Social well-being and Quality of life | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Social well-being and Quality of life |

|
| Social well-being |

|
| Quality of life: A systems model |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Social well-being and Quality of life |

|
Social well-being and Quality of life
- Quality of life is a concept that has garnered significant attention in recent years, although its origins can be traced back to ancient philosophers like Aristotle, who wrote about "the good life" and "living well," as well as the role of public policy in fostering these ideals. As geography evolved with the Critical Revolution, the focus shifted to human welfare, leading to the emergence of the concept of social well-being and quality of life.
- In general, quality of life refers to an individual's sense of well-being, including their satisfaction or dissatisfaction with life, happiness, or unhappiness. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines quality of life as "the condition of life resulting from the combination of effects of a complete range of factors such as those determining health, happiness, education, social and intellectual attainment, freedom of action, justice, and freedom of expression."
- Quality of life is contingent upon the fulfillment of basic and social needs, as well as the autonomy to enjoy life, flourish, and actively participate in a society characterized by high levels of civic integration, social connectivity, trust, fairness, equity, and other integrative norms, all within a sustainable global environment.
Quality of life encompasses both objective and subjective aspects of human living, including measurable and non-measurable factors. It is a multi-faceted concept that generally refers to overall welfare and, more specifically, to health and prosperity. Key components of quality of life include:
- Physical well-being: This relates to environmental conditions, such as climate, topography, population density, and overall physical and mental health.
- Material well-being: This involves access to household appliances, electronic devices, transportation, and communication tools.
- Social well-being: This includes social health, social security, access to social amenities, and the quality of social relationships and shared values.
- Economic well-being: This encompasses employment opportunities, income levels, savings, purchasing power, and consumption of goods and services.
- Perception of well-being: This relates to attitudes towards external factors, individual and social traits, real-world experiences, and includes an element of subjectivity.
- Spiritual well-being: This involves religious beliefs, practices, taboos, and various approaches to seeking truth and happiness.
It is important to distinguish quality of life from the concept of standard of living, which primarily focuses on income. Instead, indicators of quality of life include not only wealth and employment but also the built environment, physical and mental health, education, recreation, and leisure time, and social belonging.
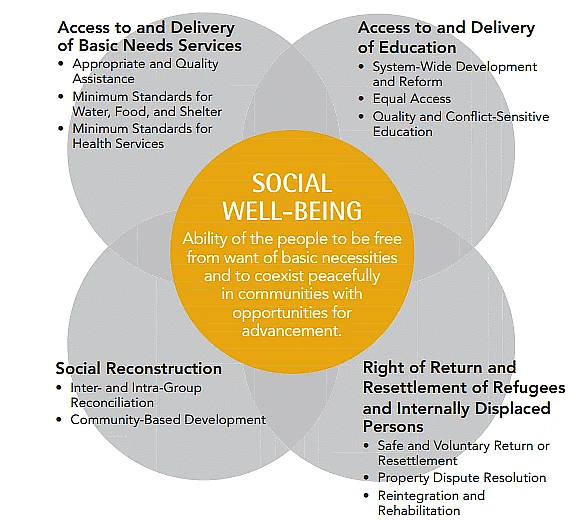
Social well-being
- The study of social well-being in geography emerged as a result of the relevance movement that began in the 1970s. This movement aimed to address the pressing issues affecting society by making geography a socially relevant discipline. As a result, geographers began to focus on welfare issues, providing a new framework for micro-level studies.
- Micro-level spatial analysis has played an important role in developing geographical studies, particularly in the field of developmental planning. Through the social relevance movement, the focus of geographical inquiry shifted from studying marginal lands to examining marginal social spaces.
- Social well-being is a critical aspect of the quality of life, as it represents a state where basic human needs are met, and people can coexist peacefully in communities with opportunities for advancement. It involves maintaining healthy relationships within society, fostering social stability, and promoting peace. Social well-being is essential in combating loneliness and fostering a sense of belonging. Effective communication networks and strong relationships among people are vital for achieving social well-being.
- A "well society" is one in which everyone has enough income to meet their basic needs, where all individuals are treated with equal dignity and have equal rights, where they have reasonable access to a range of necessary services, and where their opinions are heard and respected. The quality of a society can be assessed based on its performance in these areas, as well as variations within the society.
In summary, the study of social well-being in geography has evolved as a result of the relevance movement, which sought to address societal issues and make geography more socially relevant. This shift in focus has led to a greater emphasis on micro-level spatial analysis and the study of social well-being, which is crucial for creating strong communities and fostering a sense of belonging among individuals.
- The following are the components of measurement of social well being:
- Health
- Education
- Food and nutrition
- Equality
- Freedom
- Pollutions
- Law and order
- Social structure
- Sex ratio
- Social well-being is a highly subjective concept, as it varies depending on an individual's personal preferences, geographical location, and cultural background. For instance, people living in different areas such as villages, towns, cities, hilly or plain regions, and various climate zones may have distinct perspectives on social well-being. Additionally, age and ethnicity can also influence the perception of social well-being among people living in the same region.
- The level of social well-being in societies worldwide is influenced by cultural and technological factors. Developed countries, with their advanced technology, tend to have higher levels of well-being due to the rapid and widespread urbanization and industrialization, which in turn, leads to a shift in social needs and values.
- On the other hand, the process of industrialization and urbanization in many developing countries is slower and more selective, resulting in a more limited transformation of social needs. Social values evolve in response to these changing needs, which are influenced by factors such as geographical conditions, technological advancements, and the blending of cultures.
Cross-National indices of measuring Quality of life/Social well-being
Several cross-national indices are used to measure the quality of life and social well-being of various countries. Some of these indices include:- Human Development Index (HDI): This index measures a country's overall achievement in three essential aspects of human development: a long and healthy life, access to knowledge, and a decent standard of living. It takes into account life expectancy, education, and per capita income indicators.
- Quality of Life Index: This index assesses the well-being of individuals by considering three fundamental human needs: meeting biological necessities, facilitating social interaction, and ensuring the survival and welfare of groups. In the Quality of Life Index report, India's ranking improved from 73 in 2005 to 63 in 2021.
- Index of Social Progress: This index aims to evaluate the adequacy of social provision and track significant changes in meeting the basic social and material needs of the global population.
- World Happiness Index: The World Happiness Report is a comprehensive survey of global happiness levels in over 150 countries. It reflects the growing interest in using happiness and well-being as indicators of human development quality. In the 2021 UN's World Happiness Report, India ranked 139 out of 149 countries.
- Demographic, personal, and socio-economic factors: These factors also play a crucial role in determining the quality of life in a region.
- Economic Intelligence Unit's Quality of Life: This index measures the potential for a country to provide its citizens with a healthy, safe, and prosperous life in the future. It incorporates both subjective and objective factors, such as life satisfaction surveys, GDP per capita, job security, governance, and gender equality.
Quality of life: A systems model
- The concept of measuring the quality of life is based on the idea that various aspects of life contribute to one's overall wellbeing. These aspects, or domains, include family and friends, work, housing, community, health, education, and spirituality. While recent trends in demographic, economic, and social indicators show significant improvements in human wellbeing, particularly in developed countries, challenges remain in enhancing the quality of life for people in developing regions.
- The issues faced by the least developed countries in various aspects of wellbeing can be attributed to population pressures. The relationship between population growth and human wellbeing is complex, as an increase in population can lead to environmental degradation in developing countries. If not properly managed, this can result in severe consequences.
In summary, the quality of life is a multifaceted concept that incorporates various domains of living, each contributing to an individual's overall wellbeing. While there have been improvements in human wellbeing globally, challenges still exist in enhancing the quality of life in developing regions, especially due to the complex relationship between population growth and human wellbeing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concepts of quality of life and social well-being are essential aspects of human development, encompassing various factors such as physical, material, social, economic, and spiritual well-being. The study of these concepts has evolved significantly over time, with geography playing a vital role in understanding and addressing societal issues. Cross-national indices help measure and compare the quality of life across different countries, shedding light on the areas that need improvement. While progress has been made in enhancing human well-being globally, challenges remain, particularly in developing regions, where population growth and environmental degradation pose significant hurdles to achieving a high quality of life for all.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Social well-being and Quality of life
What is the difference between quality of life and standard of living?
Quality of life is a broader concept that encompasses various aspects of an individual's well-being, such as physical, material, social, economic, and spiritual well-being. Standard of living, on the other hand, primarily focuses on income and material aspects of life.
How does geography play a role in the study of social well-being?
Geography helps in understanding the spatial distribution of social well-being and the factors that influence it, such as environmental conditions, population density, and cultural backgrounds. Geographical studies can also analyze how different regions are affected by issues like industrialization, urbanization, and technological advancements.
What are some factors that influence an individual's perception of social well-being?
An individual's perception of social well-being can be influenced by personal preferences, geographical location, cultural background, age, and ethnicity. People living in different areas or belonging to different cultural groups may have distinct perspectives on social well-being.
How can we measure the quality of life and social well-being in different countries?
Several cross-national indices are used to measure the quality of life and social well-being of various countries, such as the Human Development Index (HDI), Quality of Life Index, Index of Social Progress, and the World Happiness Index. These indices consider factors like life expectancy, education, income, social provision, and happiness levels.
What challenges do developing countries face in enhancing the quality of life for their citizens?
Developing countries often face challenges in improving the quality of life due to factors like population pressures, environmental degradation, slower industrialization and urbanization, and limited access to resources and services. Addressing these challenges requires effective planning, management, and policy interventions.
|
304 videos|717 docs|259 tests
|




















