Previous Year Topic Wise Questions With Solutions: Speed, Time & Distance | CSAT Preparation - UPSC PDF Download
Q1. Team X scored a total of N runs in 20 overs. Team Y tied the score in 10% less overs. Had Team Y's average run rate (runs per over) been 50% higher, the scores would have been tied in 12 overs. How many runs were scored by Team X? (2025)
(a) 72
(b) 144
(c) 216
(d) Cannot be determined
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Team X scored a total of N runs in 20 overs. Team Y tied the score in 10% less overs, i.e. in 18 overs.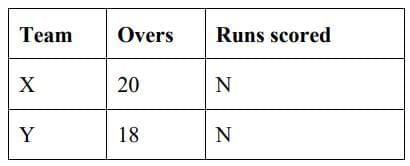 Had team Y’s average run rate (runs per over) been 50% higher, it would have scored 1.5N runs in 18 overs.
Had team Y’s average run rate (runs per over) been 50% higher, it would have scored 1.5N runs in 18 overs.
Or, in 12 overs it would have scored 1.5N × (12/18) = 1.5N × (2/3) = N runs
This information is not enough to find the value of N.
So, the number of runs scored by team X can’t be determined.
Q2. There are 7 places A, B, C, D, E, F and G in a city connected by various roads AB, AC, CD, DE, BF, EG and FG. A is 6 km south of B. A is 10 km west of C. D is 5 km east of E. C is 6 km north of D. F is 9 km west of B. F is 12 km north of G. A person travels from D to F through these roads. What is the distance covered by the person? (2025)
(a) 20 km
(b) 25 km
(c) 31 km
(d) 37 km
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The city map: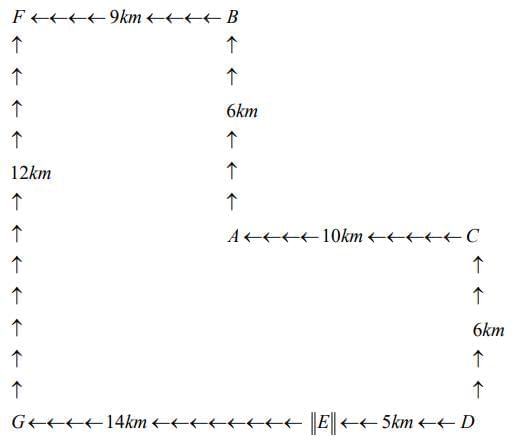
If a person wants to travel from D to F, he can opt one of the following two routes:
Route I: DG (5 km + 14 km) + GF (12 km) = 19 km + 12 km = 31 km
Route II: DC (6 km) + CA (10 km) + AB (6 km) + BF (9 km) = 6 km + 10 km + 6 km + 9 km = 31 km
In both cases, he will cover the same distance of 31 km.
Note: No questions being asked from this topic in the year 2024 and 2023.
Q3. Two friends X and Y start running and they run together for 50 m in the same direction and reach a point. X turns right and runs 60 m, while Y turns left and runs 40m. Then X turns left and runs 50m and stops, while Y turns right and runs 50 m and then stops. How far are the two friends from each other now? (2022)
(a) 100 m
(b) 90 m
(c) 60 m
(d) 50 m
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The path taken by them has been represented below: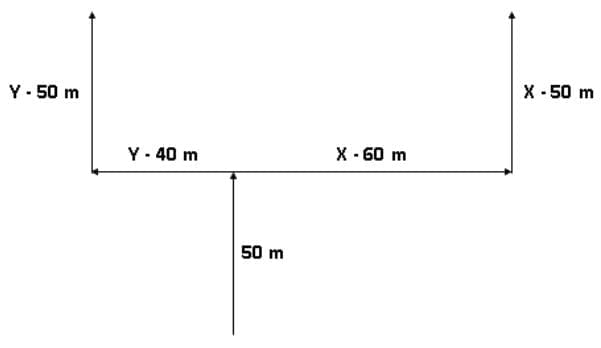 It’s pretty clear that they are 40 + 60 = 100 m apart at the end of their run.
It’s pretty clear that they are 40 + 60 = 100 m apart at the end of their run.
Q4. A man started from home at 14:30 hours and drove to village, arriving there when the village clock indicated 15:15 hours. After staying for 25 minutes, he drove back by a different route of length 1.25 times the first route at a rate twice as fast reaching home at 16:00 hours. As compared to the clock at home, the village clock is (2022)
(a) 10 minutes slow
(b) 5 minutes slow
(c) 10 minutes fast
(d) 5 minutes fast
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Total time taken by the man to come back home = 16 – 14.5 = 1.5 hours = 90 minutes
Out of which he stayed in the village for 25 minutes.
So, his total travelling time = 90 – 25 = 65 minutes
The return route was 1.25 times the initial route. So, time taken must have increased by 25% too.
So, if initial time was 100 units, now it must be 125 units.
But it is also given that while returning he drove twice as fast. So, time taken must have been halved.
So, time taken while returning back = 125/2 = 62.5 units
So, 100 + 62.5 = 65 minutes
Or 162.5 units = 65 minutes
So, 100 units = (65/162.5) × 100 = 40 minutes
So, the man took 40 minutes to reach to the village.
So, the actual time at that moment = 14:30 + 40 minutes = 15:10 hours
It’s pretty evident that the village clock is 15:15 – 15:10 = 5 minutes fast
|
205 videos|264 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Previous Year Topic Wise Questions With Solutions: Speed, Time & Distance - CSAT Preparation - UPSC
| 1. What are the basic formulas used to calculate speed, time, and distance? |  |
| 2. How can I solve problems involving two objects moving towards each other? |  |
| 3. What is the concept of relative speed in the context of speed, time, and distance? |  |
| 4. How do I approach problems that involve different units of speed, such as km/h and m/s? |  |
| 5. What are some common applications of speed, time, and distance problems in competitive exams? |  |















