Practice Questions: Decimals - CLAT PDF Download
Q1: Rashi spends 1/7th of his income on clothes,1/5th of the remaining on entertainment, 1/3rd of the remaining on books . If she still has Rs. 4800 with her, find her total income
(a) 11025
(b) 12025
(c) 10500
(d) 45256
Ans: (c)
Just concentrate on the remaining part at every step. Firstly she spends 1/7th of his income, implies he is left with 6/7th of his income. Then he spends 1/5th of that, means he saves 4/5th of that. After this she spends 1/3rd of the remaining, means he saves 2/3rd of that. In total she saves 2/3rd of 4/5th of 6/7th i.e. 2/3 × 4/5 × 6/7 of the total which is given to be 4800. Now 48/105 x = 4800 i.e. x = Rs. 10500.
Q2: Find the fractional equivalent of 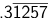
(a) 5209/16665
(b) 5219/16665
(c) 5239/16665
(d) 5211/16665
Ans: a
As it is case of mixed recurring 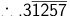 = (31257 – 3)/99990 = 31254/99990 = 5209/16665.
= (31257 – 3)/99990 = 31254/99990 = 5209/16665.
Q3: Find the fractional equivalent of 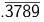
(a) 1421/1111
(b) 421/1111
(c) 4211/1111
(d) 419/1111
Ans: b
As it is case of pure recurring. 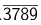 = 3789/9999 = 421/1111.
= 3789/9999 = 421/1111.
Q4: Find the fractional equivalent of .6789
(a) 5111/9000
(b) 6117/9000
(c) 6119/9000
(d) None of these
Ans: d
.6789 = (6789-678)/9000 = 6111/9000.
Q5: After spending 3/4 of his income a man is left with Rs. 100.Find his total income.
(a) 400
(b) 200
(c) 75
(d) None of these
Ans: (a)
After spending 3/4th of the income, he will be left with 1/4th of the income and that is given to be Rs. 100, thus ¼ of income is 100. So income = 100 * 4/1 = 400
Q6: Ravi spends 2/9th of his income, then he spends3/7th of the remaining. If he still has Rs. 140 with him. Find his total income.
(a) 315
(b) 3150
(c) 1175
(d) 6130
Ans: a
7/9 of 4/7 of income = 140. 4/9 of income = 140 ⇒ income = 140 x 9/4 = 315
Q7: In a library 2/3 of books are in English and the remaining 300 are of Hindi. Find the total books in library
(a) 400
(b) 900
(c) 275
(d) None of these
Ans: b
2/3 of books are in English means remaining 1 – (2/3) = 1/3 are in Hindi which is equal to 300. So 1/3rd of total = 300 ⇒ Total books = 300 x 3 = 900.
Q8: Find the fractional equivalent of 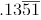
(a) 221/1650
(b) 227/1650
(c) 223/1650
(d) None of these
Ans: c
As it is case of mixed recurring = (1351 – 13) /9900 = 1338/9900 = 223/1650.
Q9: Raju has some money. He gave 1/9 of it to his son Ramu and 2/3rd of remaining to his daughter Geeta. He still has Rs. 200 left. How much money he had initially.
(a) 6400
(b) 200
(c) 675
(d) None of these
Ans: c
As he gave 1/9 to his son Ramu so he is left with 1 – (1/9) = 8/9. Now out of 8/9 he gives 2/3 to his daughter so he is left with 1/3 of 8/9. so we will solve as follows: 8/9 of 1/3 of x = 200. x = 200 x 9 x 3/8 = 675.
Q10: Find the fractional equivalent of 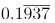
(a) 967/4995
(b) 968/4995
(c) 1968/4995
(d) None of these
Ans: b
As it is case of mixed recurring 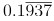 = (1937-1)/9990 = 968/4995.
= (1937-1)/9990 = 968/4995.
FAQs on Practice Questions: Decimals - CLAT
| 1. What are decimals and how are they different from whole numbers? |  |
| 2. How do you convert a fraction to a decimal? |  |
| 3. How can decimals be used in real-life situations? |  |
| 4. How can decimals be added or subtracted? |  |
| 5. How can decimals be multiplied or divided? |  |














