Class 10 Science - Previous Year Questions - Acids Bases and Salts
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: Select a pair of natural indicators from the following: (2024)(a) Litmus and methyl orange
(b) Turmeric and Litmus
(c) Phenolphthalein and methyl orange
(d) Methyl orange and Turmeric
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Turmeric and litmus are both natural indicators.
- They change colour when they come into contact with acids or bases:
- Turmeric turns red in alkaline solutions.
- Litmus turns red in acidic solutions and blue in alkaline solutions.
- This makes them useful for testing the pH of substances.
Q2: A chemical compound used in glass, soap and paper industries is (2024)
(a) Washing Soda
(b) Baking Soda
(c) Bleaching Powder
(d) Common Salt
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Washing soda, or sodium carbonate, is a chemical compound that is used in making glass, as a cleaning agent in soaps, and in the paper-making process.
- It's important for its ability to soften water and enhance cleaning.
Q3: An aqueous solution of a salt turns blue litmus to red. The salt could be the one obtained by the reaction of: (2024)
(a) HNO3 and NaOH
(b) H2SO4 and KOH
(c) CH3COOH and NaOH
(d) HCl and NH4OH
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- When hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), it forms ammonium chloride, which is an acidic salt.
- This acid can turn blue litmus paper red, indicating that the solution is acidic.
Q4: Consider the following compounds: (2024)
FeSO4, CuSO4, CaSO4, Na2CO3.
The compound having the maximum number of water of crystallization in its crystalline form in one molecule is:
(a) FeSO4
(b) CuSO4
(c) CaSO4
(d) Na2CO3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) can exist as a hydrated compound called washing soda, which has 10 water molecules attached to each formula unit (Na2CO3·10H2O).
- This means it has the highest number of water of crystallization compared to the other compounds listed.
Q5: The salt present in tooth enamel is: (2024)
(a) Calcium phosphate
(b) Magnesium phosphate
(c) Sodium phosphate
(d) Aluminium phosphate
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Tooth enamel is primarily composed of a mineral known as hydroxyapatite, which is a form of calcium phosphate.
- This mineral plays a crucial role in: Strengthening teeth and making them resistant to decay
- Thus, the correct answer is (a) Calcium phosphate.
Q6: An aqueous solution of sodium chloride is prepared in distilled water. The pH of this solution is: (2024)
(a) 6
(b) 8
(c) 7
(d) 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Sodium chloride (NaCl) is a neutral salt, formed from a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base (NaOH). When NaCl dissolves in water, it dissociates into sodium (Na⁺) and chloride (Cl⁻) ions, both of which do not react with water to affect the pH. As a result, the solution remains neutral, with a pH of 7.
Q7: Solid Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to form Calcium hydroxide accompanied by the liberation of heat. From the information given above it may be concluded that this reaction (2024)
(a) is endothermic and pH of the solution formed is more than 7.
(b) is exothermic and pH of the solution formed is 7.
(c) is endothermic and pH of the solution formed is 7.
(d) is exothermic and pH of the solution formed is more than 7.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- The reaction of solid calcium oxide with water is exothermic, meaning it releases heat.
- This reaction produces calcium hydroxide, which is a strong base.
- As a result, the pH of the solution formed is greater than 7, indicating it is alkaline.
Q8: Juice of tamarind turns blue litmus to red. It is because of the presence of an acid called: (2024)
(a) Methanoic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Tartaric acid
(d) Oxalic acid
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The juice of tamarind contains tartaric acid, a natural organic acid. This acid:
- Causes the solution to be acidic.
- Turns blue litmus paper red, indicating acidity.
Thus, the correct answer is (c) tartaric acid.
Q9: The oxide which can react with HCl as well as KOH to give corresponding salt and water is (2024)
(a) CuO
(b) Al2O3
(c) Na2O
(d) K2O
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) is an amphoteric oxide, meaning it can react with both acids and bases to form salts and water.
- Reaction with acid (HCl): Al₂O₃ + 6HCl → 2AlCl₃ + 3H₂O
Aluminum oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to form aluminum chloride and water. - Reaction with base (KOH): Al₂O₃ + 2KOH + 3H₂O → 2KAl(OH)₄
Aluminum oxide reacts with potassium hydroxide in aqueous solution to form potassium aluminate, demonstrating its ability to react with bases.
Q10: Identify the product ‘X’ obtained in the following chemical reaction: (CBSE 2024)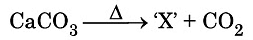 (a) Quick lime
(a) Quick lime
(b) Gypsum
(c) Lime Stone
(d) Plaster of Paris
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The product 'X' obtained from the reaction is quick lime.
Here’s a brief explanation of the process:
- Heating calcium carbonate (CaCO3) leads to its decomposition.
- This decomposition produces calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
- This process is known as calcination, commonly used in making cement and lime.
Thus, the answer is (a) quick lime.
Q11: (i) The pH of a sample of tomato juice is 4.6. How is this juice likely to be in taste? Give reason to justify your answer.
(ii) How do we differentiate between a strong acid and a weak base in terms of ion-formation in aqueous solutions?
(iii) The acid rain can make the survival of aquatic animals difficult. How? (2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) The taste of tomato juice will be slightly sour; The pH 4.6 indicates that tomato juice is an acid and acids are sour in taste.
(ii) Acids that give more H+ions / H3O+ are Strong Acids Bases that give less OH- ions are Weak Bases.
(iii) Living animals can survive within a pH range of 7·0 to 7·8. So, if the pH of river water becomes low due to acid rain (pH < 5·6), then survival of aquatic animals becomes difficult.
Q12: Case based / data based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Salts play a very important role in our daily life. Sodium chloride which is known as common salt is used almost in every kitchen. Baking soda is also a salt used in faster cooking as well as in baking industry. The family of salts is classified on the basis of cations and anions present in them.
(a) Identify the acid and base from which Sodium chloride is formed.
(b) Find the cation and the anion present in Calcium sulphate.
(c) “Sodium chloride and washing soda both belong to the same family of salts.” Justify this statement.
OR
(c) Define the term pH scale. Name the salt obtained by the reaction of Potassium hydroxide and Sulphuric acid and give the pH value of its aqueous solution. (2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Acid – HCl, Base – NaOH
(b) Cation – Ca2+ , Anion – SO42-
(c) Salts that share the same cation but have different anions are considered part of the same family. For example:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Washing soda (sodium carbonate, Na2CO3)
Both contain the Na+ cation.
OR
(c) The pH scale measures how acidic or basic a solution is, ranging from 0 (acidic) to 14 (basic), with 7 being neutral. When Potassium hydroxide (KOH) reacts with Sulfuric acid (H2SO4), it produces Potassium sulfate (K2SO4), which is a neutral salt. Its aqueous solution has a pH of approximately 7.
Q13: 1 gram of solid sodium chloride was taken in a clean and dry test tube and concentrated sulphuric acid was added to it.
(i) Name the gas evolved in the reaction.
(ii) What will be observed when this gas is tested with (I) dry, and (II) wet blue litmus paper? Write your conclusion about the nature (acidic/basic) of this gas. (2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) The gas evolved is HCl gas.
(ii) When tested with:
- Dry blue litmus paper: No change in colour.
- Wet blue litmus paper: Turns red.
Conclusion: The HCl gas is acidic in nature.
Q14: (a) A few crystals of ferrous sulphate were taken in a dry boiling tube and heated. Tiny water droplets were observed in the tube after some time.
(i) From where did these water droplets appear? Explain.
(ii) What color change will be observed during heating?
(iii) How many molecules of water are attached per molecule of FeSO4 crystal? Write the molecular formula of crystalline forms of (I) Copper sulphate, and (II) Sodium carbonate.
(iv) State how is Plaster of Paris obtained from gypsum. Write two uses of Plaster of Paris.
OR
(b) An acid ‘X’ present in tamarind when mixed with ‘Y’, produces a mixture ‘Z’. ‘Z’ on addition to a dough when heated makes cakes soft and spongy. ‘Y’ is prepared from common salt and helps in faster cooking.
(i) Write the common names of ‘X’, ‘Y’ and ‘Z’, and the chemical formula of ‘Y’.
(ii) How is ‘Y’ prepared and how does it help in making cakes soft and spongy? Illustrate the reaction with a suitable chemical equation.
(iii) Write the name and chemical formula of a mild base other than ‘Y’ used as an antacid. (2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) (i)The water droplets appear due to the evaporation of water of crystallisation in ferrous sulphate crystals when heated.
(ii) The colour change observed during heating is from green to white.
(iii) Each molecule of FeSO4 crystal has seven water molecules attached, represented as FeSO4 · 7H2O. The molecular formulas for the crystalline forms are:
- (I) Copper sulphate: CuSO4 · 5H2O
- (II) Sodium carbonate: Na2CO3 · 10H2O
(iv) Plaster of Paris is obtained by heating gypsum (CaSO4 · 2H2O) at 373 K, which causes it to lose water molecules.
Two uses of Plaster of Paris are:
- It is used by doctors to support fractured bones.
- It is also used in making decorative items.
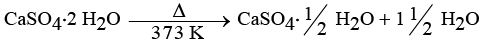
OR
(b) (i) X-Tartaric acid , Y-Baking soda , Z- Baking powder Y- NaHCO3
(ii) NaCl + H2O +CO2 +NH3 → NH4Cl +NaHCO3
NaHCO3 + H+ → CO2 + H2O + Sodium salt of acid CO2 released during heating makes the cake soft and spongy.
(iii) Magnesium hydroxide; Mg(OH)2
Q15: Write the common name and the chemical name of the compound 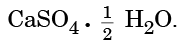 Write the method of its preparation. Give chemical equation for the reaction, when water reacts with
Write the method of its preparation. Give chemical equation for the reaction, when water reacts with 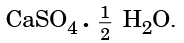 (2024)
(2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Common Name: Plaster of Paris
Chemical Name: Calcium sulphate hemihydrate
Preparation Method:
- Plaster of Paris is made from gypsum (CaSO4 · 2H2O).
- It is prepared by heating gypsum at 373 K.
Chemical Equation:
When water reacts with Plaster of Paris:
CaSO4 · ½H2O + 1½ H2O → CaSO4 · 2H2O
Q16: The following questions are source-based/case-based questions. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow: (2024)
Three metal samples of magnesium, aluminium and iron were taken and rubbed with sand paper. These samples were then put separately in test tubes containing dilute hydrochloric acid. Thermometers were also suspended in each test tube so that their bulbs dipped in the acid. The rate of formation of bubbles was observed. The above activity was repeated with dilute nitric acid and the observations were recorded.
Answer the following questions:
(a) When activity was done with dilute hydrochloric acid, then in which one of the test tubes was the rate of formation of bubbles the fastest and the thermometer showed the highest temperature?
(b) Which metal did not react with dilute hydrochloric acid? Give reason.
(c) (i) Why is hydrogen gas not evolved when a metal reacts with dilute nitric acid? Name the ultimate products formed in the reaction.
OR
(c) (ii) Name the type of reaction on the basis of which reactivity of metals is decided. You have two metals X and Y. How would you decide which is more reactive than the other?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The test tube with magnesium had the fastest rate of bubble formation and the highest temperature.
(b) All three metals react with dilute hydrochloric acid as they are more reactive than hydrogen.
(c)(i) Hydrogen gas is not produced when a metal reacts with dilute nitric acid because nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises the hydrogen gas to water. The ultimate products are water and nitrogen oxides.
OR
(c)(i) The type of reaction that determines the reactivity of metals is a displacement reaction. If metal X displaces metal Y from its salt solution, then metal X is more reactive than metal Y, and vice versa.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q1: When sodium bicarbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, the gas evolved is (2023)(a) Hydrogen; it given pop sound with burning match stick.
(b) Hydrogen; it turns lime water milky.
(c) Carbon dioxide; it turns lime water milky.
(d) Carbon dioxide; it blows off a burning match stick with a pop sound.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Sol: When sodium bicarbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide gas is liberated. The reaction that occurs is shown below:
NaHCO3 + HCI → NaCl + H2O + CO2↑
Carbon dioxide when passed into lime water gives a milky solution. This is due to the formation of an insoluble suspension of calcium carbonate: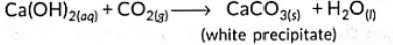
Q2: Select a pair of olfactory indicators from the following: (2023)
(a) Clove oil and vanilla essence
(b) Onion and turmeric
(c) Clove oil and litmus paper
(d) Vanilla and methyl orange
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Clove oil and vanilla essence are the correct pair of olfactory indicators.
- They change their smell in the presence of acids or bases.
- Other options like onion and turmeric do not serve as olfactory indicators.
- Litmus paper and methyl orange are not olfactory indicators.
Q3: Sodium hydroxide is termed as alkali while ferric hydroxide is not because: (2023)
(a) Sodium hydroxide is a strong base, while ferric hydroxide is a weak base.
(b) Sodium hydroxide is a base which is soluble in water while ferric hydroxide is also a base but it is not soluble in water.
(c) Sodium hydroxide is a strong base while ferric hydroxide is a strong acid.
(d) Sodium hydroxide and ferric hydroxide both are strong base but the solubility of sodium hydroxide in water is comparatively higher than that of ferric hydroxide.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Sol: Sodium hydroxide is classified as an alkali, while ferric hydroxide is not due to the following reasons:
- Sodium hydroxide is a strong base, whereas ferric hydroxide is a weak base.
- Sodium hydroxide is soluble in water, while ferric hydroxide is not.
- Sodium hydroxide is not a strong acid; it is a base, while ferric hydroxide does not fit this classification.
- Both are bases, but sodium hydroxide has a higher solubility in water compared to ferric hydroxide.
Q4: Hydronium ions are formed by the reaction between (2023)
(a) Sodium hydroxide and water
(b) Calcium chloride and water
(c) Hydrogen chloride gas and water
(d) Ethanol and water
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Sol: According to Arrhenius theory, acids are substances which dissociate in aqueous solution to give hydrogen ions (or hydronium ions).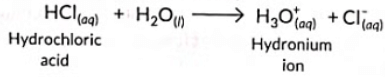
Q5: Fresh milk has a pH of 6. To delay its curdling, a chemical substance is added to it, which is (2023)
(a) Sodium carbonate
(b) Baking powder
(c) Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda)
(d) Baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Sol:
Fresh milk has a pH of about 6 and can curdle when bacteria convert lactose into lactic acid, lowering the pH further. Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO₃), commonly called baking soda, is a mild base that neutralizes this acid, maintaining the pH closer to neutral and delaying curdling.
- Reaction:
NaHCO₃ + H⁺ (from lactic acid) → Na⁺ + H₂O + CO₂
This neutralizes the acid produced, preventing the milk from souring quickly.
Q6: The name of the salt used to remove permanent hardness of water is (2023)
(a) Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3)
(b) Sodium chloride (NaCI)
(c) Sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3.10H2O)
(d) Calcium sulphate hemihydrate (CaSO4. 1/2 H2O)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Sol: Na2CO3.10H2O is used to remove permanent hardness of water. Washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O) reacts with soluble calcium and magnesium chlorides and sulphates in hard water to form insoluble carbonates, that can be removed by filtration and then water becomes soft.
Q7: A student took a small amount of copper oxide in a conical flask and added dilute hydrochloric acid to it with constant stirring. He observed a change in colour of the solution.
(i) Write the name of the compound formed and its colour.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) The compound formed is copper chloride (CuCl2) and its colour is green in aqueous solution.
(ii) The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is: CuO + 2HCl → CuCl2 + H2O
Q8: (a) Write a balanced equation to show the reaction that occurs when a piece of aluminium is dipped in a dilute solution of (i) sulphuric acid and (ii) sodium hydroxide.
(b) Write the colour of the solution formed when copper oxide is treated with hydrochloric acid. Give a reason for this observation. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) (i) 2AI + 3H2SO4 → AI2(SO4)3 + 3H2
(ii) 2AI + 2NaOH + 2H2O → 2NaAIO2 + 3H2
(b)
- The solution formed when copper oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid is a bluish-green colour.
- This occurs because copper oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce copper chloride and water.
- The copper chloride dissolves in water, resulting in the bluish-green colour of the solution.
Q9: (i) Suggest a safe procedure for diluting a strong concentrated acid.
(ii) Name the salt formed when sulphuric acid is added to sodium hydroxide and write its pH.
(iii) Dry hydrochloric acid (HCl) gas does not change the colour of dry blue litmus paper. Why? (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i)
- During the dilution of a strong concentrated acid, always add acid to water and not the water to acid.
- The dissociation of an acid in water is a highly exothermic process, as the acid has a strong affinity for water.
- Adding water to acid can cause a violent reaction due to the rapid generation of heat.
- By adding acid to water slowly and with constant stirring, the heat generated can be dissipated more effectively, ensuring a safe dilution process.
(iii) Dry hydrochloric acid (HCl) gas does not change the colour of dry blue litmus paper because:
- The colour change requires the presence of hydrogen ions (H+).
- HCl gas can only produce these ions in an aqueous solution, where it dissociates.
- Without water, HCl gas does not release H ions, hence no colour change occurs.
Q10: Two solutions M and N give red and blue colour respectively with a universal indicator.
(i) In which solution will the hydrogen ion concentration be more? Justify your answer.
(ii) If both M and N solutions are mixed and the resultant mixture is tested with a universal indicator, it turns green. What is the nature of the salt formed? Justify your answer. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Solution M gives a red color with a universal indicator, indicating that it is an acidic solution with a higher hydrogen ion concentration. Solution N gives a blue color with a universal indicator, indicating that it is a basic solution with a lower hydrogen ion concentration.
(ii) When solutions M and N are mixed, the resulting green color with a universal indicator indicates that the mixture is neutral. This suggests that a salt solution is formed, which is neither acidic nor basic.
Q11: On heating X at 373 K, it loses water molecules and becomes Y. Y is a substance which doctors use for supporting fractured bones in the right position.
(i) Identify X and V.
(ii) How can X be reobtained from Y? (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) X is gypsum (CaSO4 · 2H2O) and Y is Plaster of Paris (CaSO4 · 0.5H2O). V is the substance doctors use for supporting fractured bones in the right position.
(ii) X can be reobtained from Y by:
- Adding water to Plaster of Paris.
- This process converts it back to gypsum.
The reaction is: CaSO4 · 0.5H2O + 1.5H2O → CaSO4 · 2H2O
Q12: Consider the following salts:
(i) yCI
(ii) NH4X
(iii) ZCO3
(a) What would be the pH of the salt solution if in yCI, y is sodium? Give a reason for your answer.
(b) If in salt NH4X, X is nitrate, then its solution will give what colour with a universal indicator? Why?
(c) What would be the change in colour in a blue litmus solution if ZCO3 is added to it and Z is potassium? (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) If in yCI, y is sodium, the salt formed is NaCI. NaCI is a salt of a strong acid (HCI) and a strong base (NaOH), making it a neutral salt. Hence, the pH of the salt solution would be 7.
(b) If in salt NH4X, X is nitrate, the salt formed is NH4NO3. NH4NO3 is a salt of a weak base (NH4OH) and a strong acid (HNO3). It is an acidic salt and will give an orange-yellow colour with a universal indicator.
(c) Potassium carbonate (K₂CO₃) is a basic salt formed from a strong base (KOH) and a weak acid (H₂CO₃). In solution, it hydrolyzes to produce OH⁻ ions, making the solution basic (pH > 7):
K₂CO₃ + H₂O ⇌ 2K⁺ + HCO₃⁻ + OH⁻
Since blue litmus paper remains blue in basic solutions and only turns red in acidic solutions, adding K₂CO₃ will not change its color—it stays blue.
Q13: The industrial process used for the manufacture of caustic soda involves electrolysis of an aqueous solution of compound 'X'. In this process, two gases Y and Z are liberated. Y is liberated at the cathode and Z, which is liberated at the anode, on treatment with dry slaked lime, forms a compound 'B'. Name X, Y, Z, and B. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Compound X: Sodium chloride (NaCl).
- Gas Y: Hydrogen gas (H2) is liberated at the cathode.
- Gas Z: Chlorine gas (Cl2) is liberated at the anode.
- Compound B: Bleaching powder (CaOCl2) is formed when chlorine gas reacts with dry slaked lime (Ca(OH)2).
Q14: Select washing soda from the following:
(a) NaHCO3
(b) Na2CO3.5H2O
(c) Na2CO3.10H2O
(d) NaOH (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Washing soda is chemically known as sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na₂CO₃·10H₂O). It is commonly used as a cleaning agent.
The other options represent different compounds:
(a) NaHCO₃: This is sodium bicarbonate, also known as baking soda.
(b) Na₂CO₃·5H₂O: This is not a common form of sodium carbonate; washing soda specifically has 10 molecules of water.
(d) NaOH: This is sodium hydroxide, also known as caustic soda.
Therefore, the correct answer is (c) Na₂CO₃·10H₂O.
Q15: The table below has information regarding pH and the nature (acidic/basic) of four different solutions. Which of the following option in the table is correct? (CBSE 2023)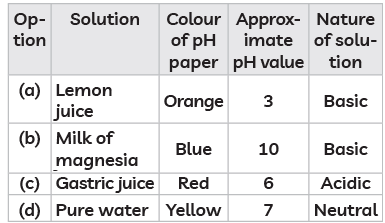
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
(a) Lemon juice: Lemon juice is acidic with a pH around 2-3, but it is acidic, not basic. So, this option is incorrect.
(b) Milk of magnesia: This is basic with a pH around 10, which would turn the pH paper blue, indicating a basic nature. This option is correct.
(c) Gastric juice: Gastric juice is acidic with a pH around 1-3, not 6. A pH of 6 is close to neutral, which is not correct for gastric juice. So, this option is incorrect.
(d) Pure water: Pure water has a neutral pH of 7, but it would usually turn the pH paper green, not yellow. So, this option is also incorrect.
Therefore, the correct answer is (b) Milk of magnesia - Blue, pH 10, Basic.
Q16: (A) A compound ‘X’ which is prepared from gypsum has the property of hardening when mixed with proper quantity of water. Identify ‘X’ and write its chemical formula.
(B) State the difference in chemical composition between baking soda and baking powder. (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) The compound ‘X’ is Plaster of Paris. It is prepared by heating gypsum at 373 K. Its chemical formula is CaSO4 · 0.5H2O.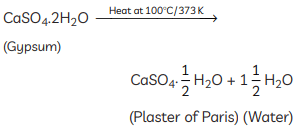 (B) The differences between baking soda and baking powder are:
(B) The differences between baking soda and baking powder are:
Baking Soda: Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃), a single compound.Pure NaHCO₃, a base that releases CO₂ when heated or combined with an acid:
2NaHCO₃ → Na₂CO₃ + H₂O + CO₂ (on heating).
Baking Powder: A mixture of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) and acid salts (e.g., monocalcium phosphate, Ca(H₂PO₄)₂), often with a filler like starch.
A leavening agent containing NaHCO₃ and an acid salt (e.g., monocalcium phosphate). When moistened, the acid reacts with NaHCO₃ to release CO₂ without needing an external acid:
NaHCO₃ + H⁺ (from acid salt) → Na⁺ + H₂O + CO₂.
Q17: (A) Suggest one remedial measure each to counteract the change in pH in human beings in following cases:
(i) Production of too much acid in stomach during indigestion.
(ii) Stung by a honey bee/nettle leaves.
(B) Fresh milk has a pH of 6. When it changes into curd, will its pH increase or decrease? Why? (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: . (A) (i) To get relief from this acidic pain, one must take antacids. These contain bases to neutralise the excess acids.
Examples: Magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia) i.e., Mg(OH)2 or Aluminium hydroxide.
(ii)
- A bee injects an acidic fluid into a person's skin when it stings them causing pain and irritation.
- Applying a baking soda solution, a base made of sodium hydrogen carbonate, is the cure.
- By neutralising the acid, the solution relieves the pain.
- Accidental contact with nettle plant leaves causes the stinging hair to inject formic or methanoic acid into the person's epidermis, causing burning discomfort.
- As the nettle sting is acidic, it can be relieved by applying a basic substance to the skin, such as baking soda.
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q1: Which of the options in the given table are correct? (2022)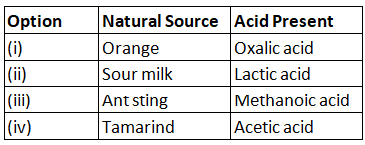 (a) (i) and (ii)
(a) (i) and (ii)(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Sol:
- Orange is a natural source of citric acid.
- Tamarind contains tartaric acid.
Q2: Three test tubes A, B and C contain distilled water, an acidic solution and a basic solution respectively. When red litmus solution is used for testing these solutions, the observed colour changes respectively will be: (2022)
(a) A - no change; B - becomes dark red; C - becomes blue
(b) A - becomes light red; B - becomes blue; C - becomes red
(c) A - becomes red; B - no change; C - becomes blue
(d) A - becomes light red; B - becomes dark red; C - becomes blue
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Sol: Colour of red litmus remains red in neutral solutions, become dark red in acidic and blue in presence of basic solutions. So, there will be no change in colour of red litmus in distilled water (test tube A). In test tube B, it becomes dark red and in test tube C, red litmus turns blue.
Q3: Concentrated H2SO4 is diluted by adding drop by drop (2022)
(a) Water to acid with constant stirring
(b) Acid to water with constant stirring
(c) Water to acid followed by a base
(d) Base to acid followed by cold water
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Sol:
- If you add water to acid, you form an extremely concentrated solution of acid initially.
- The reaction of conc. acid with water is highly exothermic, and the solution may boil very violently, splashing concentrated acid.
- If you add acid to water, the solution that forms is very dilute and a small amount of heat released.
Q4: Select from the following the statement which is true for bases. (2022)
(a) Bases are bitter and turn blue litmus red.
(b) Bases have a pH less than 7.
(c) Bases are sour and change red litmus to blue.
(d) Bases turn pink when a drop of phenolphthalein is added to them.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Sol: Bases are substances which have bitter taste, soapy touch and turn red litmus solution to blue. Bases have pH more than 7. Bases give pink colour with phenolphthalein.
Q5: A solution gives yellowish orange colour when a few drops of universal indicator are added to it. This solution is of : (2022)
(a) Lemon juice
(b) Sodium chloride
(c) Sodium hydroxide
(d) Milk of magnesia
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Sol: Few drops of universal indicators in a solution give yellowish orange colour to solution. This indicates that the solution used was acidic in nature. For example: lemon juice.
Q6: Anita added a drop each of diluted acetic acid and diluted hydrochloric acid on pH paper and compared the colours. Which of the following Is the correct conclusion? (2022)
(a) pH of acetic acid is more than that of hydrochloric acid
(b) pH of acetic acid is less than that of hydrochloric add.
(c) Acetic acid dissociates completely in aqueous solution,
(d) Acetic acid Is a strong acid.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
HCl is stronger acid than CH3COOH so, pH of acetic add is more than that of hydrochloric acid.
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q1: State the purpose for which litmus is used in laboratories. (2021C) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Litmus is used in laboratories as an indicator to identify whether a substance is acidic or basic. It works as follows:
- Litmus changes colour in response to acidity or basicity.
- Red litmus paper turns blue in basic solutions.
- Blue litmus paper turns red in acidic solutions.
- When neutral, litmus remains purple.
Q2: Out of the two hydrochloric acid and acetic acid, which one is considered as strong acid and why ? Write the name/molecular formula of one more strong acid. (2021 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Hydrochloric acid is considered a strong acid because it completely dissociates in water, releasing H+ ions. In contrast, acetic acid only partially dissociates, making it a weak acid.
Another example of a strong acid is H2SO4 (sulphuric acid).
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q1: A visually challenged student, has to perform a lab test to detect the presence of acid in a given solution. The acid-base indicator preferred by him will be: (2020)(a) Blue litmus
(b) Clove oil
(c) Red cabbage extract
(d) Hibiscus extract
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Sol: Clove oil can be used as acid-base indicator by visually challenged student. Clove oil gives different odour in acidic and basic solution.
Q2: An aqueous solution ‘A’ turns phenolphthalein solution pink. In addition of an aqueous solution ‘B’ to ‘A’, the pink color disappears. The following statement is true for solution ‘A’ and ‘B’. (2020)
(a) A is strongly basic and B is a weak base.
(b) A is strongly acidic and B is a weak acid.
(c) A has pH greater than 7 and B has pH less than 7.
(d) A has pH less than 7 and B has pH greater than 7.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Sol: As the aqueous solution of A turns phenolphthalein solution pink, hence A is basic in nature. On adding an acidic solution, the pink colour will disappear. Hence, B is an acid.
Q3: The acid produced in our stomach during digestion of food is (2020)
(a) Hydrochloric acid
(b) Oxalic acid
(c) Lactic acid
(d) Acetic acid
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is produced in the stomach and plays a vital role in digestion. Its key functions include:
- Breaking down food effectively.
- Creating an acidic environment that helps kill harmful bacteria.
- Ensuring proper digestion and maintaining stomach health.
Q4: (i) Draw a labelled diagram to show the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas in the laboratory.
(ii) Test the gas evolved first with dry and then with wet litmus paper. In which of the two cases does the litmus paper show a change in color?
(iii) State the reason for the exhibiting acidic character by dry HCl gas/HCl solution. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) To prepare hydrogen chloride gas in the laboratory:
- Set up a test tube with some solid sodium chloride (NaCl).
- Add concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4) to the test tube.
- Observe the gas evolved from the delivery tube.
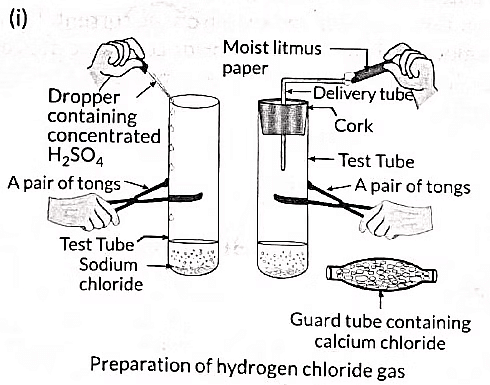
(ii) Testing the gas with litmus paper:
- Dry blue litmus paper: No colour change.
- Moist blue litmus paper: Turns red.
This indicates that hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas is not acidic without water but becomes acidic when in contact with moisture.
(iii) When hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas dissolves in water, it forms hydrochloric acid solution (HCl(aq)). In the solution, HCl dissociates and produces H+ or H3O+ ions. The presence of these ions makes HCl solution acidic. The reaction can be represented as: HCl(g) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Q5: Complete and balance the following chemical equations: (2020)
(i) NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) →
(ii) CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) →
(iii) HCl(aq) + H2O(l) →
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) 2NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) → Na2ZnO2(aq) + H2(g)
(ii) CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) → Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
(iii) HCl(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Q6: (a) You are provided with concentrated sulphuric acid. Describe the process of preparing a dilute solution of sulphuric acid.
(b) What is the effect of dilution on (H3O+/OH-) ratio?
(c) If the H3O+ ion concentration is increased in a solution, will the pH increase or decrease? What are the probable colours of pH paper if the pH range is 0-5 ? (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) To prepare a dilute solution of sulphuric acid, follow these steps:
- Start with a beaker filled with a sufficient amount of water.
- Slowly add the concentrated acid to the water while stirring continuously.
- Always add acid to water, never the other way around, to minimise the risk of splashing or glass breakage due to heat.
(b) The effect of dilution on the (H₃O⁺/OH⁻) ratio:
- When an acid or base is diluted, the concentration of ions (H₃O⁺ and OH⁻) per unit volume decreases.
- This results in a reduced (H₃O⁺/OH⁻) ratio.
(c) If the concentration of H₃O⁺ ions increases in a solution:
- The pH will decrease.
- For pH paper in the range of 0-5, the probable colours will be red or orange, indicating acidic conditions.
Q7: List the important products of the Chlor-alkali process. Write one important use of each. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The important products of the Chlor-alkali process are sodium hydroxide, chlorine, and hydrogen.
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH): It is used in the manufacture of soaps and detergents.
- Chlorine (Cl2): It is used as a germicide and disinfectant for sterilization of drinking water and swimming pools.
- Hydrogen (H2): It is used in the manufacture of ammonia, which is used for the preparation of various fertilizers.
Q8: How is washing soda prepared from sodium carbonate? Give its chemical equation. State the type of this salt. Name the type of hardness of water which can be removed by it? (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Washing soda is prepared by recrystallising sodium carbonate. The chemical equation for its preparation is:
Na2CO3(s) 10H2O(l) → Na2CO3.10H2O(s)
Washing soda is classified as a basic salt. It is effective in removing:
- Permanently hard water by eliminating calcium and magnesium ions.
- Temporary hardness caused by these ions.
Q9: Give reasons for the following:
(i) Only one half of water molecule is shown in the formula of plaster of Paris.
(ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate is used as an antacid.
(iii) On strong heating, blue-colored copper sulfate crystals turn white. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Only one half of the water molecule is shown in the formula of plaster of Paris (CaSO4.½H2O) because:
- One molecule of water is shared by two molecules of calcium sulfate (CaSO4).
- This means the effective water of crystallisation for each CaSO4 unit is half a molecule.
(ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) is used as an antacid because:
- It is a weak base.
- It reacts with excess acid in the stomach, neutralising it and providing relief from hyperacidity.
(iii) On strong heating, blue-coloured copper sulfate crystals turn white because:
- These crystals are hydrated copper sulfate (CuSO4.5H2O).
- When heated, they lose their water of crystallisation and become anhydrous copper sulfate (CuSO4), which is white.
Q10: During electrolysis of brine, a gas 'G' is liberated at the anode. When this gas 'G' is passed through slaked lime, a compound 'C' is formed, which is used for disinfecting drinking water.
(i) Write the formula of 'G' and 'C'.
(ii) State the chemical equations involved.
(iii) What is the common name of compound 'C'? Give its chemical name. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) The formula of 'G' is Cl2 and the formula of 'C' is CaOCl2.
(ii) The chemical equations involved are:
- At the anode during electrolysis of brine:
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) → Cl2(g) + H2(g) + 2NaOH(aq) - When chlorine gas (G) is passed through slaked lime:
Ca(OH)2(s) + Cl2(g) → CaOCl2(s) + H2O(l)
(iii) The common name of compound 'C' is bleaching powder. Its chemical name is calcium hypochlorite.
Q11: A cloth strip dipped in onion juice is used for testing a liquid 'X'. The liquid 'X' changes its odour. Which type of an indicator is onion juice? The liquid 'X' turns blue litmus red. List the observations the liquid 'X’ will show on reacting with the following:
(a) Zinc granules
(b) Solid sodium carbonate.
Write the chemical equations for the reactions involved. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Onion juice is an olfactory indicator. Olfactory indicators give one type of odour in acidic medium and a different odour in basic medium. As the liquid 'X' turns blue litmus red, hence it is an acidic solution.(a) Acids react with active metals such as zinc, magnesium, etc. and evolve hydrogen gas. The chemical equation for the reaction is:
Zn(s) + dil.H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
(b) Acids react with metal carbonates to give carbon dioxide with brisk effervescence. The observation with solid sodium carbonate will be the release of carbon dioxide gas. The chemical equation for the reaction is:
2HCl(aq) + Na2CO3(s) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Q12: A chemical compound 'X' is used in the soap and glass industry. It is prepared from brine.
(a) Write the chemical name, common name and chemical formula of 'X'.
(b) Write the equation involved in its preparation.
(c) What happens when it is treated with water containing Ca or Mg salts? (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The chemical name of 'X' is Sodium Carbonate, commonly known as washing soda. Its chemical formula is Na2CO3.
(b) The equation involved in the preparation of Sodium Carbonate is: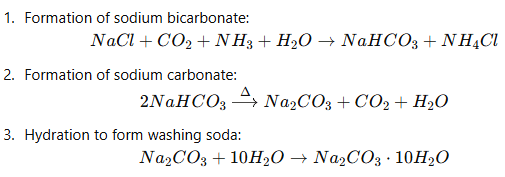
(c) When Sodium Carbonate is treated with water containing calcium (Ca) or magnesium(Mg) salts, it forms insoluble precipitates. For example:
- Na2CO3 + CaCl2 → CaCO3 + 2NaCl
- Na2CO3 + MgSO4 → MgCO3 + Na2SO4
Q13: How can it be proved that the water of crystallisation makes a difference in the state and colour of the compounds? (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The water of crystallisation gives the crystals of the salts their shape and colour.
- For example, the presence of water of crystallisation in copper sulphate crystals imparts them blue colour and crystalline shape.
- Heat a few crystals of CuSO4. 5H2O which are blue in colour in a dry boiling tube.
- On heating, the blue copper sulphate crystals turn white and a powdery substance is formed.
- Tiny droplets of water are seen in the boiling tube.
- Cool the boiling tube and add 2-3 drops of water on the white copper sulphate powder.
- The crystals of copper sulphate again become blue in colour.
- CuSO4.5H2O → CuSO4.5H2O
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q1: Blue litmus solution is added to two test tubes A and B containing dilute HCl and NaOH solution respectively. In which test tube a colour change will be observed? State the colour change and give its reason. (2019) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The colour change will be observed in test tube A containing dilute HCl. The blue litmus paper will turn red in test tube A. This is because HCl is an acid and it turns blue litmus paper red.
Q2: Out of HCI and CH3COOH, which one is a weak acid and why? Explain with the help of an example. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Out of HCI and CH3COOH, CH3COOH is a weak acid because it dissociates partially in the solution. This can be proved with the help of the following example. If 1 M HCI and 1 M CH3COOH are taken in the beaker as shown in the figure, greater deflection is observed in the case of HCI. This shows that more ions are produced by HCI in the solution, which produces more current.
Q3: (a) What does pH scale measure?
(b) Write its range.
(c) State the significance of highest and lowest values of pH scale. (2019 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) pH scale is used to measure the strength of acids and bases.
(b) The pH value ranges from 0 to 14.
(c) Lowest value of pH scale indicates the highly acidic solution. Highest value of pH scale indicates the highly basic solution.
Q4: "Sodium hydrogen carbonate is a basic salt". Justify this statement. How is it converted into washing soda? (AI 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) is basic in nature as on hydrolysis it gives a mixture of strong base (NaOH) and weak acid (H2CO3). Sodium hydrogen carbonate is converted to washing soda in the following way:
(i) Thermal decomposition of NaHCO3:
2 NaHCO3(s) → Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(g)
(ii) Recrystallization of sodium carbonate:
Na2CO3 + 10H2O → Na2CO3·10H2O (solid)
Thus, sodium hydrogen carbonate is converted into washing soda through thermal decomposition and recrystallization.
Q5: A solution 'X' gives orange colour when a drop of it falls on pH paper, while another solution Y gives bluish colour when a drop of it falls on pH paper. What is the nature of both the solutions? Determine the pH of solutions 'X' and 'Y'. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Solution 'X' is an acidic solution with a pH range of 3-4. Solution 'Y' is a basic solution with a pH of 9.
Q6: On adding a few drops of universal indicator in three colorless solutions X, Y, and Z taken separately in three test tubes, a student observed the changes in color as green in X, red in Y, and blue in Z.
(a) Arrange X, Y, and Z in increasing order of their pH values.
(b) Which one of the three X, Y, and Z will change the color of phenolphthalein? Why? (2019 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The increasing order of pH values for solutions X, Y, and Z is Y < X < Z.
(b) Solution Z will change the color of phenolphthalein because it is a basic solution that changes the color of phenolphthalein from colorless to pink.
Q7: Why is sodium hydrogen carbonate an alkaline salt? List its two important uses. (2019 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) is considered an alkaline salt because it has a pH value greater than 7.
- This occurs as it is a salt formed from a strong base and a weak acid.
- Two important uses of sodium hydrogen carbonate are:
- It serves as an antacid in medicines, helping to neutralise excess stomach acid.
- It is used as a food additive in various products, enhancing taste and texture.
Q8: Identify the acid and the base from which sodium chloride is obtained. Which type of salt is it? When is it called rock salt? How is rock salt formed? (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Sodium chloride is obtained by the neutralization of sodium hydroxide (base) with hydrochloric acid (acid).
- It is a neutral salt.
- When sodium chloride is found in the form of solid deposits with impurities, it is called rock salt.
- Rock salt is formed by the evaporation of salty water from inland lakes.
Q9: A white powder is added while baking cakes to make it soft and spongy. Name its main ingredients and explain the function of each ingredient. Write the chemical reaction taking place when the powder is heated during baking. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The white powder added while baking cakes to make them soft and spongy is baking powder.
- Its main ingredients are sodium hydrogen carbonate and a mild edible acid like tartaric acid or citric acid.
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate decomposes to give out carbon dioxide, which causes the cake to rise and makes it soft and spongy.
- The function of tartaric acid or citric acid is to neutralize sodium carbonate formed during heating, which can otherwise make the cake bitter.
- The reaction taking place when the powder is heated is : 2 NaHCO3 (heat) → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
Q10: (a) Why is electrolysis of brine called 'Chlor-alkali process'? Write the chemical equation involved in this process.
(b) A few crystals of hydrated copper sulphate are heated in a dry test-tube. Enlist any two observations. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The electrolysis of brine is called the 'Chlor-alkali process' because it produces chlorine (chlor) and sodium hydroxide (alkali). The chemical equation involved in this process is: 2NaCl + 2H2O → 2NaOH + Cl2 + H2
(b) Two observations when hydrated copper sulphate crystals are heated in a dry test-tube are:
(i) The color of copper sulphate crystals becomes white after heating.
(ii) Water droplets are noticed at the mouth side of the boiling tube, which are obtained from the water of crystallization.
Q11: State the observation and inference made by a student when he brings
(A) a wet blue litmus paper and
(B) a wet red litmus paper in contact with the gas liberated during thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Observation: The moist blue litmus paper will turn red.
Inference: The gas liberated is acidic in nature.
(B) Observation: Wet red litmus paper will remain red.
Inference: The gas liberated is acidic in nature.
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q1: 2 mL of sodium hydroxide solution is added to a few pieces of granulated zinc metal taken in a test tube. When the contents are warmed, a gas evolves which is bubbled through a soap solution before testing. Write the equation of the chemical reaction involved and the test to detect the gas. Name the gas which will be evolved when the same metal reacts with a dilute solution of a strong acid. (2018) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- It is observed that active metals like zinc react with strong bases like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to liberate hydrogen gas (H2) and the corresponding salt.
- The equation for the chemical reaction is: 2NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) → Na2ZnO2(aq) + H2(g)
- The evolution of gas is confirmed by the bubble formation in soap solution.
- The test to detect hydrogen gas (H2) is as follows:
- When a burning matchstick is kept on the mouth of the test tube, a "pop" sound is heard, which confirms the presence of hydrogen gas.
- When the same metal (zinc) reacts with a dilute solution of a strong acid, hydrogen gas (H2) will also be evolved.
Q2: The pH of a salt used to make tasty and crispy pakoras is 14. Identify the salt and write a chemical equation for its formation. (2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃), but the pH is approximately 8-9, not 14.
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) is indeed used in cooking (e.g., pakoras) to release CO₂, making the batter light and crispy:
- Preparation (Solvay process):
NaCl + H₂O + CO₂ + NH₃ → NH₄Cl + NaHCO₃
However, NaHCO₃ is a weak base (from a strong base, NaOH, and weak acid, H₂CO₃), and its aqueous solution has a pH of about 8-9, not 14. A pH of 14 indicates a strong base like NaOH, which is not used for pakoras due to its caustic nature. - Reaction in cooking:
2NaHCO₃ (heat) → Na₂CO₃ + H₂O + CO₂
Q3: Identify the compound X on the basis of the reactions given below. Also, write the name and chemical formulae of A, B and C. (CBSE 2018, 16)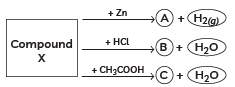
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- X must be a compound which forms water with acids.
- This means it must be a base, which reacts with acids to form salt and water.
- This base also reacts with zinc metal and releases hydrogen gas.
- So, it must be NaOH (sodium hydroxide).
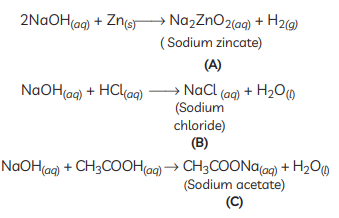 X: NaOH (Sodium hydroxide)
X: NaOH (Sodium hydroxide)A: Na2ZnO2 (Sodium zincate)
B: NaCl (Sodium chloride)
C: CH3COONa (Sodium acetate)
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q1: With the help of an example, explain what happens when a base reacts with a non-metallic oxide. What do you infer about the nature of non-metal oxide? (Board Term I, 2017) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- When a base reacts with a non-metallic oxide, it forms a salt and water.
- For example, when calcium hydroxide (a base) reacts with carbon dioxide (a non-metallic oxide), it produces calcium carbonate (salt) and water.
- The reaction can be represented as follows: CO2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCO3 + H2O
Q2: How will the following substances dissociate to produce ions in their solutions? (Board Term I, 2017)
(i) Hydrochloric acid
(ii) Sulphuric acid
(iii) Potassium hydroxide
(iv) Magnesium hydroxide
(v) Nitric acid
(vi) Sodium hydroxide
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The dissociation of the given substances to produce ions in their solutions are as follows:
(i) Hydrochloric acid (HCI): HCI → H+ + Cl-
(ii) Nitric acid (HNO3): HNO3 → H+ + NO3-
(iii) Sulphuric acid (H2SO4): H2SO4 → 2H+ + SO42-
(iv) Sodium hydroxide (NaOH): NaOH → Na+ + OH-
(v) Potassium hydroxide (KOH): KOH → K+ + OH-
(vi) Magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2): Mg(OH)2 → Mg2+ + 2OH-
Q3: Explain how an antacid works. (Board Term 1, 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: An antacid works by neutralising excess stomach acid, which can lead to discomfort and irritation. Here's how it functions:
- Antacids contain a base, such as magnesium hydroxide (found in Milk of Magnesia).
- When taken, the base reacts with the excess hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
- This reaction produces salt and water, alleviating symptoms of indigestion.
- The resulting salt, magnesium chloride, is neutral and helps relieve pain.
The reaction can be represented as follows:
Mg(OH)2 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + 2H2O
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q1: Answer the following questions: (CBSE 2016)(i) State the colour of phenolphthalein in soap solution.
(ii) Name the by-product of chlor-alkali process which is used for the manufacture of bleaching powder.
(iii) Name one indicator which specifies the Various levels of H+ ion concentration.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Phenolphthalein in soap solution turns pink.
(ii) Chlorine gas (Cl₂) is the by-product of the chlor-alkali process used to manufacture bleaching powder.
(iii) One indicator that shows various levels of H+ ion concentration is litmus.
Q2: On passing excess carbon dioxide gas through lime water, it first turns milky and then becomes colourless. Explain why? Write all the chemical equations of the reactions involved. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- When excess carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, the following occurs:
- The lime water initially turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
- With further addition of carbon dioxide, the solution becomes colourless as calcium bicarbonate (Ca(HCO3)2) is formed, which is soluble in water.
- The chemical reactions involved are:
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3(s) + H2O
CaCO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) → Ca(HCO3)2
Q3: Name of type of chemical reaction represented by the following equation : (CBSE 2016)
(i) CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
(ii) 3BaCl2 + Al2 (SO4)3 → 2AlCl3 + 3BaSO4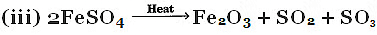
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Combination reaction.
(ii) Double displacement reaction.
(iii) Decomposition reaction.
Q4: (a) Define olfactory indicators. Name two substances which can be used as olfactory indicators.
(b) Choose strong acids from the following :
CH3COOH, H2SO4, H2CO3, HNO3 (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Indicators which work on the basis of odour are called olfactory indicators.
- Onion and vanilla extracts can be used as olfactory indicators.
Q5: (a) The soil in a field is highly acidic. List any two materials which can be added to this soil to reduce its acidity. Give the reason for your choice. (CBSE 2016)
(b) A gas produced in the laboratory is highly soluble in water. Its colourless solution turns pink when a few drops of phenolphthalein is added to it. What is the nature of this gas?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) To reduce the acidity of soil, the following materials can be added:
- Lime, (CaO) can be added to neutralize acidity.
- Chalk, (CaCO3) can also be added to neutralise acidity.
(b) The nature of gas is basic because it turns phenolphthalein pink. The following reaction takes place in aqueous solution,
Example: NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH-
Q6: (a) The pH of soil A is 7.5 while that of soil B is 4.5. Which of the two soils A or B should be treated with powdered chalk to adjust its pH and why? (CBSE 2016)
(b) Name the chemical which is injected into the skin of a person:
(i) During an ant’s sting
(ii) During the nettle leaf sting.
How can the effect of these stings be neutralised?
(c) Explain how the pH change in the river water can endanger the lives of aquatic animals like fish?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) Soil B has a pH of 4.5, making it acidic. It should be treated with powdered chalk, which is basic, to raise its pH.
(i) During an ant's sting: Formic acid (HCOOH).
(ii) During a nettle sting: Formic acid (HCOOH).
- The effects of these stings can be neutralised by rubbing the area with a mild base, such as baking soda (NaHCO3).
- It may reduce the amount of oxygen dissolved in the water.
- Both acidic and basic water can harm the skin of aquatic animals, such as fish.
Q7: State reasons for the following statements:
(i) Stain of curry on a white cloth becomes reddish brown when soap is scrubbed on it and turns yellow again when the cloth in washed with plenty of water.
(ii) Curd should not be kept in copper or brass vessels. What is done to protect it? (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i)
- A stain of curry on a white cloth turns reddish-brown when soap is scrubbed on it because:
- Turmeric in the curry reacts with sodium hydroxide in the soap, forming a red compound.
- When the cloth is rinsed with plenty of water, the sodium hydroxide becomes very dilute, stopping the reaction and returning the stain to its original yellow colour.
(ii)
- Curd should not be stored in copper or brass vessels because:
- Curd contains lactic acid, which reacts with these metals, altering the taste.
- To prevent this, curd should be kept in glass, steel, or ceramic containers that do not react with lactic acid.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q1: (a) A student detected the pH of four unknown solutions A, B, C and D as follows: 11, 5, 7 and 2.Predict the nature of the solution.
(b) Explain how an antacid works. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) A is basic, ‘B’ is acidic ‘C’ is neutral and ‘D’ is strongly acidic.
(b) Hyperacidity is Caused by excess of hydrochloric acid in stomach. Antacid is basic in nature. It neutralises excess of acid and releases CO2 gas which gives relief from pain caused by hyperacidity.
Q2: Explain the action of dilute hydrochloric acid on the following with chemical equations: (CBSE 2015)
(a) Magnesium ribbon
(b) Sodium hydroxide
(c) Crushed egg shells
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) Hydrogen gas will be formed, e.g.
Mg (s) + 2HCl (dil) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (s)
(b) Sodium chloride and water will be formed, e.g.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O (Neutralization reaction)
(c) Crushed egg shells are made up of CaCO3 which reacts with dil HCl to give brisk effervescence due to CO2, e.g.
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
Q3: What is meant by water of crystallisation? How would you show that copper sulphate crystals contain water of crystallisation? (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Water which is present in the crystals of a compound is called water of crystallisation.
- It is defined as the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt.
- Copper sulphate crystals are blue in colour.
- On heating solid copper sulphate crystals, they lose water of crystallisation and become white.
- On adding a few drops of water to the white powder, blue colour of copper sulphate is restored.
- This shows that copper sulphate crystals contain water of crystallisation.
Q4: (a) Three acidic solutions A, B and C have p H = 0, 3 and 5 respectively.
(i) Which solution has highest concentration of H+ ions?
(ii) Which solution has the lowest concentration of H+ ions?
(b) How concentrated sulphuric acid can be diluted? Describe the process. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) (i) Solution A has the highest concentration of H+ ions.
(ii) Solution C has the lowest concentration of H+ ions.
(b) To dilute concentrated sulphuric acid:
- Always add the acid to water, not the other way around.
- Start by pouring some water into a beaker.
- Gradually add concentrated sulphuric acid in small amounts to the water.
- Stir the mixture continuously with a glass rod.
- If the beaker gets hot, cool it by placing it in cold water.
Q5: Give the chemical name and formula of bleaching powder. What happens when it is exposed to air? Mention two uses of bleaching powder. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Chemical name of bleaching powder is calcium oxychloride.
Formula: CaOCl2 . On exposure to air, it absorbs moisture.
Uses:
(i) As an oxidising agent in chemical industries.
(ii) For disinfecting drinking water to make it free from germs.
Q6: (a) What is pH value of salt formed by a
(i) Weak acid and strong base?
(ii) Strong acid and strong base?
(b) 15 mL of water and 10 ml of sulphuric acid are to be mixed in a beaker
(i) State the method that should be followed with reason.
(ii) What is this process called? (CBSE 2015)
(c) What is observed when sulphur dioxide is passed through
(i) water (ii) lime water?
Also write chemical equations for the reactions that take place.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) (i) The pH value will be greater than 7.
(ii) The pH value will be less that than 7.
(b) (i) When mixing, the acid should be added slowly to water. This prevents splashing and allows for constant cooling since the reaction is highly exothermic.
(ii) This process is known as dilution.
(c) (i) Sulphurous acid is formed.
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3 (Sulphurous acid)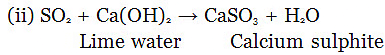
Lime water turned turns milky due to formation of calcium sulphite.
Q7: (a) State the chemical properties on which the following uses of baking soda are based:
(i) as an antacid
(ii) as soda-acid fire extinguisher
(iii) to make bread and cake soft and spongy.
(b) How washing soda is obtained from baking soda? Write balanced chemical equation. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) (i) It is weakly basic in nature and neutralises hyperacidity.
(ii) It liberates CO2 with H2SO4 reacts with it, which extinguisher fire.
(iii) It liberates CO2 on heating which makes bread and cake soft and sponge.
(b) 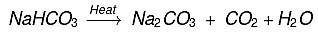 Baking soda on heating gives sodium carbonate which on crystallisation from aqueous solution gives washing soda, e.g.
Baking soda on heating gives sodium carbonate which on crystallisation from aqueous solution gives washing soda, e.g.
Na2CO3 + 10H2O → Na2CO3.10H2O
Q8: State reason for the following statements: (CBSE 2015)
(a) Tap water conducts electricity whereas distilled water does not.
(b) Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not turn blue litmus red whereas dilute hydrochloric acid does.
(c) During summer season, a milk man usually adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(d) For a dilution of acid, acid is added into water and not water into acid.
(e) Ammonia is a base but does not contain hydroxyl group.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) Tap water conducts electricity because it contains ions that facilitate electrical flow, while distilled water lacks these ions.
(b) Dry hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas does not turn blue litmus red because it does not form ions. In contrast, dilute hydrochloric acid releases H and Cl- ions, which are responsible for its acidic properties.
(c) A milkman adds a small amount of baking soda to fresh milk to prevent it from souring. Baking soda inhibits the formation of lactic acid, which causes milk to spoil.
(d) When diluting an acid, it is crucial to add acid to water rather than the other way around. This is because adding water to acid can cause a violent reaction and splashing due to the heat generated.
(e) Ammonia is classified as a base despite not containing a hydroxyl group. When dissolved in water, it produces hydroxide ions (OH-), which gives it basic properties. NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH-
Q9: (a) Define universal indicator. Mention its one use.
(b) Solution A gives pink colour when a drop of phenolphthalein indicator is added to it. Solution B gives red colour when a drop of methyl orange is added to it. What type of solutions are A and B and which one of the solutions A and B will have a higher pH value?
(c) Name one salt whose solution has pH more than 7 and one salt whose solution has pH less than 7. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) A Universal indicator is a mixture of several indicators. It shows different colours at different concentrations of H+ ion concentrations.
(b) Solution A is alkaline in nature.Solution B is acidic in nature.
Solution A has a higher pH value.
(c) Salts of weak acid and strong base give a solution which have pH more than 7. i.e. basic salt Sodium acetate is an example of such salts. Salts of strong acid and weak base give a solution which has pH less than 7. i.e. Acidic salt. Ammonium chloride is an example of such salts.
|
80 videos|661 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science - Previous Year Questions - Acids Bases and Salts
| 1. What are the properties of acids, bases, and salts? |  |
| 2. How do acids and bases react with each other? |  |
| 3. What is the role of pH in determining the strength of acids and bases? |  |
| 4. How can we identify an unknown solution as an acid, base, or salt? |  |
| 5. What are some common examples of acids, bases, and salts? |  |

















