Sex Determination in Drosophila & Human | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
Despite the commonality of XX females and XY males in both mammals and fruit flies, the mechanisms underlying sex determination differ significantly between the two groups. This distinction is particularly evident in Drosophila, where sex is determined by a unique balance of X chromosome and autosome determinants. Unlike mammals, where the Y chromosome plays a crucial role, Drosophila relies on a distinct system, making it an intriguing subject for genetic studies.
Drosophila Sex Determination
In Drosophila, sex determination is based on the interplay between female X chromosome determinants and male autosome determinants. The presence of one X chromosome in a diploid cell results in a male fly (1X:2A), while two X chromosomes lead to a female fly (2X:2A). Notably, XO Drosophila individuals are sterile males. Unlike mammals, the Y chromosome in fruit flies is not involved in sex determination but carries genes essential for sperm production.
Drosophila melanogaster (Common Fruit Fly)
Drosophila melanogaster, a member of the Drosophilidae family in the Diptera order, is commonly known as the fruit fly. Its mitotic and polytene chromosomes exhibit distinct morphologies and functions, with polytene chromosomes being prominent in differentiated cells, especially in larval and adult ovarian tissues. Larval growth in Drosophila involves endoreplication, contributing to increased nuclear gene content and polyploidy.
Genome of D. melanogaster
The genome of D. melanogaster, with four chromosome pairs (X/Y and three autosomes), was sequenced and annotated in 2000. Notably, the fourth chromosome is often overlooked due to its small size. The genome comprises approximately 15,682 genes, with over 60% being functional non-protein-coding DNA regulating gene expression. Despite being fully heterochromatic, the Y chromosome contains at least 16 genes, primarily assumed to have male-specific activities.
Human-like Characteristics
Research comparing the fruit fly and human genomes reveals a remarkable conservation of around 60% of genes between the two species. Drosophila has been a valuable genetic model for various human diseases, including Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, spinocerebellar ataxia, and Alzheimer’s. Approximately 75% of human disease-related genes have identifiable matches in the fruit fly genome, demonstrating its significance in biomedical research.
Sex Determination Mechanisms
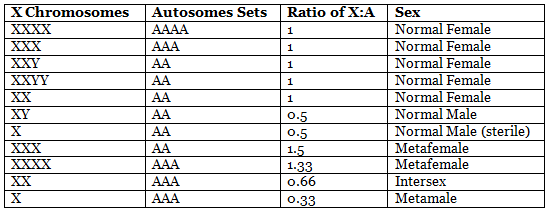
In Drosophila, sex determination is governed by the X:A ratio, representing the ratio of X chromosomes to autosomes. The equilibrium between female-determining proteins on the X chromosome and male-determining factors on autosomes determines the sex-specific transcription pattern. Unlike mammals, all X chromosomes in Drosophila remain active, with males regulating X-linked gene products by doubling expression. An additional X chromosome disrupts the cellular balance, leading to aneuploidy.
Unique Aspects of Drosophila Sex Determination
Drosophila's sex determination contrasts with mammals in several ways. Firstly, it occurs immediately after fertilization without a waiting period. Secondly, sex-specific features are not hormone-induced; instead, each embryo cell detects the X:A ratio, triggering either female or male-specific transcription sequences. Microarray research has identified extensive sex-specific gene expression differences, with around 30% of Drosophila genes exhibiting sex-specific biases.
|
198 videos|351 docs
|
FAQs on Sex Determination in Drosophila & Human - Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is Drosophila melanogaster and why is it commonly studied in scientific research? |  |
| 2. How is sex determined in Drosophila melanogaster? |  |
| 3. Is the sex determination mechanism in Drosophila similar to that of humans? |  |
| 4. How does the study of sex determination in Drosophila contribute to our understanding of human biology? |  |
| 5. What are some potential applications of understanding sex determination in Drosophila? |  |
















