Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Previous Year Questions - Control and Coordination
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: The plant hormone whose concentration stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light is: (1 Mark)
(a) Cytokinins
(b) Gibberellins
(c) Adrenaline
(d) Auxins
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Auxins
Explanation:
- Auxins are plant hormones made at the shoot tip.
- When light shines on one side, auxins move to the shaded side of the shoot.
- This makes cells on the shaded side grow longer, causing the shoot to bend towards light.
- This movement is called phototropism, which helps plants get more sunlight.
Q2: The plant hormone present in greater concentration in the areas of rapidly dividing cells is: (1 Mark)
(a) Auxin
(b) Cytokinins
(c) Gibberellins
(d) Abscisic acid
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Cytokinins
Explanation:
Cytokinins are plant hormones that promote cell division.
They are found in higher amounts in areas where cells divide quickly, like fruits and seeds.
This helps in the growth of new cells in these parts of the plant.
Q3: Question consist of two statements are given — one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below. (1 Mark)
Assertion (a): In our actions of writing or talking, our nervous system communicates with the muscles.
Reason (R): Cranial nerves and spinal nerves form the peripheral nervous system.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
- Assertion: Writing and talking are voluntary actions where the brain sends signals to muscles via the nervous system, which is true.
- Reason: The peripheral nervous system includes cranial nerves (from the brain) and spinal nerves (from the spinal cord), which is true.
- However, the reason does not fully explain how the nervous system communicates with muscles, as it only describes the components of the peripheral nervous system.
- The communication involves the brain, spinal cord, and nerves working together, not just the peripheral nervous system.
Q4: The growth of the pollen tubes towards ovules is an example of: (1 Mark)
(a) Phototropism
(b) Hydrotropism
(c) Geotropism
(d) Chemotropism
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Chemotropism
Explanation:
Chemotropism is the growth of a plant part towards a chemical stimulus.
Pollen tubes grow towards ovules due to chemicals released by the ovule.
This helps in plant reproduction by guiding the pollen to the ovule for fertilization.
Q5: The plant hormones promoting rapid cell division in seeds and wilting of leaves respectively are: (1 Mark)
(a) Auxins and Abscisic acid
(b) Cytokinins and Abscisic acid
(c) Gibberellins and Auxins
(d) Abscisic acid and Gibberellins
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Cytokinins and Abscisic acid
Explanation:
Cytokinins promote rapid cell division in areas like seeds and fruits.
Abscisic acid inhibits growth and causes leaves to wilt, especially during stress like drought.
These hormones help plants grow or survive tough conditions.
Q6: Electrical impulse travels in a neuron from: (1 Mark)
(a) Nerve ending → Axon → Cell body → Dendrite
(b) Dendrite → Cell body → Axon → Nerve ending
(c) Cell body → Dendrite → Axon → Nerve ending
(d) Dendrite → Axon → Nerve ending → Cell body
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Dendrite → Cell body → Axon → Nerve ending
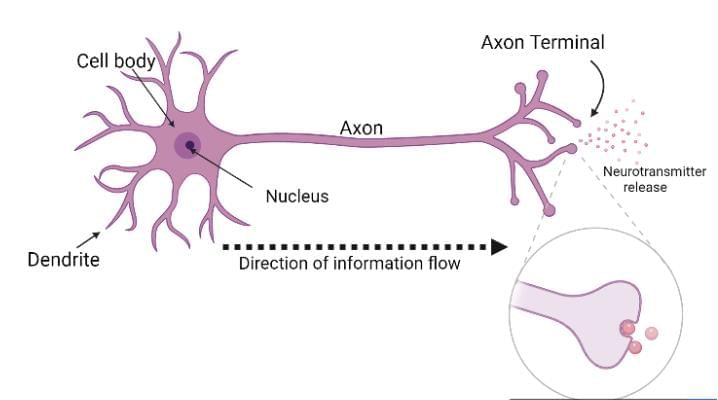
A neuron receives a signal at the dendrite from another neuron or the environment.
The signal moves to the cell body, which processes it.
It then travels along the axon to the nerve ending.
At the nerve ending, the signal triggers chemicals to pass to the next neuron or muscle.
Q7: Study the given diagram and write the type of movement exhibited by: (2 Marks)
(a) Root, and
(b) Shoot, mentioning the stimulus in each case.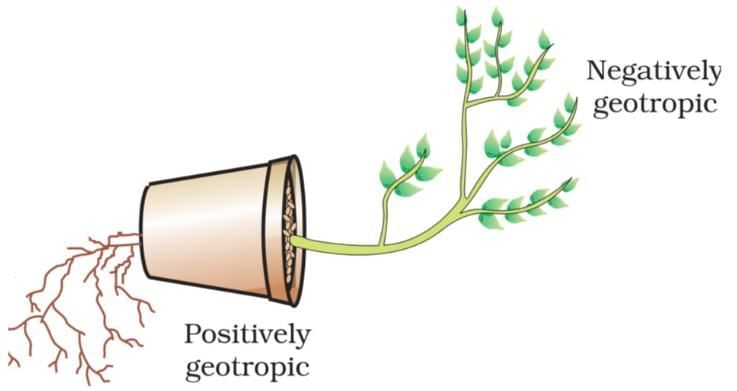
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) Root: Positive Geotropism; Stimulus: Gravity
(b) Shoot: Positive Phototropism; Stimulus: Light
Explanation:
Root (Positive Geotropism):
Roots grow downward due to gravity, called positive geotropism.
Auxins collect on the lower side, slowing growth there, so the root bends downward.
This helps the plant anchor in soil and reach water.
Shoot (Positive Phototropism):
Shoots grow towards light, called positive phototropism.
Auxins move to the shaded side, making cells grow longer there, so the shoot bends towards light.
This helps the plant get more sunlight for photosynthesis.
Q8: A person is making a list to purchase few things from a nearby market. Explain how the fore-brain plays an important role in performing this activity. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
The fore-brain is the thinking part of the brain.
It receives information from senses, like seeing what’s missing in the house.
It uses memory to recall what items are needed or available in the market.
It helps decide which items to write down and controls the hand to write the list.
Q9: (a) How is brain protected in our body?
(b) A doctor finds in one of his patients that he is not maintaining a proper posture and balance of his body. State the region of brain and also the part of brain which is responsible for it. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) The brain is protected by the skull and cerebrospinal fluid.
(b) Region: Hind-brain; Part: Cerebellum
Explanation:
(a) Brain Protection:
The skull is a hard, bony structure that shields the brain from physical injury.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounds the brain, acting like a cushion to absorb shocks.
(b) Posture and Balance:
The hind-brain controls many automatic functions.
The cerebellum, a part of the hind-brain, maintains posture and balance.
It coordinates muscles to ensure steady and smooth movements.
Q10: Plants have neither a nervous system nor muscles, even then they respond to stimuli. For example, the leaves of chhui-mui (touch-me-not) plant when touched begin to fold up and droop.
(a) How is the information communicated in "touch-me-not" plants?
(b) What enables the plant cells to bring out the observable response?
(c) Differentiate the movement mentioned above from the movement of tendrils in a pea plant. (3 Marks)
Ans: (a)
Plants like chhui-mui (Mimosa pudica) do not have a nervous system, but when touched, the stimulus is passed from cell to cell through electrical-chemical means.
This is how information about the stimulus is transmitted in the plant body.
(b)
The signal causes a change in water movement in the plant cells.
As water leaves the cells, they lose their turgidity (swollen state).
The sudden loss of turgidity makes the leaves fold up and droop, which is the visible response.
(c)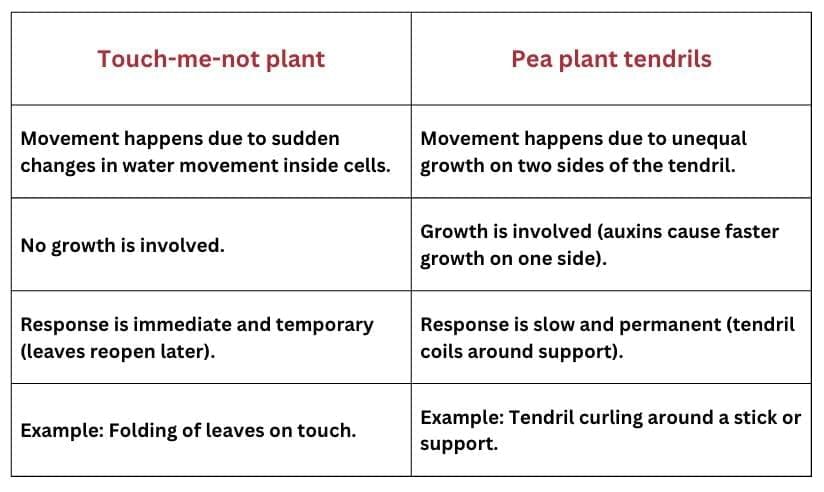
Q11: A hormone 'X' is secreted in blood when a person is under scary situation. (3 Marks)
(a) Identify the hormone 'X' and the gland that secretes it.
(b) Explain its role in dealing with scary or emergency situations.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
(a) Hormone 'X': Adrenaline; Gland: Adrenal glands
(b) Adrenaline prepares the body for quick action in emergencies.
Explanation:
(a) Hormone and Gland:
Hormone 'X' is adrenaline.
It is secreted by the adrenal glands, located above the kidneys.
(b) Role in Scary Situations:
Adrenaline is called the emergency hormone.
It increases heart rate to supply more oxygen to muscles.
It speeds up breathing to provide more oxygen.
It diverts blood from the skin and digestive system to muscles, preparing for "fight or flight."
Q12: (a) Define hormone.
(b) "Hormones should be secreted in precise quantities. We have a feedback mechanism through which this is done." With the help of an example justify the statement. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate body functions.
(b) Feedback mechanism ensures correct hormone levels, e.g., insulin regulation.
Explanation:
(a) Hormone Definition:
Hormones are chemicals made by endocrine glands.
They travel through blood to specific organs.
They control functions like growth and metabolism.
(b) Feedback Mechanism (Insulin Example):
Hormones must be released in the right amount to avoid health issues.
Insulin, from the pancreas, lowers blood sugar after eating.
If sugar levels rise, the pancreas releases more insulin.
If sugar levels fall, insulin release decreases, maintaining balance.
Q13: (a) What is meant by the reflex arc? Where are they formed in the human body?
(b) Why have reflex arcs evolved in animals? (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Reflex arc:
A reflex arc is the pathway through which nerve impulses pass during a reflex action.
It consists of receptor → sensory neuron → spinal cord → motor neuron → effector (muscle/gland).
Reflex arcs are formed in the spinal cord of the human body.
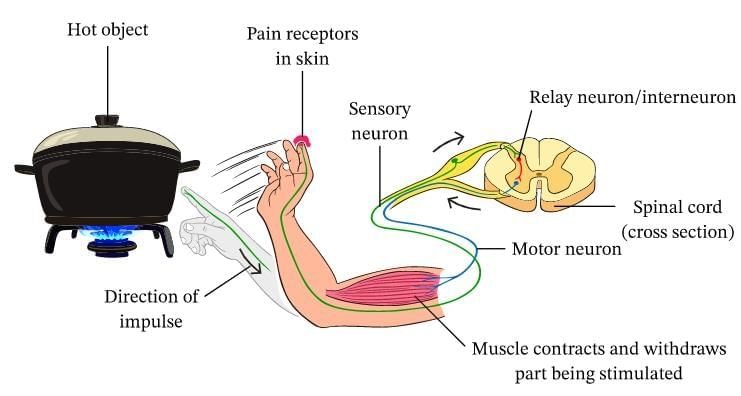
Reflex arcs have evolved in animals:
Reflex arcs have evolved because they enable quick, automatic, and involuntary responses to harmful stimuli.
This helps protect the body from injury without waiting for instructions from the brain.
Example: Immediately withdrawing hand from a hot object.
Q14: State two limitations of electrical impulses in multicellular organisms. Why is chemical communication better than electrical impulses as a means of communication between cells in multicellular organisms? (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In multicellular organisms, electrical impulses have certain limitations:
The electrical impulse will reach only those cells that are connected by the nervous tissue, not every cell of the body.
After an electrical impulse is generated in a cell and transmitted, the cell needs some time to reset before it can generate another impulse.
Because of these limitations, electrical impulses alone cannot perform all communication functions.
Hence, chemical communication through hormones is better because:
Hormones are secreted directly into the blood and can reach all cells of the body, not just nerve-connected ones.
The effect of hormones, though slower, is widespread and longer lasting compared to short-lived electrical impulses.
Q15: When a seed germinates, the root grows downwards and a small shoot grows upward. This shoot is known as: (1 Mark)
(a) Radicle
(b) Stem
(c) Cotyledon
(d) Plumule
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Plumule
Explanation:
When a seed germinates:
The root grows downward due to geotropism → called the radicle.
The small shoot grows upward due to phototropism → called the plumule.
Q16: (a) Analyse the given situations and interpret the possible reasons for each: (5 Marks)
(i) Iodine deficiency in diet increases the possibility of a disease of swollen neck in a person.
(ii) Some people in the population may have very short heights (dwarfs).
(iii) Thick facial hairs develop in boys at the age of 10–12 years.
(b) Explain two reasons that necessitate the need for chemical communication in multicellular organisms.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
(a) Situations and Reasons:
(i) Iodine deficiency in diet causes goitre (swollen neck) because iodine is necessary for the production of thyroxin by the thyroid gland.
(ii) Some people have very short heights (dwarfs) because of deficiency of growth hormone, secreted by the pituitary gland.
(iii) Thick facial hairs develop in boys around age 10–12 due to secretion of testosterone hormone by the testes during puberty.
(b) Need for Chemical Communication:
Electrical impulses cannot reach every cell in the body — hormones (chemical messengers) can reach all cells through blood.
The effect of hormones is longer-lasting, whereas electrical impulses are short-lived.
Q17: A person, while climbing up a rocky hill, comes into a panic state and fear. His body starts reacting in a "fight-or-flight" condition to adjust to the dangerous and stressful situation.
(a) (i) Name the hormone secreted in the blood of the person in this situation. (2 Marks)
OR
(a) (ii) Name the source gland of the hormone secreted in this condition. (2 Marks)
(b) State any two responses in the body of the person as a result of the secretion of this hormone. (1 Mark)
(c) How does the action of the chemical signal in terms of hormones differ from the electrical impulses via nerve cells? (1 Mark)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) (i) The hormone secreted in this condition is Adrenaline.
OR
(a) (ii) The source gland is the Adrenal glands (located above the kidneys).
(b) Two responses in the body due to adrenaline secretion:
Increases heartbeat and blood pressure, supplying more oxygen to muscles.
Increases breathing rateand diverts more blood to skeletal muscles, preparing the body for “fight-or-flight”.
(c) Difference between hormonal action and electrical impulses:

Q18: In life there are certain changes in the environment called 'stimuli' to which we respond appropriately. Touching a flame suddenly is a dangerous situation for us. One way is to think consciously about the possibility of burning and then moving the hand. But our body has been designed in such a way that we save ourself from such situations immediately.
(i) Name the action by which we protect ourself in the situation mentioned above and define it. (1 Mark)
(ii) Write the role of (a) motor and (b) relay neuron. (1 Mark)
(iii) (a) What are the two types of nervous system in the human body? Name the components of each of them. (2 Mark)
OR
(iii) (b) Which part of the human brain is responsible for: (1 Mark)
(a) thinking
(b) picking up a pencil
(c) controlling blood pressure
(d) controlling hunger
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Action: Reflex action
Definition: Reflex action is an automatic, immediate, and involuntary response to a stimulus without the involvement of the conscious part of the brain.
Example: Withdrawing the hand instantly when touching a hot flame.
(ii) Role of neurons:
(a) Motor neuron: It carries the message from the spinal cord to the effector organ (like muscles or glands) to produce a response.
(b) Relay neuron (interneuron): It connects the sensory neuron to the motor neuron inside the spinal cord and helps in transmitting the impulse.
(iii) (a) Types of Nervous System and Components:
Central Nervous System (CNS):
Components: Brain and spinal cord
Function: Processes information and controls responses
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
Components: Nerves arising from the brain (cranial nerves) and spinal cord (spinal nerves)
Function: Connects CNS to the rest of the body
OR
(iii) (b) Brain Parts:
(a) Thinking → Cerebrum
(b) Picking up a pencil → Cerebellum
(c) Controlling blood pressure → Medulla oblongata
(d) Controlling hunger → Separate part of fore-brain
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: In a nerve cell, the site where the electrical impulse is converted into a chemical signal is known as: (2024)
(a) Axon
(b) Dendrites
(c) Neuromuscular junction
(d) Cell body
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
This is the place where the electrical impulse traveling along a nerve cell is converted into a chemical signal to communicate with a muscle cell. At this junction, neurotransmitters are released, allowing the nerve cell to signal the muscle to contract.
Q2: (A) How is the movement of the leaves of a sensitive plant different from the downward movement of the roots? (2024)
OR
(B) There is a hormone which regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in our body. Name the hormone and the gland which secretes it. Why is it important for us to have iodised salt in our diet?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) 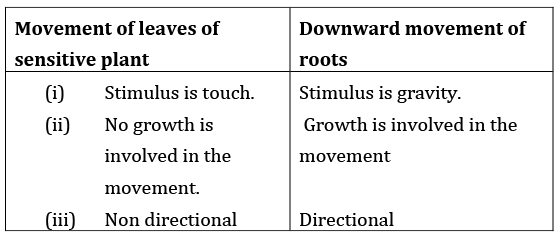 OR
OR
(B)
- The hormone that regulates carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism is thyroxine.
- It is secreted by the thyroid gland.
- Iodine is crucial for the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine.
- A lack of iodine can lead to a condition called goitre, which causes swelling in the neck.
Q3: Define reflex action. With the help of a flow chart show the path of a reflex action such as sneezing. (2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Reflex action is a quick and automatic response to a stimulus in the environment. An example of this is sneezing.
The process of a reflex action can be summarised as follows:
- Stimulus: An irritant, such as dust, enters the nose.
- Receptors: Nerve endings in the nasal passages detect the irritant.
- Signal Transmission: A sensory neuron sends a signal to the spinal cord.
- Reflex Arc: The signal is processed in the spinal cord, and a response is sent through a motor neuron.
- Effector: The muscles in the diaphragm and chest contract, causing a sneeze.
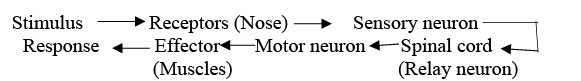
Q4: Select out of the following a gland which does NOT occur as a pair in the human body : (2024)
(a) Pituitary
(b) Ovary
(c) Testis
(d) Adrenal
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The pituitary gland is a single gland located at the base of the brain.
- It is often called the "master gland" because it regulates many other hormone glands in the body.
- In contrast, the ovaries, testes, and adrenal glands exist in pairs, one on each side of the body.
Q5: (a) (i) Distinguish between hormonal co-ordination in plants and animals. (2024)
(ii) Which part of the brain is responsible for —
(1) Intelligence
(2) riding a bicycle
(3) vomiting
(4) controlling hunger
(iii) How is the brain and spinal cord protected against mechanical injuries?
OR
(b) (i) What are tropic movements? Give an example of a plant hormone that (1) inhibits growth and (2) promotes cell division.
(ii) Explain the directional movement of a tendril in a pea plant in response to touch. Name the hormone responsible for this movement.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i)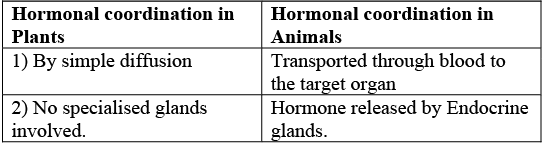
(ii) (1) Cerebrum/forebrain,
(2) cerebellum i.e part of hindbrain
(3) medulla in hindbrain
(4) Separate part of forebrain.
(iii) Brain – Bony box/skull/cranium/fluid filled balloon in skull, Spinal cord – Backbone/Vertebral column.
OR
(b) (i) Plant growth movements in response to stimuli in a particular direction/directional movements due to light, gravity etc.
(1) Plant growth inhibitor: Abscisic Acid
(2) Promotes cell division: Cytokinins
(ii) When the tendrils come in contact with any support, auxins move away from the point of contact of the support. More growth occurs on the side away from the support. As a result, unequal growth occurs on its two sides and thus tendrils coil/ circle around the support.
Auxins
Q6: Select from the following a plant hormone which promotes cell division. (CBSE 2024)
(a) Gibberellins
(b) Auxins
(c) Abscisic Acid
(d) Cytokinins
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Cytokinins are plant hormones that promote cell division.
- They stimulate the growth of shoots and leaves.
- Cytokinins play a vital role in:
- Fruit development
- Delaying aging in plant tissues
Q7: A plant growth inhibitor hormone that causes wilting of leaves is called: (2024)
(a) Auxin
(b) Cytokinin
(c) Abscisic acid
(d) Gibberellin
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Abscisic acid is a plant hormone that inhibits growth and plays a crucial role in how plants respond to stress, such as drought. Its main effects include:
- Causing the stomata to close, which reduces water loss.
- Leading to the wilting of leaves when the plant is under stress.
This hormone is essential for helping plants manage their resources during challenging conditions.
Q8: Where are auxins synthesized? How do they promote phototropism? (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Auxins are synthesized primarily at the shoot tip and root tip of plants.
They promote phototropism through the following process:
- When light shines on one side of the plant, auxins move towards the shady side.
- This increased concentration of auxins causes the cells on the shady side to grow longer.
- As a result, the plant bends towards the light.
Q9: (a) (i) Define a reflex arc. Why have reflex arcs evolved in animals? Trace the sequence of events which occur, when you suddenly touch a hot object. (2024)
(ii) Name the part of the nervous system which helps in communication between the central nervous system and other parts of the body. What are the two components of this system?
OR
(b) (i) Leaves of ‘chhui-mui’ plant begin to fold up and droop in response to a stimulus. Name the stimulus and write the cause for such a rapid movement. Is there any growth involved in the movement?
(ii) Define geotropism in plants. What is meant by positive and negative geotropism? Give one example of each type.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) (i)
- Reflex arc: The pathway through which impulses travel during a reflex action.
- Evolution: Reflex arcs have developed in animals because the brain's thinking processes are not quick enough for immediate responses, which helps avoid injury.
- Sequence of events when touching a hot object:
- Stimulus detected by receptors in the skin.
- Impulse travels through the sensory neuron to the spinal cord.
- Relay neuron transmits the impulse to the motor neuron.
- Motor neuron sends a message to the muscle, causing a quick withdrawal from the hot object.
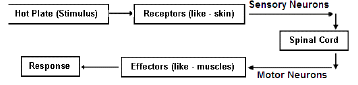
(ii) Peripheral Nervous System Components : Cranial Nerves; Spinal Nerves
OR
(b) (i)
- Stimulus: Touch
- The leaves fold due to changes in water content.
- No growth is involved in this rapid movement.
(ii) Geotropism: The growth of a plant part in response to gravity.
- Positive geotropism: Movement towards gravity (e.g., roots growing downwards).
- Negative geotropism: Movement away from gravity (e.g., shoots growing upwards).
Q10: The correct sequence of events when someone’s hand touches a hot object unconsciously: (2024)
(a) Receptors in skin → Motor neuron → Relay neuron → Sensory neuron → Effector muscle in arm
(b) Receptors in skin → Relay neuron → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Effector muscle in arm
(c) Receptors in skin → Sensory neuron → Relay neuron → Motor neuron → Effector muscle in arm
(d) Receptors in skin → Sensory neuron → Effector muscle in arm → Motor neuron → Relay neuron
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Receptors in skin → Sensory neuron → Relay neuron → Motor neuron → Effector muscle in arm.
When you touch something hot, the receptors in your skin detect the heat and send a signal through sensory neurons to the relay neurons in the spinal cord. Then, relay neurons send the signal to motor neurons, which activate the effector muscles in your arm to pull away quickly, helping you avoid injury.
Q11: Sense organ in which olfactory receptors are present is: (2024)
(a) Nose
(b) Skin
(c) Tongue
(d) Inner ear
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Olfactory receptors, which are responsible for the sense of smell, are located in the nasal cavity of the nose. When you inhale, these receptors detect different scents and send signals to the brain, allowing you to identify various smells.
Q12: Taking the example of any two animal hormones along with their gland of secretion, explain how these hormones help (i) in growth and development and (ii) regulate metabolism, in the body. (2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Growth and Development:
- Growth Hormone: Secreted by the pituitary gland.
- Stimulates growth in all organs, promoting overall development.
(ii) Regulation of Metabolism:
- Thyroxin: Produced by the thyroid gland.
- Regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, essential for healthy growth.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q1: The sensory nerve of a reflex arc carries information from the receptor cells to the (2023)(a) spinal cord
(b) brain
(c) muscles of the effector organ
(d) bones of the receptor organ
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Sol: A Reflex arc is the pathway that nerve impulses follow during a reflex action. It involves:
- Information travelling from receptor organs (like the skin) to the spinal cord.
- Then, signals are sent from the spinal cord to effector organs (like muscles) to produce a response.
Q2: Name the part of the brain which is responsible for the following actions: (2023)
(i) Maintaining posture and balance
(ii) Beating of heart
(iii) Thinking
(iv) Blood pressure
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Cerebellum: Responsible for maintaining posture and balance.
(ii) Medulla oblongata: Controls the beating of the heart.
(iii) Cerebrum: Involved in thinking processes.
(iv) Medulla oblongata: Regulates blood pressure.
Q3: (a) How are the brain and spinal cord protected in human beings?
(b) State one main function of
(i) Medulla and
(ii) Cerebellum. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Brain and spinal cord are protected by skeleton- brain by the cranium and spinal cord by vertebral column,
(b) (i) Medulla - It controls involuntary actions like heart beat, respiration, etc.
(ii) Cerebellum - It maintains posture and balance of body
Q4: (a) Where are auxins synthesised in a plant?
(b) Which organ of the plant shows:
(i) Positive phototropism
(ii) Negative geotropism
(iii) Positive hydrotropism (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Auxin is synthesised at tip of the stem apices or shoots.
(i) Shoots
(ii) Shoots
(iii) Roots (bend towards water)
Q5: Name a plant hormone responsible for bending of a shoot of a plant when it is exposed to unidirectional light. How does it promote phototropism? (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Auxin is responsible for bending of a shoot of a plant when it is exposed to unidirectional light.
- In the presence of sunlight, the auxin present in the stem starts accumulating in the region away from sunlight, due to which the concentration of auxin in the region of the stem increases, resulting in bending of a shoot of a plant when it is exposed to unidirectional light.
- Thus, auxin promotes phototropism that is the regulation of physiology or development in response to day length.
Q6: Select from the following the correct statement about tropic movement in plants.
(a) It is due to the stimulus of touch and temperature.
(b) It does not depend upon the direction of stimulus received.
(c) It is observed only in roots and not in stem.
(d) It is a growth-related movement. (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Tropic movements in plants are growth-related movements that occur in response to specific directional stimuli, such as light, gravity, water, or chemicals.
- These movements are typically slow and involve growth in a particular direction, either towards (positive tropism) or away from (negative tropism) the stimulus.
- Therefore, the correct answer is (d) It is a growth-related movement.
Q7: (A) Write the role of insulin in regulating blood sugar levels in the human body. Mention the disease caused due to it.
(B) How is the timing and the amount of release of insulin in the blood regulated? (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A)
- Glucose enters the blood stream as soon as meals containing carbohydrates is digested by the body.
- As a result, the body's blood glucose levels rise.
- In order to direct all of the body's cells to take in the glucose, the pancreas releases chemical signals in the form of insulin.
- The majority of this glucose is consumed by the cells as energy.
- The liver and muscle cells take the extra glucose in the bloodstream and convert it to glycogen for later usage.
- In the end, insulin secretion reduces blood sugar levels.
- Diabetes is either caused due to the insufficient production of insulin by the pancreas or it may occur if the cells of the body are not effectively responding to the insulin produced.
- Hormones are chemicals that our body secretes in a precise quantity and at a certain time.
- The release of hormones and the timing of their release are controlled by particular regulatory centres in our bodies.
- For instance:
- Regulation of insulin release - the pancreas secretes insulin, which regulates blood glucose levels.
- The higher blood glucose concentration affects how much insulin is produced.
- When blood glucose levels are really high, the pancreas releases more insulin.
Previous Year Questions 2020
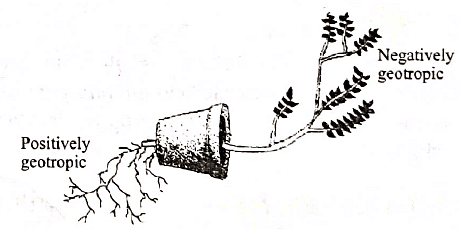
Q1: Define geotropism. Draw a labelled diagram of a plant showing the geotropic movement of its parts. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Geotropism is the growth of plant parts in response to gravity. It can be classified into two types:
- Positive geotropism: This occurs when roots grow downwards, following the direction of gravity.
- Negative geotropism: This happens when shoots grow upwards, against the pull of gravity.
Q2: A squirrel is in a scary situation. Its body has to prepare for either fighting or running away. State the immediate changes that take place in its body so that the squirrel is able to either fight or run. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: When a squirrel finds itself in a scary situation, its body undergoes several immediate changes to prepare for either fighting or running away. These changes are triggered by the nervous system, which stimulates the adrenal glands to release more adrenaline into the bloodstream. The key changes include:
- Increased heartbeat: This helps pump more blood to the muscles.
- Faster breathing: This increases oxygen intake.
- Enhanced blood flow: Blood is redirected to the muscles, improving their performance.
- More glucose in the blood: The liver releases stored glucose, providing extra energy.
These responses collectively prepare the squirrel's body for quick action, whether it needs to fight or flee.
Q3: Why is chemical communication better than electrical impulses as a means of communication between cells in a multicellular organisms? (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- In animals, the message communicated in the form of nerve impulses, from receptors to central nervous system and from effectors is very quick.
- But nerve impulses can reach only those animal cells which are connected by the nervous tissue.
- These cells after generation and transmission of nerve impulses, take some time to reset their mechanism before a new impulse is generated and transmitted.
- It means, cells cannot continuously generate and transmit electrical impulses.
- This is the reason most multicellular organisms use another means of communication called chemical communication.
- In chemical communication, information spreads out throughout the body by blood and its effects lasts longer.
- Chemical communication is however slow, but it can reach all the cells of body regardless of nervous connections.
Q4: A cheetah, on seeing a prey moves towards him at a very high speed. What causes the movement of his muscles? How does the chemistry of cellular components of muscles change during this event? (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The cheetah's movement towards its prey is initiated by its ability to sense the prey through photoreceptors. This information is transmitted to the central nervous system via neurons. The hormonal system also plays a crucial role in this process.
When the cheetah spots its prey, the adrenal glands release the hormone adrenaline into the bloodstream. This triggers several physiological responses:
- Increased heart rate: This helps pump more blood throughout the body.
- Enhanced breathing: This increases oxygen intake.
- Improved blood flow: Blood is directed to the leg muscles, providing them with the necessary energy.
- Release of glucose: The liver releases stored glucose into the bloodstream, supplying energy for rapid movement.
These combined actions of adrenaline generate a significant amount of energy, enabling the cheetah to run at high speeds.
Q5: What constitutes the central and peripheral nervous systems? How are the components of central nervous system protected? Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury? (2020 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Central nervous system consists of brain and spinal cord. It contains centres for controlling various activities of the body. Peripheral nervous system consists of cranial nerves and spinal nerves. Components of the central nervous system are protected by:
(i) Brain is contained within the skull while the spinal cord is encircled by a series of vertebrae.
(ii) Meninges are a succession of tissue layers that reside within these bony structures.
(iii) Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colourless, slightly alkaline fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord that protects from infections.
The following signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury:
- Reflex action
- Impulses from various body parts will not be conducted to brain.
- Message from brain will not be conducted to various organs of the body.
Q6: (a) Name the hormone secreted by (i) Pituitary, and (ii) Thyroid stating one main function of each. Name the disorder a person is likely to suffer from due to the deficiency of the above mentioned hormones.
(b) How is the timing and amount of hormone released regulated ? Explain with an example. (2020 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) (i)
- Pituitary secretes hormones GH, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, PRL, MSH, oxytocin and vasopressin.
- Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropic hormone controls the overall development of body, muscles, bones and tissues.
- Disorder related to the thyroid gland: Goitre (enlarged thyroid gland) can occur due to inadequate dietary intake of iodine which results in low level of thyroid hormones (since iodine is essential to make thyroid hormones).
- Low levels of thyroid hormones stimulate the pituitary gland to secrete more TSH, which causes thyroid gland enlargement.
- Hyposecretion of growth hormone (GH) during growth years results in dwarfism.
- This could happen due to the hyperactivity of the pituitary gland.
- The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin.
- Thyroxine and triiodothyronine maintain the basal metabolic rate (BMR) of the body by regulating the rate of oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins and production of energy in our body.
- They promote growth of body tissues and development of mental faculties.
- Both the timing and amount of hormone released are regulated by feedback mechanism.
- For example, the pancreas is involved in the secretion and release of the hormone insulin when the positive feedback is signalled by the increased blood glucose level.
- The insulin sequesters the glucose in adipose tissue and liver cells as glucose and fats respectively.
- When the blood glucose level decreases, the negative feedback will signal the pancreas to stop the secretion of insulin.
Q7: (a) Name one organ each where growth hormone is synthesized in man and plant.
(b) List the sequence of events that occur when a plant is exposed to unidirectional light, leading to bending of a growing shoot. Also name the hormone and the type of movement. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) In humans, growth hormone is synthesized in the pituitary gland. In plants, growth hormone is synthesized in the apical meristem.
(b) When a plant is exposed to unidirectional light, the following sequence of events occur leading to bending of a growing shoot:
1. Photoreceptors in the shoot tip detect the direction and intensity of light.
2. Auxin, a plant hormone, is produced in higher concentrations on the shaded side of the shoot tip.
3. The higher concentration of auxin promotes cell elongation on the shaded side, causing the shoot to bend towards the light source.
4. The bending of the shoot towards the light is known as phototropism.
5. The bending helps the plant optimize its exposure to light, allowing for efficient photosynthesis.
Q8: Write in tabular form the location and function of the hormones secreted by each of the following glands present in the human body: (A) Pituitary gland
(B) Thyroid gland
(C) Pancreas (CBSE 2020)
Ans: (A) Pituitary Gland
- Location: At the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain.
- Function: Secretes growth hormone, which regulates the growth and development of the body.
(B) Thyroid Gland
- Location: In the neck region.
- Function: Secretes thyroxine hormone, which regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in the body.
(C) Pancreas
- Location: Just below the stomach.
- Function: Secretes insulin hormone, which lowers the blood sugar level.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q1: What is a nerve impulse? State the direction followed by a nerve impulse while travelling in the body of an organism. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A nerve impulse is a gradual change in the nerve fibre's membrane that occurs after it is stimulated. This impulse travels in the following direction:
- From the dendrite to the cell body
- Along the axon to its end
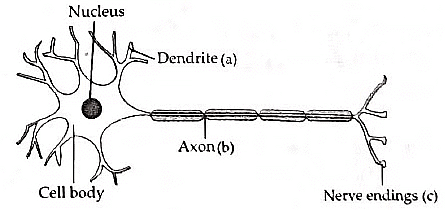
Q2: Draw a diagram of neuron and name and label the part
(a) where information is acquired,
(b) through which information travels as an electric impulse, and
(c) where the electric impulse must be converted into a chemical signal for onward transmission. (2019 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Diagrammatic representation of a neuron:
(a) The part where information is acquired is the dendrite.
(b) Information travels as an electrical impulse through the axon.
(c) The electric impulse is converted into a chemical signal at the synapse.
Q3: Why does the flow of signals in a synapse from axonal end of one neuron to dendritic end of another neuron take place but not in the reverse direction? Explain. (NCERT.AI 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: At the synapse (functional junction between neurons), axon terminal comes in close proximity to the dendron terminal of next neuron. Axon terminal is expanded to form pre-synaptic knob and the other dendrite terminal forms post-synaptic depression. In between the two, lies a narrow fluid filled space called synaptic cleft. As the nerve impulse reaches the pre-synaptic knob, the synaptic vesicles get stimulated to release neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the gap to come in contact with post-synaptic membrane. In this way, nerve impulse passes across the minute gap to stimulate dendron of another neuron. The synapse acts as a one-way valve to conduct impulse in one direction only. This is so because chemical substance called neurotransmitter is secreted only on one side of the gap, i.s., on axons side. It carries impulse across the synapse and passes it to the dendron of the other neuron. In this way, impulses travel across the neurons only in one direction, i.e., from axon of one neuron to dendron of other neuron through a synapse.
Q4: List in tabular form three distinguishing features between cerebrum and cerebellum. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Distinguishing features between cerebrum and cerebellum:
Q5: How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support? (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- When tendrils touch a support, the part in contact grows more slowly than the part away from it. This is due to the action of the auxin hormone.
- The side of the tendril touching the support has less auxin.
- The free side has more auxin, which promotes growth.
- This difference in growth causes the tendril to coil around the support.
Q6: State the function of each of the following plant hormones:
(a) Gibberellins
(b) Auxins
(c) Abscisic acid (2019 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) In genetically dwarf plants, the length of internode is very much reduced but the number of nodes remains the same. Gibberellins overcome the phenotypic expression of dwarfism in certain plants. Besides general increase in stem length, gibberellins specifically induce internodal growth in some genetically dwarf varieties of plants like pea and maize. Gibberellins, however, have little or no effect when they are applied to the normal plant.
(b) Auxin is the plant hormone which promote cell enlargement and cell differentiation in plants. It also plays a role in apical dominance (i.e., the phenomenon in which presence of apical bud does not allow the nearby lateral buds to grow). When the apical bud is removed, the lateral buds sprout. This produces dense bushy growth. The phenomenon is widely used in tea plucking. Apical bud inhibits the growth of lateral buds by release auxin.
(c) Abscisic acid or ABA is a plant hormone or phytohormone which acts as growth inhibitor. It promotes dormancy in seeds and buds, abscission (falling of leaves) and senescence in leaves and thus inhibits growth of plant.
Q7: What are plant hormones? Name the plant hormones responsible for the following:
(i) Growth of stem
(ii) Promotion of cell division
(iii) Inhibition of growth
(iv) Elongation of cells (NCERT, Delhi 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Plant hormones or phytohormones are chemical substances produced naturally in plants and capable of translocation and regulating one or more physiological processes when present in low concentration. These are also known as plant growth substances or plant growth regulators.
The plant hormones responsible for different functions are as follows:
(i) Growth of stem: Gibberellins (Gibberellic acid) promote growth in stems.
(ii) Promotion of cell division: Cytokinins promote cell division in plants.
(iii) Inhibition of growth: ABA (Abscisic acid) promotes dormancy in seeds as well as in buds and thus inhibits growth.
(iv) Elongation of cells: Auxin and cytokinin both cause cell elongation.
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q1: (a) What are sensory and motor neurons? Write their function. (CBSE 2018C)
(b) Different parts of brain are associated with specific functions. Name the part of human brain which perform the following functions:
(i) Sensation of feeling full
(ii) Vomiting
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Two types of neurons are:
(i) Sensory neurons - They transmit information from the receptors to the central nervous system.
(ii) Motor neurons - They transmit information from the brain to the effector organs.
(b)
(i) Forebrain (a centre for hunger)
(ii) Hindbrain (medulla)
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q1: (a) Name the part of human brain which controls: (2017)
(i) voluntary actions (ii) involuntary actions.
(b) State the significance of peripheral nervous system. Name the components of this nervous system and distinguish between their origins.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) (i) Voluntary actions are controlled by the cerebrum (the forebrain).
(ii) Involuntary actions are controlled by mid-brain (the medulla oblongata).
(b) Peripheral nervous system facilitates the communication between central nervous system and other body parts.
Components of peripheral nervous system are:
(i) Cranial Nerves: Originating from brain.
(ii) Spinal Nerves: Originating from spinal cord.
Q2: (a) Name the gland that secrete:
(i) insulin, (ii) thyroxin.
(b) Explain with an example how the timing and amount of hormone secreted are regulated in a human body. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Gland that secretes:
(i) Insulin - Pancreas
(ii) Thyroxine - Thyroid gland
(b) The timing and amount of hormone secreted are regulated by the “Feedback mechanisms”. For example:
(i) High glucose level in blood induces the pancreatic cells to produce more insulin which converts glucose to glycogen.
(ii) Low glucose level in the blood does not induce the pancreatic cells to produce insulin so that less conversion of glucose to glycogen occurs.
Q3: (a) State the role performed b y plant hormones. Name a plant hormone which is essential for cell division.
(b) Name and explain the role of plant hormone involved in phototropism. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Role of plant hormones:
Chemical control in the plants is performed through plant hormones. They help to coordinate growth, development and responses to the environment.
Plant hormones auxin and cytokinin help in cell division.
(b) In phototropism, the hormone auxin plays a crucial role. It is produced at the shoot tip and helps cells grow longer. When a plant senses light from one side, auxin moves to the shaded side, causing those cells to elongate. This results in the plant bending towards the light.
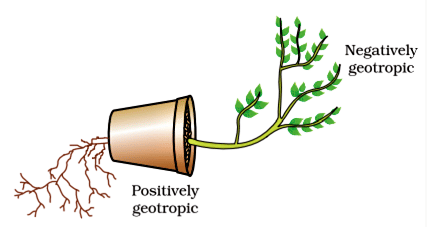
Q4: What is geotropism? Draw a labelled diagram of a potted plant showing positive geotropism and negative geotropism (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Geotropism refers to the directional growth of plants in response to gravity.
- Positive geotropism: This is when roots grow downwards towards the Earth's centre.
- Negative geotropism: This is when shoots grow upwards away from the ground.
Q5: How does the feedback mechanism regulate hormone secretion? Explain with the help of an example. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The feedback mechanism is a regulatory system that controls hormone secretion based on their levels in the body. This process can either promote or inhibit the production of hormones.
An example of this is the regulation of thyroxine production:
- If blood levels of thyroxine are high, the hypothalamus detects this and reduces the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
- With less TSH, the thyroid gland produces less thyroxine, leading to a decrease in its blood levels.
- Conversely, if thyroxine levels are low, the hypothalamus increases TSH production.
- This TSH travels through the bloodstream to the thyroid, prompting it to secrete more thyroxine.
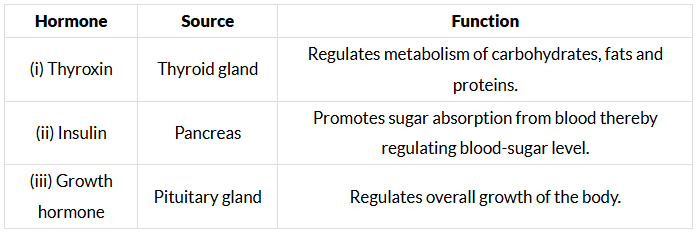
Q6: State the source of secretion and function of the following hormones: (2017)
(i) Thyroxin
(ii) Insulin
(iii) Growth hormone.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Q7: What are trophic levels? Make a food chain of four trophic levels. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Trophic levels refer to each step in a food chain where energy is transferred.
They illustrate how energy moves through an ecosystem
Example: (i) Plants → Grasshopper Frog → Snake
(ii) Plants Deer → Hyena Tiger
Q8: Different parts of brain are associated with specific functions. Name the part of human brain which performs the following functions: (CBSE 2017-18 C)
(a) Sensation of feeling full
(b) Vomiting
(c) Picking up a pencil
(d) Riding a bicycle.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Hypothalamus - Forebrain
(b) Medulla - Hind brain
(c) Cerebellum - Hind brain
(d) Cerebellum - Hind brain
Q9: (a) What are phytohormones? List four types of phytohormones. Where are these hormones synthesised?
(b) What happens when a growing plant detects light? Explain in brief. (Board Term I, 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Phytohormones are chemical substances that regulate various physiological processes in plants. They are produced naturally by plants and control growth, development, and responses to environmental stimuli.
Four types of phytohormones are:
- Auxins: These hormones regulate cell elongation, apical dominance, and phototropism. They are mainly synthesized in the apical meristem, young leaves, and developing seeds.
- Gibberellins: These hormones promote stem elongation, seed germination, and fruit development. They are primarily synthesized in the apical meristem, young leaves, and developing seeds.
- Cytokinins: These hormones promote cell division and differentiation, delay senescence, and regulate apical dominance. They are synthesized in actively growing tissues such as roots, embryos, and fruits.
- Abscisic Acid: This hormone controls seed dormancy, stomatal closure, and stress responses. It is synthesized in mature leaves, fruits, and seeds.
(b) When a growing plant detects light, it triggers a series of responses known as photomorphogenesis. The plant's photoreceptors, specifically phytochrome and cryptochrome, detect the light signal and initiate various physiological changes. These changes include:
- Phototropism: The plant bends towards the light source, which is controlled by auxin distribution in the stem.
- Chloroplast movement: Chloroplasts within the plant cells move to optimize light absorption for photosynthesis.
- Stomatal opening: Light stimulates the opening of stomata, allowing for gas exchange and transpiration.
- Flowering: Light is crucial for triggering the flowering process in many plants.
Overall, the detection of light by plants is essential for their growth, development, and ability to respond to their environment.
Q10: Draw a diagram of the cross-sectional view of human brain as given below on your answer sheet and label: (CBSE 2017-18 C)
(а) The part that helps in performing voluntary actions.
(b) The part that controls salivation and vomiting.
(c) The largest part of forebrain.
(d) A fluid that protects the brain.
(e) Meninges.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Cerebrum
(b) Medulla
(c) Cerebrum
(d) Cerebrospinal fluid
(e) Meninges or three membranes covering the brain.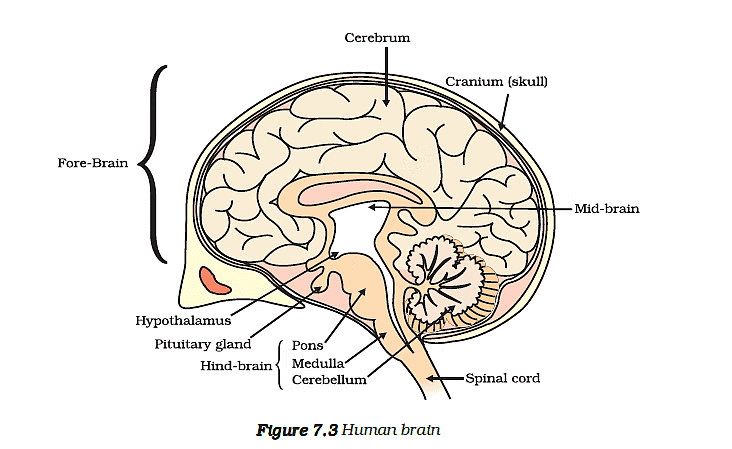
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q1: Name the two components of central nervous system. How are they protected? Name the component which is considered as highest coordinating centre of the body. Describe its three regions. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Brain and spinal cord are the two components of central nervous system.
- Human brain is protected by a bony skull, also called as cranium. Internal to the skull it is covered from outside by three membranes called meninges. In between the meninges there is a fluid called as cerebrospinal fluid. Beneath the membranes, the brain is subdivided into three major parts namely fore-brain, midbrain, and hind brain.
- Brain is considered as the highest coordinating centre of the body.
- Its three regions are given below:
- Fore-brain is the main thinking part of the brain. It has different regions or areas such as:
- Sensory area - It receives sensory impulses from various receptors.
- Auditory area - It is concerned with hearing.
- Olfactory area - It is concerned with smell.
- Gustatory area - It is concerned with taste.
- Optic area - It is concerned with sight.
- Association area - This area interprets various sensory informations and makes decision how to respond.
- Motor area - Decisions made by association area are passed on to this area which control the movement of voluntary muscles.
- Midbrain comprises of four lobes. So it is also known as copra quadrigemina. Actions of involuntary muscles are controlled by the mid-brain and hind-brain.
- Hind-brain comprises of cerebellum, pons varolii, and medulla oblongata. Cerebellum is the second largest part of brain that coordinates muscular activity of the body as well as maintains body equilibrium or posture. Pons connects cerebellum and medulla oblongata and functions as a relay centre among different parts of brain. It possesses pneumotaxic area of respiratory centre. Medulla oblongata lies below the cerebellum and continues behind the spinal cord. Involuntary actions like blood pressure, salivation, and vomiting are controlled by the medulla in the hind-brain.
- Fore-brain is the main thinking part of the brain. It has different regions or areas such as:
Q2: With the help of suitable examples explain the terms phototropism, geotropism and chemotropism. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The stimulus oriented movement of plant or plant part is called tropism. The direction of movement is related to the direction of stimulus. These movements are always growth oriented movements. They are of different types namely phototropism (growth movement in response to light), hydrotropism (water), geotropism (force of gravity), thigmotropism (contact) and chemotropism (chemicals).
- Phototropism is a directional growth movement which occurs in response to unidirectional exposure to light. The region of photoreception is shoot apex where auxin is produced. Auxin moves from the illuminated region to the shaded region. This causes more growth on the dark side of the stem causing it to bend towards the source of light. Movement of shoot towards light is called phototropism.
- Roots are positively geotropic and negatively phototropic. Shoots are positively phototropic and negatively geotropic.
- Growth of pollen tube inside the style, ovary and ovule in response to the chemicals produced by them is an example of chemotropism.
Q3: (a) Define hormone. Write four characteristics of hormones in humans.
(b) Name the disorder caused by the following situations:
(i) Under secretion of growth hormone.
(ii) Over secretion of growth hormone.
(iii) Under secretion of insulin.
(iv) Deficiency of iodine. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Hormones are chemical informational molecules that are required in minute quantities and are directly poured in the blood stream by the glands. They act on a specific organ called target organ. So their site of production varies from site of action.
Their characteristics are:
- They are poured into blood stream.
- Are generally proteinaceous or steroid.
- Their secretion is regulated by feedback mechanism.
- Their site of action and secretion is different.
(b)
(i) Dwarfism
(ii) Gigantism
(iii) Diabetes
(iv) Goitre
Q4: Name the hormone which is released into the blood when its sugar level rises. Name the organ which produces this hormone and its effect on blood sugar level. Also, mention the digestive enzymes secreted by this organ with one function of each. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: When blood sugar level rises in blood, a hormone named ‘insulin" is produced by β-cells of islet of Langerhans in the organ Pancreas. Pancreas also produces pancreatic juice which contains pancreatic enzymes such as trypsin, pancreatic amylase and pancreatic lipase.
Insulin promotes glucose absorption by individual cells and absorption and formation of glycogen in liver and muscles. This reduces glucose level in blood. As soon as the blood sugar comes to normal the pancreatic cells stops secretion of insulin.
Pancreas secretes slightly alkaline pancreatic juice which contains three major following enzymes:
- Trypsin which digests proteins.
- Lipase which digests fats.
- Amylase which digests carbohydrates.
Q5: What are phytohormones? List four types of phytohormones. Where are these synthesised? (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Phytohormones are chemical substances that help plants coordinate their growth and respond to environmental stimuli. They can either promote or inhibit growth.
Five major types of plant growth hormones are auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid and ethylene.
These plant growth regulators are also known as phytohormones.
These are synthesised at shoot apices, leaves, developing embryos, root tips etc.
Q6: Name the plant growth hormone which is synthesized at shoot tip. Explain with the help of a diagram why does a plant bend towards light during growth. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Auxin is a phytohormone which is synthesized at shoot tip.
(ii) When a plant is exposed to light coming from one side of the plant then auxin located at the shoot tip diffuses towards the shaded side of the shoot. High concentration of auxin in the shaded region stimulates the cells to grow longer in comparison to the region exposed to light. So the shoot tends to bend towards the light.
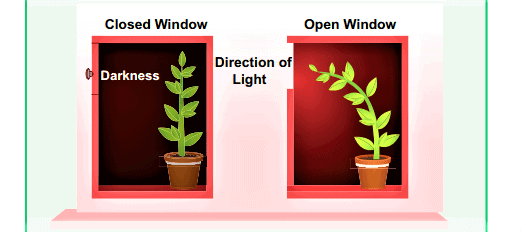
Q7: Name the hormone which regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in our body. Which gland secretes this hormone? Why is it important for us to have iodised salt in our diet? (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Thyroxine regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in our body.
- It is secreted by the thyroid gland.
- A deficiency of iodine in our diet can lead to a condition called goitre, where the thyroid gland enlarges as it tries to absorb more iodine.
- Iodine is essential for the production of thyroxine.
- To ensure we get enough iodine, it is added to salt, making it iodised salt.
Q8: Name the two components of central nervous systems in humans. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The two components of the Central Nervous System in humans are the brain and spinal cord.
Q9: In the absence of muscle cells, how do plant cells show movements? (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Plants do not have a nervous system and muscles.
- Even then they exhibit well coordinated and controlled movements.
- Plants possess chemical coordination.
- They respond to stimuli by secreting chemical substances called plant growth regulators.
- They either stimulate or retard growth.
- Five major types of plant growth hormones are:
- Auxins
- Gibberellins
- Cytokinins
- Abscisic acid
- Ethylene
- Certain changes in the orientation of plant parts in relation to other parts caused by intrinsic or external stimuli are non-directional, growth independent movements.
- They are referred to as nastic movements.
- Thus, plants show movements due to growth or change in turgor pressure.
Q10: (a) Write two points of differences between enzymes and hormones. (CBSE 2016)
(b) Name one endocrinal gland in our body which performs dual function. Write the functions.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Differences between enzymes and hormones:
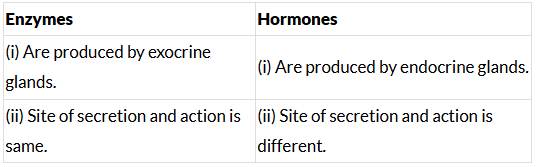
(b) Pancreas performs dual function. It produces enzymes like Trypsin, Lipase etc., which aid in digestion. It also produces insulin hormone which regulates blood-sugar level.
Q11: Name the system which facilitates the communication between the central nervous system and the other body parts of the body. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Peripheral nervous system.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q1: What is synapse? In a neuron cell how is an electrical impulse created and what is the role of synapse in this context? (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Synapse is the junction between two nerve cells, specifically between the axon ending of one neuron and the dendrite of another.
- The process of transmitting a nerve impulse involves several steps:
- When information reaches the end of a neuron’s dendrite, it triggers a chemical reaction.
- This reaction generates an electrical impulse that travels from the dendrite to the cell body and along the axon.
- At the axon’s end, the electrical impulse causes the release of chemicals.
- These chemicals cross the synapse and initiate a similar electrical impulse in the next neuron's dendrite.
- In summary, the synapse plays a crucial role in transmitting impulses from one neuron to another, facilitating communication throughout the body.
Q2: “As the blood sugar level in our body falls insulin secretion is reduced.” Justify this statement in the reference of feedback mechanism that regulates the timing and amount of hormone released. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Insulin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels.
- It helps convert excess sugar in the blood into glycogen for storage.
When blood sugar levels are high:
- The pancreas detects the increase.
- It responds by producing more insulin.
Conversely, when blood sugar levels fall:
- Insulin secretion is reduced.
This is part of a feedback mechanism where blood sugar levels directly influence insulin production.
This regulation ensures that our body maintains balanced blood sugar levels, preventing harmful effects from both high and low sugar levels.
Q3: State the role played by ovaries in a human female. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Roles of ovary:
- Ovaries produce female gametes, known as ova.
- They also produce the female sex hormone, oestrogen, which is vital for:
- The development of secondary sex organs.
- The emergence of secondary sexual characteristics, such as a high-pitched voice and the growth of mammary glands.
Q4: What is meant by reflex-action? With the help of a labelled diagram trace the sequence of events which occur when we touch a hot object. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Reflex action is defined as an unconscious, automatic and involuntary response of effector, i.e. muscle and gland to a stimulus which is monitored through the spinal cord.
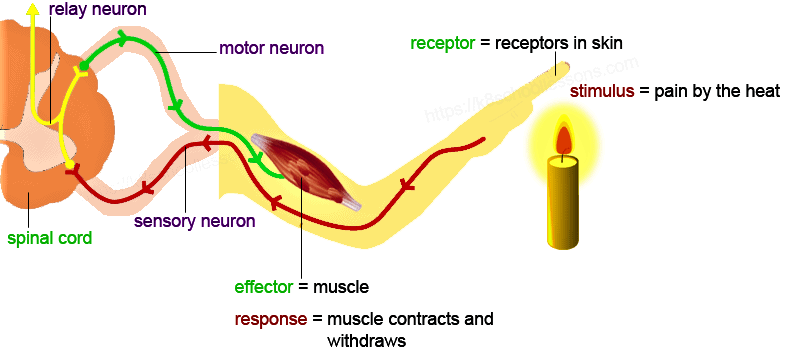 Sequence of events when we touch a hot object are:
Sequence of events when we touch a hot object are:
- Receptor organ skin receives the stimulus and activates a sensory nerve impulse.
- Sensory neuron carries the message in the form of sensory impulse to the spinal cord.
- The spinal cord acts as a modulator. The neurons of the spinal cord transmit the sensory nerve impulses to the motor neuron.
- Motor nerve conducts these impulses to the effector organ hand which responds by pulling back the hand away from the hot object.
Q5: Write the names of the hormones secreted by the pituitary gland and adrenal gland. State their functions in the body. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 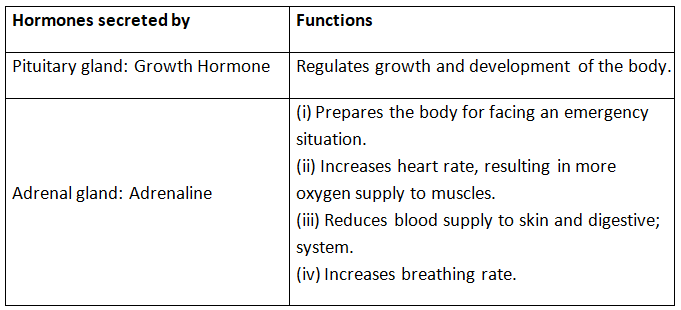
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Previous Year Questions - Control and Coordination
| 1. What is control and coordination in human beings? |  |
| 2. How do nerve impulses travel in the body? |  |
| 3. What role do hormones play in coordination? |  |
| 4. What are reflex actions, and how do they work? |  |
| 5. How do plants coordinate their growth and responses to the environment? |  |






















