UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Himalayas- Northern Mountains | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
From 2020 to 2025, a total of six questions on Geography have been asked, with varying levels of difficulty: two easy (33.33%), two medium (33.33%), and two difficult (33.33%). Emphasis is generally placed on topics such as mountain ranges, continental drift, river systems, and regional hill formations.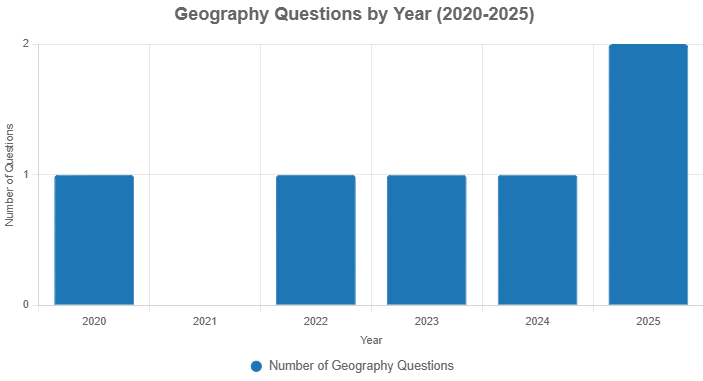 Q1. Consider the following countries:
Q1. Consider the following countries:
I. Bolivia
II. Brazil
III. Colombia
IV. Ecuador
V. Paraguay
VI. Venezuela
Andes mountains pass through how many of the above countries? (2025)
(a) Only two
(b) Only three
(c) Only four
(d) Only five
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The Andes mountain range, one of the longest and highest mountain ranges in the world, runs along the western edge of South America. To determine how many of the listed countries—Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Paraguay, and Venezuela—it passes through, let’s evaluate each country:
- Bolivia: The Andes run through western Bolivia, with significant features like the Altiplano and peaks such as Illimani. Bolivia is definitely included.
- Brazil: Brazil is primarily located in eastern South America, with its terrain dominated by the Amazon Basin and highlands. The Andes do not extend into Brazil, as they are confined to the western side of the continent.
- Colombia: The Andes enter northern South America and run through western Colombia, forming ranges like the Cordillera Occidental and Cordillera Central. Colombia is included.
- Ecuador: The Andes pass through central Ecuador, with notable peaks like Chimborazo and Cotopaxi. Ecuador is included.
- Paraguay: Paraguay lies east of the Andes, primarily consisting of lowlands and the Chaco region. The Andes do not extend into Paraguay.
- Venezuela: The Andes extend into western Venezuela, forming the Cordillera de Mérida, which includes peaks like Pico Bolívar. Venezuela is included.
Thus, the Andes pass through Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela. That’s four countries.
Q2. Which of the following are the evidences of the phenomenon of continental drift?
I. The belt of ancient rocks from Brazil coast matches with those from Western Africa.
II. The gold deposits of Ghana are derived from the Brazil plateau when the two continents lay side by side.
III. The Gondwana system of sediments from India is known to have its counterparts in six different landmasses of the Southern Hemisphere.
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (2025)
(a) I and III only
(b) I and II only
(c) I, II and III
(d) II and III only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
All three statements are classic evidences of continental drift by Wegener:
I: Similar rock formations found on the coasts of Brazil and Western Africa suggest they were once joined.
II: Similar mineral deposits (like gold in Ghana) found on both sides of the Atlantic imply a common origin.
III: The Gondwana system of sediments found in India has close geological counterparts in Africa, South America, Antarctica, and Australia.
Q3. With reference to the Himalayan rivers Joining the Ganga downstream of Prayagraj from West to East, which one of the following sequences is correct? (2024)
(a) Ghaghara — Gomati — Gandak — Kosi
(b) Gomati — Ghaghara — Gandak - Kosi
(c) Ghaghara — Gomati — Kosi - Gandak
(d) Gomati — Ghaghara — Kosi - Gandak
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Gomati joins Ganga first (westmost).
- Then Ghaghara, followed by Gandak.
- Kosi joins Ganga farthest to the east.
Thus, the correct west-to-east order is: Gomati → Ghaghara → Gandak → Kosi
Q4. Consider the following statements: (2023)
1. Amarkantak Hills are at the confluence of Vindhya and the Sahyadri Ranges.
2. Biligirirangan Hills constitute the easternmost part of Satpura Range.
3. Seshachalam Hills constitute the southernmost part of Western Ghats.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Statement 1: Amarkantak Hills are at the confluence of Vindhya and the Sahyadri Ranges (Incorrect)
Amarkantak Hills lie at the meeting point of the Vindhya and Satpura ranges, not the Sahyadri (Western Ghats).
Statement 2: Biligirirangan Hills constitute the easternmost part of Satpura Range (Incorrect)
Biligirirangan Hills are located in Karnataka and lie at the junction of the Eastern and Western Ghats, not the Satpura Range.
Statement 3: Seshachalam Hills constitute the southernmost part of Western Ghats (Incorrect)
Seshachalam Hills are part of the Eastern Ghats, located in Andhra Pradesh, not the Western Ghats.
Thus, the correct Answer is (d) None
Q5. Consider the following pairs: (2022)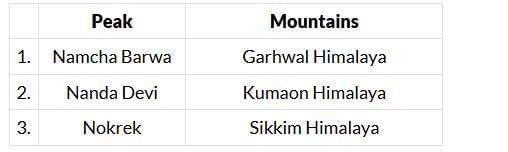
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
1. Namcha Barwa — Garhwal Himalaya (Incorrect)
- Namcha Barwa is located in Arunachal Pradesh, near the easternmost bend of the Himalayas.
- It belongs to the Eastern Himalayas, not the Garhwal Himalaya (which is in Uttarakhand).
2. Nanda Devi — Kumaon Himalaya (Correct)
Nanda Devi, the second-highest peak in India, lies in Uttarakhand, part of the Kumaon Himalaya range.
3. Nokrek — Sikkim Himalaya (Incorrect)
Nokrek Peak is in Meghalaya, part of the Garo Hills, and not associated with the Sikkim Himalaya.
Thus , correct answer is (b) 2 only
Note: No questions have been asked from this topic in the years 2021
Q6. Siachen Glacier is situated to the (2020)
(a) East of Aksai Chin
(b) East of Leh
(c) North of Gilgit
(d) North of Nubra Valley
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Siachen Glacier lies in the eastern Karakoram range in the northernmost part of India, within the Union Territory of Ladakh.
- It is located to the north of Nubra Valley, which serves as the access route to the glacier from the Indian side.
- It is not east of Aksai Chin (Aksai Chin lies to the east of Siachen).
- It is north-east of Leh, but not directly east.
- It is south-east of Gilgit, not north of it.
Thus, the correct answer is (d) North of Nubra Valley
|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Himalayas- Northern Mountains - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the major mountain ranges in Northern India? |  |
| 2. What is the average height of the Himalayan mountain range? |  |
| 3. How were the Himalayas formed? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the Himalayas? |  |
| 5. What are some popular tourist destinations in the Himalayas? |  |

















