Reproductive Health Class 12 Notes Biology Chapter 3
Reproductive health – problem and strategies
(a) India was amongst the first countries in the world to initiate to the programme “family planning” initiated in 1951.
(b) Reproductive health in a society forms a crucial part of general health.
(c) Improved programs covering wider reproduction-related areas are currently in operation under the popular name ‘Reproductive and child health care (RCH) program.’
(d) Health and education of young people and marriage and child bearing during more mature stages of life are important attributes to the reproductive health of a society.
Population explosion and birth control
(a) The rapid increase in human population size over a relatively short period is called human population-explosion.
(b) Population growth rate depends on factors like fertility, natality, mortality, migration, age and sex structure.
(c) Increased health facilities and better living conditions are the cause behind population explosion.
(d) Out of 6 billion world population 1.3 billion populations is of Indians.
(e) Rapid decline in death rate, maternal mortalility rate (MMR) and infant mortality rate (IMR) are major cause of population growth.
(f) Growth rate of Indian population is around 1.7 percent.
(g) Most of the urban people are uneducated.
(h) The regulation of conception by preventive methods or devices to limit the number of offsprings is called birth control.
(j) A birth control method which deliberately prevents fertilization are referred to as contraception.
(i) Contraceptive methods are preventive methods and are of two types – temporary and permanent.
Characteristics of an ideal contraceptive are:-
(a) User friendly
(b) Easily available
(c) Nor or least side – effects
(d) No way interferes with sexual drive
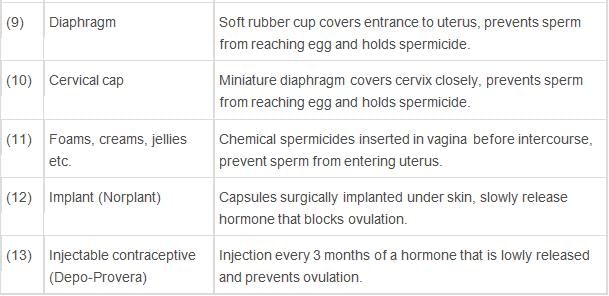
Methods of Birth Control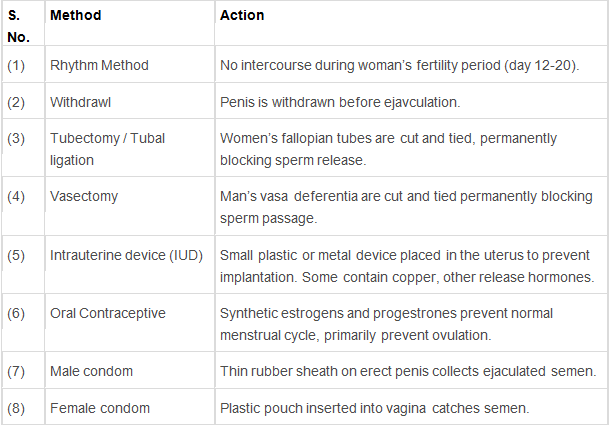
Amniocentesis
(a) During pregnancy, the fetus is surrounded by amniotic fluid which is a water-like substance.
(b) Amniotic fluid contains live fetal skin cells and other substances, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP).
(c) These substances provide important information about baby's health before birth.
(d) These days amniocentesis is being misused also, i.e., for detecting the sex of the foetus.
(e) Normal foetus is being aborted if it is a female.
Sexually transmitted diseases ( STDs)
Diseases which are transmitted sexually through sexual intercourse are collectively called as Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) or Venereal Diseases (VDs) or reproductive tract infections (RTI). STDs can be classified as viral, bacterial, protozoan, fungal, etc.
Causes of STD’s
STDs can be spread with any type of sexual activity, depending on the disease. STDs are most often caused by viruses and bacteria.
Types of Sexually Transmitted DiseasesThe various types of sexually transmitted diseases include genital herps, chancroid, gonorrhoea, syphilis and most common HIV leading to AIDS.
(i) Chlamydiasis
(a) Chlamydiasis is a sexually transmitted disease in humans caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
(b) It is a major infectious cause of human genetial and eye diseases.
(ii) Gonorrhoea
(a) Gonorrhoea is transmitted sexually, by oral, anal or genital sex.
(b) Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Prevention
STDs are a major threat to a healthy society.
(i) Avoid sex with unknown partners as well as multiple partners.
(ii) Always use condoms during coitus.
(iii) In case of any doubt, go to a qualified doctor for early detection and get complete treatment if diagnosed with disease.
Infertility
(a) Inability to conceive or produce children even after 2 years of unprotected sexual cohabitation is called infertility.
(b) A large no of couples all over India are infertile.
(c) The reasons for this could be many-physical, congenital, diseases, drugs, Immunological or even Psychological.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
Includes all fertility symptoms in which both sperms and eggs are handled. These are special techniques that assist couples to have children.
The main ART- techniques include:
(i) In-vitro fertilisation (IVF)
(ii) Zygote intra fallopian transfer (ZIFT)
(iii) Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection(ICSI)
(iv) Gamete intra fallopian transfer(GIFT)
(v) Artifical insemination (AI)
(1) In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
(a) Fertilization outside the body in almost similar conditions as are in the body.
(b) This method is popularly known as test tube baby programme.
(c) In this technique, ova from the wife / donor (female) and sperms from the husband / donor (male) are collected and are induced to form the zygote under simulated conditions in the lab.
(d) The zygote or early embryos could then be transferred into the fallopian tube (ZIFT -zygote intra fallopian transfer).
(2) Zygote intra fallopian transfer (ZIFT)
(a) ZIFT is an assisted reproductive procedure similar to in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer.
(b) The difference is that the fertilized embryo is transferred into the fallopian tube instead of the uterus.
(c) As the fertilized egg is transferred directly into the tubes, the procedure is also referred to as tubal embryo transfer (TET).
(3) Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
(a) Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is an assisted reproductive technology (ART)
(b) It is used to treat sperm-related infertility problems.
(c) ICSI is used to enhance the fertilization phase of in vitro fertilization (IVF) by injecting a single sperm into a mature egg.
(d) The fertilized egg is then placed in a woman's uterus or fallopian tube.
(4) Gamete intra fallopian tube (GIFT)
(a) The process of transfer of an ovum collected from a donor into the fallopian tube of another female who cannot produce one, but can provide suitable environment for fertilisation and further development is another method attempted.
(b) GIFT uses multiple eggs collected from the ovaries, which are placed into a thin flexible tube (catheter) along with the sperm to be used.
(c) The gametes (both eggs and sperm) are then injected into the fallopian tubes using a surgical procedure called laparoscopy under general anesthesia.
(5) Artificial Insemination (AI)
(a) Infertility cases either due to inability of the male partner to inseminate the female or due to very low sperm count in the ejaculates could be corrected by artificial insemination (AI).
(b) In this technique, the semen collected either from the husband or a healthy donor is artificially introduced into the vagina or into the uterus (IUI - Intra Uterine Insemination) of the female.
FAQs on Reproductive Health Class 12 Notes Biology Chapter 3
| 1. What is reproductive health? |  |
| 2. What are the common reproductive health issues in both men and women? |  |
| 3. How can one prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs)? |  |
| 4. What are the available contraception methods for family planning? |  |
| 5. How can one maintain good reproductive health? |  |
















