Short & Long Answer Question: Chemical Kinetics | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
Q.1 Define molecularity of a reaction.
Answer: Number of reacting molecules colliding simultaneously to give product is called molecularity.
Q.2 In what condition order and molecularity of a reaction become equal?
Answer: In elementary reaction (single step process) order and molecularity are same.
Q.3 In which type of reaction order and molecularity are different?
Answer: In complex reaction (multi-step process) order and molecularity are different.
Q.4 What do you mean by rate determining step?
Answer: Order of overall reaction is order of slowest step. This is called rate determining step.
Q.5 What is collision frequency?
Answer: The number of collisions per second per unit volume of the reaction mixture is known as collision frequency.
Q.6 What is effective collision?
Answer: Collision of reactant molecules having energy greater than or equal to threshold energy in a proper orientation in which actually the bond breaking and bond formation takes place is called effective collision.
Q.7 Mention differences between order and molecularity of a reaction.
Answer:
| Order of reaction | Molecularity of reaction |
| Sum of powers of concentration of reactants present in rate equation. | Number of reactant molecules which collide simultaneously to give product is called molecularity. |
| It is an experimental property. | It is a theoretical property. |
| It may be zero or fractional. | It can not be zero or fractional. |
| Order is applicable to both elementary and complex reaction. | Molecularity is not applicable to complex reaction. |
Q.8. What is zero order reaction? Give one example of zen order reaction.
Answer: A reaction in which rate is independent of concentration of reactants is called zero order reaction. e.g. thermal decomposition of HI on gold surface.
Q.9 Write expression for rate constant of first order reaction. Mention unit of rate constant of a first order reaction.
Answer: The reaction in which rate is proportional to first power of the concentration of the reactant, e.g. all natural and artificial radioactive decays follow first order kinetics.
Q.10 What is intermediate complex theory of catalysis?
Answer: A catalyst is a substance which alters the rate of a reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. It increases the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy.
Q.11 How does a catalyst increase the rate of a reaction?
Answer: According to this theory, a catalyst participates in a chemical reaction by forming temporary bonds with the reactants resulting in an intermediate complex. This has a transitory' existence and decomposes to yield product and catalyst.
Q.12 What is the drawback of collision theory?
Answer: Catalyst provides an alternate pathway by reducing the activation energy between reactant and product and hence lowering the potential energy barrier,
Q.13 Mention the necessary condition for collision of reaction molecules to give product.
Answer: It considers atoms/molecules to be hard spheres and ignores their structural aspects.
Q.14 Reaction having molecularity greater than three is not observed. Explain.
Answer: The probability that more than three molecules can collide and react simultaneously is very small. Hence, the molecularity greater than three is not observed,
Q15. Catalyst does not affect the equilibrium rather helps in quick attainment of equilibrium. Explain this statement.
Answer: Catalyst does not change the equilibrium constant of a reaction rather, it helps in attaining the equilibrium faster, that is, it catalyses the forward as well as the backward reaction to the same extent so that the equilibrium state remains same but is reached earlier.
Q.16 What are the limitations of a catalyst?
Answer: Catalyst cannot initiate a non spontaneous reaction rather it alters the rate of a spontaneous reaction.
Q.17 What is reaction rate?
Answer: Reaction rate is the change in molar concentration of any of the reactant or product species per unit time.
Q.18 Identify the reaction order from each of the following rate. (i) k=2.3×105Jmol−1s−1 (ii) k=3.1×10−4s−1
Answer: (i) Second order (ii) First order.
Q.19 Name the photosensitizer in the photosynthesis of plants.
Answer: Chlorophyll is the photosensitizer which carries photosynthesis in plants.
Q.20 For a reaction A+H2O→B;Ratek∝ [ A ] . What is its (i) Molecularity (ii) Order?
Answer: (i) Pseudo uni-molecular reaction
(ii) order = 1.
Q.21 Average rate of reaction does not give the true picture of the reaction rate. Explain.
Answer: Average reaction rate obtained by dividing the change in molar concentration by the time taken for the change does not give the true picture of the reaction rate. Actually, the change in molar concentration at a particular instant of time depends upon the actual concentration at this point of time. As the actual molar concentration of the species keeps on changing with time, so is the change in molar concentration. Therefore, the molar concentration does not change at a uniform rate and average rate of reaction fails to give the true picture of the reaction rate.
Q.22 Powdered sugar dissolves in water faster than crystalline sugar. Why?
Answer: Sugar in the powdered state has more surface area as compared to the crystalline sugar. As a result, the powdered sugar is expected to dissolve in water at a faster rate than crystalline sugar.
Q.23 Why does it take more time to boil an egg or cook rice at higher altitudes?
Answer: The boiling point of water decreases at higher altitudes since the atmospheric pressure decreases. The decrease in(temperature is expected to decrease the reaction rate or the cooking process. Therefore, time taken is generally more as compared to the plains.
Q.24 Why is time saved when cooking is done in a pressure cooker?
Answer: The pressure inside the cooker is higher than the atmospheric pressure. As the boiling point of water in the pressure cooker gets raised, the rate of cooking process therefore, increases or the cooking is done in less time.
Q.25 There is no difference in the cooking time between sea level and higher altitude when a pressure cooker is used at both the places. Discuss.
Answer: The pressure inside the cooker is independent of the atmospheric pressure. Therefore, it is not likely to change as the altitude changes. Hence there is no difference in the cooking time when done either at sea level or at higher altitude.
Q.26 Slow reactions require less activation energy as compared to fast reactions. Do you agree with the statement?
Answer: No, the statement is not correct. The rate of a reaction is inversely proportional to the activation energy. This means that slow reactions will need more activation energy than the fast reactions.
Q.27 A lump of coal burns at moderate rate in air while coal dust burns explosively. Explain.
Answer: In case of coal dust, greater surface area is available as compared to the solid coal. This means that coal dust will react faster than the lump of coal. Since combustion is an exothermic reaction, greater amount of heat evolved in the combustion of coal dust leads to explosion also.
Q.28 Why does liquid bromine react slowly as compared to vapours of bromine?
Answer: In the vapour state, the molecules of bromine have more kinetic energy than in the liquid state. Therefore, collisions with the molecules of other reactants in the vapours state will be faster than in the liquid state. Moreover, in the vapour state, the surface area available for the chemical reaction is more as compared to the liquid state. Hence, bromine in the vapour state reacts at a faster rate compared with the liquid state.
Q.29 Identify, giving reasons, the faster reaction in each of the following:
(i) 2Na(s)+I2(s)→2NaI(s) 2Na(s)+I2(g)→2NaI(s)
(ii) C(s)+2H2O(g)→2H2(g)+CO2(g) C(s)+2H2O(s)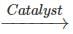 2H2(g)+CO2(g)
2H2(g)+CO2(g)
(iii) C(s)+1/2O2(g)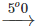 CO(g) C(s)+1/2O2(g)
CO(g) C(s)+1/2O2(g)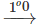 CO(g) (iv)N2(10atm)+3H2(10atm)→2NH3(g) N2(5atm)+3H2(5atm)→2NH3(g)
CO(g) (iv)N2(10atm)+3H2(10atm)→2NH3(g) N2(5atm)+3H2(5atm)→2NH3(g)
Answer: (i) The second reaction is expected to be faster because iodine molecules in the gaseous state have greater surface area and more kinetic energy than the molecules in the solid state.
(ii) The reaction carried in the presence of catalyst is faster because in the catalysed reaction the activation energy needed is less as compared to the uncatalysed reaction.
(iii) The second reaction is faster because the increase in temperature increases the number of effective collisions among the reacting species.
(iv) The first reaction will proceed at a faster speed because under high pressure the number of reactant molecules per unit volume are more compared with low pressure. This means that when the pressure is high, the collisions among the reactant molecules are more and as a result, the chemical reaction will be fast compared with low pressure.
Q.30 A reaction proceeds with a uniform rate throughout. What do you conclude?
Answer: If a reaction proceeds at a uniform rate throughout, this means that the reaction rate is not affected by change in concentration of the reactants. The reaction is of zero order.
Q.31 What is the order of reaction whose rate constant has the same units as the rate of reaction?
Answer: The reaction is of zero order because the reaction rate and zero order reaction have the same units i.e.,L−1s−1
Q.32 Why does not coal burn by of its own but once initiated by flame, it continues to burn?
Answer: The activation energy needed for the combustion of coal i.e., the oxidation of carbon is very high and is not available at room temperature. When brought in contact with the flame, a part of the coal in its contact absorbs heat as activation energy. Since combustion is an exothermic reaction, the heat energy which is liberated further provides activation energy for the combustion to continue.
Q.33 Why are reactions of high molecularity less in number?
Answer: The basic condition for a chemical reaction is the simultaneous collisions among the reacting species. As the number of the reacting molecules taking part in a reaction increases, the chances of their simultaneous collisions go on decreasing. This means that the number of the reacting molecules which are colliding simultaneously is less than the number of the molecules actually present. Therefore, the reactions of high molecularity are less in number.
Q.34 In a first order reaction, the units of the rate constant do not depend upon the concentration of the reactants. Justify.
Answer: Rate equation for the first order reaction is 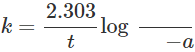 Here a is the initial concentration of reactants and (a−x) is concentration after time t. Since the units of a and(a−x)are to cancel out, therefore, units of rate constant (k) do not depend upon the concentration of the reactants.
Here a is the initial concentration of reactants and (a−x) is concentration after time t. Since the units of a and(a−x)are to cancel out, therefore, units of rate constant (k) do not depend upon the concentration of the reactants.
Q.35 State one condition under which a bimolecular reaction may be kinetically of first order reaction.
Answer: A bimolecular reaction can be kinetically first order in behaviour provided one of the reactants is taken in such a large excess that its concentration may hardly change. Such a reactant will not contribute to the order. Thus, a bimolecular reaction will be of first order. These reactions are known as pseudo chemical reactions.
Q.36 Why does not equilibrium constant change on adding a catalyst in a reaction?
Answer: In a reversible chemical reaction under equilibrium, a catalyst increases the speed of both the forward and the backward reactions to the same extent. Therefore, it does not change the equilibrium constant for the reaction.
Q.37 If half-life of a reaction is inversely proportional to initial concentration of the reactant, what is the order of reaction?
Answer: The reaction is of second order because for a second order reaction, t1/2 = 1/ka .
Q.38 E1 and E2 are the activation energies of the reactant and product respectively. If E2>E1, predict the nature of the reaction.
Answer: As E2>E1, this means that the reaction is exothermic in nature.
Q.39 Following reaction takes place in one step: 2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g) How will the rate of above reaction change if the volume of the reaction vessel is diminished to one third of its original volume? Will there be any change in the order of reaction with the reduced volume?
Answer: Reaction rate =k[NO]2[O2] Since the volume of the vessel is reduced to one third (1/3) of the original volume, the concentration of the reactants per unit volume will become thrice. Rate with respect to NO will become nine times. Rate with respect to O2 will become thrice. Overall reaction rate will increase to 27 times. There will no change in the order of the reaction.
Q.40 In some reactions, it is found that a large number of colliding molecules have energy more than the threshold value, yet they are quite slow. Explain.
Answer: In addition to activation energy, another important factor which influences the reaction rate is the orientation factor. This means that if the colliding molecules are not properly oriented at the time of collisions, still most of the collisions will be wasted without yielding any product though the reactants may have energy more than the activation energy. Such reactions will be quite slow.
Q.41 Is it possible for a chemical reaction to have zero activation energy?
Answer: No, it is not possible. This is explained with the help of Arrhenius equation according to which k=AeEa/RT. If Ea is zero, then k=Ae0=A. This means that the rate constant is equal to collision frequency and every collision among the reacting species will lead to the products. Since this does not happen, it is not possible for a chemical reaction to have activation energy equal to zero.
|
117 videos|223 docs|237 tests
|
FAQs on Short & Long Answer Question: Chemical Kinetics - Physical Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What is chemical kinetics? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of studying chemical kinetics? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the rate of a chemical reaction? |  |
| 4. How is reaction rate determined experimentally? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between rate constant and reaction rate? |  |

















