Practice Questions: Odd Man Out | Logical Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
Directions: For each question, identify the odd man out and choose the correct option.
Q1: 9, 16, 25, 36, 125, 169, 196, 225
(a) 36
(b) 196
(c) 169
(d) 125
Ans: (d)
All numbers except 125 are perfect squares.
53=125. Hence, the odd number is 125.
Q2: 121, 275, 396, 385, 891, 932
(a) 275
(b) 396
(c) 891
(d) 932
Ans: (d)
The middle digit is the sum of the other two digits.
121, 275, 396, 385, 891 all have a middle digit as the sum of the other two digits.
Hence, 932 is the correct answer.
Q3: 9, 12, 17, 20, 25, 28, 34, 36, 41
(a) 25
(b) 28
(c) 34
(d) 41
Ans: (c)
Here, the differences between two successive numbers from the beginning are 3, 5, 3, 5... 34 is the wrong term
because the next number should have a difference of 5, i.e., the number should be 33.
Hence, the odd number is 34.
Q4: 6, 12, 20, 30, 42, 54, 72, 90, 110
(a) 20
(b) 42
(c) 54
(d) 90
Ans: (c)
The numbers in the series are in order as shown:
2×3= 6,
3×4= 12,
4×5=20,
5×6=30,
6×7=42,
7×8=56,
8×9=72,
The numbers in the series are in order as shown above.
After 42,the next number in series should be 56instead of 54.
Hence the odd number is 54
Q5: Find the odd man out.
2, 5, 10, 17, 26, 37, 50, 64
(a) 50
(b) 37
(c) 26
(d) 64
Ans: (d)
The pattern is
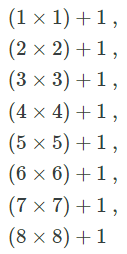
But, 64 is out of pattern
Q6: Find out the wrong number in the given sequence of numbers.
56, 72, 90, 110, 132, 150
(a) 72
(b) 110
(c) 132
(d) 150
Ans: (d)
The numbers are 7×8, 8×9, 9×10, 10×11, 11×12, 12×13
So, 150 is the wrong number.
Q7: Find the odd term from the given series of numbers ?
125, 127, 130, 135, 142, 153, 165 ?
(a) 153
(b) 165
(c) 142
(d) 127
Ans: (b)
From the beginning, the next term comes by adding prime numbers in a sequence of 2, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13... to its previous term. But 165 will not be in the series as it must be replaced by 166 since
Q8: Find out the wrong number in the given sequence of numbers.
582, 605, 588, 611, 634, 617, 600
(a) 634
(b) 611
(c) 605
(d) 600
Ans: (a)
Alternatively, 23 is added, and 17 is subtracted from the terms. So, 634 is the wrong number.
Q9: Find out the wrong number in the series.
7, 8, 18, 57, 228, 1165, 6996
(a) 8
(b) 18
(c) 228
(d) 1165
Ans: (c)
Let the given numbers be A, B, C, D, E, F, G. Then A,
A×1+1,
B×2+2,
C×3+3,
D×4+4,
E×5+5,
F×6+6 are the required numbers.
Clearly, 228 is wrong.
Q10: Find the odd man out.
253, 136, 352, 324, 631, 244
(a) 324
(b) 136
(c) 352
(d) 631
Ans: (a)
The sum of the digits in each number, except 324, is 10. But 324 is not in line with this pattern.
|
38 videos|144 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Practice Questions: Odd Man Out - Logical Reasoning for CLAT
| 1. What is the concept of "Odd Man Out" in the CLAT exam? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare for the "Odd Man Out" questions in the CLAT exam? |  |
| 3. Are there any specific strategies or techniques to solve "Odd Man Out" questions in the CLAT exam? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of an "Odd Man Out" question in the CLAT exam? |  |
| 5. How much time should I allocate to solve "Odd Man Out" questions in the CLAT exam? |  |
















