Plate Tectonics Theory | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
- Plate tectonics is a scientific concept formulated in the 1960s to explain the formation of major landforms through movements within the Earth.
- The theory revolutionized the field of earth sciences by providing insights into processes like mountain formation, volcanic activities, and seismic events.
- In plate tectonics, the Earth's lithosphere, consisting of the crust and upper mantle, is segmented into large plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere.
- Driven by convection currents in the asthenosphere and lithosphere, these plates drift at speeds ranging from two to 15 centimeters per year.
What are Tectonic Plates?
Before we delve into the intricacies of the Plate Tectonics Theory, it is crucial to grasp the concept of tectonic plates. These are large, irregularly shaped slabs of solid rock, typically made up of both continental and oceanic lithosphere. The Earth's lithosphere is divided into numerous such plates, and it is the interactions at their boundaries that lead to significant geological phenomena such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Composition of Tectonic Plates
Tectonic plates consist of two main types of lithospheric crust:
- Continental Crust: This type forms the continents we inhabit. It is thicker and less dense compared to oceanic crust, primarily composed of granitic rock.
- Oceanic Crust: This crust makes up the ocean floors. It is thinner but denser than continental crust, mainly composed of basaltic rock.
Types of Tectonic Plates
As we delve deeper into the mysterious realm of tectonic plates, we encounter a fascinating assortment of Earth's puzzle pieces, each with its unique characteristics. These plates can be broadly categorized into two groups: major plates and minor plates. Let's embark on an intriguing journey to explore the complexities of these tectonic plates.
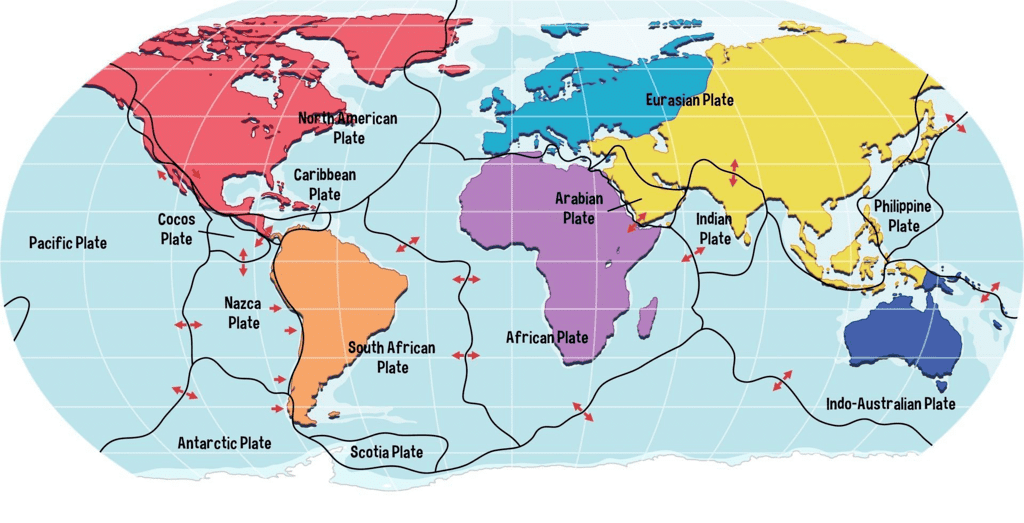
Major Plates
The major tectonic plates are the large, prominent segments that mold the Earth's lithosphere. They play a crucial role in plate tectonics and significantly influence the geological processes on our planet. Let's closely examine some of the major plates:
- The Pacific Plate: One of the largest tectonic plates, the Pacific Plate borders several other major plates, including the North American Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate. It is known for its dynamic interactions, leading to frequent seismic activity in the region.
- The Eurasian Plate: Encompassing a vast expanse of territory, the Eurasian Plate spans from Europe to Asia, incorporating regions of diverse geological features. Its collision with the Indian Plate gave rise to the formation of the Himalayas, showcasing the immense forces at play in plate tectonics.
- The African Plate: Positioned beneath the African continent, this plate is surrounded by various other plates, such as the South American Plate and the Antarctic Plate. The African Plate's movements have influenced the formation of rift valleys and volcanic activity across the region.
- The Antarctic Plate: Covering the continent of Antarctica, the Antarctic Plate plays a crucial role in the dynamics of the Southern Hemisphere. Its interactions with neighboring plates contribute to the shaping of Antarctica's landscape and impact global climatic patterns.
Minor Plates
While the major tectonic plates often steal the spotlight, we must not overlook the significance of their lesser-known companions, the minor plates. Despite their lack of fame, these smaller plates hold crucial roles in the intricate dance of tectonic movements, shaping specific regions in unique ways.
Exploring the Minor Plates
- Caribbean Plate: Nestled in the Caribbean Sea, this minor plate actively participates in sculpting the stunning Caribbean islands, such as the Greater Antilles and Lesser Antilles.
- Philippine Sea Plate: Positioned in the vast expanse of the western Pacific Ocean, the Philippine Sea Plate takes responsibility for the creation of the Philippine Islands. Its presence is marked by intense seismic activities in the area.
- Nazca Plate: Lying adjacent to the western coast of South America, the Nazca Plate is renowned for its subduction beneath the South American Plate. This process has given birth to the majestic Andes Mountains and various volcanic regions.
- Arabian Plate: Enveloping the Arabian Peninsula, the Arabian Plate engages in a dramatic collision with the Eurasian Plate. This collision has led to the formation of the striking Zagros Mountains and continues to uplift the region.
Movement of Plates
- The movement of tectonic plates is a fundamental process driven by convection currents in the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath the Earth's lithosphere.
- The Earth's lithosphere is dynamic, with plates continuously shifting, albeit at a pace slower than the growth of human fingernails.
- Tectonic plates essentially float on the denser asthenosphere layer, leading to their perpetual motion.
Tectonic Plate Boundaries and Their Characteristics
- Plate boundaries are dynamic zones where tectonic plates interact, shaping the Earth's geology.
- There are three main types of plate boundaries: convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries.
Convergent Boundaries
- Convergent boundaries involve the collision of tectonic plates, leading to various geological phenomena.
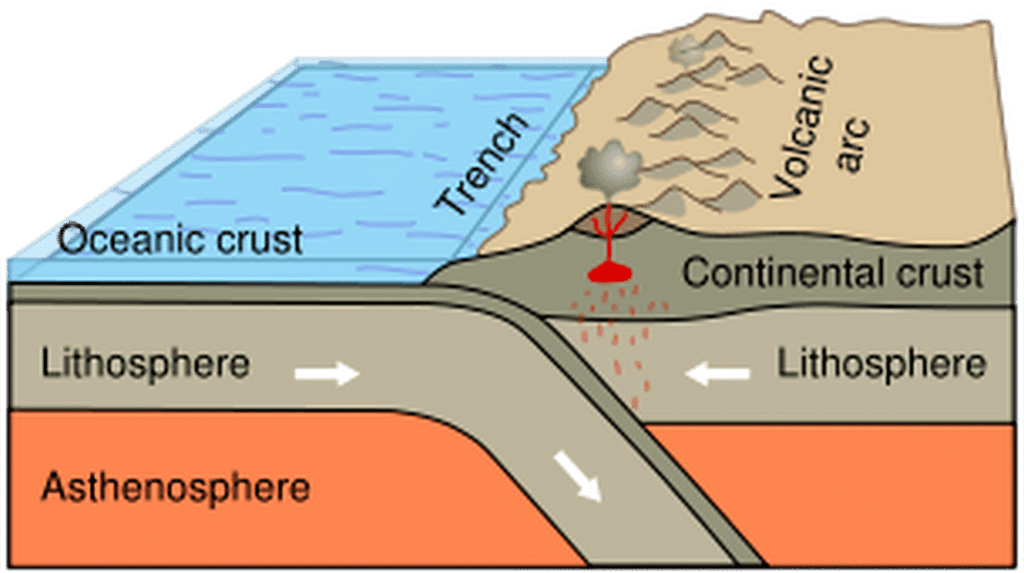
- When an oceanic plate converges with another plate, subduction occurs, creating features like deep-sea trenches.
- Conversely, when two continental plates collide, they crumple and form mountain ranges.
- Examples include the Mariana Trench and the Himalayas, resulting from different types of convergent boundaries.
Divergent Boundaries: The Creators of New Earth
- Unlike convergent boundaries, divergent boundaries are sites where new crust is formed. Instead of colliding, two plates move apart, allowing magma to rise, cool, and solidify, creating fresh lithospheric material.
- Underwater, divergent boundaries generate mid-ocean ridges like the expansive Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the world's longest underwater mountain range. On land, they can lead to the development of rift valleys such as the East African Rift Valley.
- Divergent boundaries play a crucial role in shaping Earth's surface, contributing continuously to its transformation.
Transform Boundaries
- Transform boundaries involve two plates sliding horizontally past each other. Despite not colliding or moving apart, the plates' movement is not smooth due to friction, occasionally causing them to become stuck.
- When the built-up stress overcomes the friction, the plates suddenly release energy, resulting in powerful earthquakes.
Theory of Plate Tectonics
- The Theory of Plate Tectonics serves as a comprehensive model explaining the large-scale movements of Earth's lithosphere.
- This scientific concept emerged in the late 1960s by integrating two earlier ideas: Continental Drift and Sea-floor Spreading.
Continental Drift
- Proposed by Alfred Wegener, a German geophysicist, in 1912, the Continental Drift theory postulated that all continents were once part of a supercontinent called Pangaea.
- Wegener's theory suggested that Pangaea fragmented over time, with the continents gradually moving to their current positions on the globe.
- Despite compelling geological and paleontological evidence supporting his theory, Wegener struggled to provide a convincing mechanism explaining the movement of such massive landmasses.
Sea-floor Spreading
- In the 1960s, Harry Hess introduced the concept of Sea-floor Spreading. This idea suggests that fresh oceanic crust is formed at mid-ocean ridges and subducted at deep-sea trenches.
- This continuous cycle of crust creation and destruction offered a vital mechanism absent in Wegener's Continental Drift theory.

Postulates of the Theory of Plate Tectonics
- The Theory of Plate Tectonics can be condensed into four fundamental postulates:
- The Earth's lithosphere is segmented into various rigid tectonic plates.
- These plates rest on the semi-fluid asthenosphere below them, enabling their movement.
- Interactions at plate boundaries can result in the formation of new crust (at divergent boundaries), destruction of crust (at convergent boundaries), or horizontal sliding of crust (at transform boundaries).
- These plate movements are steered by mantle convection currents triggered by the Earth's internal heat.
Importance of the Theory of Plate Tectonics
- The theory of Plate Tectonics is crucial for understanding Earth's geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic activities, and the formation of mountain ranges and deep-sea trenches.
- It provides valuable insights into Earth's history, helps us make sense of the present, and aids in predicting future geological events.
|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Plate Tectonics Theory - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are tectonic plates and why are they important? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of tectonic plates? |  |
| 3. How do tectonic plates move? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristics of tectonic plate boundaries? |  |
| 5. What is the theory of plate tectonics and its main postulates? |  |






















