Spectrum Summary: Three Prime Ministers in Three Years (1996–1999) | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Political Changes in India (1996-1999) |

|
| The United Front Government |

|
| Political Events in India under Gujral's Leadership |

|
| General Elections of 1998 |

|
Political Changes in India (1996-1999)
There were several changes in the Indian government between 1996 and 1999, during which three different individuals held the position of Prime Minister.
In 1996, the BJP won the most seats in the elections, but they did not have enough to form a government on their own and needed support from other parties. The National Front aimed to replace either the Congress or the BJP as the main governing party. This period also highlighted the significant influence of smaller regional and state parties in shaping the government.
Vajpayee's Brief Term as Prime Minister
Atal Bihari Vajpayee
The BJP , being the largest party, was invited by President Shankar Dayal Sharma to form a government as they had the most seats in the Lok Sabha . Atal Bihari Vajpayee , the BJP leader, became the Prime Minister but realized he would not win the confidence vote due to a lack of support from other parties.
Vajpayee decided to resign after just 13 days when it became clear that no other party was willing to help the BJP .
United Front Government: Deve Gowda and I.K. Gujral
After Vajpayee's government fell, the Congress , the second-largest party, chose not to form a government.
Deve Gowda Government (1996-97)

The United Front Government
The United Front, a coalition of around 13 parties including the National Front , Tamil Maanila Congress , DMK , and Asom Gana Parishad , selected Deve Gowda as the leader of the government. The Congress party provided external support, and later, the Communists joined in. During its short time in power, the government made agreements with China for confidence-building measures and with Bangladesh regarding Ganga water . They decided against signing the significant Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT) , which aims to prohibit all nuclear explosions. Although the United Nations General Assembly adopted it in 1996, it has not yet entered into force because some key countries, including the United States , have not ratified it. In April 1997, the government collapsed when the Congress party withdrew its support. To avoid new elections, the Congress party agreed to back a government led by a new leader.
Gujral Government (1997-98)
Following Deve Gowda , L.K. Gujral was appointed as the new leader selected by the United Front, and he took office as prime minister on April 21, 1997 .
The Gujral Doctrine
The Gujral Doctrine was a set of principles that guided India's relations with its neighbouring countries, particularly in South Asia . Its main goal was to promote friendly and cooperative relationships based on mutual respect and non-interference. The doctrine outlined five key ideas:
- Generosity to Neighbours: India, under the Gujral Doctrine, chose not to expect anything in return from its neighbours such as Nepal , Bangladesh , Bhutan , Maldives , and Sri Lanka . Instead, it offered help and support in good faith.
- Non-Use of Territory Against Each Other: The Doctrine highlighted that no country in South Asia should allow its land to be used against another country's interests. This meant not supporting harmful activities towards neighbours.
- Non-Interference in Internal Affairs: According to the Doctrine, no South Asian country should meddle in the internal issues of another. Each nation should respect the sovereignty and independence of others.
- Respect for Territorial Integrity: The Doctrine insisted that all South Asian nations must recognise and respect each other's territorial boundaries and sovereignty.
- Peaceful Dispute Resolution: The Gujral Doctrine stressed that any disagreements between South Asian countries should be settled through peaceful discussions, rather than conflict, encouraging bilateral negotiations.
In summary, the Gujral Doctrine aimed to create a peaceful and cooperative environment among South Asian nations, fostering understanding, trust, and good relations without expecting immediate benefits in return.

Political Events in India under Gujral's Leadership
Gujral was able to maintain good relations with the Congress , which supported his government from the outside. However, he faced challenges from within his own party.
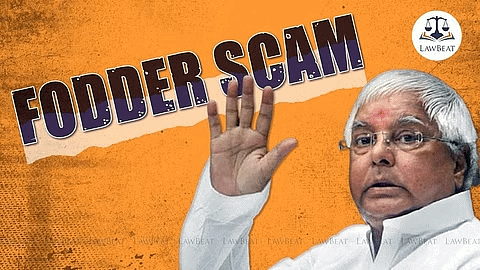
Fodder Scam in Bihar
- A major political event took place in Bihar concerning the Fodder Scam . The Governor permitted the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) to investigate allegations of corruption against the state's leader, Lalu Prasad Yadav , related to the purchase of animal feed.
- Despite his initial reluctance to step down, Yadav eventually left his party and, in July 1997, founded the Rashtriya Janata Dal .
- Nevertheless, his new party continued to support the United Front government, helping to keep it stable.
Controversial Decision in Uttar Pradesh
- In Uttar Pradesh , Gujral's government faced a significant political dispute. They proposed imposing president's rule due to escalating violence in the assembly, which was under the leadership of Kalyan Singh from the BJP.
- However, this idea was contested by the President and the Allahabad High Court , both of whom disagreed with the decision to impose president's rule, leading to a clash over authority in the state.
Jain Commission Report
- The Jain Commission was established to look into various matters, and its conclusions had a notable influence on the political scenario.
General Elections of 1998
- The Jain Commission , a team set up by the RA , investigated the circumstances surrounding the assassination of Rajiv Gandhi . Their findings indicated that the DMK party had indirectly aided the Tamil militants involved in the assassination.
- This revelation sparked significant controversy and turmoil in government discussions. The Congress party , displeased with the implications, demanded the dismissal of DMK members from the government, arguing that it was inappropriate for them to hold key positions.
- However, Gujral , the then leader, opposed this demand and refused to remove the DMK members from their positions.
- Eventually, on November 28, 1997 , the Congress party withdrew its support from Gujral's government, ending their cooperation.
Sonia Gandhi Contesting the 1998 Elections
- In the elections held in February and March 1998 , Sonia Gandhi , the widow of Rajiv Gandhi , entered politics and campaigned for the Congress party . This was the fourth time since 1989 that elections resulted in no single party having a clear majority.
- The BJP won more seats than other parties but still did not have enough to govern alone. To overcome this, the BJP formed alliances with regional parties from Karnataka , Tamil Nadu , Andhra Pradesh , Orissa , and West Bengal , building new partnerships after the elections.

|
216 videos|855 docs|219 tests
|




















