Sources of Modern Indian History | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
The history of modern India is based on many different sources. The East India Company’s records give a clear picture of trade and administration from 1600 to 1857, while British government records provide details about how India was governed during colonial rule. Records of other European companies like the Portuguese, Dutch, and French also help in understanding the events of the 17th and 18th centuries. Personal writings such as diaries, travel accounts, and biographies offer valuable insights into life during that time. Additionally, forts, buildings, and paintings serve as physical reminders of the period’s history. These sources together help us understand modern India better.
Literary Sources of Modern History
Literary sources like diaries, biographies, and travel accounts provide valuable insights into the social, political, and economic conditions of modern India. These writings capture personal experiences and observations, offering unique perspectives on historical events and everyday life during the period.
Archives: Unlocking the Vault of Knowledge
- The National Records of India, situated in New Delhi, house significant records from the Government of India.
- These archives are dependable sources for comprehending various facets of modern Indian history.
- The Survey of India, initiated by James Rennell, the inaugural Surveyor General of Bengal, methodically mapped the country and its surroundings. This mapping effort furnished crucial geographical and socioeconomic data.
- The proceedings of public, judicial, and legislative departments provide valuable insights, shedding light on the social and religious policies of the colonial government.
- Additionally, educational documents outline the government's approach to education and the expansion of the school system during the colonial era.
- Records pertaining to the emergence of the nationalist movement and archives of prominent regional powers are also part of these archives.
- For instance, the Kingdom of Lahore, which was under British influence, offers essential historical material.
European Records: Tracing the Footprints of the Past
- The records maintained by the European East India companies, such as the Portuguese, Dutch, French, and British, are vital for understanding the history of the 17th and 18th centuries.
- The Portuguese archives in Goa and the Dutch records in Cochin and Malabar hold particular significance.
- These archives contain a wealth of information, including orders, dispatches, responses, and reports, which shed light on the intricate colonial relationships between European powers and India.
- Furthermore, the French archives from Chandernagore and Pondicherry, which were transported to Paris before the French left their settlements, provide valuable historical insights.
Biographies, Memoirs, and Travel Accounts: Personal Narratives of the Past
The accounts of visitors to India, including traders, missionaries, and civil workers, provide detailed insights into different regions and cultures. Their reports, memoirs, and travel accounts offer vivid descriptions and impressions of various parts of the country. Notable examples include:
- Baron Charles. "Travels in Kashmir and Punjab"
- Alexander Burnes. "Travels Into Bokhara"
Insights into Socio-Cultural Dynamics
- These personal narratives uniquely illustrate the socio-cultural dynamics of the 18th and early 19th centuries.
- They are shaped by key historical events and cultural exchanges during this period.
Newspapers and Journals: Chronicles of a Changing Nation
Newspapers and journals from the 19th and 20th centuries are crucial and genuine sources for understanding the history of modern India. The earliest attempts to start newspapers in India were made by some workers of the English East India Company. The Bengal Gazette, founded by James Augustus Hickey, marked the beginning of Indian journalism. Many early newspapers and journals mainly catered to European and Anglo-Indian readers. However, in the latter half of the 19th century, significant publications edited and published by influential journalists began to emerge.
Interestingly, notable figures like Dadabhai Naoroji and Gopal Krishna Gokhale, who were prominent journalists, were founding members of the Indian National Congress in 1885.
Key Newspapers and Journals
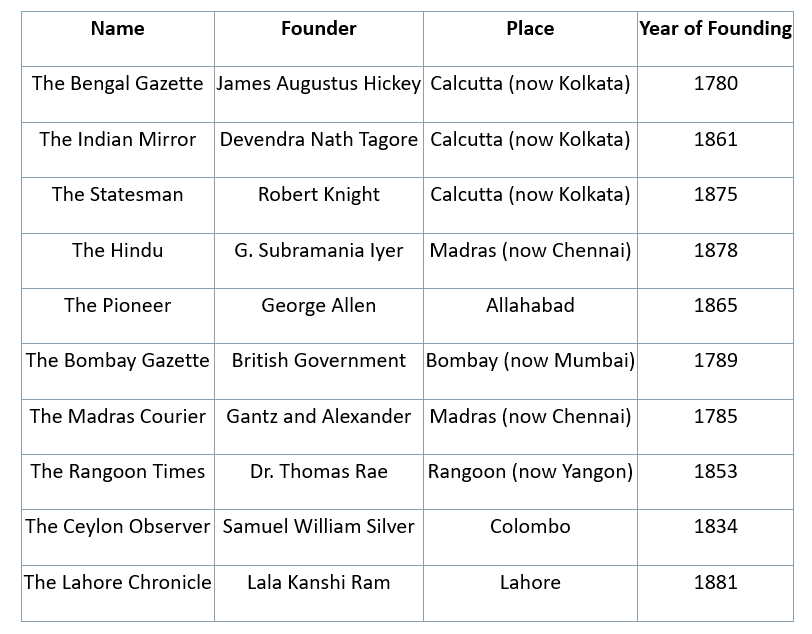
One particularly influential article in The Hindu sparked public debate on civil rights, demonstrating the impact of journalism in shaping societal opinions.
Literature: The Novels That Shaped an Era
- The novel, a prominent literary form in the later part of the 19th century, played a crucial role in the Indo-European encounter.
- During this time, Bankim Chandra Chatterji, a prominent Bengali novelist, became one of the most significant writers.
- His historical novels, such as Anandamath, are famous for the powerful lyric 'Vandemataram' and for depicting the Sanyasi Revolt, offering valuable insights into the period.
- Icharam Suryaram Desai, a notable Gujarati literary historian, wrote 'Hind and Britannia', one of the early Indian novels with political implications.
Archaeological Sources
Archaeological sources offer tangible evidence of the past through material remnants. In the context of modern Indian history, these sources provide valuable insights into British India. Here are some key archaeological sources:
Paintings
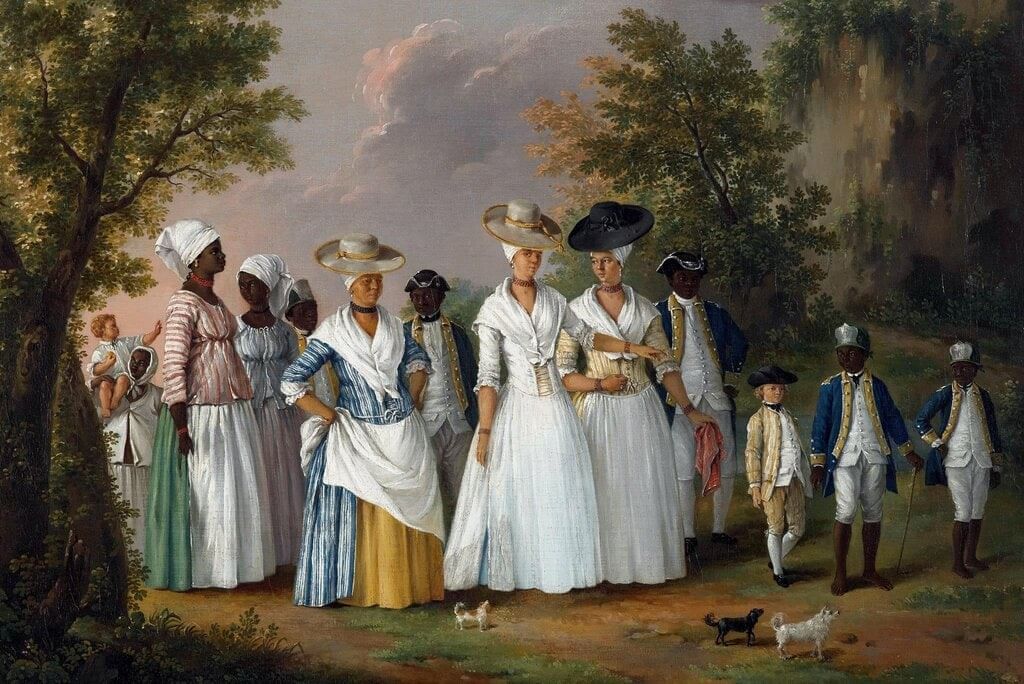 Paintings of Colonial Period
Paintings of Colonial Period
- Paintings from the colonial period give us a glimpse into the social, economic, and cultural life of that era.
- The East India Company commissioned 'Company Paintings' or 'Patna Kalam,' which depicted trades, festivals, dances, and traditional clothing.
- Artworks such as Thomas Jones Barker’s Relief of Lucknow (1859) and Joseph Noel Paton’s In Memoriam highlighted events like the Revolt of 1857.
- By the late 19th century, Indian nationalism inspired a new art movement with contributions from artists like Raja Ravi Varma and Nandalal Bose. The Bengal School, led by Abanindranath Tagore and supported by E.B. Havell and A.K. Coomaraswamy, was prominent during this time.
Forts
- Forts symbolized military strength and served as strategic and administrative centers during British rule.
- Many forts were built across India, such as Fort St. George in Chennai, which was the East India Company’s southern headquarters.
Colonial Buildings
- Colonial buildings reflected the architectural styles and needs of the British in India.
- Structures like the Victoria Memorial in Kolkata combined British and Indian architectural influences, serving as landmarks of the period.
Coins
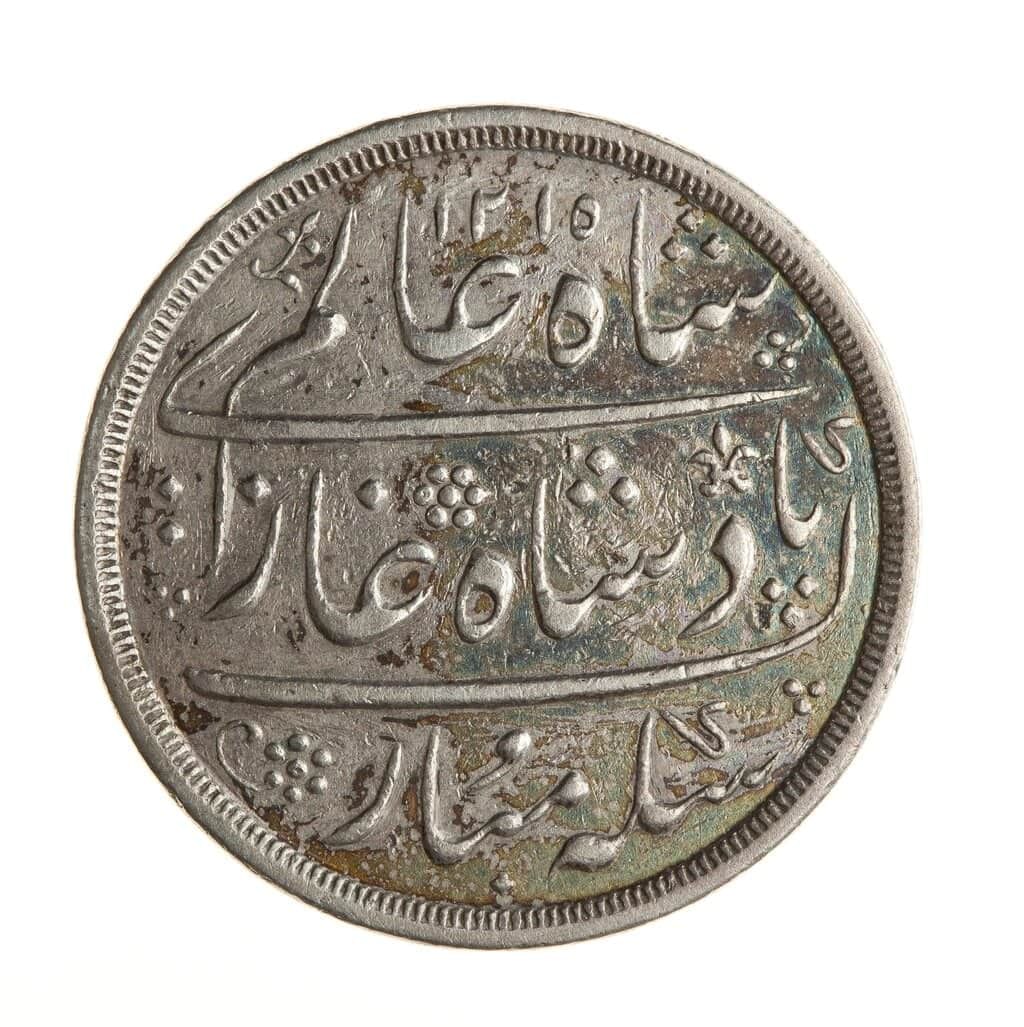 Coins
Coins
- Coins provide evidence of trade and economic systems under British rule.
- The "Bombay Presidency One Rupee" coin of 1858 is an example of the integration of British currency into the Indian economy.
Trade Warehouses
- Trade warehouses were crucial for storing goods traded between Britain and India.
- The Cotton Exchange Building in Mumbai, formerly the Bombay Cotton Exchange, was a hub for the cotton trade during the colonial era.
In summary, the sources of modern Indian history form a rich tapestry, blending literary and archaeological treasures. As we explore these sources, we discover the multifaceted nature of India's past, enriched by personal narratives, official records, visual depictions, and material remnants. Let us embrace the opportunity to delve into these sources, unlocking the mysteries and stories that have shaped modern India.
|
1179 videos|2219 docs|849 tests
|
FAQs on Sources of Modern Indian History - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What are the primary sources of modern Indian history? |  |
| 2. How can archives be accessed for research on modern Indian history? |  |
| 3. What role do newspapers and journals play in understanding modern Indian history? |  |
| 4. Why are biographies and memoirs important for studying history? |  |
| 5. How do archaeological sources contribute to our understanding of modern Indian history? |  |

















