Science & Technology: September 2022 Current Affairs | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Saturn’s Mysterious Rings & Extreme Tilt |

|
| Non-Communicable Diseases |

|
| Nuclear Fusion |

|
| Inspire Awards |

|
| First Meeting of the Reconstituted National Medical Device Promotion Council (NMDPC) |

|
Saturn’s Mysterious Rings & Extreme Tilt
In News
Recently, according to a new study, a pre-existing moon named ‘Chrysalis’ likely left Saturn with its bright rings and extreme tilt.
- Chrysalis likely orbited Saturn for several billion years. Roughly 160 million years ago, Chrysalis became unstable and came too close to its planet. This encounter likely pushed the moon away or destroyed it.
About the recent research
- Four planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune and Uranus are known to have rings.
- Saturn’s rings composed of water ice particles ranging from microns to tens of metres in size are the brightest.
- Tilt: Saturn has a tilt of 26.73 degrees, Earth 23.45 degrees and Jupiter 3 degrees.
- Saturn is unlikely to have had a tilt during its formation stages, the researchers said.
- Currently, gas giants Neptune, Uranus and Saturn have a substantial tilt suggesting that this feature did not arise during the formation stages.
- Jupiter, also a gas giant, is the only exception.
- Saturn got its tilt due to gravitational interactions with its neighbour Neptune according to a well-known theory.
- But the new study argues that Saturn is no longer under Neptune’s gravitational influence.
- Titan, which is Saturn’s largest satellite, may have been responsible, suggested observations from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, which orbited Saturn from 2004-2017.
- Titan’s fast migration caused the planet to tilt further, reducing Neptune’s gravitational influence on Saturn.
Saturn
- Saturn is the second largest planet of the solar system in mass and size and the sixth nearest planet in distance to the Sun.
- Saturn has an overall hazy yellow-brown appearance.
- Saturn’s atmosphere is composed mostly of molecular hydrogen and helium.
- Saturn has 83 moons with confirmed orbits that are not embedded in its rings.
- The moons of Saturn are numerous and diverse, ranging from tiny moonlets only tens of metres across to enormous Titan, which is larger than the planet Mercury.
To read more information about Space
Non-Communicable Diseases
Why in News?
- Recently, the World Health Organisation (WHO) released its report “Invisible Numbers — The True Extent of Non-communicable Diseases and What To Do About Them”, which stated that every two seconds, one person under the age of 70 dies of a non-communicable disease (NCD) with 86% of those deaths occurring in low- and middle-income countries.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Globally, one in three deaths – 17.9 million a year – are due to cardiovascular diseases (CVDs).
- Two-thirds of the people with hypertension live in low- and middle-income countries, but almost half of the people with hypertension are not even aware they have it, it currently affects around 1.3 billion adults aged between 30 and 79.
- Major Diseases
- Diabetes: One in 28 deaths - 2.0 million people a year – is due to diabetes.
- More than 95% of diabetes cases globally are of type 2 diabetes.
- Cancer: It causes one in six deaths – 9.3 million people a year, a further 44% of cancer deaths could have been prevented or delayed by eliminating risks to health.
- Respiratory Disease: It indicated that 70% of deaths due to chronic respiratory diseases could have been prevented or delayed by eliminating risks to health.
- Diabetes: One in 28 deaths - 2.0 million people a year – is due to diabetes.
- Further, Covid-19 highlighted the links between NCDs and infectious disease, with serious impacts on NCD care. In the early months of the pandemic, 75% of countries reported disruption to essential NCD services.
- As per WHO portal only a handful of countries were on track to meet the Sustainable Development Goal target to reduce early deaths from NCDs by a third by 2030.
What are Non-Communicable Diseases?
- About
- Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), also known as chronic diseases, tend to be of long duration and are the result of a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioural factors.
- The main types of NCD are cardiovascular diseases (such as heart attacks and stroke), cancers, chronic respiratory diseases (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma) and diabetes.
- Causes
- Tobacco use, unhealthy diet, harmful use of alcohol, physical inactivity and air pollution are the main risk factors contributing to these conditions.
- Status of Non-Communicable Diseases in India
- According to WHO, over 60.46 lakh people died due to NCDs in India in 2019.
- Over 25.66 lakh deaths in 2019 in the country were due to cardiovascular diseases while 11.46 lakh deaths were due to chronic respiratory diseases.
- Cancer led to 9.20 lakh deaths while 3.49 lakh deaths in the country were attributed to diabetes.
- Indian Initiatives
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS) is being implemented under the National Health Mission (NHM).
- The Central Government is implementing the Strengthening of Tertiary Care Cancer facilities scheme to support the setting up of State Cancer Institutes (SCI) and Tertiary Care Centres (TCCC) in different parts of the country.
- Oncology in its various aspects has a focus in case of new AIIMS and many upgraded institutions under Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY).
- Affordable Medicines and Reliable Implants for Treatment (AMRIT) Deendayal outlets have been opened at 159 Institutions/Hospitals with an objective to make available Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases drugs and implants at discounted prices to the patients.
- Jan Aushadhi stores are set up by the Department of Pharmaceuticals to provide generic medicines at affordable prices.
- Global
- Agenda for Sustainable Development: As part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, heads of state and government committed to develop ambitious national responses, by 2030, to reduce by one third premature mortality from NCDs through prevention and treatment (SDG target 3.4).
- WHO plays a key leadership role in the coordination and promotion of the global fight against NCDs.
- Global action Plan: In 2019, the World Health Assembly extended the WHO Global action plan for the prevention and control of NCDs 2013–2020 to 2030 and called for the development of an Implementation Roadmap 2023 to 2030 to accelerate progress on preventing and controlling NCDs.
- It supports actions to achieve a set of nine global targets with the greatest impact towards prevention and management of NCDs.
- Agenda for Sustainable Development: As part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, heads of state and government committed to develop ambitious national responses, by 2030, to reduce by one third premature mortality from NCDs through prevention and treatment (SDG target 3.4).
Way Forward
- There is need for robust health system programmes that promote health, detect and control risk factors early and effectively, treat disease cost effectively and prevent untimely deaths.
- Further, NCDs need to be accorded higher priority in financial allocation and health system-strengthening initiatives with strong emphasis on primary care.
Nuclear Fusion
Context: Researchers have said that South Korea’s nuclear fusion (KSTAR) reactor has reached the temperature of over 100mn degrees Celcius (nearly 7 times that of the core of the Sun) Significance:
- The reactor achieved simultaneous sustainability of heat & plasma stability for 30 seconds of the reaction. This promises a viable fusion reactor that can be scaled up in the future.
- One kilogram(kg) of fusion fuel contains about 10 million times as much energy as a kg of coal, oil or gas
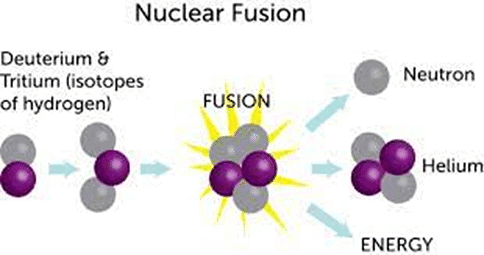
What is Nuclear Fusion?
- Nuclear fusion is defined as the combining of several small nuclei into one large nucleus with the subsequent release of huge amounts of energy.
- It is the opposite reaction of fission, where heavy isotopes are split apart.
- Harnessing fusion, the process that powers the Sun, could provide a limitless, clean energy source.
- In the sun, the extreme pressure produced by its immense gravity creates the conditions for fusion to happen.
- Fusion reactions take place in a state of matter called plasma. Plasma is a hot, charged gas made of positive ions and free-moving electrons that has unique properties distinct from solids, liquids and gases.
- At high temperatures, electrons are ripped from atom’s nuclei and become a plasma or an ionised state of matter. Plasma is also known as the fourth state of matter.
What are Advantages of Nuclear Fusion?
- Abundant energy: Fusing atoms together in a controlled way releases nearly four million times more energy than a chemical reaction such as the burning of coal, oil or gas and four times as much as nuclear fission reactions (at equal mass).
- Fusion has the potential to provide the kind of baseload energy needed to provide electricity to the cities and the industries.
- Sustainability: Fusion fuels are widely available and nearly inexhaustible. Deuterium can be distilled from all forms of water, while tritium will be produced during the fusion reaction as fusion neutrons interact with lithium.
- No CO2: Fusion doesn't emit harmful toxins like carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Its major by-product is helium: an inert, non-toxic gas.
- No long-lived radioactive waste: Nuclear fusion reactors produce no high activity, long-lived nuclear waste.
- Limited risk of proliferation: Fusion doesn't employ fissile materials like uranium and plutonium (Radioactive tritium is neither a fissile nor a fissionable material).
- No risk of meltdown: It is difficult enough to reach and maintain the precise conditions necessary for fusion—if any disturbance occurs, the plasma cools within seconds and the reaction stops.
What are Other International Initiatives on Nuclear Fusion Energy?
- International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) Assembly: It aims to build the world's largest tokamak to prove the feasibility of fusion as a large-scale and carbon-free source of energy. The ITER members include China, the European Union, India, Japan, South Korea, Russia and the United States.
- China’s Artificial Sun: The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) device designed by China replicates the nuclear fusion process carried out by the sun.
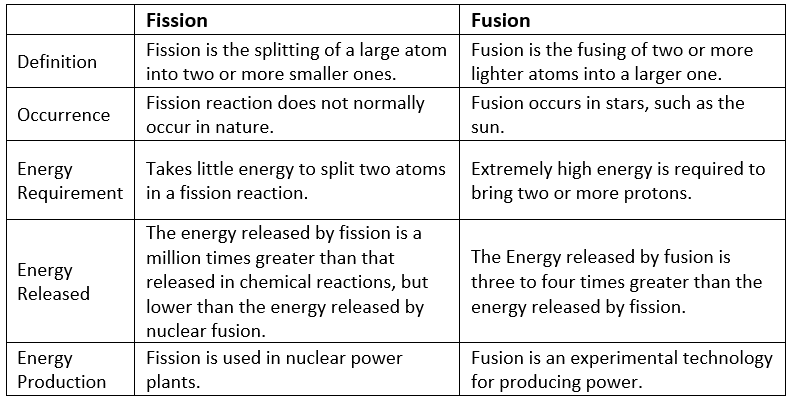
What is the difference between Nuclear Fusion & Nuclear Fission?
To read more information on nuclear energy
Inspire Awards
Why in News?
Recently, the 9th National Level Exhibition and Project Competition (NLEPC) for the INSPIRE Awards – MANAK (Million Minds Augmenting National Aspiration and Knowledge), has commenced.
What is the INSPIRE (Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research) Award?
- About
- It is aligned with the ‘Start-up India’ initiative and is being executed by DST (Department of Science and Technology) with National Innovation Foundation – India (NIF), an autonomous body of DST.
- Under this, the students are invited from all government or private schools throughout the country, irrespective of their educational boards (national and state).
- Financial support of Rs 10,000 each would be provided so that they could develop prototypes of the ideas which they submitted for the scheme.
- As a next step, they competed at respective District Level Exhibition and Project Competition (DLEPC) and State Level Exhibition and Project Competition (SLEPC) and finally National Level Exhibition and Project Competition (NLEPC).
- Aim
- To motivate students to become future innovators and critical thinkers.
- Objectives
- To target one million original ideas/innovations rooted in science and societal applications to foster a culture of creativity and innovative thinking among school children.
- To address the societal needs through science and technology and nurture them to become sensitive and responsible citizens and innovation leaders of tomorrow.
- Inspire Awards 2022
- The INSPIRE Awards were presented to 60 Start-Ups and financial support was provided to 53,021 students.
- It touched an unparalleled level of inclusivity by representing ideas and innovations of 702 districts of the country (96%) including 123 out of 124 aspirational districts, with 51% representation from girls, 84% participation from schools located in rural areas of the country and 71% of the schools run by the State / UT Governments.
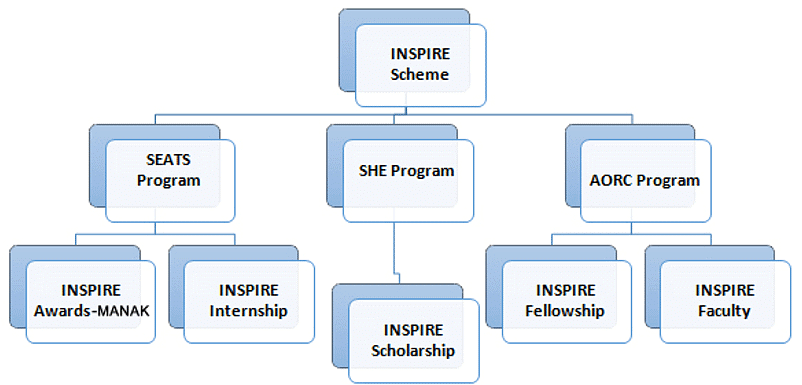
What do we Know about INSPIRE Scheme?
- The INSPIRE (Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research) scheme is one of the flagship programmes of the Ministry of Science and Technology.
- Its objective is to communicate to the youth population of the country the creative pursuit of science and attract talent to the study of science at an early stage and build the required critical human resource pool for strengthening and expanding the Science & Technology system and Research & Development base.
- The Government of India has successfully implemented the INSPIRE scheme since 2010. The scheme covers students in the age group of 10-32 years and has five components.
- The INSPIRE Awards- MANAK is one of its components.
What are the Other Related Initiatives?
- Draft National Science Technology and Innovation Policy, 2020: Its aim is to identify and address strengths and weaknesses of the Indian Science Technology and Innovation (STI) ecosystem to catalyse socio-economic development of the country and also make the Indian STI ecosystem globally competitive.
- SERB-POWER Scheme: It is a scheme designed exclusively for women scientists to mitigate gender disparity in science and engineering research in various science and technology (S&T) programmes in Indian academic institutions and Research and Development (R&D) laboratories.
- Swarna Jayanti Fellowship: It provides special assistance and support to a selected number of young scientists with a proven track record to enable them to pursue basic research in frontier areas of science and technology.
First Meeting of the Reconstituted National Medical Device Promotion Council (NMDPC)
Why in News?
Recently, important issues of Medical Technology (MedTech) Industry were taken-up at the first meeting of the reconstituted National Medical Device Promotion Council (NMDPC).
What were the Key Highlights of the Meeting?
- Agenda
- Central Drugs Standards and Control Organisation (CDSCO) and the State Licensing Authorities (SLAs) provided updates for the smooth transition to licensing of Class A and B Medical Devices w.e.f 1st October 2022.
- Medical devices under Medical Devices Rules, 2017 are classified as:
- Class A (low risk): E.g., absorbent cotton balls, alcohol swabs.
- Class B (low moderate risk): E.g., thermometer, BP monitoring device.
- Class C (moderate high risk): E.g., implants.
- Class D (high risk): E.g., heart valves.
- Department of Pharmaceuticals provided the latest status of the various initiatives such as 100% Foreign direct Investment (FDI) in MedTech Sector on automatic route, Production-Linked Incentive Scheme (PLI) scheme for Medical Devices, Medical Devices Parks in four States (Himachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh), etc.
- The discussion regarding the requirement of National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL) accreditation of In-House labs of the manufacturers of specific Medical Devices was taken-up during the meeting.
- Concerns Highlighted
- There is a regulatory burden of labelling requirements of Medical Devices.
- There are only 18 certified Medical Device Testing Laboratories that have been approved by CDSCO and that is grossly insufficient keeping in view the size of the country.
- Indian Medical Devices Industry presently lacks research ecosystem and infrastructure for manufacturing of high tech, advanced medical devices (Class C&D).
What were the Key Recommendations made by the NMDPC?
- Harmonize the Labelling Provisions: There is a need to move forward to harmonize the provisions of labeling of Medical Devices under the Legal Metrology (Packaged Commodity) Rules, 2011 into Medical Device Rules, 2017, for licensed medical devices.
- Investment in the Medical Devices Park: The Medical Devices Industry Associations representatives were encouraged to actively engage with states, which were sanctioned Medical Devices Parks by the Department for creating common infrastructure facilities and come forward to invest in the proposed parks to boost domestic manufacturing.
- Active Participation in the National MedTech Expo, 2022: The industry’s support was also asked for the proposed National MedTech Expo, 2022 to showcase the strengths and capabilities of Indian Medical Devices Industry.
- Need of More Certified Medical Devices Testing Laboratories: An adequate common infrastructure including accredited laboratories in various regions of the country for standard testing should be in place.
- Post-market Surveillance system and Medical Device Registry: There must be a robust IT enabled feedback driven post-market surveillance system and medical device registry, particularly for implants to ensure traceability of patient who has received the implant in order to assess the performance of the implant.
- New Legislation for a New Regulator
- The Committee has recommended that the new legislation should set up a new set of regulators at different levels for regulating the medical devices industry.
- The Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers should allow the new regulator to involve institutions such as Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and network of Indian Institute of Technology (IITs) to test medical devices for safety and efficacy.
- Medical device regulations must be dispensed with by qualified and well-trained Medical Device Officers to give a boost to the Medical Device industry in the country.
- Research Linked Incentive (RLI) Scheme: The Committee recommended the Department to start a RLI Scheme in Line with the PLI scheme.
- Upskilling of the Medical Device Officers: The Ministry should work in synergy with State governments and impart the necessary skills to the local medical device officers.
- A Single Window Clearing Platform
- A single window clearing platform for application of license for manufacturing, export, import must be set up that shall also integrate all these bodies involved in the regulation of medical devices.
- The Ministry must incorporate such an all-encompassing “single window clearing/approval system” in the proposed new separate Act for the regulation of Medical Devices.
What is NMDPC?
- About
- National Medical Device Promotion Council (NMDPC) is chaired by the Secretary, Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
- It has members from stakeholder departments/ organizations, functions of which have a bearing on the growth of the sector.
- Also, it has representation from several medical device industry associations, representing the sector in India.
- Significance
- NMDPC, going forward, is expected to become a vibrant forum for all issues relating to the medical devices sector, which is a sunrise sector with huge potential for social obligations and the economic aspirations of India.
|
61 videos|5403 docs|1144 tests
|
FAQs on Science & Technology: September 2022 Current Affairs - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. What are some interesting facts about Saturn's rings? |  |
| 2. Why is Saturn's tilt considered extreme? |  |
| 3. What are non-communicable diseases (NCDs)? |  |
| 4. What is nuclear fusion? |  |
| 5. What is the purpose of the National Medical Device Promotion Council (NMDPC)? |  |















