Political, Social & Economic Life of the people during IVC - UPSC PDF Download
POLITICAL CONDITION OF THE PERIOD
The population of Indus civilization was cosmopolitan in character, having four ethnic types, viz., Proto-Australoid, Mediterranean, Mongoloid and Alpine. The construction of planned cities and roads, drainage system, organized trade and uniformity of the means of weights and measurements proved that there existed a strong centralized government.
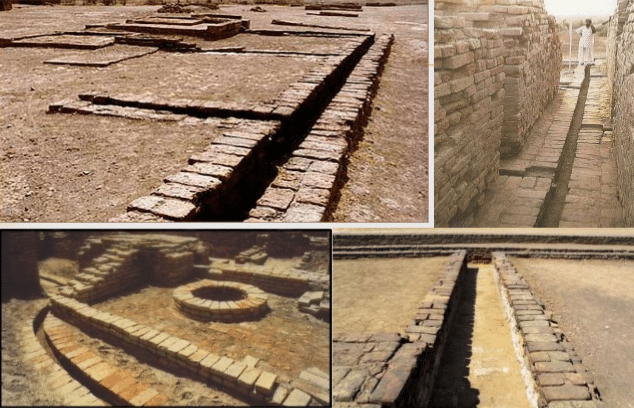 Water supply and drainage system of the IVC period
Water supply and drainage system of the IVC period
There may be two forms of the central government of the IVC period:

Thus, it is said that there are two main theories as to what kind of centralizing authority ruled the region and none have been proved beyond doubt.
Social Condition of the Period
In IVC, the historian tries to map the social conditions of the people by looking at a wide variety of aspects and indirectly infer the societal structure. These aspects include agriculture, food habits, clothes & ornaments, cosmetics, games and sports. Let us take a look at each of these aspects in detail.
(A) Agriculture
- Wheat and barley were the staple foods and besides that sesame, lentils and cotton were also grown.
- Horticulture was practiced i.e. fruits and vegetables were cultivated.
- There is evidence of domestication of animals in IVC.
- These domesticated animals, mainly, were cattle, sheep, goat, water buffalo, dog, pig, ass, camel, elephant, and fowl.
- Raising livestock was a useful investment against crop failure.
- Terracotta figurines, statues, and seals of bulls also suggest that oxen might have been used for ploughing.
(B) Food Habits
The staple food of the people comprised wheat, barley, milk, and some vegetables like peas, sesamum, and fruits like date palms. The diet also included non-vegetarian components such as mutton, pork, poultry, fish etc.
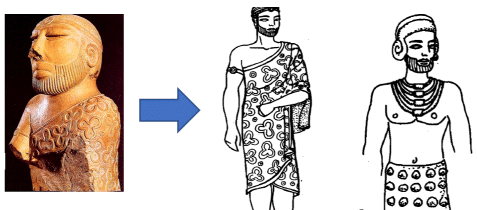
(C) Clothes
- The Harappan people used cotton and wool for their garments. Cotton was the prominent fabric used for clothing.
- Many spindles were discovered at the Harappan sites. This proves the use of cotton for weaving cloths. Spinning and weaving were practiced in the houses of Mohenjodaro, as would appear from the large find of spindle-whorls.
- Needles and buttons have been discovered indicating that perhaps stitching was also known.
- There was no special difference between the dress of men and women. The clothes consisted of some lower garment like dhoti and upper garment like a shawl. Dress or fabric has not survived, but statues and figurines suggest two pieces of clothes were used by both men and women.

Harappan Garments
- On a potsherd from Harappa is found a person wearing a dhoti at the waist and a shawl as an upper garment. This is suggested by the well -known steatite statuette from Mohenjodaro who is supposed to be of a priest
(D) Cosmetics, Hair-style & Ornaments
- The ladies of Mohenjo-Daro were Conscious of Beauty & Fashion.
- Cinnabar was used as a cosmetic and face-paint, lipstick and collyrium (eyeliner) were also known to them. They knew face paint made of ivory.
- Bronze oval mirrors, ivory combs of various shapes, even small dressing tables have been found at Mohenjo-Daro and other sites.
- Women used hairpins made out of ivory.
 Jewelry during IVC period
Jewelry during IVC period - Men wore long hair, parted in the middle and kept tidy at the back. The women of Indus valley usually wore long hair in plait with fan-shaped bow at the end. Fillets made of gold or silver were used to keep the hair in particular position.
- Both men and women of Harappa were fond of ornaments made of gold, silver and copper. The ornaments were decorated with precious stones like jade, carnelian, agate and lapis-lazuli. The female beauties of the Indus valley had a taste for toilet culture. The “vanity case” and the toilet jars found at Harappa consisted of ivory powder, face-paint and many other varieties of cosmetics.
- Ornaments for the poor were made of bone shell or terracotta.
- Beads made from carnelian, amethyst, quartz, steatite, etc were quite popular and were produced on a large scale, as is evident from the factories discovered in Chanhu-daro and Lothal.
(E) House-hold articles
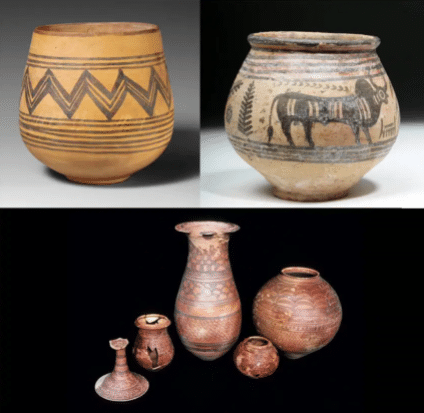
- Most of the house-hold articles were made of pottery or of metals like copper and bronze. The art of pottery attained wonderful excellence at Mohenjo-Daro. This is proved by painted and glazed wares. Most of the kitchen utensils including jars, vessels, dishes etc. were made of earth and stone.
 Art of pottery during Mohenjo-Daro
Art of pottery during Mohenjo-Daro - Domestic implements like axe, knife, needles, saws etc. were made of bronze or copper. Copper supply was limited as it had to be imported from outside. As copper was scarce, common men could hardly afford to possess copper weapons. The ruling class had a monopoly of the copper weapons.
- Chairs and tools were used for decorating rooms and for sitting comfortably.
(F) Games, Sports, Amusement and Entertainment
- They amused themselves by hunting, fishing and rearing animals as pets. The remains of terracotta of humped bull, buffalo, sheep, elephant, pig and camel have been found. Dogs, cats were also domesticated. The bones and skeletons of horses have been found at Kalibangan and Sukanjodaro in the upper layers which shows that horses were also domesticated.
- The existence of wild animals like rhinoceros, tiger, and bison in the Indus forests is confirmed by terracotta figures of these animals.
- Objects like dice games and play cards have been found. A sort of gender-play stereotyping is evident in IVC.
- They also enjoyed singing, dancing, and painting. A bronze statuette of a girl in the dancing pose has also been discovered at Mohenjodaro.
 Dancing girl, Mohenjodaro
Dancing girl, Mohenjodaro - Children used to play with toys and marbles. Generally they were clay models of birds, animals, men and women, rattles or presentation of carts.

Dice found in IVC and seals of hunting scenes
- A study of the social conditions of the period clearly shows that society was unequal. There was a strong ruling class – whether theocratic or Oligarchy – that is not known.
- Clear cut distinctions existed in the access to resources, such as copper, for the different classes.
- Class distinction is also supported by the town planning – those who lived in the upper portion of the cities near the forts formed a ruling class.
- There was also a strong family organization and a sense of conveying and transferring the knowledge, skills and resources to the next generation.
Economic Condition of the Period
Let us classify the economy of the IVC into primary, secondary and tertiary sectors;
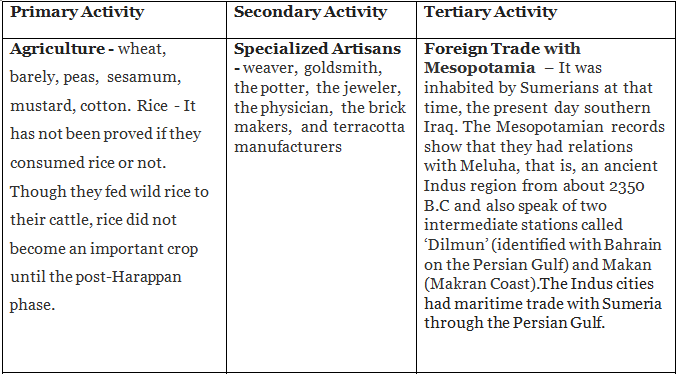
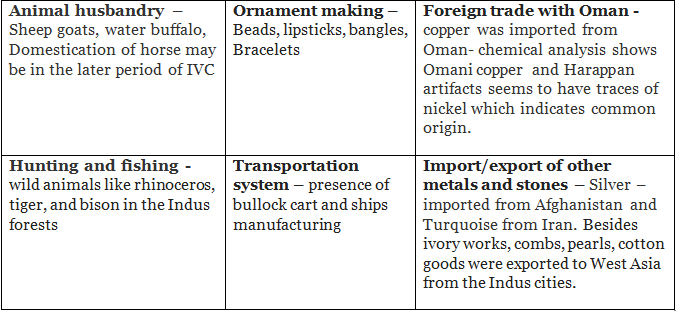
Apart from the historical remains, the existence of foreign trade is proved by the use various types of weights and measures. A strict control was exercised to maintain proper standard of weight. The decimal system was also known to them.
Comparison of IVC with contemporary civilizations
While comparing IVC with its contemporary civilizations we will see both the similarities and differences between the two. One of the striking feature of all the contemporary civilizations is that all of them developed along the river banks; Egyptian – Nile river, IVC – Indus River, Mesopotamian – Tigris-Euphrates river, Chinese – Yangtze river.
Another common features are the existence of pictorial writings, bronze and copper artifacts, pottery and worship of mother goddess in some civilizations. The main distinctions between IVC and Mesopotamia is given below:
FAQs on Political, Social & Economic Life of the people during IVC - UPSC
| 1. What was the political condition during the Indus Valley Civilization? |  |
| 2. How did the social life of the people in the Indus Valley Civilization look like? |  |
| 3. What was the economic life of the people in the Indus Valley Civilization? |  |
| 4. How did the political condition of the Indus Valley Civilization impact its society? |  |
| 5. What are the main challenges in understanding the political condition of the Indus Valley Civilization? |  |