UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geology Optional for UPSC > Slopes, and Drainage
Slopes, and Drainage | Geology Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Slope Elements and Slope Evolution |

|
| Genetic Classification of Slopes |

|
| Elements of Slope |

|
| Factors Influencing Specific Slope Elements |

|
Slope Elements and Slope Evolution
- The physical landscape consists of slopes, which are integral to landform study.
- Geomorphologists have long been intrigued by the origin and form of slopes.
- Various theories and models have been formulated to explain slope origin and form.
- Slope study faces challenges in determining nature, process rate, and trajectory of development.
- Two key aspects of landform study are form and process.
Form and Process
- Form: Refers to the morphology of a region at a given time.
- Process: Denotes the operation of agents causing changes in the physical environment.
- Agents include soil creep, surface wash, weathering, etc.
Approaches to Understanding Slope Development
- Historical Approach:
- This approach focuses on the historical evolution of slopes from origin to present form.
- Challenges include correct reconstruction of past forms and determining slope age.
- Various theories attempt to explain slope evolution but often rely on speculation.
- Process-Form Approach:
- This approach assumes a causal relationship between weathering, erosion, transportation, and deposition in shaping slope form.
- Challenges include observing slow processes and determining direct relationships between processes and form.
- Climate, rock types, and vegetation influence the types of slope forms produced.
Challenges and Considerations
- Determining slope age and reconstructing past forms pose difficulties.
- Slow processes like weathering and creep are not readily observable.
- Tools and methods for recording processes accurately are necessary.
- Relationships between slope form and climate are complex and not always straightforward.
Conclusion
- Both historical and process-form approaches aid in understanding slope evolution.
- Each approach has its challenges and considerations in studying slope development.
- A comprehensive understanding requires considering both historical sequences and present-day processes.
Genetic Classification of Slopes
- Slopes result from both endogenetic and exogenetic processes.
- They are broadly categorized into Endogenetic Slopes and Exogenetic Slopes.
Endogenetic Slopes
- Originate from processes within the Earth, such as earth movements leading to folds, faults, and rift valleys.
- Also known as tectonic slopes.
- Volcanic eruptions contribute to the formation of new features like volcanic hills, plateaus, and cones.
- Features formed undergo modification by subaerial processes.
Exogenetic Slopes
- Result from external processes near or at the Earth's surface, including weathering, mass wasting, erosion, and deposition.
- Can be erosional (degradational) or depositional (aggradational).
- Erosional slopes formed by wind, running water, waves, and glaciers, producing various landforms.
- Depositional slopes formed by similar agents, resulting in features like alluvial fans, natural levees, and sand dunes.
Elements of Slope
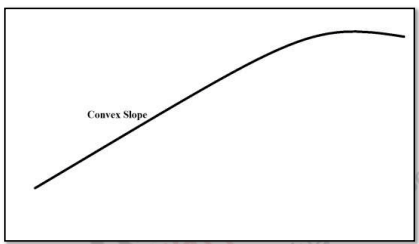
Convex Slope
- Often found at the top of a slope, assumed to be characteristic of humid temperate regions.
- Formed due to denudational processes, associated with certain rock types like chalk and limestone.
- Commonly referred to as "crest" or "summit slope."
- Angle of the slope increases downslope from the crest.
- Weathering and soil creep contribute to summital convexity.
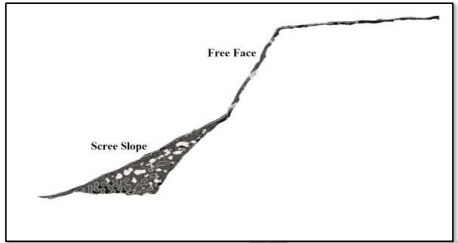
Cliff or Free Face
- Steep wall-like slope, bare due to steepness, often called a scarp or free face.
- Develops along coastlines, in river valleys, glacial regions, and faulted landscapes.
- Material falls or slides down and accumulates at the base, forming talus slopes.
- Talus slope angle determined by size of weathered materials.
- Continuous supply of weathered material gradually covers the free face, eventually replaced by a depositional slope.
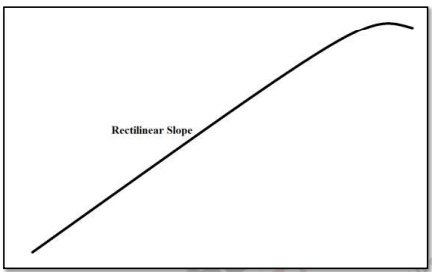
Rectilinear Slope
- Straight slope section, mostly below the cliff or free face, also known as constant slope.
- Angle largely remains constant, varies in dimension, may extend from summit to valley bottom.
- Can be denudational forms underlain by solid rock with a veneer of detritus.
- Referred to as "debris-controlled slope" or "repose slope."
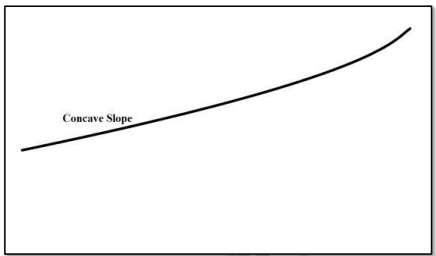
Concave Slope
- Located at the lowest part of the slope profile, extends to the river valley.
- Usually covered with a layer of debris, rainwash spreads finer particles farther, leading to concavity.
- Sharp break of gradient in arid regions, smooth transition in humid conditions.
- Referred to as "waning slope."
Combination of Elements
- Not all elements may be present in a slope profile, combinations vary.
- Various factors influence the presence and combination of slope elements.
- Multiple combinations are theoretically possible, but some occur more frequently than others.
Common Composite Slope Profiles
- Composite slope profiles exhibit various combinations of slope elements.
- Three common combinations have been identified:
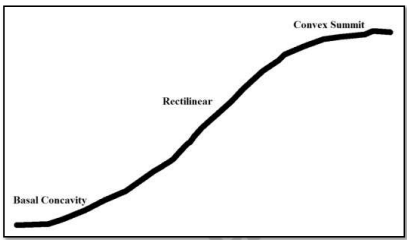
Convexo-Rectilinear-Concave Slope Profile
- Consists of upper convex, middle rectilinear, and lower concave forms.
- Smoothly graded elements give a curving slope profile.
- Most common in regions with weak rock types, such as lowland England.
- Variations in length of slope elements observed in landscapes.
Composite Slope Profile in Regions with Alternating Massive and Thinly Bedded Weak Strata
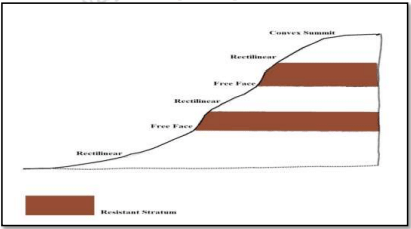
- Characterized by several free faces and rectilinear slopes.
- Summital convexity and basal concavity limited or absent.
- Free face formed where massive strata occur, rectilinear slopes where weak and thinly bedded rock exists.
- Occurs in regions with high relief, deep valleys, and active weathering.
Composite Slope Profile in Arid Regions with Hard Crystalline Rocks
- Consists of a free face, boulder-controlled mid-section, and concave (pediment) slope.
- Free face has a slope of 40° or more, mid-section has a slope angle of 25° or more.
- Concave slope at the bottom is very gentle, with angles below 7 degrees.
- Develops due to the occurrence of hard crystalline rocks in arid regions.

Factors Influencing Specific Slope Elements
Historical Explanations
- Early explanations attributed specific slope forms to processes like rainwash and soil creep.
- N. M. Fenneman associated convexo-concave profiles with the action of running water.
- Fenneman's hypothesis suggested that convexity develops due to greater erosion away from the summit and concavity forms where water gets concentrated into small channels.
Opposing Views and Support
- Opponents argued that Fenneman's hypothesis neglects the role of soil creep in shaping slopes.
- Horton supported Fenneman's idea, stating that erosion is absent in certain sections of the slope due to lack of energy in runoff.
- Gilbert attributed soil creep to rounding hilltop summits and developing convexity.
- Lawson disagreed with Fenneman, suggesting that wash is most effective at the slope summit.
Complex Interplay of Factors
- Various scientists and geomorphologists proposed theories based on soil creep and rainwash as key processes in shaping slopes.
- Interplay of factors influencing slope form is highly complex.
- Dominant factors may play a key role, but other factors also contribute to specific slope forms.
The document Slopes, and Drainage | Geology Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Geology Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
64 videos|135 docs
|
Related Searches




















