground stems), tubers (enlarged potato-like structures), and bulbs (underground storage organs like onions).
Leaves
- Leaves are the primary sites for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
- Leaves that are flat and wide are more effective at capturing sunlight for this process.
- The anatomy of a leaf includes epidermal cells (outer protective layer), stomata (tiny openings for gas exchange), xylem (water transport), and phloem (sugar transport) arranged in a vascular bundle.
- There is a wide variety of leaf arrangements, shapes, and margins among different plant species, allowing them to adapt to various environments.
Reproductive Structures
- Plants reproduce in two main ways: sexually through spores and seeds, and asexually via vegetative propagation, where new plants grow from parts of the parent plant.
- Flowers are the reproductive organs of flowering plants, containing both male and female parts. After fertilization, flowers develop into fruits that contain seeds, which can grow into new plants.
- Non-flowering plants reproduce using cones (like pine cones), spores (tiny cells that can develop into a new organism), and sporangia (structures that produce spores).
Vascular Tissue
- The xylem is responsible for carrying water and minerals absorbed by the roots upwards to the rest of the plant.
- The phloem distributes sugars produced during photosynthesis throughout the plant.
- Together, xylem and phloem form vascular tissue, which is essential for supporting the plant's growth and structure.
Meristems
- Meristems are specialized tissues in plants containing undifferentiated cells that divide rapidly, allowing for continuous growth.
- Apical meristems are located at the tips of shoots and roots, supporting primary growth and extending the plant's height and root depth.
- Lateral meristems contribute to secondary growth, increasing the diameter of stems and roots, which is why some plants become thicker over time.
Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis is the process through which plants convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in glucose, a type of sugar.
- This process takes place in chloroplasts found in the mesophyll cells of leaves. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a pigment that captures sunlight, and during photosynthesis, oxygen is released as a byproduct.
|
1179 videos|2219 docs|849 tests
|
FAQs on Plant Kingdom - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. Who classified living organisms? |  |
| 2. What is the Plant Kingdom also known as? |  |
| 3. What are the characteristics of Kingdom Plantae? |  |
| 4. How is Kingdom Plantae classified? |  |
| 5. How does Kingdom Plantae contribute to the ecosystem? |  |
















