Satellite Towns | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Purpose of Satellite Towns |

|
| Problems of satellite towns |

|
| Types of satellite towns |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Satellite Towns |

|
Introduction
Urbanization is a direct result of industrialization. The Industrial Revolution in Europe and America led to significant urban growth, with large numbers of people migrating to cities for employment opportunities. This influx of people resulted in various urban issues, such as overcrowding and pollution.
- To address these problems, major cities and industrial centers began to look for ways to decongest urban areas. As a result, suburban growth occurred along major transportation lines, characterized by unplanned and haphazard development. In response to this situation, A. Howard proposed the concept of the Garden City, which would be situated away from city limits and include residential areas, institutions, schools, services, and entertainment facilities. The idea was to provide a better quality of life for industrial workers by relocating them away from congested and polluted cities. This concept was rooted in socialist ideology and intended to be a philanthropic solution to urban problems.
- However, after World War I, the term "Garden City" was replaced by "Satellite Town" due to the rapid industrial growth that led to the establishment of manufacturing units within these towns. They also came to be known as "Dormitory Towns" as they served primarily as residential areas for workers.
- A Satellite Town is defined as an urban center that is functionally integrated with a larger city and located along a major transportation line connecting the two. It serves as a secondary settlement to the main city. Over time, Satellite Towns have evolved into mature towns with their own municipalities, well-defined functions, central business districts, and centers of in-migration.
- Eventually, Satellite Towns become part of a larger urban agglomeration and, later, integrated into the main city. In contemporary settlement planning, Satellite Towns play a crucial role in alleviating overcrowding and absorbing economic pressure from larger cities. These towns can be either new or old and are typically separated from the main city by physical barriers such as hills, rivers, or other natural features. While Satellite Towns may be partially or entirely independent from the main city, they still maintain a functional dependence on it.
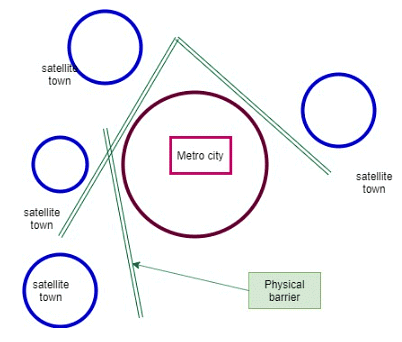
Purpose of Satellite Towns
The purpose of satellite towns is to provide a residential area for city workers, helping to reduce congestion in the main urban center. These towns often house manufacturing units that are labor-intensive and polluting, moving them away from the main city. Satellite towns have their own administrative and municipal areas, and are functionally integrated with the central city as part of the daily urban system.
Due to the lower cost of land, satellite towns can develop institutional areas and establish their own Central Business District (CBD) or commercial hub, specializing in specific functions. They also offer various transportation facilities, such as bus stations and railway stations, to facilitate commutation between the main city and the satellite town.
Some examples of satellite towns include:
- Navi-Mumbai and Pune as satellite cities for Mumbai.
- Kalyanpur for Kolkata.
- Faridabad and Noida for Delhi.
- Meruth, Noida, Gurgaon, and Ghaziabad as satellite cities for Delhi.
- Secunderabad for Hyderabad, which has now become a twin city.
In the United States, nearly 50% of the urban population resides in satellite cities. For example, Allentown serves as a satellite city for New York City.
In summary, satellite towns play a crucial role in alleviating urban congestion and supporting the main city's economy and infrastructure by providing residential, commercial, and industrial spaces for the population.
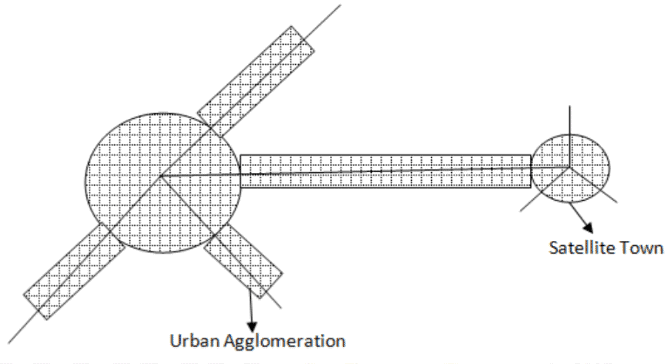
Problems of satellite towns
All the problems related to urban areas are included in this such as:
(i) Crime
(ii) Vandalism
(iii) Slums and squatter settlements etc.
- Lack of basic support such as road, good health & education system.
- Lack of economic activities & employment generation.
- Poor connectivity to the metro city.
Factors for growth of Satellite Town
Presently after Second World War, 6 major factors are considered as the basis of emergence of Satellite Town.
- Rapid population growth of the mother city
- Rapid population growth in major cities is a significant issue faced by developing countries, such as India. For example, Delhi and Mumbai experience an annual population increase of around 4 lakhs each. The World Disaster Report has described the tremendous growth of these metropolitan areas as disastrous.
- Ecologists have referred to this accelerated and unsustainable growth as a unique phenomenon, primarily affecting colonial cities. To address this challenge, city planners often develop satellite towns to accommodate the rising population. In the case of Delhi, nearby areas like Ghaziabad and Faridabad have emerged as satellite towns, primarily serving industrial purposes. However, their primary purpose is to alleviate the population explosion in Delhi.
- A similar example can be found in Japan, with Kawasaki serving as an industrial satellite town for Tokyo.
- Functional specialization
- Functional specialization refers to the growing trend in both developed and developing nations to designate specific areas or satellite towns for particular purposes. In contrast to old towns, which often served multiple functions, modern planning efforts increasingly focus on creating separate zones for distinct functions.
- For example, in Europe, there are dormitory towns designed primarily for residential purposes, as opposed to mixing residential, commercial, and industrial activities in a single location.
- Development of transport
- The development of significant transportation routes often leads to the emergence of satellite towns near major cities. These transport hubs serve as central locations for providing transportation services to the main city.
- For example, Jasidih has become a satellite town for Deogarh, and Khurda Road serves as a satellite town for Puri. As transportation infrastructure continues to grow and evolve, these satellite towns play an increasingly important role in connecting and supporting the main urban centers.
- Environmental factors
- Environmental factors play a significant role in the development of satellite towns, particularly in developed countries. This is because older towns often suffer from pollution and congestion, prompting the need for new residential areas to be established nearby.
- Satellite towns serve as a solution to these issues, as they provide a cleaner and less crowded living environment for residents while still being in close proximity to the main city. Furthermore, satellite towns can also serve as a location for more polluting industries to be relocated, reducing the overall pollution levels in the main city.
- For example, the development of New London near Boston and Sparrow Point near Baltimore has allowed for the relocation of a steel plant from Baltimore, effectively addressing both the pollution and congestion issues faced by the main city.
- Implementation of urban planning principles
- Nowadays, urban planning has shifted its focus towards regional planning. Prior to the Second World War, urban planning mainly involved creating master plans for individual towns without considering the broader regional context. However, the current approach emphasizes the importance of regional planning, which includes the development of satellite towns.
- For example, the National Capital Region (NCR) Planning initiative has developed seven satellite towns to help alleviate the pressure on Delhi. This approach ensures that urban development considers regional factors and promotes a more sustainable and balanced growth.
- Nearby villages developing into satellite town
- Villages near cities in developing countries often transform into satellite towns as a result of the spread of urban influences. This occurs as villagers establish connections with city dwellers, leading to increased economic dependence on the city.
- Consequently, the villagers' daily earnings and living standards improve, causing changes in the village's structure and appearance. As the village becomes more urbanized, city residents may also choose to move in, further contributing to the area's development.
- Examples of such satellite towns include Bahadurgarh and Ballabhgarh near Delhi, and Sarnath near Varanasi.
Types of satellite towns
- Satellite towns can be classified into 6 types
- Dormitory satellite towns: These towns have a deserted appearance during the day as the working population is away. They become lively in the evening when commuters return home. The roads are busy during the morning and evening rush hours. Examples include Loni in Delhi, New Ghaziabad, and Patliputra colony in Patna.
- Industrial satellite towns: These towns are developed primarily to serve industrial functions. While they may have other functions, the main reason for their existence is the presence of industries. Examples are Faridabad and Ghaziabad.
- Administrative satellite towns: These towns have emerged recently due to the rapid growth of older administrative towns that are becoming more developed. For example, Gandhinagar is a satellite town of Ahmadabad, while Dispur is a satellite town of Guwahati.
- Transport satellite towns: These towns develop due to the presence of a significant transportation hub, such as a railway station, that serves the surrounding city. An example is Waltair, a satellite town of Vizag.
- Educational satellite towns: These towns are established because of the presence of educational institutions. Examples include Cambridge as a satellite town of London, Shantiniketan for Bolpur, Banaras Hindu University (BHU) for Varanasi, and so on.
- Mixed satellite towns: In this type of satellite town, a village typically transforms into a satellite town with various functions. Examples are South Hill of London, Phulwarisharif of Patna, and Bahadurgarh of Delhi.
Overall, the classification of satellite towns is based on their primary functions, such as providing residential areas for commuters, serving industrial purposes, functioning as administrative centers, acting as transportation hubs, housing educational institutions, or having a mix of various functions.
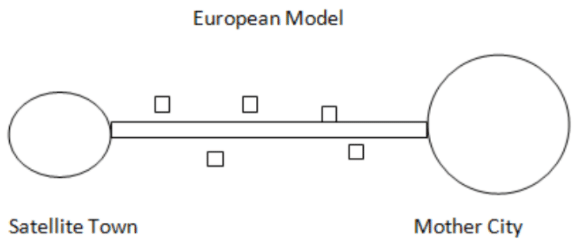
- Recently there has been a tendency of urban sprawl and this tendency has been basically due to two factors:
- Spread of farmhouse tendency (cottage houses in Europe): here it is seen that people in urban areas have the tendency to remain in the city at day time and they prefer open space to take rest at night. This provides a continuum to main city with satellite towns.
- Environmental consciousness.
- Due to above factors mother city satellite town continuum is emerging.
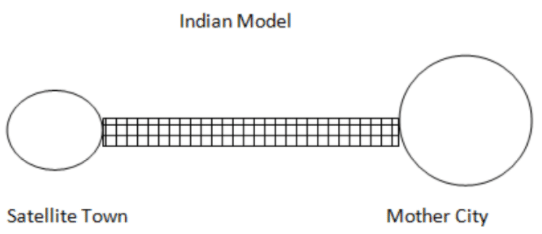
- In India the growth of satellite town is continuous along the transportation line, which is due to:
- Social factors: People tend to remain near to their urban relatives and friends, which leads to the development of satellite town in close proximity to the city.
- Transport: Indian workers don’t own fast moving vehicles, therefore depend on public transport system tend to settle near city.
- In both the cases there is impact of diffusion of urban elements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, satellite towns play a crucial role in alleviating urban congestion, supporting the main city's economy, and providing residential, commercial, and industrial spaces for the population. They emerge due to factors such as rapid population growth, functional specialization, transportation development, environmental concerns, and the implementation of urban planning principles. Satellite towns can be classified based on their primary functions and can exist in various forms, such as dormitory, industrial, administrative, transport, educational, and mixed satellite towns. The growth of satellite towns in India is primarily driven by social factors and transportation lines. As urban sprawl and environmental consciousness continue to be significant concerns, satellite towns will remain an essential aspect of sustainable urban planning and development.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Satellite Towns
What is the primary purpose of satellite towns?
The primary purpose of satellite towns is to provide a residential area for city workers, helping to reduce congestion in the main urban center. They also often house manufacturing units that are labor-intensive and polluting, moving them away from the main city.
How do satellite towns help alleviate urban congestion and support the main city's economy?
Satellite towns provide additional residential, commercial, and industrial spaces for the population, helping to alleviate overcrowding and absorb economic pressure from larger cities. They also offer various transportation facilities to facilitate commutation between the main city and the satellite town.
What are the factors that contribute to the growth of satellite towns?
Factors contributing to the growth of satellite towns include rapid population growth of the main city, functional specialization, development of transport, environmental factors, implementation of urban planning principles, and nearby villages developing into satellite towns.
How are satellite towns classified based on their functions?
Satellite towns can be classified into six types: dormitory satellite towns, industrial satellite towns, administrative satellite towns, transport satellite towns, educational satellite towns, and mixed satellite towns.
What are some examples of satellite towns in India and other countries?
In India, examples of satellite towns include Navi-Mumbai and Pune for Mumbai, Faridabad and Noida for Delhi, and Secunderabad for Hyderabad. In the United States, Allentown serves as a satellite city for New York City. In the United Kingdom, Cambridge is a satellite town for London.
|
304 videos|717 docs|259 tests
|
FAQs on Satellite Towns - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the purpose of satellite towns? |  |
| 2. What are some common problems faced by satellite towns? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of satellite towns? |  |
| 4. How do satellite towns contribute to urban planning and development? |  |
| 5. What are the key factors to consider when planning a satellite town? |  |




















