Previous Year Questions 2025: Quantitative | Quantitative Techniques for CLAT PDF Download
Passage 1
According to the estimates of the World Inequality Report 2022, in India, men earn 82 percent of the labour income, whereas women earn 18 percent of it. A woman agriculture field labourer makes Rs. 88 per day lesser than her male counterpart, according to the Ministry of Agriculture’s data for 2020-21. While a man is paid Rs. 383 a day on an average, a woman makes a mere Rs. 294 a day. The gap in their daily wages is more than the cost of two kilograms of rice. This gap differs from State to State. Field laborers, for instance, make the most money in Kerala. While a man gets Rs. 789 per day, a woman is paid Rs. 537. While this is the highest amount paid to a woman labourer in a State, it is also Rs. 252 lesser than what her male counterpart was paid. As of 2020-21, Tamil Nadu has the highest gender wage gap among agriculture field laborers at 112 per cent. It is followed by Goa (61 percent) and Kerala. The wage gap is the lowest in Jharkhand and Gujarat (6 percent each), but the women laborers there get paid just Rs. 239 and Rs. 247 per day, respectively.
Men earn more than women across all forms of work, the gap greatest for the self-employed. In 2023, male self-employed workers earned 2.8 times that of women. In contrast, male regular wage workers earned 24% more than women and male casual workers earned 48% more. The gender gap in earnings is still a persistent phenomenon. However, there are differences in trends. The gender gap has increased for self-employed workers, while falling for regular wage workers. Male regular wage workers earned 34% more than women from 2019 to 2022, with the gap falling to 24% in 2023.
Q1: If the wages paid to men working in agricultural sector in Goa are Rs. 335 on an average, what is the amount of wages paid to women in the region?
(a) Rs. 204 approx.
(b) Rs. 330 approx.
(c) Rs. 239 approx.
(d) None of these
Ans: (a)
Sol: From the passage:
The gender wage gap in Goa is 61% , meaning men earn 61% more than women.
Let the wage of a woman be x. Then the wage of a man would be x + 0.61x = 1.61x.
Given that 1.61x = 335, solve for x: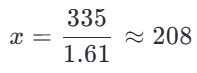
Closest approximation is Rs. 204 .
Q2: With reference to the information in Ques. 109 above, which region of the below mentioned states offers the least wages to the women workers in any sector?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Goa
(c) Kerala
(d) Jharkhand
Ans: (b)
Sol: From the passage:
Wages for women in various states:
- Jharkhand: Rs. 239
- Gujarat: Rs. 247
- Goa: From Question 109: ~Rs. 204
- Kerala: Rs. 537
The lowest among these is Goa at around Rs. 204.
Q3: In 2023, if the average annual income of female self-employed workers is Rs. 250, how much do male self-employed workers earn on an average?
(a) Rs. 550
(b) Rs. 673
(c) Rs. 700
(d) None of these
Ans: (c)
Sol: From the passage:
- Male self-employed workers earned 2.8 times that of women in 2023.
- So, if women earn Rs. 250, then men earn: 2.8 × 250 = 700
Q4: If a female casual worker earns Rs. 200 per hour, what is the hourly wage of a male casual worker, given that male casual workers earn 48% more than female casual workers?
(a) Rs. 480
(b) Rs. 296
(c) Rs. 248
(d) Cannot be determined
Ans: (b)
Sol: Given:
- Female hourly wage = Rs. 200
- Male earns 48% more: 200 + (0.48 × 200) = 200 + 96 = 296
Q5: Assume that in 2022, the earnings gap between male and female self-employed workers was 2.5 times. In 2023, the gap increased to 2.8 times. What is the percentage increase in the earnings gap for self-employed workers from 2022 to 2023?
(a) 12%
(b) 5%
(c) 4.8%
(d) 24%
Ans: (a)
Sol: Percentage increase: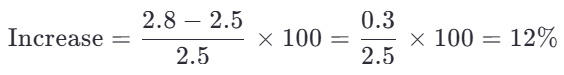
Q6: Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) The wage gap of Goa and Kerala state is less than Tamil Nadu
(b) The wage gap of Tamil Nadu is greater than Jharkhand and Gujarat
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c)
Sol: From the passage:
- Tamil Nadu has the highest gap (112%), followed by Goa (61%) and Kerala.
- Jharkhand and Gujarat have the lowest gaps (6%).
So:
- (A): Goa and Kerala have lower gaps than Tamil Nadu → True
- (B): Tamil Nadu's gap is greater than Jharkhand and Gujarat → True
Passage 2
Mr. Das is working in a construction company. He has a family, including his wife and a daughter. His total monthly income includes a salary of Rs. 9228/- and a 10% house rent allowance. Due to increasing inflation, he is keeping a home budget that accounts for the income and expenses of the household. Out of his total monthly income, he spends 25% on food expenses, 18% on paying the house-rent, 9% on entertainment, 23% on the education of his child, 13% on medical expenses, and he saves 12% of his total monthly income.
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
Q7: How much money does Mr. Das pay as the house-rent?
(a) Rs. 1827 /-
(b) Rs. 1661 /-
(c) Rs. 1783 /-
(d) Rs. 1935 /-
Ans: (a)
Sol: Mr. Das’s salary = Rs. 9228
House rent allowance = 10% of salary = 0.10 × 9228 = 922.8
Total monthly income = Salary + HRA = 9228 + 922.8 = 10150.8
He spends 18% of total income on house rent: 0.18 × 10150.8 = 1827.14 ≈ 1827
Q8: If Mr. Das gets 12% annual interest on the savings and he wishes to save Rs. 30,000/- in two years period, how much extra should he save in the next year?
(a) Rs. 1200/-
(b) Rs. 1300/-
(c) Rs. 1400/-
(d) There is no need for saving
Ans: (d)
Sol: He saves 12% of his income: 0.12 × 10150.8 = 1218.10 per month
Yearly savings = 1218.10 × 12 = 14,617.2
With 12% annual interest over 2 years, total savings with compounding will exceed Rs. 30,000.
Q9: Which of the following is true regarding the home budget of Mr. Das?
(a) The total amount spent on house-rent, entertainment and education is greater than the total amount spent on food expenses, medical expenses and savings
(b) The total amount spent on entertainment, medical expenses and education is equal to the total amount spent on house-rent, food expenses and savings
(c) The total amount spent on savings, medical expenses and education is less than the total amount spent on house-rent, food expenses and entertainment
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c)
Sol: Breakdown:
- House rent (18%) + Food (25%) + Entertainment (9%) = 52%
- Savings (12%) + Medical (13%) + Education (23%) = 48%
Q10: How much money remains for other expenses after the house-rent and savings?
(a) Rs. 7061/-
(b) Rs. 7601/-
(c) Rs. 7106/-
(d) Rs. 7016/-
Ans: (c)
Sol: Total income = Rs. 10150.8
House rent = 18% = Rs. 1827
Savings = 12% = Rs. 1218.10
Remaining = 10150.8−1827−1218.10=7105.7≈7106
Q11: If the expenditure on food and entertainment is increased by 10% due to inflation in prices, what will be the new percentage of savings in the same monthly salary?
(a) 8.4%
(b) 8.6%
(c) 8.8%
(d) 8.2%
Ans: (b)
Sol: Initial:
- Food = 25% = Rs. 2537.7
- Entertainment = 9% = Rs. 913.6
- Total = Rs. 3451.3
After 10% increase:
- New food expense = 2537.7 × 1.10 = 2791.5
- New entertainment = 913.6 × 1.10 = 1004.96
- New total = 2791.5 + 1004.96 = 3796.46
New total expenditure increases by 3796.46 − 3451.3 = 345.16
So, savings reduce by this amount:
- Original savings = Rs. 1218.10
- New savings = 1218.10−345.16=872.94
New % of savings: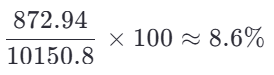
Q12: How much total money has he spent on food and entertainment?
(a) Rs. 3541/-
(b) Rs. 3461/-
(c) Rs. 3371/-
(d) None of the above
Ans: (d)
Sol: As calculated earlier:
- Food = 25% of Rs. 10150.8 = Rs. 2537.7
- Entertainment = 9% = Rs. 913.6
- Total = 2537.7 + 913.6 = 3451.3
None of the options match this value exactly.
|
51 videos|172 docs|73 tests
|
















