Science and Technology: October 2024 UPSC Current Affairs | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
DRDO's Deep Tech Efforts for Defence

Why in news?
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is set to unveil a new initiative focused on enhancing emerging military technologies. This effort will support five deep-tech projects, each funded with up to Rs 50 crore, aimed at fostering the indigenisation of defence products and bolstering national security.
- This initiative is part of a larger Rs 1-lakh crore fund introduced in the Interim Budget 2024-2025, intended to catalyze transformative research within the defence sector.
Key Points About the Projects
- Objective: The primary aim of DRDO is to lessen the dependency on imports for systems, subsystems, and components needed by the tri-services through indigenisation. The focus is on innovative solutions for technologies that are currently unavailable in India or globally, especially in the realms of futuristic and disruptive technologies.
- Futuristic and Disruptive Tech: DRDO has outlined three main categories for proposal submissions: indigenisation, futuristic and disruptive technology, and cutting-edge technology. It emphasizes advancing research in areas such as quantum computing, blockchain, and artificial intelligence. These technologies are designed to significantly transform existing industries and societal norms by introducing novel methods, products, or services.
- Global Models: DRDO's initiative draws inspiration from similar programs led by state defence research organizations worldwide, notably the US DARPA (United States Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency).
- Funding and Collaboration: Investments for these deep tech projects will be managed through DRDO's Technology Development Fund (TDF), which collaborates with private industries, particularly MSMEs and start-ups, to develop the military hardware and software required by the armed forces.
What is the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)?
About:
- DRDO serves as the research and development branch of the Ministry of Defence, dedicated to equipping India with advanced defence technologies.
- Its efforts toward self-reliance have led to the successful indigenous development of several strategic systems, including missile systems like Agni and Prithvi, the Light Combat Aircraft Tejas, and various air defence systems.
Formation
- Established in 1958, DRDO resulted from the merger of the Technical Development Establishments (TDEs) of the Indian Army and the Directorate of Technical Development & Production (DTDP) with the Defence Science Organisation (DSO).
- It comprises over 50 laboratories focused on various defence technology areas, including aeronautics, armaments, electronics, and engineering systems.
Technology Clusters of DRDO
- Aeronautics: Develops aviation technologies, including aircraft and UAVs.
- Armament and Combat Engineering: Creates weapon systems and ammunition for armed forces.
- Missiles and Strategic Systems: Specializes in various missile technologies.
- Electronics and Communication Systems: Focuses on radar and communication technologies.
- Life Sciences: Innovates technologies for human survival in harsh conditions.
- Materials and Life Sciences: Develops advanced materials and biotechnology for military uses.
Achievements of DRDO
- Agni and Prithvi Missile Series: Successfully developed ballistic missile systems that enhance India's strategic capabilities.
- Tejas Light Combat Aircraft (LCA): An indigenous multi-role fighter aircraft developed by DRDO in cooperation with other organizations.
- Akash Missile System: A medium-range air defence missile system for the Indian Army and Air Force.
- BrahMos Missile: Recognized as the world's fastest supersonic cruise missile, created collaboratively with Russia.
- Arjun Main Battle Tank (MBT): An indigenous battle tank designed for the Indian Army with advanced capabilities.
- INSAS Rifle Series: Development of indigenous small arms for the armed forces.
- Light Combat Helicopter (LCH): Designed to meet specific operational needs of the military.
- NETRA UAV: An indigenous UAV developed for surveillance and reconnaissance purposes.
- Submarine Sonar Systems: Creation of sonar and underwater communication systems for the Indian Navy.
Challenges Faced by DRDO
- Delays in Project Execution: Numerous projects, including advanced weapon systems, have experienced delays that hinder timely deployment and escalate costs.
- Technology Gaps and Dependence on Imports: Despite a robust production and R&D base, the Indian defence sector still relies heavily on imports for major systems and critical components.
- Budgetary Constraints: The DRDO budget for FY 2024-25 is Rs 23,855 crore, which, while an increase, remains modest compared to the government's focus on modernisation and indigenisation.
- Collaboration with Industry and Academia: Although DRDO strives to improve partnerships with private sectors and academic institutions, effectively aligning these collaborations with defence R&D needs is an ongoing challenge.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Industry Collaboration: DRDO should enhance partnerships with private sectors and MSMEs to foster innovation and develop cutting-edge technologies.
- Focus on Time-bound Execution: Implementing stricter timelines and agile management practices could help overcome delays in project delivery.
- Increased Investment in R&D: Allocating more resources for research and development is crucial for bridging technological gaps and reducing import reliance.
- Fostering Global Collaborations: Expanding partnerships with international defence research agencies can provide access to advanced technologies and expertise.
Mains Question
Q: Analyze the significance of DRDO's technology clusters and highlight notable achievements in recent years. How do these achievements contribute to India's strategic autonomy?
The Nobel Prize in Physics 2024

Why in News?
The Nobel Prize in Physics 2024 has been awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to John J. Hopfield and Geoffrey E. Hinton, two pioneers whose groundbreaking work laid the foundation for modern artificial neural networks (ANNs) and machine learning (ML). Their research has had significant implications across multiple fields including physics, biology, finance, and medicine, impacting technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) applications, notably OpenAI’s ChatGPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer).
What is the Contribution of John Hopfield?
Hopfield Network: John Hopfield is renowned for developing the Hopfield network, a type of recurrent neural network (RNN) foundational to artificial neural networks and AI.
- Created in the 1980s, it stores simple binary patterns (0s and 1s) across a network of artificial nodes (neurons).
- A key aspect of this network is its associative memory, enabling it to retrieve complete information from incomplete or distorted inputs, akin to how the human brain recalls memories.
- The network operates on Hebbian learning principles, where repeated neuronal interactions strengthen connections.
- By using statistical physics, Hopfield achieved pattern recognition and noise reduction by minimizing energy states, advancing neural networks and AI to mimic biological brain functions.
- Impact: Hopfield's model has been instrumental in solving computational tasks, completing patterns, and enhancing image processing.
What is the Contribution of Geoffrey Hinton?
- Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs): Building on Hopfield's foundational work, Geoffrey Hinton developed a learning algorithm for Restricted Boltzmann Machines in the 2000s, which propelled deep learning by stacking multiple layers of neurons.
- RBMs can learn from examples rather than requiring explicit instructions, allowing machines to recognize new patterns based on previously learned data.
- This approach enables the Boltzmann machine to recognize categories it has never encountered if they match learned patterns.
- Applications: Hinton's contributions have led to breakthroughs in diverse fields, including healthcare diagnostics, financial modeling, and AI technologies such as chatbots.
What are Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)?
About:
- Artificial Neural Networks are inspired by the structure of the human brain, where biological neurons interconnect to perform complex tasks.
- In ANNs, artificial neurons (nodes) process information collectively, allowing data to flow through the system in a manner akin to brain synapses.
Common Architectures of ANNs:
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Trained on sequential or time series data, these networks create machine learning models capable of making predictions or conclusions based on sequential inputs.
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Specifically designed for grid-like data (e.g., images), CNNs utilize three-dimensional data for tasks such as image classification and object recognition.
- Feedforward Neural Networks: This is the simplest architecture where information flows in one direction from input to output through fully connected layers.
- Autoencoders: Used for unsupervised learning, they compress input data to retain only essential parts, later reconstructing the original data from this compressed version.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): A powerful type of neural network used for unsupervised learning, consisting of a generator (which creates fake data) and a discriminator (which distinguishes between real and fake data).
- Through adversarial training, GANs produce realistic, high-quality samples and are widely used in image synthesis, style transfer, and text-to-image synthesis, revolutionizing generative modeling.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that utilizes data and algorithms to enable computers to learn from experience and improve their accuracy over time.
Operating Mechanism
- Decision Process: Algorithms predict or classify data based on input, which can be either labeled or unlabeled.
- Error Function: This function assesses the model's predictions against known examples to evaluate its accuracy.
- Model Optimization Process: The model iteratively adjusts its weights to enhance its predictions until it achieves an acceptable accuracy level.
Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Networks
- Hierarchy: AI encompasses ML; ML encompasses deep learning, which relies on neural networks.
- Deep Learning: A subset of machine learning utilizing neural networks with multiple layers (deep neural networks) capable of processing unstructured data without labeled datasets.
- Neural Networks: A specific type of machine learning model organized into layers (input, hidden, output) that mimic human brain functionality.
- Complexity: As one progresses from AI to neural networks, the complexity and specificity of tasks increase, with deep learning and neural networks serving as specialized tools within the broader AI framework.
Mains Question
Q: Analyze the impact of neural networks and machine learning on modern technology. Provide examples of their applications in various sectors.
Nobel Prize 2024 in Physiology or Medicine
Why in news?
Recently, the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden. The scientists received this prestigious honor for their groundbreaking discovery of microRNA and its significant role in post-transcriptional gene regulation.
What Discovery of microRNA led to the Nobel Prize?
- Early Research:The researchers focused on the roundworm C. elegans to gain insights into tissue development.
- Mutant Strains:They examined mutant strains, specifically lin-4 and lin-14, which exhibited genetic programming abnormalities.
- Ambros' Research:Ambros discovered that lin-4 suppressed the activity of lin-14 but was initially unable to ascertain the mechanism behind this suppression.
- He cloned lin-4 and identified a short RNA molecule that lacked protein-coding potential, suggesting that this RNA could inhibit lin-14.
- Ruvkun's Research:Ruvkun determined that lin-4 did not prevent the production of lin-14 mRNA; instead, it regulated it by inhibiting protein synthesis. A specific sequence from lin-4 matched crucial complementary regions in lin-14 mRNA. Ultimately, Ambros and Ruvkun found that lin-4 microRNA binds to lin-14 mRNA, effectively blocking protein production.
- Significance:Ruvkun's team later discovered let-7, a microRNA found across the animal kingdom.
- Current understanding:MicroRNAs are prevalent and play vital roles in gene regulation in multicellular organisms.
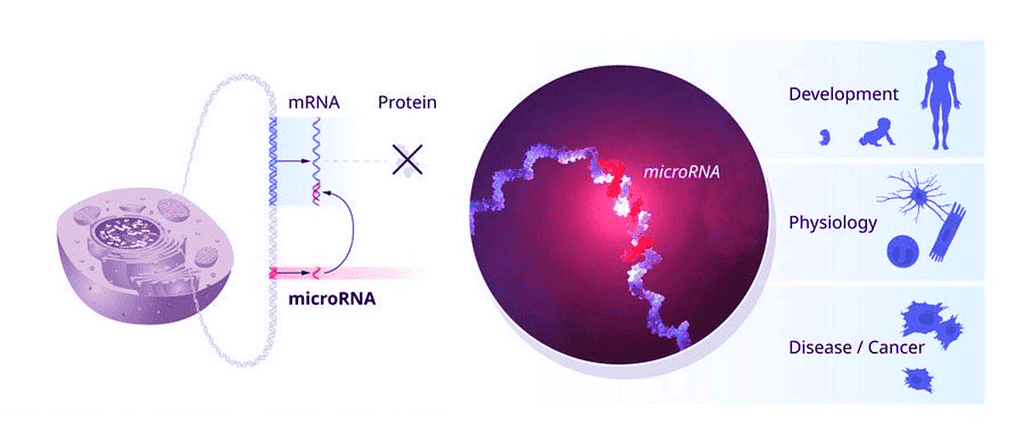
What are microRNAs?
- The body synthesizes proteins through a complex process divided into two main stages: transcription and translation.
- During the transcription phase, Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in the cell nucleus is transcribed into messenger Ribonucleic Acid (mRNA).
- The mRNA leaves the nucleus, traverses the cytoplasm, and binds to a ribosome.
- In the translation step, transfer RNA (tRNA) brings specific amino acids to the ribosome, where they are assembled in the order specified by the mRNA to create the protein.
- Micro RNA (miRNA) serves a regulatory function in protein synthesis by binding to and silencing mRNA at particular points in the process.
- This regulation occurs via post-transcriptional gene regulation, ensuring that protein synthesis is tightly controlled.
What are the applications of the Discovery?
- Abnormal Regulation and Diseases: Disruptions in microRNA regulation can contribute to various diseases, including cancer.
- Mutations: Mutations in microRNA genes have been associated with conditions such as hearing loss, as well as eye and skeletal disorders.
- Future Applications: While microRNAs show immense potential, there are currently no direct clinical applications. Further research and a deeper understanding of microRNAs are required for future therapeutic applications.
Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2024

Why in News?
Recently, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2024. One half of the prize was awarded to David Baker for his pioneering work in computational protein design, while the other half was jointly awarded to Demis Hassabis and John M. Jumper for their contributions to protein structure prediction.
What is the Contribution of David Baker?
- Revolutionising Protein Engineering: Baker's research group has innovatively employed computational methods to create novel proteins from scratch. This advancement has significantly transformed the field of protein engineering. By manipulating the 20 distinct amino acids that constitute proteins, his team has successfully designed new proteins that are not found in nature.
- Applications in Medicine and Technology: The artificially designed proteins crafted by Baker's team hold immense potential, especially in the realms of pharmaceuticals, vaccines, nanomaterials, and biosensors. For instance, Baker has engineered proteins with unique functions, such as degrading plastics and performing tasks that exceed the capabilities of natural proteins.
- First Breakthrough in 2003: Baker's initial major achievement occurred in 2003 when his team succeeded in designing a protein entirely different from any existing in nature.
What is the Contribution of Demis Hassabis and John Jumper?
- Protein Folding Problem: Since the 1970s, the scientific community has encountered challenges in predicting how sequences of amino acids fold into their intricate three-dimensional structures. The structure of a protein is vital because it dictates its function, making it crucial for progress in drug discovery, treatment of diseases, and advancements in biotechnology.
- Breakthrough with AlphaFold2: In 2020, Hassabis and Jumper unveiled AlphaFold2, an AI-driven system that transformed the landscape of protein structure prediction. This model achieved the remarkable feat of predicting the structure of nearly every known protein, totaling approximately 200 million. This accomplishment effectively resolved a 50-year-old dilemma in structural biology.
- Widespread Use and Impact: AlphaFold2 has been adopted by over two million researchers globally, facilitating breakthroughs across various scientific fields. For example, it has played a crucial role in enhancing our understanding of antibiotic resistance and in creating enzymes capable of breaking down plastics.
Space Based Surveillance (SBS) Mission

Why in news?
The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) has recently given its approval for phase 3 of the Space Based Surveillance (SBS) mission. This initiative aims to enhance land and maritime domain awareness for both civilian and military purposes.
- The SBS mission will include the deployment of a minimum of 52 satellites in low Earth orbit and geostationary orbit for comprehensive surveillance.
- Among these, 21 satellites will be developed by ISRO, while the remaining 31 will be constructed by private sector companies.
- The National Security Council Secretariat and the Defence Space Agency, both operating under the Ministry of Defence, are overseeing the SBS mission.
- Each branch of the armed forces will be equipped with dedicated satellites tailored for their respective land, sea, or air operations.
- Previous phases include SBS 1, launched in 2001 with four satellites like Risat 2, and SBS 2, launched in 2013 with six satellites such as Risat 2A.
- The SBS 3 mission will also benefit from India's acquisition of 31 Predator drones from the United States, collaborative construction of military satellites with France, and the development of anti-satellite missile capabilities.
- India's goal with this mission is to enhance its ability to detect enemy submarines in the Indo-Pacific region and to monitor critical infrastructure developments by adversaries along its land and maritime borders.
Precision Medicine in India

Why in news?
Precision medicine is marking a transformative phase in personalized healthcare. This innovative field emerged prominently following the completion of the Human Genome Project (HGP). It now integrates genomics to diagnose and treat various conditions, including cancers, chronic diseases, immunological disorders, cardiovascular issues, and liver diseases.
What is Precision Medicine?
- Precision medicine represents a groundbreaking approach to disease treatment and prevention, taking into account individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle differences.
- This strategy focuses on customizing medical care to fit the unique traits of each patient, moving away from generic treatment methods.
- By doing so, healthcare professionals can more precisely determine which treatments and preventive strategies are most effective for specific patient groups.
- Role of Biobanks:
- Biobanks play a critical role in research by storing biological samples such as DNA, cells, and tissues.
- The diversity of these biobanks is essential for ensuring that precision medicine benefits a wider population.
- Recent research utilizing biobank data has been instrumental in identifying previously undiagnosed rare genetic disorders.
What is the State of Precision Medicine and Biobanks in India?
Market Growth
- The precision medicine market in India is anticipated to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 16% and is expected to surpass USD 5 billion by 2030.
- Currently, it contributes to 36% of the national bioeconomy, covering sectors such as cancer immunotherapy, gene editing, and biologics.
Policy Development
- The advancement of precision therapeutics is part of the new ‘BioE3’ policy aimed at promoting high-performance biomanufacturing across various industries.
Recent Approvals and Developments
- In 2023, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation approved NexCAR19, which is India’s first domestically developed CAR-T cell therapy.
- In 2024, a dedicated center for CAR-T cell therapy was established at IIT Bombay, marking a significant step in this field.
State of Biobanks in India
- Genome India Programme: The ‘Genome India’ program has successfully sequenced 10,000 genomes from 99 different ethnic groups to aid in the identification and treatment of rare genetic diseases.
- Phenome India Project:The pan-India ‘Phenome India’ project has collected 10,000 samples aimed at enhancing predictive models for cardio-metabolic diseases.
- Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) Mission: This mission focuses on discovering new genes or variants to develop targeted therapies for genetic disorders affecting children.
- Regulatory Challenges: In India, existing biobanking regulations present significant challenges that hinder the realization of precision medicine's full potential. Unlike the UK, US, Japan, and several European countries that have robust regulations addressing biobanking (such as informed consent, privacy, and data protection), India's regulatory framework remains inconsistent.
Diphtheria
Why in news?
To manage the diphtheria outbreak in the Deeg district of Rajasthan, teams from the state health department and the World Health Organization (WHO) have been deployed to the area to initiate vaccination efforts.
Overview
- Diphtheria is a serious infectious disease caused by the Corynebacterium diphtheriae bacteria, which produce a harmful toxin.
About Diphtheria
This infection primarily affects the throat and nose, leading to severe health complications if left untreated.
Transmission
- Diphtheria spreads easily between individuals through respiratory droplets, such as those released during coughing or sneezing.
- It can also be transmitted by direct contact with infected sores or ulcers.
- While the bacteria can infect the skin, skin infections are less likely to cause serious illness compared to respiratory infections.
- If untreated, diphtheria can severely impact the heart, kidneys, and nervous system.
Symptoms
- Common symptoms of diphtheria include a sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, and overall weakness.
- Within 2 to 3 days of infection, a thick grey coating made of dead tissue may develop in the respiratory tract, which can obstruct breathing and swallowing.
Treatments
- Initial treatment includes the administration of Diphtheria Antitoxin (DAT) to counteract the unbound toxin.
- Antibiotics are prescribed to curb further bacterial multiplication.
- Supportive care is critical to manage complications such as airway blockage and myocarditis.
Europa Clipper
Why in news?
NASA is preparing to launch the Europa Clipper mission, which is designed to investigate Jupiter's icy moon, Europa.
Overview of the Europa Clipper Mission
- The Europa Clipper is a NASA mission focused on studying Europa's icy surface.
- This mission will place a spacecraft in orbit around Jupiter to conduct a comprehensive exploration of Europa.
- It is the first NASA spacecraft specifically dedicated to exploring an ocean world beyond Earth.
- The primary goal of the Europa Clipper is to assess whether the ice-covered moon could potentially support life.
- Europa exhibits compelling evidence of a subsurface ocean of liquid water beneath its icy exterior.
- The spacecraft will measure 100 feet (30.5 meters) in length and about 58 feet (17.6 meters) in width.
- It will be the largest spacecraft ever developed by NASA for a planetary mission.
Mission Objectives
- Europa Clipper will orbit Jupiter and perform 49 close flybys of Europa.
- The mission aims to gather critical data to identify regions beneath the thick ice crust that might be conducive to life.
- The spacecraft is equipped with nine scientific instruments along with a gravity experiment that utilizes its telecommunications system.
- During each flyby, all scientific instruments will function simultaneously to maximize data collection.
- Scientists will compile and layer the data to create a detailed understanding of Europa.
Power Supply
- The spacecraft features large solar arrays that will harness sufficient sunlight to meet its power requirements while operating in the Jupiter system.
Understanding Solar Arrays
- A solar array consists of multiple solar panels interconnected to produce electrical output.
- To create a complete solar power system, a solar array is typically combined with additional components like an inverter and batteries.
Ossification Test

Why in News?
Recently, one of the individuals accused in the murder case of a political leader underwent an ossification test to determine if he was a minor.
What is the Ossification Test?
- Ossification is the natural process of bone formation that starts during the early developmental stages of a fetus and continues into late adolescence, with individual variations.
- The ossification test helps estimate a person’s age based on the development stage of their bones.
- This test involves taking X-rays of specific bones, typically in the hands and wrists, to assess skeletal and biological growth.
- X-ray images are compared against standard developmental benchmarks to help ascertain age.
- A scoring system may be used to evaluate the growth of individual bones in the hands and wrists against established maturation standards relevant to a specific population.
Reliability
- Variations in bone maturation observation can affect the precision of ossification tests.
- Minor developmental differences among individuals can introduce potential errors in age estimation.
- Ossification tests generally provide an age range, like 17-19 years.
- Courts have debated the margin of error in this age range, discussing whether to accept the lower or upper limits.
- For instance, in 2024, the Delhi High Court ruled that for cases under the POCSO (Protection of Children from Sexual Offences) Act, 2012, the upper age limit of the ossification test's reference range should be considered.
- The court also stated that a margin of error of two years should be applied when determining age.
Court’s View About the Test
- According to Section 94 of the Juvenile Justice Act, if there are reasonable grounds for doubt regarding a person’s age, the Board must initiate the process of age determination.
- Primary evidence for age verification should be a school-issued birth certificate or a matriculation certificate from the appropriate examination board.
- If these documents are not available, a birth certificate from a municipal authority, corporation, or panchayat can be considered.
- The Act specifies that ossification tests or other medical age determination tests should only be conducted if these documents are absent, as directed by the Committee or Board.
- In a March 2024 ruling, the Supreme Court underscored that ossification tests should be treated as a last resort for age determination.
- Courts have maintained that ossification tests cannot supersede documentary evidence.
Why is Age Determination Significant in the Criminal Justice System?
- Criminal law differentiates between minors and adults regarding legal procedures, correction methods, rehabilitation, and punishment.
- In India, individuals under the age of 18 are classified as minors.
- Minors are subject to the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015.
- A child in conflict with the law is not sent to an adult prison; instead, they are placed in an observation home and brought before a Juvenile Justice Board (JJB), which includes a magistrate and two social workers specialized in child welfare, instead of a conventional court.
- After an inquiry, the JJB can decide to admonish the child, require community service, or place them in a special home for a maximum of three years, among other options.
- The Juvenile Justice Amendment Act 2021 stipulates that for children above 16 accused of heinous offenses (punishable by at least 7 years' imprisonment), the JJB must conduct a preliminary assessment of the child's mental and physical capacity to commit the offense.
- This assessment also considers the child's understanding of the consequences and the circumstances surrounding the offense to determine if they should be tried as an adult.
Space Docking Experiment (SPADEX)
Why in news?
Recently, a company based in Hyderabad delivered two satellites, each weighing 400 kg, to ISRO. These satellites will play a crucial role in the upcoming Space Docking Experiment set to occur later this year.
Overview
- ISRO is taking significant strides towards developing autonomous docking technology.
- The Space Docking Experiment (SPADEX) involves two spacecraft, referred to as the ‘Chaser’ and the ‘Target’, that will connect in space.
- Docking systems are vital as they allow spacecraft to link in orbit, facilitating essential operations such as:
- Assembling space stations
- Refueling missions
- Transferring astronauts and cargo
- The experiment will assess how well the two spacecraft maintain stability and control post-docking, which is critical for the success of future missions.
- SPADEX is distinctive as it aims to develop indigenous, scalable, and cost-effective docking technology.
- This experiment will showcase two spacecraft docking autonomously in orbit, emphasizing precision, navigation, and control—skills essential for upcoming missions.
- SPADEX is adaptable for various spacecraft sizes and mission types, enabling collaborations for constructing space stations or exploring deep space.
History of Docking Systems
- The history of docking systems dates back to the Cold War era.
- The first successful docking in space occurred on October 30, 1967, when the Soviet Union achieved a historic link between Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188.
- This was the first fully automated docking between two unmanned spacecraft, paving the way for future space exploration, including extended missions aboard space stations.
Significance
SPADEX is crucial for advancing India's long-term goals in space exploration.
It supports objectives such as:
- Manned spaceflight
- Satellite maintenance
- Construction of future space stations
Eliminating Kala Azar

Why in news?
India could be on the verge of eradicating Kala-azar as a public health issue, as the nation has successfully maintained a case rate below one per 10,000 individuals for two consecutive years, meeting the WHO criteria for elimination certification.
Overview
- Kala-azar, also known as visceral leishmaniasis (VL), is a severe form of leishmaniasis caused by the protozoan parasite Leishmania donovani.
- It is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected female sandfly, primarily Phlebotomus argentipes in India.
- The disease affects some of the world’s poorest people and is associated with malnutrition, population displacement, poor housing, a weak immune system and lack of financial resources.
- People with HIV and other conditions that weaken their immune system, are more likely to get sick from a Leishmania infection.
- Symptoms: The disease is characterized by irregular bouts of fever, substantial weight loss, swelling of the spleen and liver, and severe anaemia if left untreated, which can lead to death within two years.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis combines clinical signs with parasitological or serological tests, such as the rK39 diagnostic kit.
- Treatment: There are several anti-parasitic medications available that treat leishmaniasis.
Cancer Detection with Ultrasound
Why in news?
Recently, scientists have introduced a groundbreaking ultrasound technique aimed at enhancing cancer detection. This method presents a less invasive and more affordable alternative to traditional biopsy procedures. It operates by releasing various biomarkers, including RNA, DNA, and proteins, from the affected tissue into the bloodstream, thereby facilitating early detection.
What is Cancer?
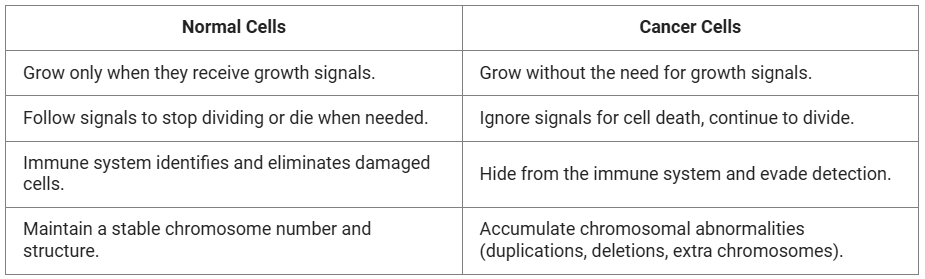
- About: Cancer is a medical condition characterized by the uncontrolled growth of certain cells in the body, which can lead to the spread of these cells to other regions.
- Cause: Cancer arises in any body part when the normal processes of cell growth and division fail. This malfunction results in the creation of abnormal cells that may form tumors, which can be classified as either cancerous or non-cancerous.
Types of Cancer
- Carcinoma: Cancer that originates in epithelial cells, which are found in skin and glands. Examples include breast, lung, and prostate cancer.
- Sarcoma: This type develops in connective tissues such as bones, muscles, and fat.
- Leukemia: Affects the blood-forming tissues, leading to the production of abnormal white blood cells.
- Lymphoma: Begins in immune cells called lymphocytes. The main types are Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Multiple Myeloma: A cancer that arises from plasma cells found in the bone marrow.
- Melanoma: Starts in the pigment-producing cells, primarily affecting the skin.
Comparison of Normal Cells and Cancer Cells
Fluorescent nanodiamonds (FNDs)

Why in news?
Scientists at Purdue University have figured out how to levitate and spin Fluorescent Nanodiamonds (FNDs) in a vacuum.
What are their Applications?
- Medical Diagnostics: FNDs are used for high-resolution imaging and tracking cells over extended periods due to their non-toxic nature.
- Temperature Sensing: FNDs can measure temperatures at the microscale, making them useful for scientific experiments.
- Correlative Microscopy:Their fluorescent properties make them ideal for combining different types of imaging techniques.
- Sensor Technologies: Due to their sensitivity to acceleration and electric fields, FNDs can be used in industry sensors and gyroscopes for rotation sensing.
- Quantum Computing: FNDs doped with nitrogen can be used for quantum superposition experiments and future quantum computing applications.
Treatment of Rare Diseases

Why in News?
The Delhi High Court recently gave orders to improve the access to orphan drugs for treating rare diseases.
About the Delhi High Court Verdict
- The court's directives focus on making orphan drugs more available for those suffering from rare diseases.
- This action aims to tackle problems related to the high costs of these treatments and the difficulties patients face in accessing them in India.
Rare Diseases in India and Their Classification
- Definition: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), rare diseases are serious, lifelong illnesses that affect 1 or fewer people in every 1,000.
- Conditions Recognized as Rare: About 55 conditions in India are recognized as rare diseases, including Gaucher’s disease, Lysosomal Storage Disorders (LSDs), and certain muscular dystrophies.
- National Registry: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) oversees the National Registry for Rare and Other Inherited Disorders (NRROID), which has recorded 14,472 patients with rare diseases.
Classification of Rare Diseases in India
- Group 1: Diseases that can be treated with a one-time cure, such as certain enzyme replacement therapies.
- Group 2: Conditions needing long-term or permanent treatment that are relatively less costly and have proven benefits, requiring regular check-ups.
- Group 3: Diseases with available treatments that are very expensive and need ongoing therapy, making it hard to select beneficiaries due to high costs.
Current Funding Policy in India
- National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD) 2021: This was introduced to help fund treatments for rare diseases, allowing patients at specific Centres of Excellence (CoE) to receive financial help up to Rs 50 lakh.
- Centres of Excellence: Notable institutions include AIIMS in Delhi, PGIMER in Chandigarh, and the Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research at SSKM Hospital in Kolkata.
- Crowdfunding and Voluntary Donations Portal (2022): The Health Ministry launched an online platform for donors to support rare disease patients at CoEs, featuring details about patients, their conditions, treatment costs, and bank details for CoEs.
Challenges Associated with Orphan Drugs
- Limited Treatment Options: There are therapies for less than 5% of rare diseases, leading to fewer than 10% of patients getting specific treatment.
- High Treatment Costs: Many treatments are very expensive, creating a heavy financial burden on patients and their families.
- Regulatory Delays: Approval from bodies like the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) can take a long time, affecting the availability of treatments.
- Bureaucratic Hurdles: Administrative delays and red tape complicate access to necessary drugs, impacting patient care.
- Challenges in Beneficiary Selection: Due to high costs, it is difficult to identify and prioritize patients for financial help, which may leave some without support.
Way Forward
- Streamline Regulatory Approvals: Speed up the approval process for orphan drugs by reducing bureaucratic delays and creating a fast-track system for essential treatments, ensuring patients get timely access to life-saving medications.
- Increase Financial Support and Expand Coverage: Raise the funding limits under the National Policy for Rare Diseases and provide financial help to more patients, while promoting partnerships and innovative funding methods like insurance for rare disease treatments.
India’s Semiconductor Market to exceed 100 billion dollars by 2030
Why in News?
India's semiconductor market is projected to surpass $100 billion by 2030.
Market Insights
- The market was valued at $45 billion in 2023.
- It is expected to grow at an annual rate of 13%.
- Key drivers of this growth include high demand and government initiatives like the production-linked incentive scheme.
- Semiconductors are crucial for various sectors, including electronics, defence, healthcare, and automotive.
What are Semiconductors?
- Semiconductors are materials that have electrical properties between those of conductors (like metals) and insulators (like rubber).
- They can conduct electricity under certain conditions while acting as insulators in others.
- Commonly made from pure elements like silicon or germanium, they are also known as integrated circuits (ICs) or microchips.
- A process called doping involves adding small amounts of impurities to these pure elements, significantly changing their conductivity.
Applications of Semiconductors
- Semiconductors are essential in a wide range of electronic devices.
- Transistors, which are key components of modern electronics, depend on semiconductor materials.
- They serve as switches or amplifiers in devices such as computers and cell phones.
- They are also used in solar cells, LEDs, and integrated circuits.
Increased Focus on Semiconductors
- Semiconductors are vital for the economy, making them a strategic industry for many nations.
- Countries are investing heavily in research and development to stay competitive and foster innovation.
- The chip shortage in 2021 highlighted the global industry's reliance on a few key suppliers.
- Taiwan is the largest chipmaker, holding about 44% of the global market share, followed by China (28%), South Korea (12%), the U.S. (6%), and Japan (2%).
- To reduce this dependency, governments are investing heavily to develop stronger domestic chip industries.
- India aims to become a significant player in the semiconductor industry amid growing competition with China.
- This situation has led the U.S. and allied countries to enhance tech cooperation with India.
Factors Favoring India
- Skilled Workforce: India has a large number of graduates in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM), providing the needed talent for semiconductor manufacturing, design, research, and development.
- Cost Advantage: India benefits from lower labour costs, efficient supply chains, and a developing ecosystem for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Global Supply Chain Diversification: India is becoming a favored site for back-end assembly and testing operations, with potential for future front-end manufacturing.
- Policy Support: The Indian government is actively promoting India as an alternative to China in the global semiconductor supply chain, especially after the pandemic-related supply issues.
Government Initiatives
- Semicon India: This initiative focuses on developing the semiconductor and display manufacturing ecosystem in India.
- The program aims to financially support companies investing in semiconductors, display manufacturing, and the design ecosystem.
- India Semiconductor Mission: A dedicated division within the Digital India Corporation, its goal is to build a robust semiconductor and display ecosystem to make India a major player in electronics manufacturing and design.
The government provides incentives for manufacturing setups in India:
- Under the Semiconductor Fab Scheme, there is fiscal support of 50% of the project cost for all technology nodes.
- Under the Display Fab Scheme, fiscal support of 50% of the project cost is also available.
- Under the Compound Semiconductor Scheme, fiscal support of 50% of capital expenditure is offered, including for discrete semiconductor fabs.
- Through the Chips to Startup (C2S) Programme, being implemented at 113 institutions, 85,000 high-quality engineers are being trained in various areas.
- In February 2024, the government approved the establishment of three semiconductor plants—two in Gujarat and one in Assam.
Future Outlook
- With the growth of digital technologies, including AI, IoT, and 5G, the demand for semiconductors is increasing rapidly.
- India is positioned well to take advantage of this trend due to its expanding tech industry.
- Foreign Investment: Major global companies like Intel and TSMC are looking at opportunities in India, which will help develop local expertise and infrastructure.
- Startup Ecosystem: India has a thriving startup scene focused on semiconductor design and related technologies, promoting innovation and growth in the sector.
- Infrastructure Development: Development of improved infrastructure, including special economic zones (SEZs) for electronics manufacturing, is underway to support the semiconductor industry.
- Talent Pool: India has a large number of engineering graduates and skilled professionals to meet the workforce needs of the semiconductor sector.
Parkinson's Disease

About Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily impacts the nervous system and the parts of the body controlled by nerves. It often leads to a stage where a person has limited or no control over their movements and balance.
- The risk of developing Parkinson's disease increases with age, with the average onset around 60 years. There is also a noticeable difference in how the disease affects genders, as indicated by various studies worldwide.
Causes of Parkinson’s Disease
- Nerve Cell Degeneration: The disease is a result of the degeneration of nerve cells in the substantia nigra, a brain region responsible for movement.
- Dopamine Deficiency: Research shows that individuals with Parkinson's lose the ability to produce dopamine, a chemical crucial for coordinating movement.
- Movement Impairment: A lack of dopamine can lead to slowed movements and tremors.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease vary among individuals and often start out mild. Typically, symptoms begin on one side of the body and may be more severe on that side. Some common symptoms include:
- Tremors: Trembling sensations can occur in the hands, arms, legs, and jaw.
- Rigidity: A feeling of stiffness in the limbs is common.
- Bradykinesia: This refers to a condition where movements become slow.
- Postural Instability: Individuals may experience balance and coordination issues.
- Swallowing Issues: Simple activities like chewing and speaking can become difficult.
- Urinary Problems: Individuals may face urinary difficulties, along with issues like constipation, skin problems, anxiety, depression, emotional changes, and sleep disturbances.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
While there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease, treatments can help improve symptoms. This makes symptom management challenging for patients. It is important to note that there are currently no blood tests or imaging tests available for diagnosing Parkinson’s disease.
Current Major Research in Parkinson’s Disease
Researchers are focused on improving diagnosis and treatment for Parkinson's disease. Key areas of research include:
- Genetic Studies: Geneticists and neuroscientists around the world are exploring various genetic variations to better understand Parkinson's disease.
- Inherited Forms: A more focused approach is being taken towards rare families with inherited parkinsonism to identify gene mutations linked to the disease.
- New Genetic Variants: A new genetic variant known as RAB32 Ser71Arg has been identified, which is associated with Parkinson's in multiple families globally.
- Genome-wide Association Studies (GWAS): These studies are comparing genetic data from Parkinson's patients and healthy individuals, discovering over 92 genomic locations and 350 genes that may relate to Parkinson’s risk.
|
90 videos|488 docs|209 tests
|
















