UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > History for UPSC CSE > Quick Revision : Modern History
Quick Revision : Modern History | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
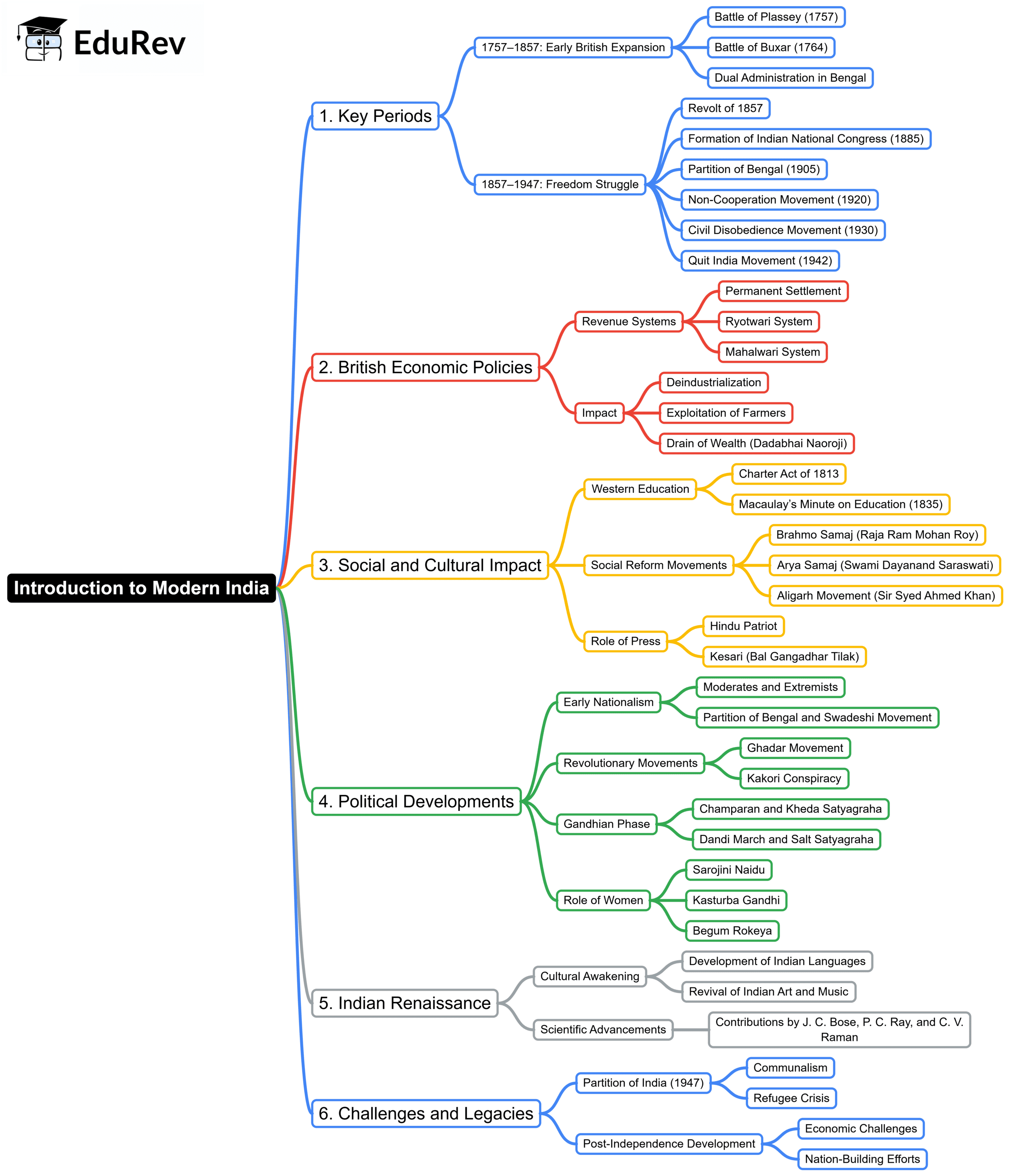
Introduction to Modern India
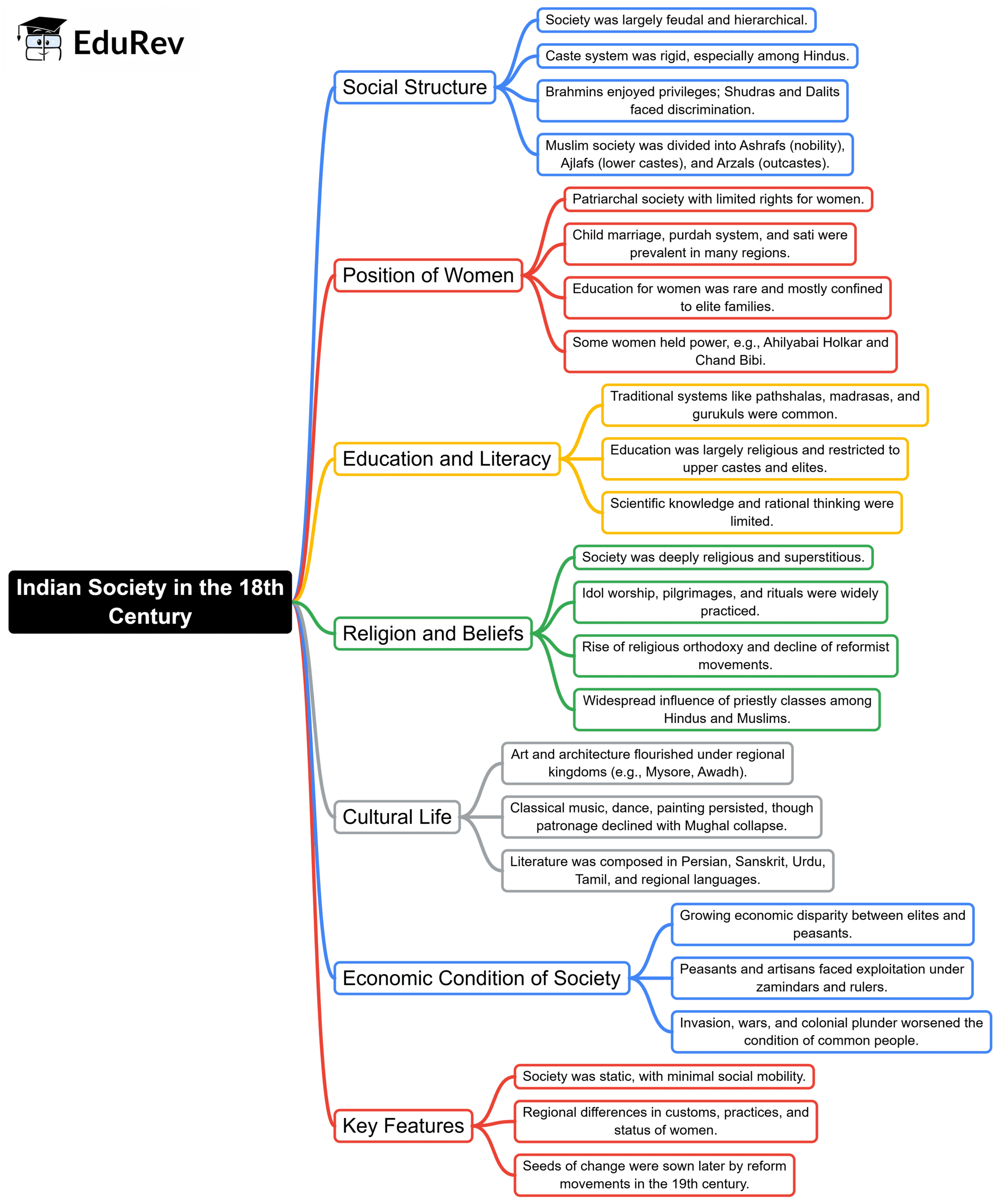
Indian Society in 18th Century
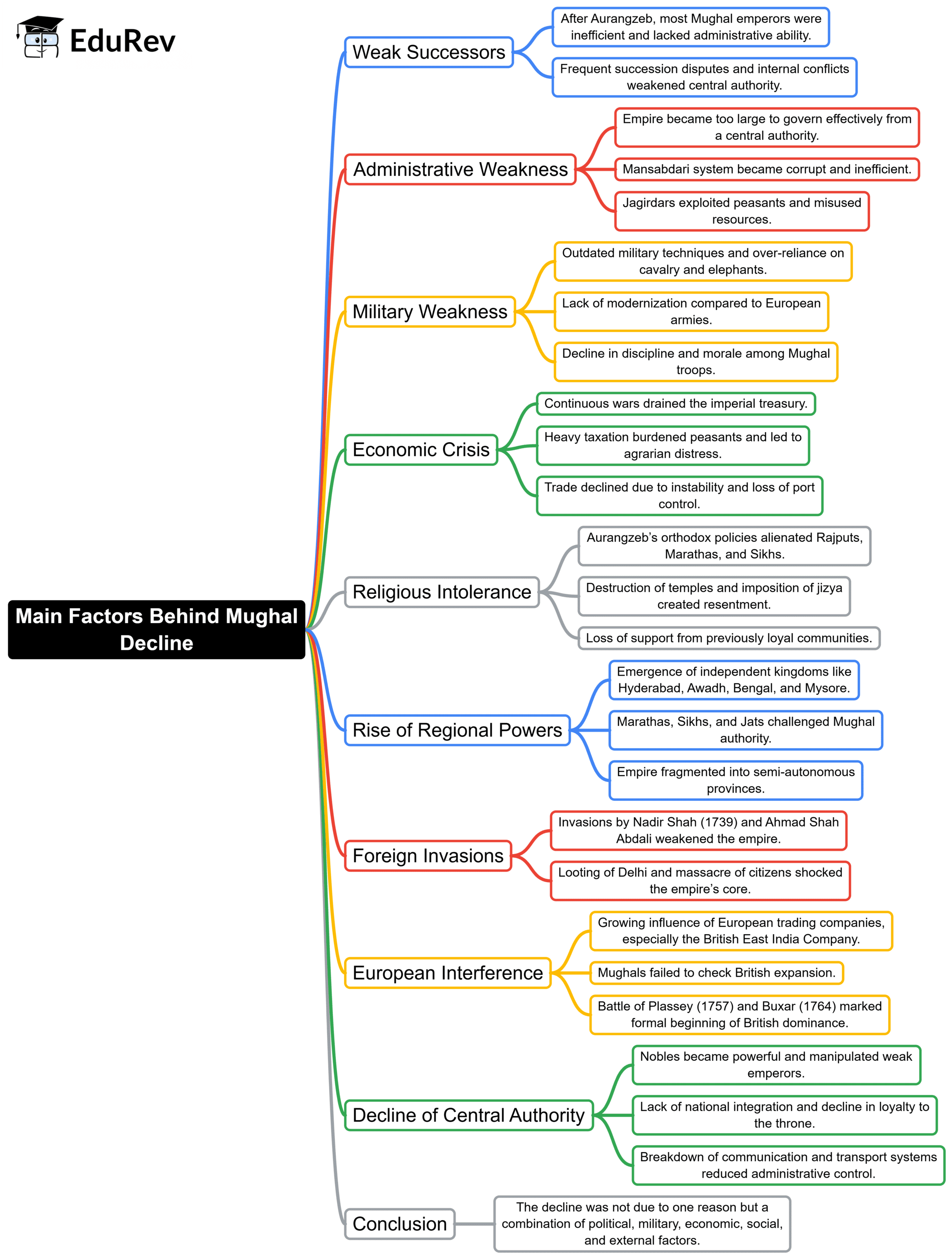
Main factors behind Mughal Decline
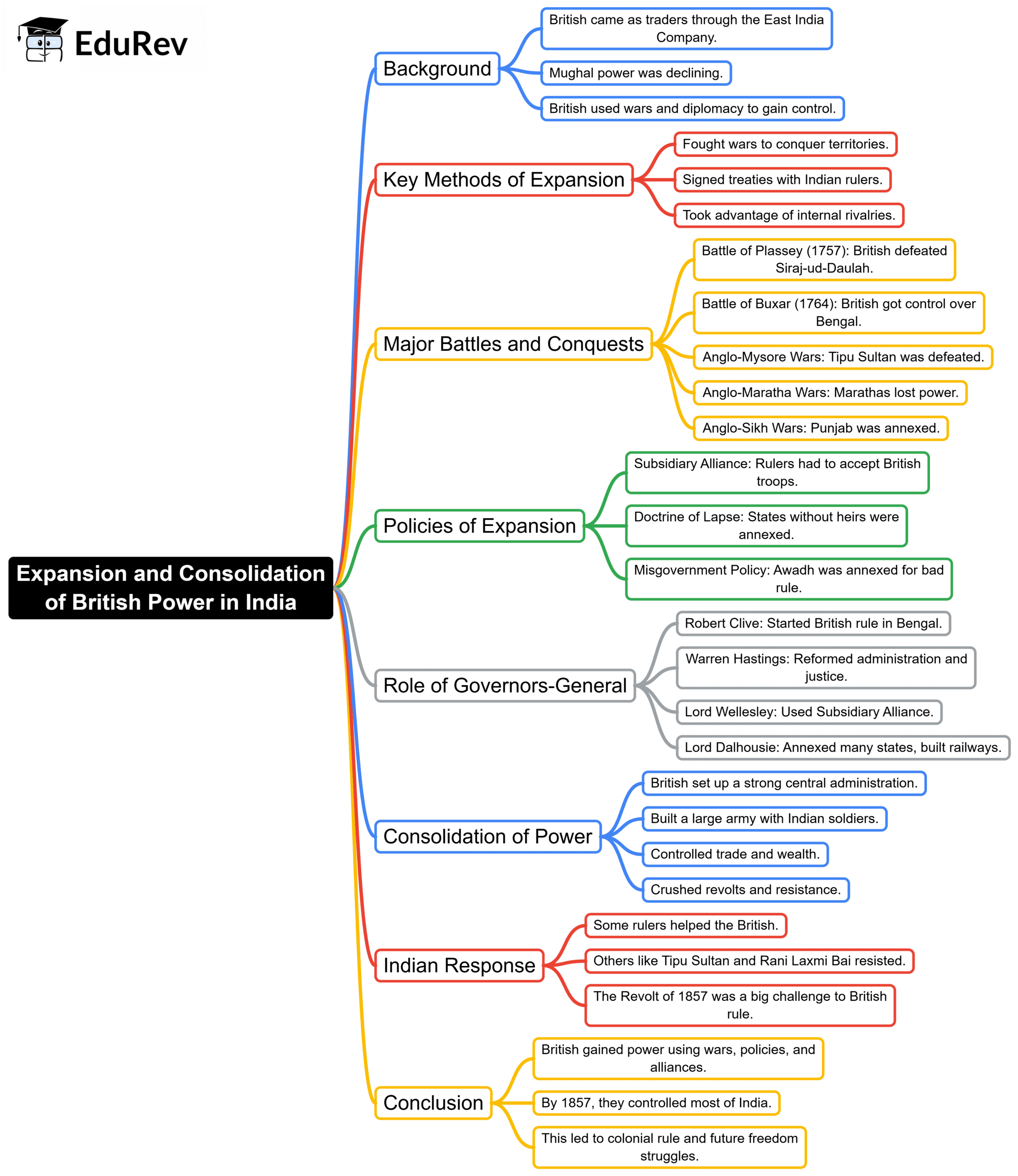
Expansion & Consolidation of British Power in India
The East India Company And The Bengal Nawabs
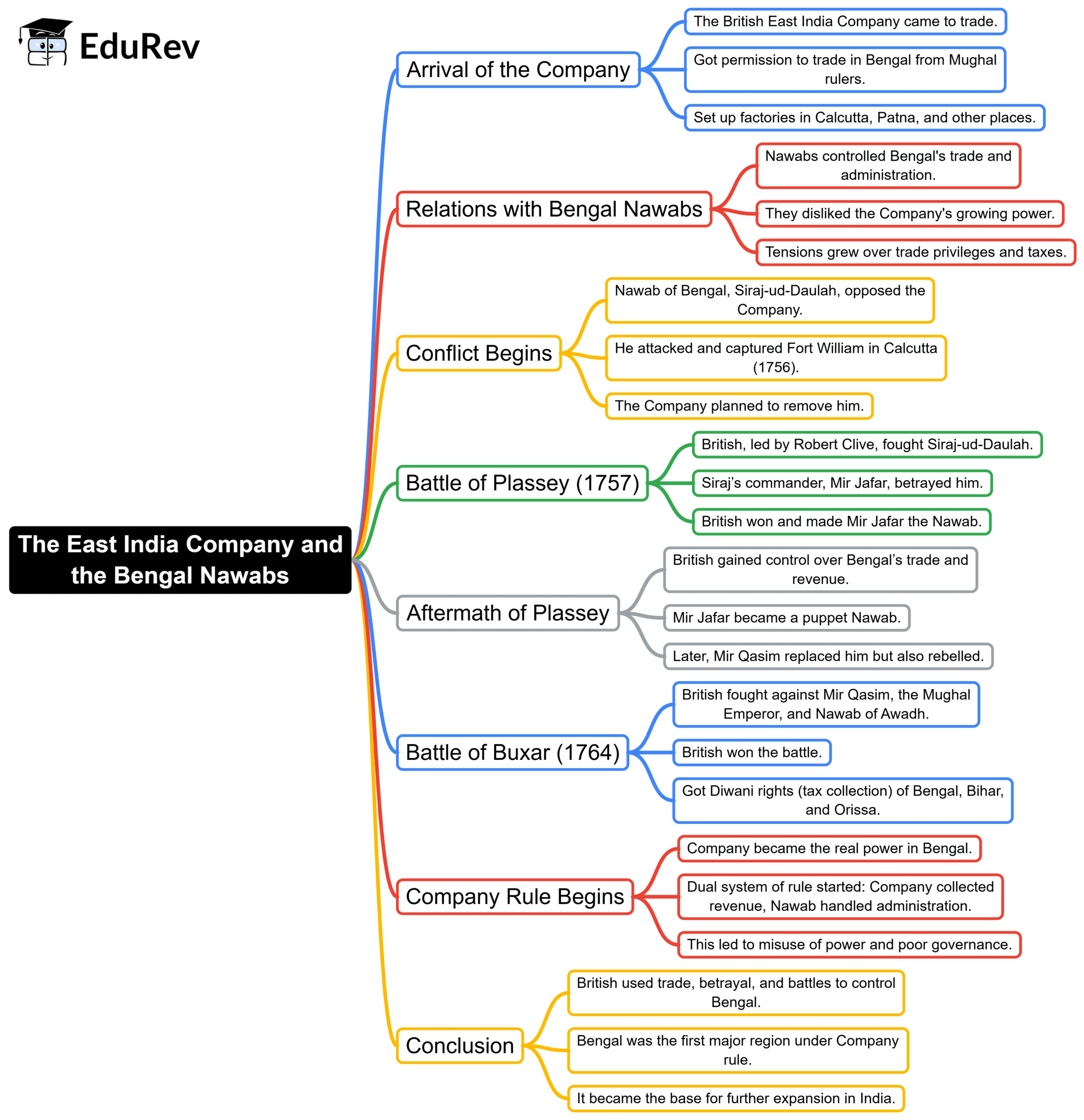
Social and Cultural Awakening, The Lower Caste, Trade Union And Peasants Movements
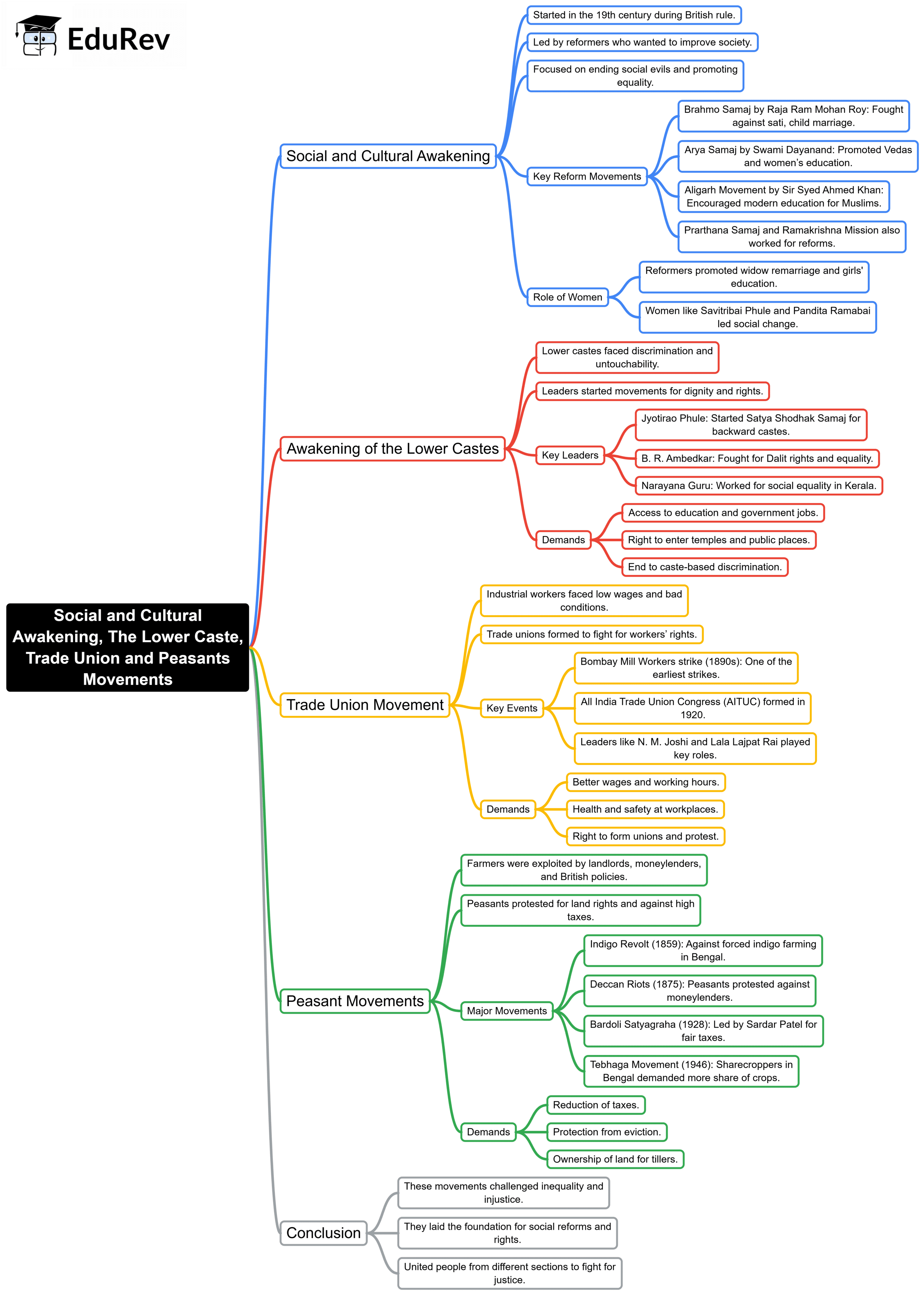
The Revolt of 1857
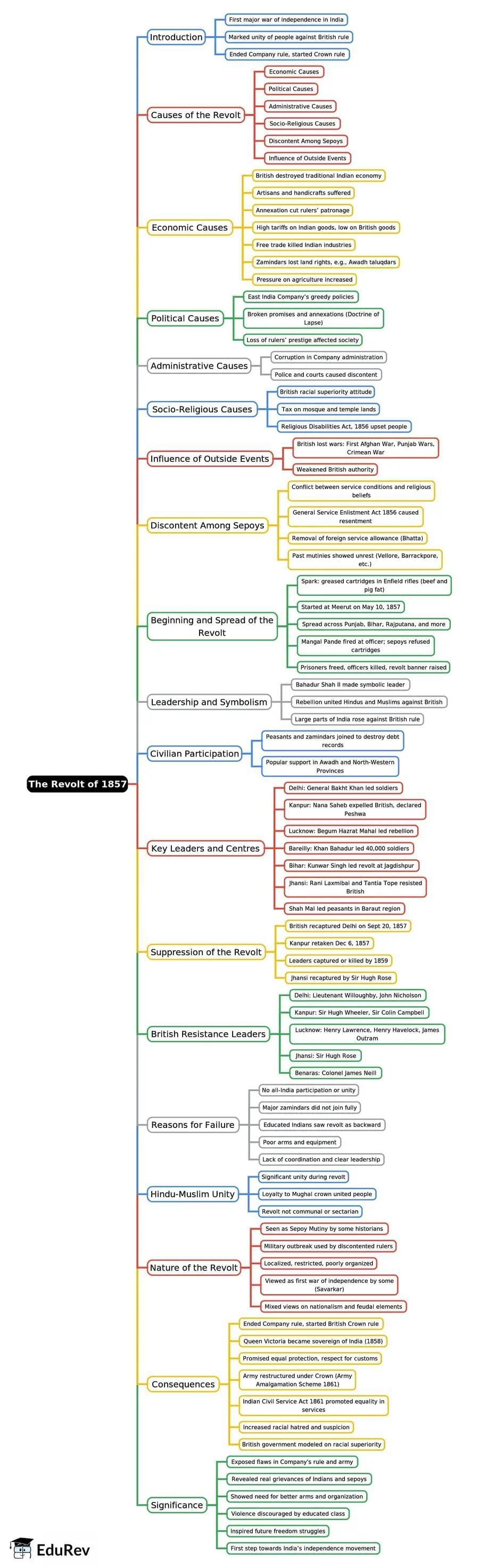
Reform Movements
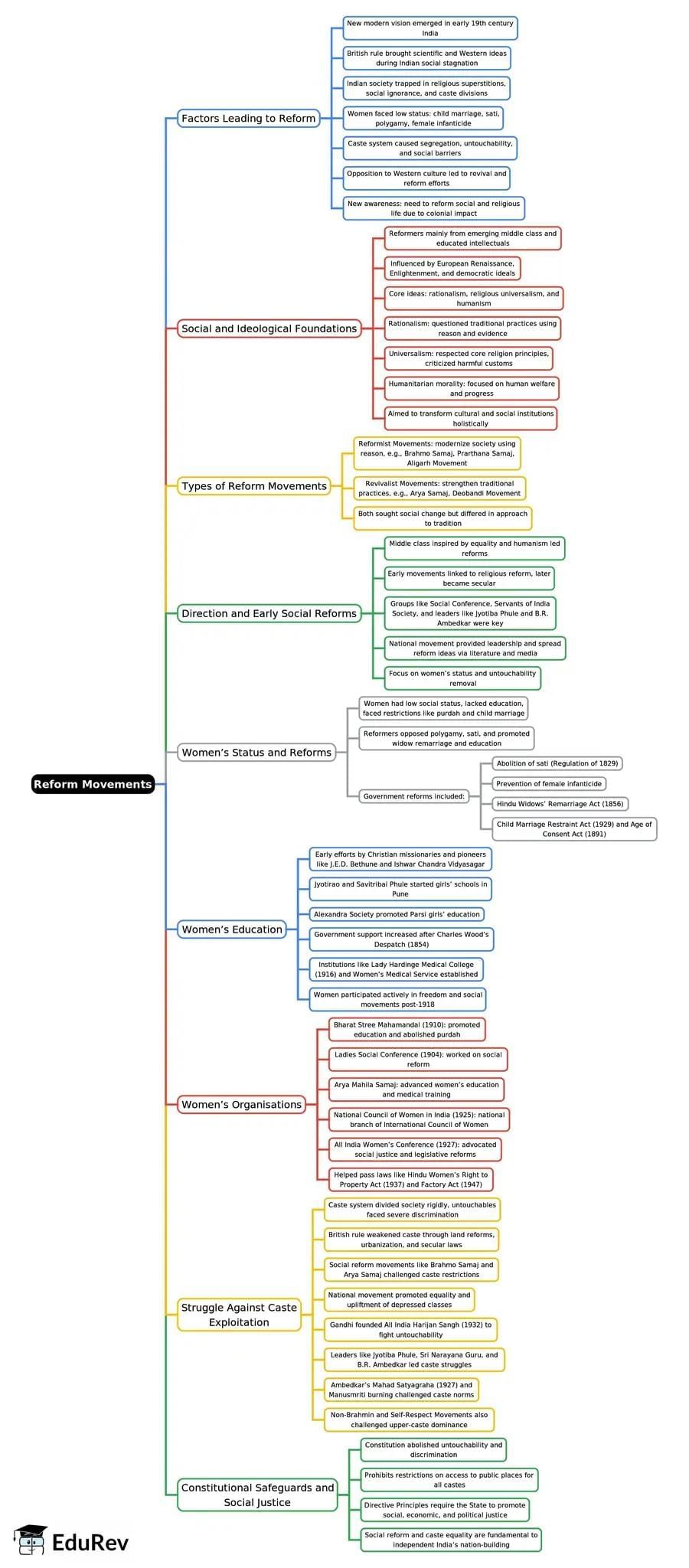
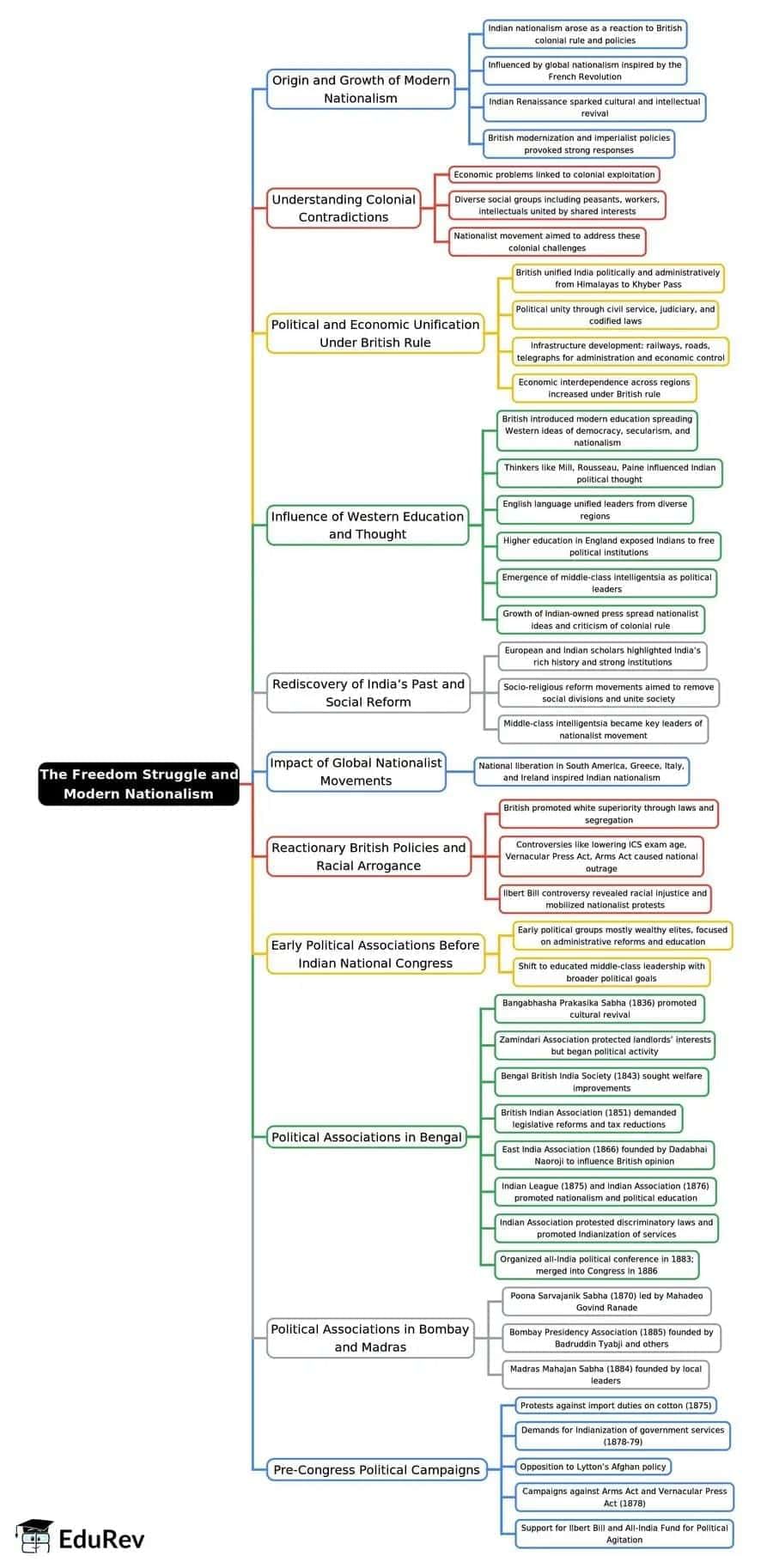
The Freedom Struggle and Modern Nationalism
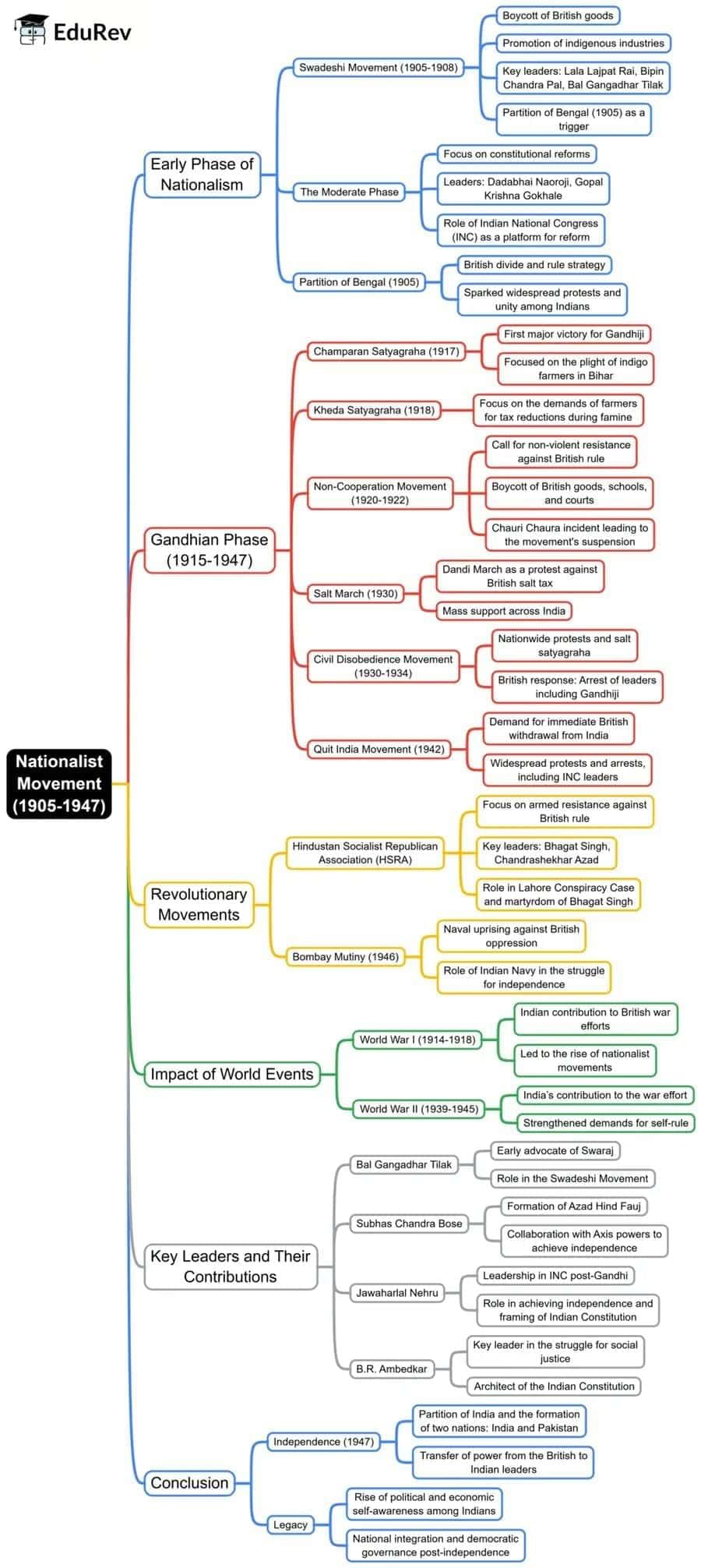
Nationalist Movement (1905-1947)
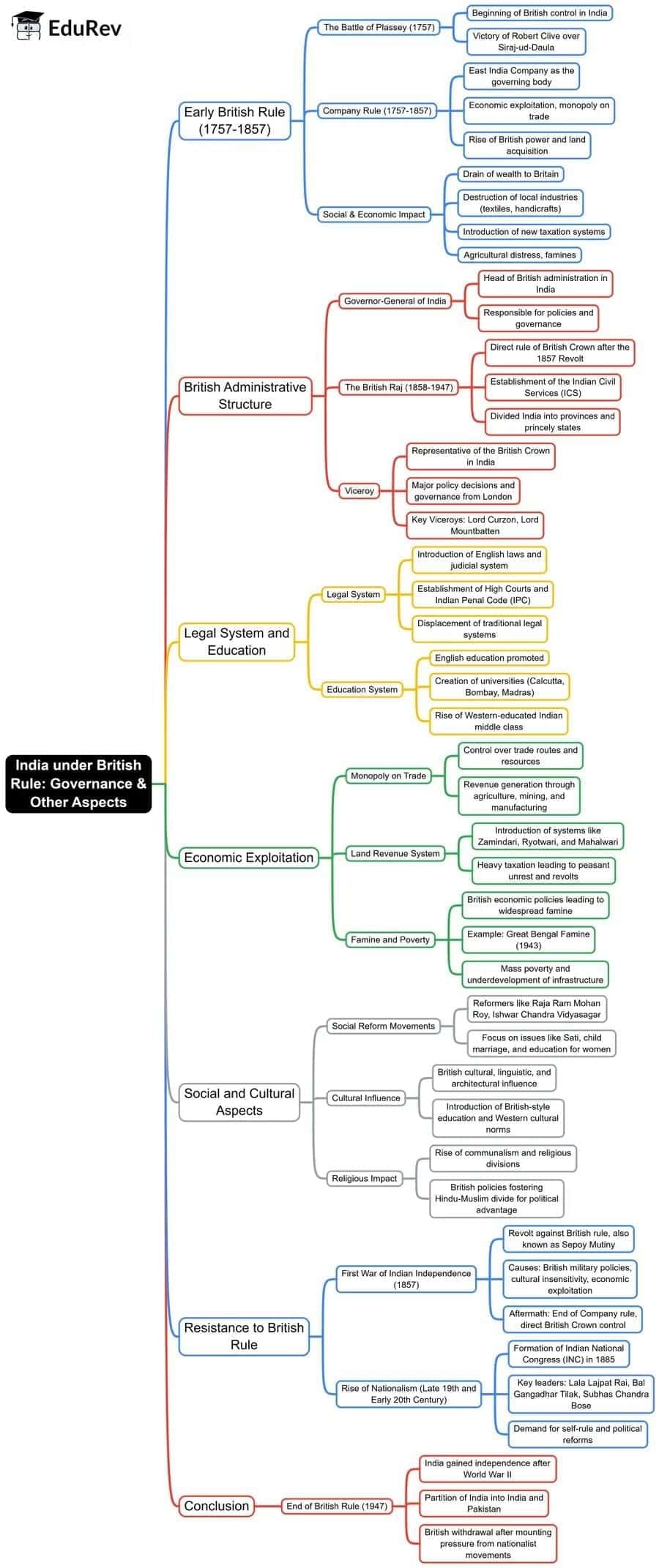
India Under British Rule: Governance & Other Aspects
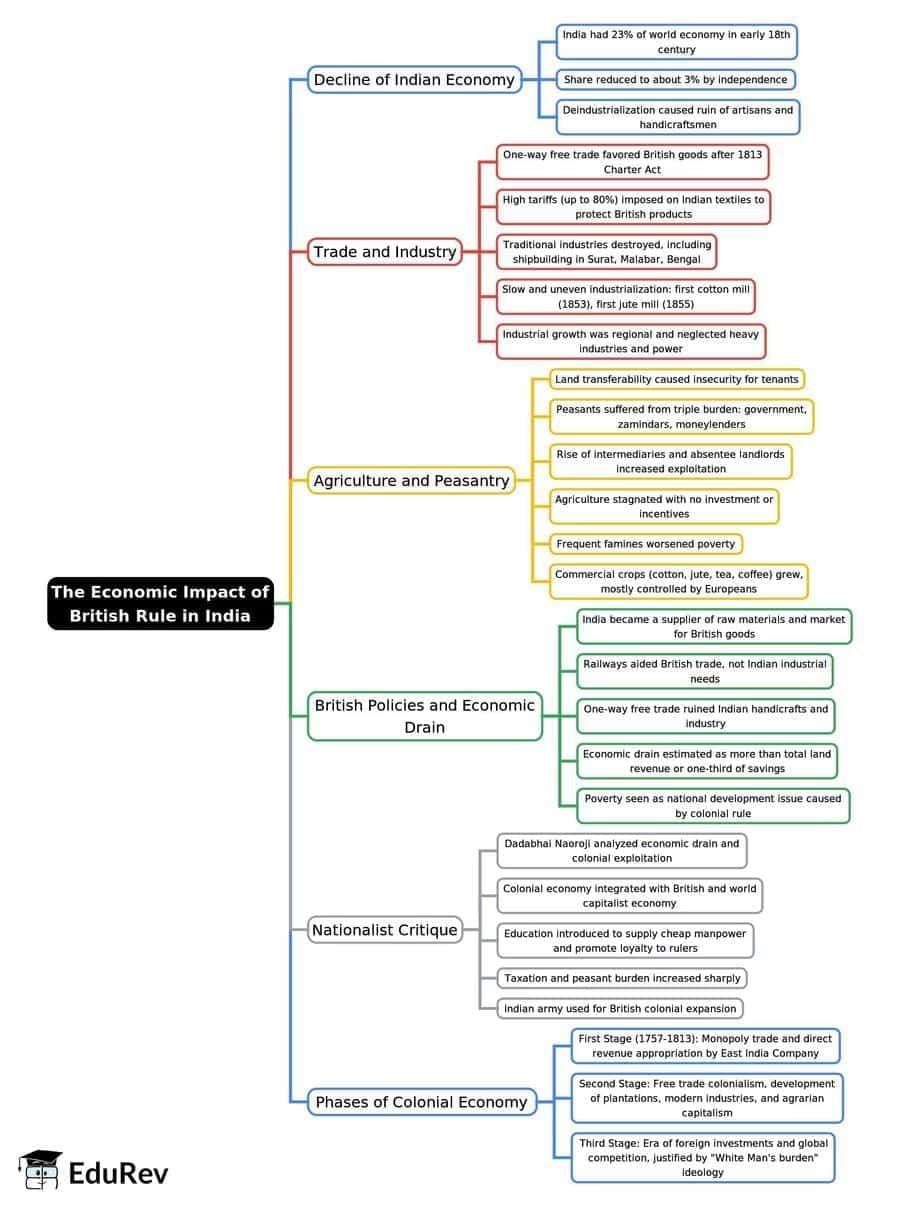
The Economic Impact of British Rule in India
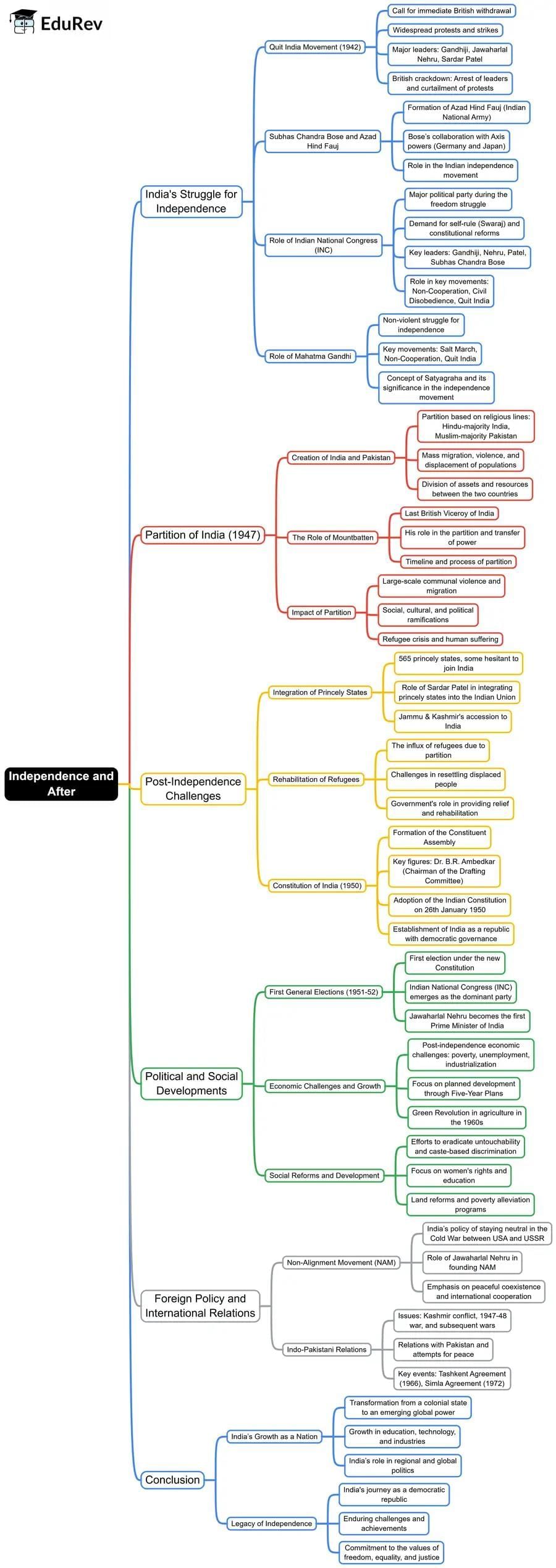
Independence and After
The document Quick Revision : Modern History | History for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course History for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
210 videos|853 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Quick Revision : Modern History - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What were the key factors leading to the Indian independence movement? |  |
Ans. The Indian independence movement was fueled by a combination of factors such as British colonial rule, economic exploitation, cultural awakening, and the impact of global events. Key events included the First War of Independence in 1857, the formation of the Indian National Congress in 1885, and the rise of nationalist leaders. The socio-political awakening among Indians, influenced by the ideas of freedom, equality, and self-governance, played a significant role in galvanizing public support for independence.
| 2. How did World War II impact India's struggle for independence? |  |
Ans. World War II had a profound impact on India's struggle for independence. The British decision to involve India in the war without consulting Indian leaders led to widespread unrest. The Quit India Movement in 1942 marked a significant escalation in the demand for independence. The war also weakened Britain economically and militarily, making it difficult for them to maintain control over India. Additionally, the emergence of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers promoted decolonization and influenced India's political landscape.
| 3. What was the significance of the Government of India Act 1935? |  |
Ans. The Government of India Act 1935 was significant as it provided a constitutional framework for governance in India. It introduced provincial autonomy, expanded the electorate, and established a federal structure, albeit with limited powers for Indian provinces. This act was a response to the demands for self-governance and set the stage for increased political participation. However, its limitations also led to discontent among Indian leaders, paving the way for more assertive demands for complete independence.
| 4. Who were the prominent leaders of the Indian National Movement, and what were their contributions? |  |
Ans. Prominent leaders of the Indian National Movement included Mahatma Gandhi, who spearheaded non-violent resistance; Jawaharlal Nehru, who was crucial in articulating the vision of a modern India; Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, known for his role in unifying the nation; and Subhas Chandra Bose, who advocated for armed rebellion against British rule. Each leader brought unique strategies and ideologies to the movement, contributing to the diverse approaches in the fight for independence.
| 5. What role did social reform movements play in the Indian independence struggle? |  |
Ans. Social reform movements played a critical role in the Indian independence struggle by addressing social issues such as caste discrimination, women's rights, and education. Leaders like B.R. Ambedkar and Raja Ram Mohan Roy worked towards social justice and equality, which helped in mobilizing the masses against colonial rule. These movements also fostered a sense of national identity and unity among diverse communities, which was essential for the collective struggle for independence.
Related Searches















