Six Sigma | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
Six Sigma holds significant importance in the business arena as it focuses on eliminating mistakes and errors to achieve perfection. It has been recognized as an advanced tool in quality management and process improvement for over two decades. The methodology, rooted in statistical foundations, aims to measure process deviation from perfection, with a target of producing no more than 3.4 defective parts per million.
Evolution and Application of Six Sigma
Originally developed at Motorola in the early 1980s, Six Sigma gained widespread acceptance, particularly among Fortune 500 companies in the 1990s. Companies like GE played a crucial role in promoting and refining Six Sigma, extending its application to small and medium-sized businesses. Over time, Six Sigma evolved into a comprehensive system for achieving and maximizing business success, with applications spanning various industries beyond manufacturing, including logistics, healthcare, and government sectors. Additionally, Six Sigma is often associated with Lean Manufacturing principles and Design for Six Sigma methodologies, further enhancing its effectiveness in improving organizational processes and products.
Key Principles of Six Sigma
At its core, Six Sigma is centered on several fundamental principles:
- Critical to Quality (CTQ): These are the attributes most crucial to satisfying the customer's requirements and expectations.
- Defect: This refers to any failure to deliver what the customer desires or expects.
- Process Capability: It indicates the potential of a process to meet the specified requirements consistently.
- Variation: This encompasses the deviations in processes that directly impact what the customer perceives and experiences.
- Stable Operations: Ensuring that processes are consistent and predictable, thereby enhancing what the customer perceives and experiences.
- Design for Six Sigma (DFSS): This involves designing products or processes to align with customer needs and process capability right from the outset.
Key Features of Six Sigma
- Six Sigma aims primarily to eliminate waste and enhance customer satisfaction by meeting or exceeding customer expectations consistently.
- It operates on a structured methodology, assigning specific roles to participants involved in the improvement process.
- Six Sigma relies heavily on data-driven analysis, requiring precise data collection to thoroughly understand and optimize processes.
- The results of Six Sigma initiatives are directly reflected in financial statements, highlighting its focus on tangible business outcomes.
Six Sigma is a comprehensive, business-driven approach that addresses various dimensions of improvement:
- Enhancing processes
- Reducing defects
- Minimizing process variability
- Cutting costs
- Improving customer satisfaction
- Boosting profitability through increased efficiency and effectiveness
Calculation of Six Sigma
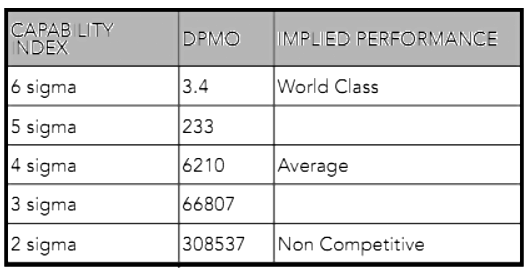
The Six Sigma model serves to eradicate defects or variations in processes to align with customer requirements. Attaining a level of quality equivalent to six sigma signifies that processes yield only 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO). Beyond merely a methodology for enhancing process capability, Six Sigma is regarded as a philosophy that strives for continuous perfection. Below are the capability index, DPMO, and the implied performance at various levels:
Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)
Understanding the significance of Design for Six Sigma (DFSS), its importance lies in scrutinizing robust design and functional requirements, employing noise strategies to develop a resilient design, and comprehending concepts like tolerance design and statistical tolerance. It utilizes process capability data to calculate tolerances.
Methodology of Six Sigma
- Six Sigma operates through three methodologies:
- Business Process Management System (BPMS)
- DMAIC (Six Sigma improvement methodology)
- DMADOV (Creating new processes to perform at Six Sigma)
- Six Sigma can also be integrated within the DMAIC and DMADV models.
DMAIC:
DMAIC stands as the most prevalent process improvement methodology, comprising Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. Recognized for its simplicity in performance enhancement, DMAIC employs statistical software extensively. The process unfolds as follows:
- Define the goals of the improvement activity
- Measure the existing system
- Analyze the system
- Improve the system
- Control the new system
- This quality tool emphasizes change.

In essence, DMAIC is employed to enhance existing processes or services to achieve the company's objectives or project goals. On the other hand, the DMADV model, abbreviated as "Define-Measure-Analyze-Design-Verify," focuses primarily on the Design and Verify stages.
Advantages of Six Sigma
Six Sigma offers a multitude of benefits that appeal to companies:
- It fosters sustained success.
- It establishes performance goals for all stakeholders.
- It amplifies value for customers.
- It accelerates the pace of improvement.
- It encourages learning and cross-pollination of ideas.
- It facilitates strategic change.
Drawbacks of Six Sigma
- Despite its advantages, Six Sigma's application across all phases of production and planning processes may introduce inflexibility and bureaucracy, leading to delays and stifled creativity. Additionally, its customer-centric focus can sometimes be taken to extremes, resulting in the rejection of internal quality-control measures that make sense for the company but conflict with the overarching goal of achieving Six Sigma levels of consumer satisfaction.
- For instance, a cost-effective measure carrying a slightly higher defect rate may be disregarded in favor of a more expensive alternative solely to meet Six Sigma standards, even if it adversely affects profitability.
Conclusion
Six Sigma stands as an influential tool for enhancing quality in today's competitive business landscape, offering the potential to revolutionize current logistics improvement approaches. By reducing waste and minimizing variations, Six Sigma yields benefits such as heightened customer satisfaction, increased profits, reduced cycle times, and enhanced flexibility. Originating from Motorola in 1985, Six Sigma encompasses a comprehensive set of strategies and tools aimed at refining existing business practices and systematic processes to achieve organizational objectives. Initially designed to identify and eliminate process faults or defects systematically to enhance quality, Six Sigma found its roots in manufacturing industries but has since proven applicable to logistics companies, given its customer-centric focus. As supply chain management plays a pivotal role in enhancing organizational efficiency and achieving goals such as improved competitiveness, enhanced customer care, and increased profitability, Six Sigma emerges as a successful methodology for delivering business benefits through variant reduction.
FAQs on Six Sigma - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the concept of Six Sigma? |  |
| 2. How is Six Sigma calculated? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of implementing Six Sigma? |  |
| 4. What are the key principles of Six Sigma? |  |
| 5. What are the drawbacks of Six Sigma? |  |





















