Short & Long Answer Questions: Surface Chemistry - 3 - NEET PDF Download
Q.101 Critical temperature of N2,CO and CH4 are 126, 134 and 190 K respectively. Arrange them in increasing order of adsorption on the surface of activated charcoal.
Answer: Critical temperature may be defined as the minimum temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied however large its pressure may be. It may be noted that greater the critical temperature, easier will be the ease of liquefaction of the gas and more will be its extent of adsorption on a particular solid such as activated charcoal. Therefore the increasing order of the extent of adsorption is: N2<CO<CH4
Q.102 Gelatin is generally added to ice cream. Why?
Answer: Ice cream is an emulsion of milk or cream in water (oil in water). Gelatin is added in the preparation of ice cream to act as emulsifier i.e., it helps in the formation of a stable emulsion and as a result, ice cream can be preserved.
Q.103 The addition of ferric hydroxide sol to arseneous sulphide sol results in the precipitation of both. Explain.
Answer: This is possible only in case equimolar sols (solutions with same number of moles) are mixed. Since the ferric hydroxide sol carries positive charge and arseneous sulphide sol is negatively charged, on mixing they will get their charge neutralized and get coagulated or precipitated.
Q.104 Lyophilic sols are called reversible colloids. Assign reason.
Answer: Lyophilic sols are generally known as reversible colloids. In fact, if the dispersed phase is removed completely, the colloidal solution can be formed again by mixing the dispersed phase (residue) left with a fresh sample of dispersion medium. For example, if a colloidal sol of starch in water is dried completely, it can be reformed by mixing the residue with fresh water.
Q.105 Artificial rain can be caused by spraying charged dust particles over clouds. Discuss.
Answer: Clouds represent the colloidal solutions of water drops in air (liquid in gas type). These drops are expected to carry some charge (positive or negative). In order to neutralize the charge on these, charged dust particles carrying opposite charge are sprayed over a certain layer of cloud. These will neutralize the charge on water droplets resulting in their coagulation. The bigger water drops can no longer be retained by the atmosphere and will result in the artificial rain.
Q.106 Ferric hydroxide sol is more readily coagulated by Na3P04 in comparison to KCl. Why?
Answer: Ferric hydroxide sol is positively charged and to cause its coagulation, ions carrying negative charge are needed. Since PO3−4 ions have higher negative charge than Cl− ions therefore, Na3PO4 coagulates the ferric hydroxide sol most efficiently. This is according to Hardy-Schulze law. For details, consult Section 5.23.
Q.107 Delta is generally formed where river meets the ocean. How will you account for it?
Answer: River water is generally muddy and carries along with colloidal dust particles which are charged in nature. Sea water contains a large number of electrolytes. When the river comes in contact with the sea water, the colloidal particles get their charge neutralized by the oppositely charged ions present in sea water and are coagulated. This ultimately results a hard solid mass known as delta.
Q.108 The layer of fat in the pans used for manufacturing soaps can be removed by adding boiling washing soda solution. How will you account for it?
Answer: Washing soda (Na2CO3) gets hydrolysed to form NaOH as follows: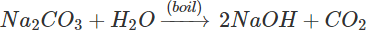 NaOH reacts with fat which is a triglyceride to form soap and glycerol by saponification reaction. The soap thus formed helps in cleaning the pan.
NaOH reacts with fat which is a triglyceride to form soap and glycerol by saponification reaction. The soap thus formed helps in cleaning the pan.
Q.109 Which out of the following solutions having the same concentration will be most effective in causing the coagulation of the arsenic sulphide sol that is yellow in colour: KCl,MgCl2,AlCl3 or Na3PO4?
Answer: Arsenic sulphide (As2S3) sol has a negative charge on it. To cause its coagulation or precepitation, the active ions must be positively charged. According to Hardy-SchuIze rule, greater the magnitude of the positive charge on the ion, more will be its coagulating power. Thus, AlCl3 containing Al3+ ions will be the most effective in causing the coagulation of the sol.
Q.110 100 mL of a standard sol requires 240 mg of starch for its protection against coagulation. Calculate gold number of starch.
Answer: Amount of starch required for 100 mL of gold sol = 240 mg Amount of starch required for 10 mL of gold sol = 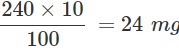 Therefore, gold number of starch = 24
Therefore, gold number of starch = 24
Q.111 Adsorption is always exothermic in nature ; Do you agree?
Answer: According to Gibb's Helmholtz equation: ΔG=ΔH−TΔS. Since entropy decreases as a result of adsorption,ΔS is -ve. Now, ΔG i.e., free energy change must be also -ve in case adsorption is to take place. At a given temperature, if ΔG is to be negative, then ΔH must be negative. This means that adsorption must be always exothermic in nature.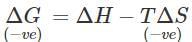
FAQs on Short & Long Answer Questions: Surface Chemistry - 3 - NEET
| 1. What is surface chemistry? |  |
| 2. What is adsorption? |  |
| 3. How does surface area affect adsorption? |  |
| 4. What is catalysis? |  |
| 5. How does surface chemistry relate to corrosion? |  |




















