Satellite Launch Vehicles | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
The primary instruments for space applications are satellites but they must be placed in carefully determined orbits in order to be useful. A variety of rocket systems have been developed for this purpose. Launch vehicles that send satellites and other spacecraft into space must be far more powerful than other types of rockets because they carry more cargo farther and faster than other rockets.
- Satellite Launch Vehicles are essential for space missions and for sending satellites into orbit.
- These vehicles, commonly referred to as rockets, are responsible for transporting satellites and other payloads into space.
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has made great strides in this field, significantly enhancing India's ability to explore space and compete globally.
- ISRO's Satellite Launch Vehicles have been crucial in placing satellites into different orbits, serving purposes such as communication, earth observation, scientific research, and commercial missions.
What are Launch Vehicles?
- A launch vehicle is a rocket-powered vehicle used to transport a spacecraft beyond Earth’s atmosphere, either into orbit around Earth or to some other destination in outer space. The launch vehicles have been used to send crewed spacecraft, uncrewed space probes, and satellites into space since the 1950s.
- Launch Vehicles are used to transport and put satellites or spacecraft into space. In India, the launch vehicles development program began in the early 1970s. The first experimental Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV-3) was developed in 1980. An Augmented version of this, ASLV, was launched successfully in 1992. India has made tremendous strides in launch vehicle technology to achieve self-reliance in the satellite launch vehicle program with the operationalization of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV).
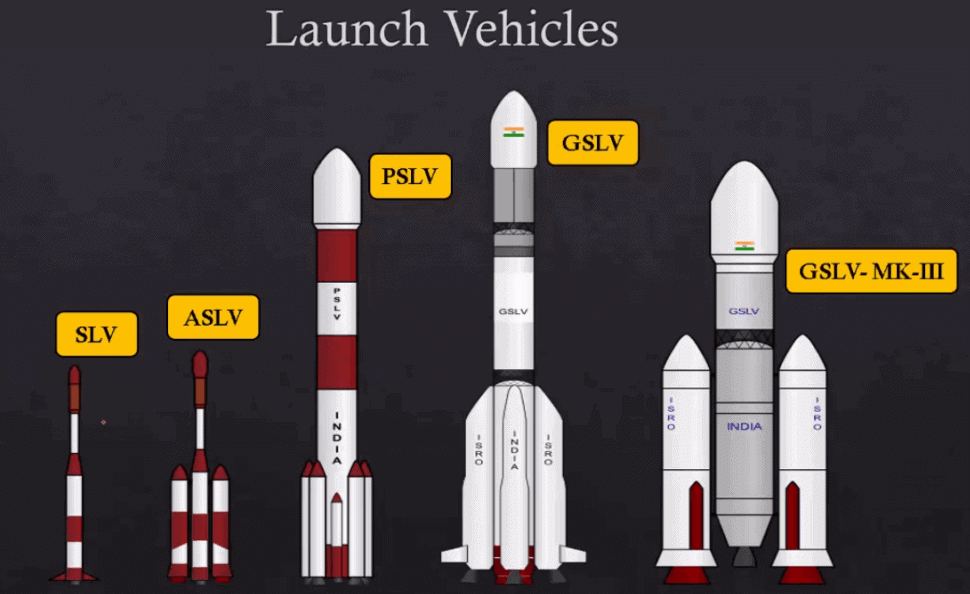
Working of Launch Vehicles
Rocket Propulsion System:
- A propellant is a chemical mixture burned to produce thrust in rockets and consists of a fuel and an oxidizer.
- Fuel is a substance that burns when combined with oxygen-producing gas for propulsion.
- An oxidizer is an agent that releases oxygen for combination with a fuel. The ratio of oxidizer to fuel is called the mixture ratio.
Propellants are classified according to their state – liquid, solid, or hybrid.
Liquid Propellants: In a liquid propellant rocket, the fuel and oxidizer are stored in separate tanks and are fed through a system of pipes, valves, and turbopumps to a combustion chamber where they are combined and burned to produce thrust.
- Advantages: Liquid propellant engines are more complex than their solid propellant counterparts, however, they offer several advantages. By controlling the flow of propellant to the combustion chamber, the engine can be throttled, stopped, or restarted.
- Disadvantages: The main difficulties with liquid propellants are with oxidizers. Storable oxidizers, such as nitric acid and nitrogen tetroxide are extremely toxic and highly reactive, while cryogenic propellants being stored at low temperature and can also have reactivity/toxicity issues.
Liquid propellants used in rocketry can be classified into three types: petroleum, cryogens, and hypergolic.
- Petroleum fuels are those refined from crude oil and are a mixture of complex hydrocarbons, i.e. organic compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen. The petroleum used as rocket fuel is a type of highly refined kerosene.
- Cryogenic propellants are liquefied gases stored at very low temperatures, most frequently liquid hydrogen (LH2) as the fuel and liquid oxygen (LO2 or LOX) as the oxidizer. Hydrogen remains liquid at temperatures of -253 oC (-423 oF) and oxygen remains in a liquid state at temperatures of -183 oC (-297 oF).
- Hypergolic propellants and oxidizers that ignite spontaneously on contact with each other and require no ignition source. The easy start and restart capability of hypergolic make them ideal for spacecraft manoeuvring systems.
Since hypergolic remain liquid at normal temperatures, they do not pose the storage problems like cryogenic propellants. Hypergolic are highly toxic and must be handled with extreme care. Hypergolic fuels commonly include hydrazine, monomethyl-hydrazine (MMH) and unsymmetrical dimethyl-hydrazine (UDMH).
Solid propellant: These are the simplest of all rocket designs. They consist of a casing, usually steel, filled with a mixture of solid compounds (fuel and oxidizer) that burn at a rapid rate, expelling hot gases from a nozzle to produce thrust. When ignited, a solid propellant burns from the center out towards the sides of the casing.
- There are two families of solids propellants: homogeneous and composite. Both types are dense, stable at ordinary temperatures, and easily storable.
(i) Composites are composed mostly of a mixture of granules of solid oxidizers, such as ammonium nitrate, ammonium dinitramide, ammonium perchlorate, or potassium nitrate in a polymer binding agent.
(ii) Single-, double-, or triple-bases (depending on the number of primary ingredients) are homogeneous mixtures of one to three primary ingredients. - Advantages: Solid propellant rockets are much easier to store and handle than liquid propellant rockets. High propellant density makes for compact size as well.
- Disadvantages: Unlike liquid-propellant engines, solid propellant motors cannot be shut down. Once ignited, they will burn until all the propellant is exhausted.
Hybrid propellant: These engines represent an intermediate group between solid and liquid propellant engines. One of the substances is solid, usually the fuel, while the other, usually the oxidizer, is liquid. The liquid is injected into the solid, whose fuel reservoir also serves as the combustion chamber.
- The main advantage of such engines is that they have high performance, similar to that of solid propellants, but the combustion can be moderated, stopped, or even restarted. It is difficult to make use of this concept for very large thrusts, and thus, hybrid propellant engines are rarely built.
Multiple Stages: Launch vehicles are built with multiple stages that separate and fall away as the rocket ascends. Each stage has its own engines and propellant and is discarded when no longer needed, making the rocket lighter and more efficient. ISRO is developing the Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV), designed for a 30-tonne payload to Low Earth Orbit, incorporating reusable stages for cost efficiency, with private sector collaboration by 2025.
Retired Satellite Launch Vehicles of ISRO
Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV):- The SLV was India’s first experimental satellite launch vehicle, designed to place small payloads into Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
- It was a four-stage vehicle, all powered by solid fuel, capable of launching payloads weighing up to 40 kg into LEO.
- The first successful launch of the SLV took place on July 18, 1980, from Sriharikota, where it successfully placed the Rohini satellite (RS-1) into orbit.
- This achievement made India the sixth country in the world to develop and operate its own satellite launch vehicle.
Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV):
- Following the SLV, the ASLV was introduced and operated until the 1990s, paving the way for more advanced vehicles like the PSLV.
- The ASLV was a five-stage vehicle, also using solid propellant, designed to launch satellites weighing up to 150 kg into circular orbits at an altitude of 400 km.
Active Satellite Launch Vehicles of ISRO
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV)
- Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV)
- Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk III (LVM3)
- Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)
Sounding Rockets:
- Sounding rockets are usually one or two-stage solid propellant rockets. They are primarily intended for probing the upper atmospheric regions using rocket-borne instrumentation. They also serve as platforms for testing prototypes of new components or subsystems intended for use in launch vehicles and satellites.
- The launch of the first sounding rocket US-made ‘Nike Apache’ from Thumba near Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala on November 21, 1963, marked the beginning of the Indian Space Programme.
- In 1965, ISRO started launching a series of our own sounding rockets named Rohini from TERLS. RH-75, with a diameter of 75mm was the first truly Indian sounding rocket, which was followed by RH-100 and RH-125 rockets.
- The sounding rocket program was indeed the bedrock on which the edifice of launch vehicle technology was built.
- The experience gained was of immense value in the mastering of solid propellant technology and allied systems of the launch vehicles. Several scientific missions with national and international participation have been conducted using the Rohini sounding rockets.
Operational Sounding Rockets
Currently, operational sounding rockets include three versions namely RH-200, RH-300-Mk-II, and RH-560-Mk-III. These cover a payload range of 8 to 100 kg and an apogee range of 80 to 475 km. The details are given below.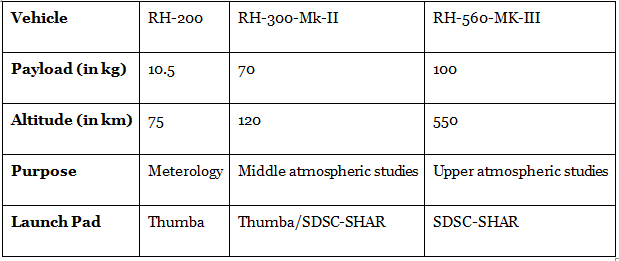
Operational sounding rockets are further divided in two groups:
- Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV)
- Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV)
1. Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV)
- The Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) project was born out of the need for achieving indigenous satellite launch capability for communications, remote sensing and meteorology.
- The Satellite Launch Vehicle-3 (SLV-3) was India’s first experimental satellite launch vehicle, which was an all solid, four-stage vehicle weighing 17 tonnes. It had a height of 22m and it was capable of placing 40 kg class payloads in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
- The first experimental flight of SLV3, in August 1979, was only partially successful. The next launch on July 18, 1980, from Sriharikota Range (SHAR), successfully placed Rohini satellite, RS-1, into orbit, thereby making India the sixth member of an exclusive club of space-faring.
- Apart from the July 1980 launch, there were two more launches held in May 1981 and April 1983, orbiting Rohini satellites carrying remote sensing sensors.
The successful culmination of the SLV-3 project showed the way to advanced launch vehicle projects such as the Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV), Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV).
2. Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV)
- Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV) was developed to act as a low-cost intermediate vehicle to demonstrate and validate critical technologies.
- With a lift-off weight of 40 tonnes, the 23.8 m tall ASLV was configured as a five-stage, all-solid propellant vehicle, with a mission of orbiting 150 kg class satellites into 400 km circular orbits.
- The strap-on stage consisted of two identical 1m diameter solid propellant motors, Under the ASLV program, four developmental flights were conducted.
- The first developmental flight took place on March 24, 1987, and the second on July 13, 1988.
- ASLV-D3 was successfully launched on May 20, 1992, when SROSS-C (106 kg) was put into an orbit of 255 x 430 km.
- ASLV-D4 launched on May 4, 1994, orbited SROSS-C2 weighing 106 kg. It had two payloads, Gamma Ray Burst (GRB) Experiment and Retarding Potential Analyser (RPA), and functioned for seven years.
ASLV provided valuable inputs for further development.
Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV):
 1. Overview: India’s third-generation launch vehicle, first successfully launched in October 1994.
1. Overview: India’s third-generation launch vehicle, first successfully launched in October 1994.
2. Features: First Indian launch vehicle with liquid stages, capable of launching multiple satellites into different orbits.
3. Stages:
- First Stage: Solid rocket motor (S139).
- Second Stage: Earth-storable liquid rocket engine (Vikas engine).
- Third Stage: Solid rocket motor (S7) for high thrust.
- Fourth Stage: Two Earth-storable liquid engines.
4. Variants: PSLV-XL, QL, and DL use strap-on motors for added thrust. Core-alone version (PSLV-CA) does not use strap-ons.
5. Reliability: Known as “the workhorse of ISRO” for Low Earth Orbits (LEO), with over 50 successful launches by 2025.
6. Payload Capacity: Up to 1,750 kg to 600 km altitude Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbits.
7. Notable Launches: Chandrayaan-1 (2008), Mars Orbiter Mission (2013), Amazonia-1 (2021).
Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV):
 GSLV1. Overview: Fourth-generation launch vehicle designed for geostationary transfer orbit using a cryogenic third stage.
GSLV1. Overview: Fourth-generation launch vehicle designed for geostationary transfer orbit using a cryogenic third stage.
2. Features: Three-stage vehicle with four liquid strap-ons. Now uses fully indigenous cryogenic stages, improving reliability by 2025.
3. Stages:
- First Stage: Solid rocket motor (S139) with 4 liquid strap-ons.
- Second Stage: Vikas engine.
- Third Stage: Cryogenic Upper Stage (CE-7.5).
4. Payload Capacity: Up to 6 tonnes in Low Earth Orbits, 2,250 kg in Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
5. Notable Launches: Communication satellites such as INSAT, GSAT, and NISAR (2025, with NASA).
LVM3 (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk III):
 1. Overview: Next-generation launch vehicle, previously known as GSLV MkIII, key for human spaceflight and heavy payloads.
1. Overview: Next-generation launch vehicle, previously known as GSLV MkIII, key for human spaceflight and heavy payloads.
2. Features: Three-stage vehicle with two solid strap-on motors, one liquid core stage, and a high-thrust cryogenic upper stage.
3. Stages:
- Core Stage: S200 solid motor.
- Liquid Stage: Two Vikas engines.
- Cryogenic Upper Stage: Indigenous high-thrust cryogenic engine (CE-20).
4. Payload Capacity: Up to 4 tonnes into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbits, 8,000 kg into 600 km Low Earth Orbits.
5. Notable Launches: Chandrayaan-3 (2023), Aditya-L1 (2023), Gaganyaan test flights (2024).
Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV):
 1. Overview: Designed for low-cost, rapid-turnaround launches of small satellites, operational since February 2023.
1. Overview: Designed for low-cost, rapid-turnaround launches of small satellites, operational since February 2023.
2. Features: Four-stage vehicle with three solid stages and a liquid velocity trimming module, managed by NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) for commercial launches.
3. Stages:
- First Stage: Solid rocket motor (SS1).
- Second Stage: Solid rocket motor (SS2).
- Third Stage: Solid rocket motor (SS3).
- Fourth Stage: Liquid velocity trimming module (VTM).
4. Payload Capacity: Up to 500 kg to 500 km Low Earth Orbit, 300 kg to Sun-Synchronous Orbit.
5. Notable Launches: SSLV-D2 (2023) delivered EOS-07 and student satellites, supporting India’s commercial space sector.
Satellite Launch Vehicles of ISRO Under Development
Human Rated Launch Vehicle (HRLV):
- A modified version of the LVM3, developed for the Gaganyaan human spaceflight program, with a crewed mission planned for 2025-26.
- Capable of launching the Orbital Module into a 400 km Low Earth Orbit, with test flights conducted in 2024.
- Includes a Crew Escape System (CES) powered by quick-acting and high-burn rate solid motors, with international collaboration for astronaut training.
Reusable Launch Vehicle - Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD):
- Resembles an aircraft, combining the complexities of launch vehicles and airplanes, with successful landing tests (Pushpak) by 2025.
- Comprises a nose cap, fuselage, two delta wings, and two vertical tails, along with active control surfaces like elevons and rudder.
- Future plans include scaling it up to become the first stage of India’s reusable two-stage orbital launch vehicle, reducing launch costs.
Scramjet Engine - Technology Demonstrator (TD):
- Operates at hypersonic speeds with supersonic combustion, using hydrogen as fuel and atmospheric oxygen as the oxidizer.
- The first experimental mission was successfully conducted in 2016, making India the fourth country to demonstrate flight testing of a scramjet engine, with further tests by 2025.
Notable Foreign Launch Vehicles Used by ISRO
- Ariane 5: Heavy-lift launcher used by the European Space Agency, capable of carrying over 20 metric tons to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and more than 10 metric tons to Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO). India has used Ariane 5 for launching communication and earth observation satellites, including INSAT-3D and GSAT-30.
- Falcon 9: The world’s first orbital-class reusable rocket designed by SpaceX. Falcon 9 can launch payloads of 22 metric tons to LEO and 8 metric tons to GTO, used by India for select commercial missions.
- Space Launch System (SLS): Super heavy-lift rocket developed by NASA, capable of launching 70 metric tons to LEO. SLS is designed for the Orion spacecraft, four astronauts, and large cargo to the Moon in a single mission, with crew and service modules and a launch abort system.
- Soyuz 5: One of the heaviest launch vehicles from the Russian Space Agency, with the capability of launching 17 metric tons to LEO, used for select ISRO missions.
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Satellite Launch Vehicles - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main types of launch vehicles used by ISRO? |  |
| 2. What is the working principle of launch vehicles? |  |
| 3. Can you name some retired satellite launch vehicles of ISRO? |  |
| 4. What foreign launch vehicles has ISRO used for satellite launches? |  |
| 5. What are the satellite launch vehicles currently under development by ISRO? |  |

















