Revision Notes: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Introduction to Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physico-chemical process by which green plants (autotrophs) synthesize organic compounds (e.g., glucose) using light energy, providing food for all living organisms (heterotrophs). It is the primary source of food and oxygen on Earth, with sunlight as the ultimate energy source.
What Do We Know?
Basic experiments show photosynthesis requires:
- Chlorophyll (green pigment).
- Light (starch forms in lit green areas of variegated leaves).
- CO₂ (starch absent in CO₂-deprived leaf parts with KOH).
Early Experiments
- Joseph Priestley (1770): Showed plants restore air damaged by candles/animals, linking to oxygen discovery (1774).
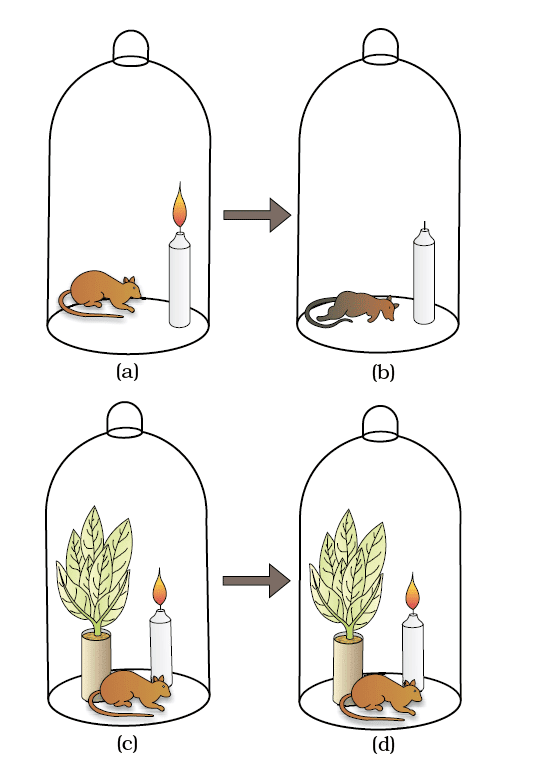 Priestley’s experiment
Priestley’s experiment - Jan Ingenhousz: Proved sunlight drives oxygen release from green plant parts (aquatic plant bubbles).
- Julius von Sachs (1854): Demonstrated glucose production (stored as starch) in chloroplasts.
- T.W. Engelmann: Mapped action spectrum using Cladophora and bacteria, showing blue/red light peaks.
- Cornelius van Niel: Proposed photosynthesis splits H₂O (not CO₂) for O₂, confirmed by radioisotopes; equation: 6CO₂ + 12H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6H₂O + 6O₂.
Where Does Photosynthesis Take Place?
Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, mainly in leaf mesophyll cells, where chloroplasts align along walls for optimal light. Within chloroplasts:
- Grana (thylakoid stacks): Light reactions (ATP, NADPH synthesis).
- Stroma: Dark reactions (sugar synthesis using ATP, NADPH).
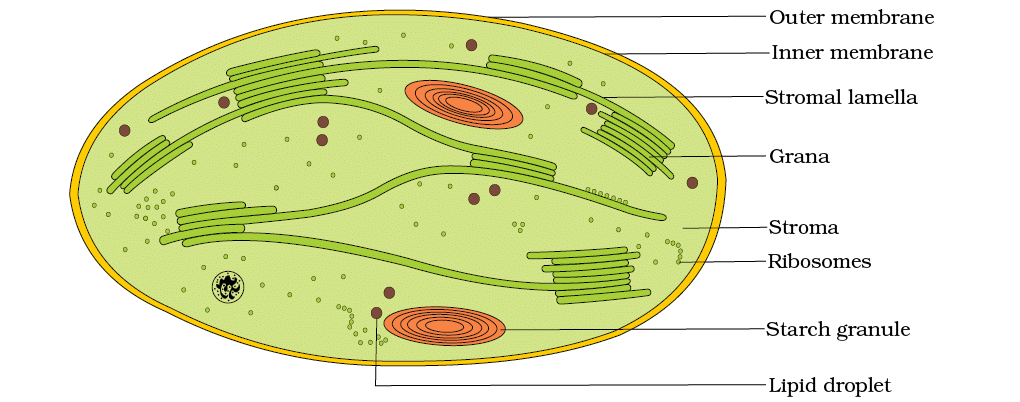 Electron micrograph of a section of chloroplast
Electron micrograph of a section of chloroplast
Pigments Involved in Photosynthesis
Paper chromatography reveals four pigments:
- Chlorophyll a (blue-green, chief pigment, max absorption at blue/red).
- Chlorophyll b (yellow-green).
- Xanthophylls (yellow).
- Carotenoids (yellow-orange).
Accessory pigments (b, xanthophylls, carotenoids) absorb wider wavelengths, transfer energy to chlorophyll a, and protect it from photo-oxidation.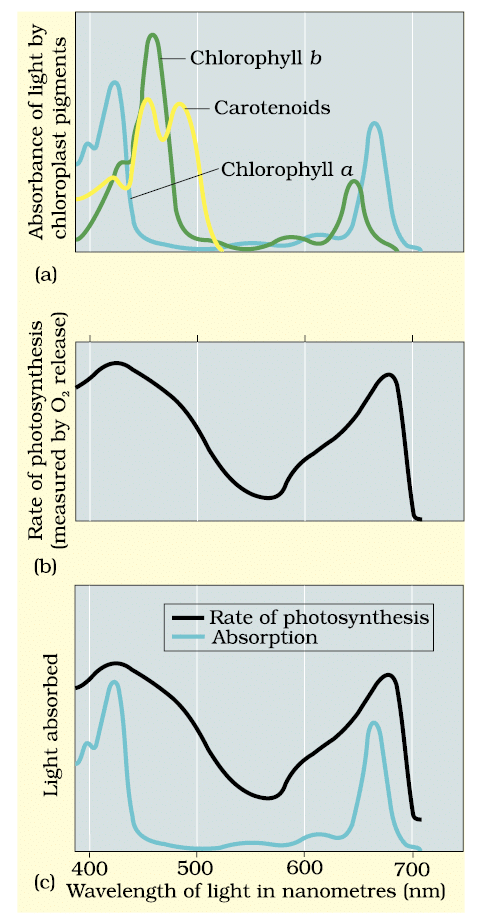
Light Reaction
Light reactions (photochemical phase) involve light absorption, water splitting, O₂ release, and ATP/NADPH formation in thylakoids via:
- Photosystem I (PS I, P700, 700 nm peak).
- Photosystem II (PS II, P680, 680 nm peak).
- Light Harvesting Complexes (LHC): Antenna pigments funnel light to reaction centre chlorophyll a.
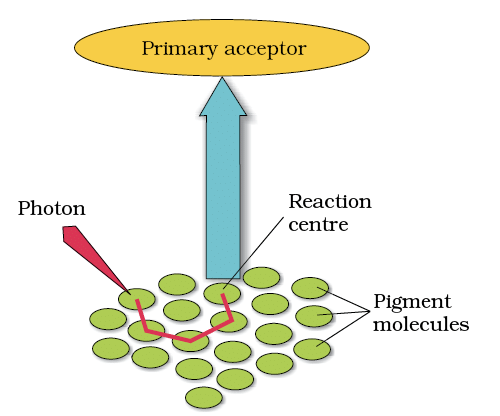 The light harvesting complex
The light harvesting complex
Electron Transport
- Z Scheme: PS II (680 nm) excites electrons, passed via cytochromes to PS I (700 nm), then to NADP⁺ forming NADPH + H⁺.
- Splitting of Water: PS II splits H₂O (2H₂O → 4H⁺ + O₂ + 4e⁻), replacing electrons, releasing O₂ into thylakoid lumen.
- Photophosphorylation:
- Non-cyclic: PS II → PS I, produces ATP and NADPH.
- Cyclic: PS I only (stroma lamellae), ATP only, no NADPH.
- Chemiosmosis: Proton gradient (lumen high, stroma low) drives ATP synthesis via ATP synthase (CF₀ channel, CF₁ enzyme).
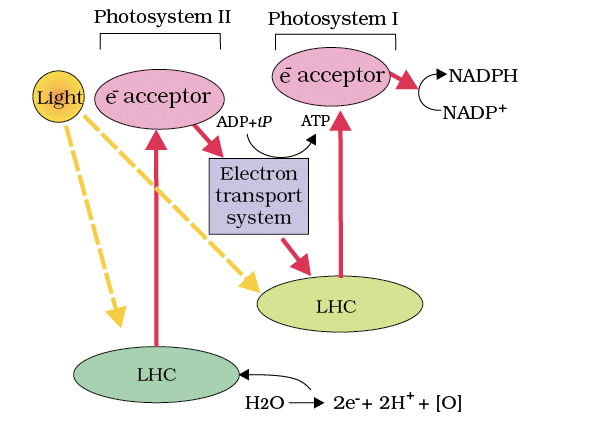 Z scheme of light reaction
Z scheme of light reaction
Where Are ATP and NADPH Used?
Biosynthetic phase (dark reactions) uses ATP and NADPH to fix CO₂ into sugars in the stroma, continuing briefly without light.
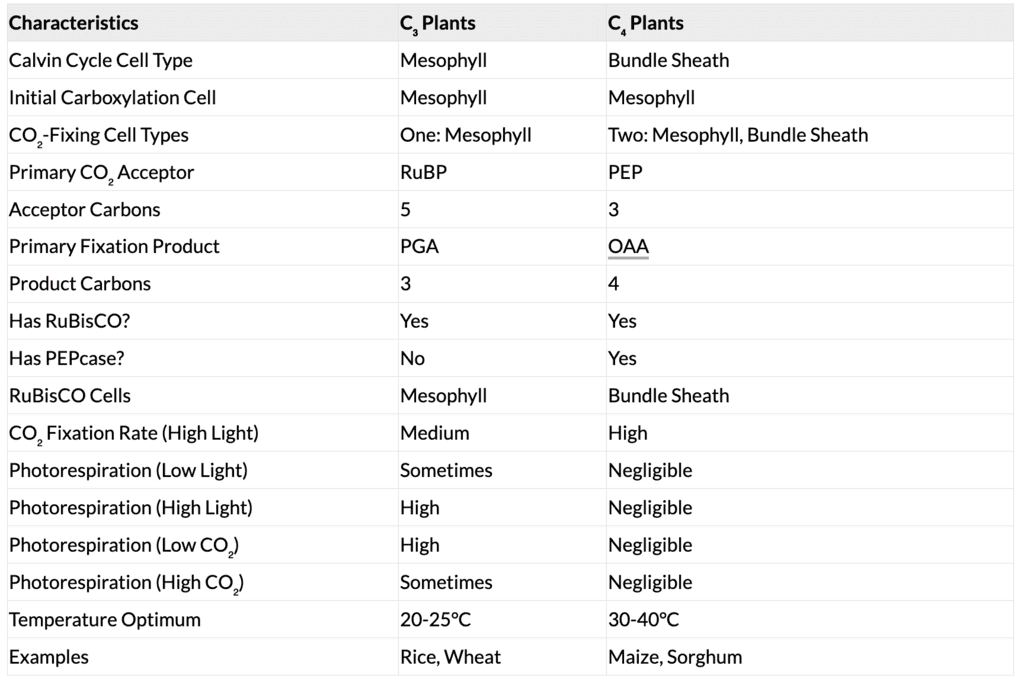
Calvin Cycle (C₃ Pathway)
- Primary Acceptor: RuBP (5-carbon).
- Stages:
- Carboxylation: RuBisCO fixes CO₂ into RuBP → 2 × 3-PGA.
- Reduction: 3-PGA → glucose (2 ATP, 2 NADPH per CO₂).
- Regeneration: RuBP reformed (1 ATP per CO₂).
- Total for 1 Glucose: 6 CO₂, 18 ATP, 12 NADPH.
Discovered by Melvin Calvin using ¹⁴C, earning him the 1961 Nobel Prize.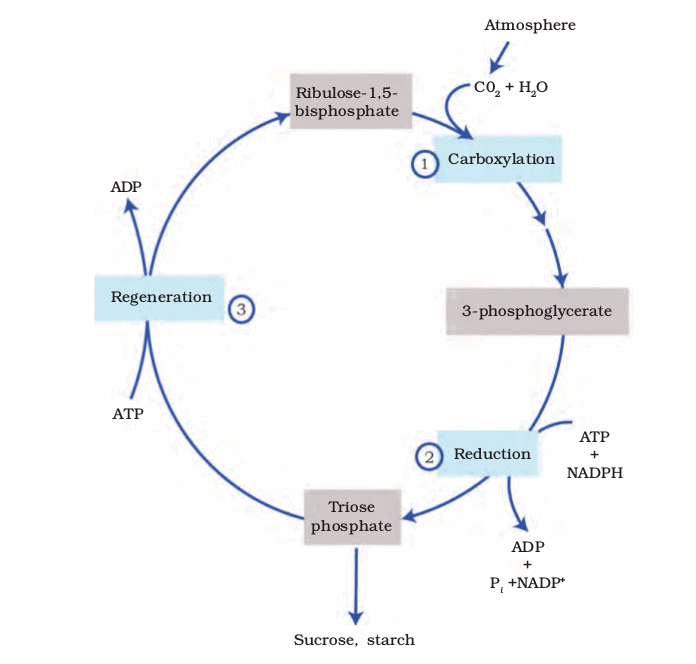
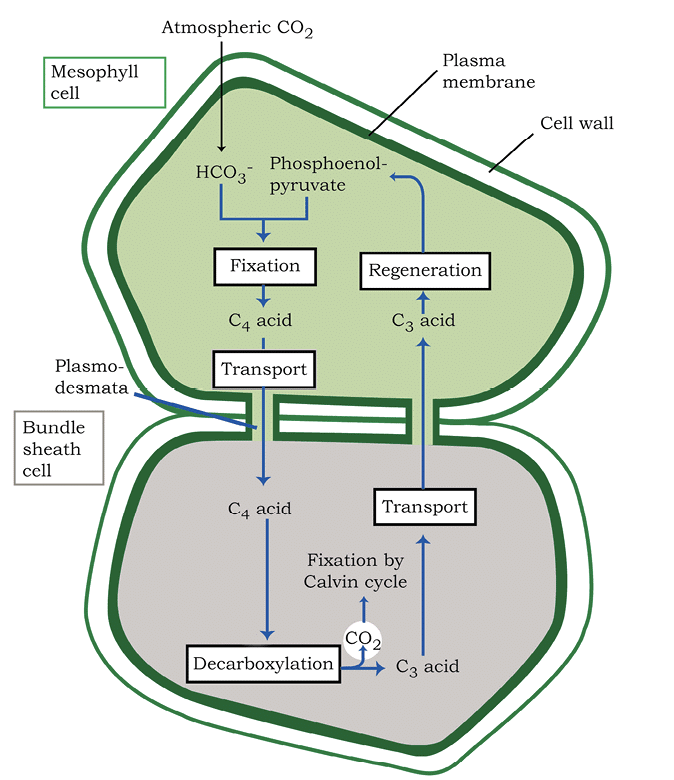
The C₄ Pathway
C₄ plants (e.g., maize, sorghum) use the Hatch and Slack Pathway, adapted for dry tropics:
- Anatomy: Kranz anatomy (bundle sheath cells with thick walls, many chloroplasts, no spaces).
- Process: PEP (3-carbon) in mesophyll fixes CO₂ → OAA (4-carbon) → malate/aspartate → bundle sheath → CO₂ for Calvin cycle.
- Features: High temperature/light tolerance, no photorespiration, high productivity.
Photorespiration
In C₃ plants, RuBisCO’s oxygenase activity (O₂ > CO₂) forms phosphoglycerate + phosphoglycolate, releasing CO₂, using ATP, with no sugar/NADPH synthesis. C₄ plants avoid this by concentrating CO₂ in bundle sheath cells.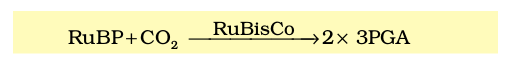
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Rate depends on internal (leaf traits, chlorophyll) and external factors (light, CO₂, temperature, water), limited by the least available factor (Blackman’s Law).
- Light: Linear increase at low intensity, saturates at 10% full sunlight.
- CO₂: Limiting at 0.03-0.04%, C₄ saturates at 360 μL⁻¹, C₃ at >450 μL⁻¹.
- Temperature: C₄ higher optimum than C₃; varies by habitat.
- Water: Stress closes stomata, reducing CO₂ and leaf area.
Comparison: C₃ vs C₄ Plants
Summary
Photosynthesis in green plants converts CO₂ and H₂O into glucose and O₂ using light energy in chloroplasts. Light reactions in thylakoids produce ATP, NADPH, and O₂ via PS II and PS I (Z scheme). Dark reactions (Calvin cycle) in stroma fix CO₂ into sugars. C₄ plants enhance efficiency with Kranz anatomy, avoiding photorespiration. Factors like light, CO₂, temperature, and water influence the rate.
|
150 videos|401 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the overall equation for photosynthesis in higher plants? |  |
| 2. What are the main stages of photosynthesis in higher plants? |  |
| 3. How do chlorophyll and other pigments contribute to photosynthesis? |  |
| 4. What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in higher plants? |  |
| 5. Why is photosynthesis considered essential for life on Earth? |  |
















