Previous Year Topic Wise Questions With Solutions: Coding & Decoding | CSAT Preparation - UPSC PDF Download
Q1. If in a certain code, ‘ABCD’ is written as 24 and ‘EFGH’ is written as 1680, then how is ‘IJKL’ written in that code? (2024)
(a) 11880
(b) 11240
(c) 7920
(d) 5940
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Here, the code is being calculated by multiplying the position values of the alphabet.
ABCD = 24 1 × 2 × 3 × 4 = 24
EFGH = 1680
5 × 6 × 7 × 8 = 1680
IJKL = 9 × 10 × 11 × 12 = 11880
Q2. If in a certain code, ‘POT’ is written as ATOP and ‘TRAP’ is written as APART, then how is ‘ARENA’ written in that code? (2024)
(a) AARENA
(b) AANREA
(c) AANEAR
(d) AANERA
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
In a certain code, ‘POT’ is written as ‘ATOP’ and ‘TRAP’ is written as ‘APART’, Logic: Here the word is being reversed and prefix ‘A’ is being added to the front. Reverse order of POT = TOP
Thus, code of POT will be ’ATOP’. Reverse order of TRAP = PART
Thus, code of TRAP will be ’APART’.
Similarly, Reverse order of ARENA = ANERA Thus, code of ARENA will be ’AANERA’.
Q3. If 'ZERO' is written as 'CHUR', then how is 'PLAYER' written? (2023)
(a) SOCACT
(b) SODBGT
(c) SODBHT
(d) SODBHU
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Here, we are required to decipher or decode the pattern.
ZERO is written as CHUR. We can see that the underlying pattern is very simple, as shown below:
Z + 3 = C
E + 3 = H
R + 3 = U
O + 3 = R
We will follow a similar pattern to code PLAYER.
P + 3 = S
L + 3 = O
A + 3 = D
Y + 3 = B
E + 3 = H
R + 3 = U
So, the required code is SODBHU.
Hence, option (d) is correct.
Q4. Consider the sequence ABC_ _ABC_DABBCD_ABCD that follows a certain pattern.
Which of the following completes the sequence? (2023)
(a) DACB
(b) CDAB
(c) DCCA
(d) DDCA
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Method I: The given sequence: ABC_ _ABC_DABBCD_ABCD
We can break this sequence in five sets of 4 elements each.
On analysing it in this manner, we can see that the last element moves to the first position in a cyclic manner.
The complete sequence is: ABCD DABC CDAB BCDA ABCD
Hence, option (d) is correct.
Method II: The given sequence: ABC_ _ABC_DABBCD_ABCD
There are 20 elements in this series. Let’s break this sequence in four sets of 5 elements each.
ABC_ _
ABC_D
ABBCD
_ABCD
The third set ABBCD gives us a clue that one letter is being repeated. Now, we can check from the options to further confirm our presumption.
Using option (d), we get the complete sequence: ABCDD ABCCD ABBCD AABCD
We can see that in the first set 4th letter D is getting repeated, in the second set 3rd letter is getting repeated, and so on.
Hence, option (d) is correct.
Q5. If the order of the letters in the English alphabet is reversed and each letter represents the letter whose position it occupies, then which one of the following represents 'LUCKNOW'? (2022)
(a) OGXPMLD
(b) OGXQMLE
(c) OFXPMLE
(d) OFXPMLD
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
We basically need to find the opposite letter of the letters in the given word.
Opposite Letter Position = 27 – Letter Position
So, in case of LUCKNOW, we get:
27 – 12 = 15 = O
27 – 21 = 6 = F
27 – 3 = 24 = X
27 – 11 = 16 = P
27 – 14 = 13 = M
27 – 15 = 12 = L
27 – 23 = 4 = D
The word that we get is OFXPMLD.
Q6. In a code language 'MATHEMATICS' is written as 'LBSIDNZUHDR'. How is CHEMISTRY' written in that code language? (2021)
(a) DIDLHRSSX
(b) BIDNHTSSX
(c) BIDLHTSSX
(d) DGFLIRUQZ
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
In a code language 'MATHEMATICS' is written as 'LBSIDNZUHDR'.
The pattern used in the above coding is as follows:
M (13) → L (12), i.e. reduction of 1
A (1) → B (2), i.e. increase of 1
T (20) → S (19), i.e. reduction of 1
H (8) → I (9), i.e. increase of 1
And so on.
So, the code of CHEMISTRY will be: BIDNHTSSX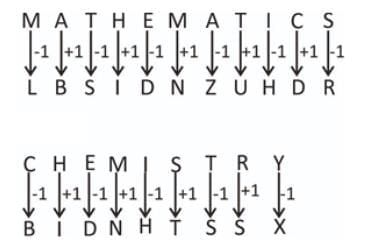
|
205 videos|265 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Previous Year Topic Wise Questions With Solutions: Coding & Decoding - CSAT Preparation - UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of coding and decoding in competitive exams like UPSC? |  |
| 2. What are some common types of coding and decoding questions asked in UPSC exams? |  |
| 3. How can candidates effectively prepare for coding and decoding questions in UPSC? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific strategies to solve coding and decoding problems quickly? |  |
| 5. How important is it to understand the basics of coding and decoding for the UPSC exam? |  |





















