Syllogism Based Questions | CSAT Preparation - UPSC PDF Download
Directions: In each questions given below, there are three statements followed by three conclusions numbered I, II and III. You have to take the given statements to be true, even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Q1: Statements
- All tablas are sitars.
- All sitars are harmoniums.
- All harmoniums are violins.
Conclusions
I. Some violins are tablas.
II. Some violins are sitars.
III. Some harmoniums are sitars.
(a) Only I follows
(b) Only II follows
(c) I and II follow
(d) All follow
Ans: (d)
Sol: 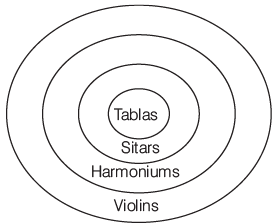
Hence, all follow.
Q2: Statements
- Some beauties are ugly.
- All ugly are smart.
- No smart is handsome.
Conclusions
I. Some smarts are beauties.
II. Some smarts are ugly.
III. No smart is ugly.
(a) I and II follow
(b) Either I or II follows
(c) Either II or III follows
(d) Only III follows
Ans: (a)
Sol: 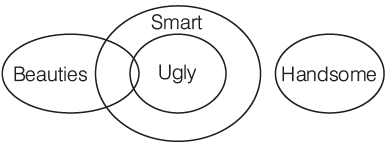
Hence, I and II follow.
Q3: Statements
- All mobiles are tablets.
- No PC is tablet.
- All calculators are PC’s.
Conclusions
I. No calculator is mobile.
II. No calculator is tablets.
III. No PC is mobile.
(a) Only III follows
(b) I and II follow
(c) II and III follow
(d) All follow
Ans: (d)
Sol: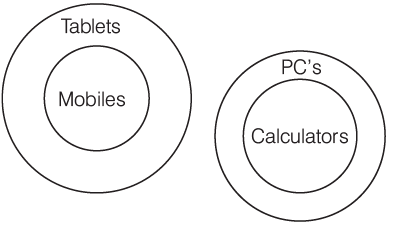
Hence, all follow.
Directions: In each questions given below, there are four statements followed by four conclusions numbered I, II, III and IV. You have to take the given statements to be true, even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statement.
Q4: Statements
- All televisions are computers.
- No computers are LCDs.
- No LCDs are VCR.
- No VCR is floppy disk.
Conclusions
I. No televisions are LCDs.
II. No televisions are VCR.
III. No LCDs are floppy disk.
IV. No computers are VCR.
(a) None follows except I
(b) None follows except II
(c) None follows except III
(d) All follow
Ans: (a)
Sol: 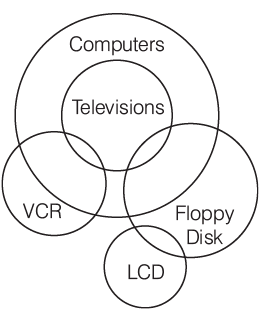
Hence, none follows except I.
Q5: Statements
- All buses are cars.
- Some buses are not motorcycles.
- No motorcycles are scooters.
- All scooters are tempos.
Conclusions
I. Some tempos are not cars.
II. Some tempos are not motorcycles.
III. No cars are tempos.
IV. Some cars are not motorcycles.
(a) Only IV follows
(b) Only II follows
(c) II and IV follow
(d) I and II follow
Ans: (a)
Sol: 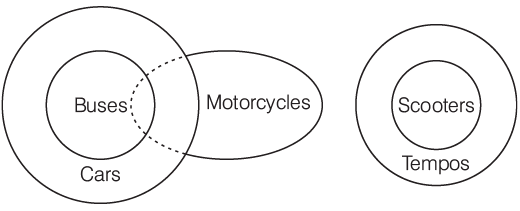
Hence, only IV follows.
Directions: In each of the questions given below, some statements followed by some conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Q6: Statements
- pencils are windows.
- windows are roads.
- Some roads are cups.
- All cups are chains.
Conclusions
I. Some chains are pencils.
II. Some cups are pencils.
III. Some chains are windows.
IV. Some roads are pencils.
(a) None follows
(b) Only II follows
(c) Only IV follows
(d) III and IV follow
Ans: (c)
Sol: 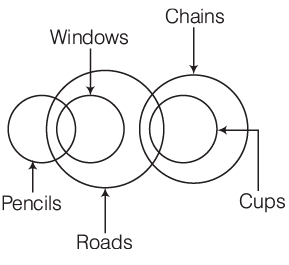
Hence, only Conclusion IV follows.
Q7: Statements
- Some beds are mirrors.
- Some mirrors are dolls.
- Some dolls are cheques.
- Some cheques are pins.
Conclusions
I. Some pins are dolls.
II. Some cheques are beds.
III. Some cheques are mirrors.
IV. Some dolls are beds.
(a) None follows
(b) Only I follows
(c) Only II follows
(d) Only III follows
Ans: (a)
Sol: 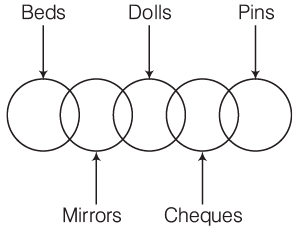
Hence, none follows.
Q8: Statements
- All chocolates are holders.
- No holder is a lamp.
- Some lamps are desks.
- All desks are pens.
Conclusions
I. Some pens are holders.
II. Some desks are lamps.
III. No pen is a holder.
IV. Some pens are chocolates.
(a) Only I follows
(b) Only II follows
(c) Only III follows
(d) Either I or III and II follow
Ans: (d)
Sol: 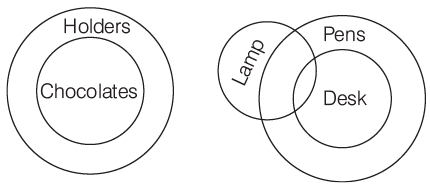
Conclusion II follows. Conclusions I and III do not follow. But they form a complementary pair.
Hence, either I or III and II follow.
Q9: Statements
- All glasses are rooms.
- Some rooms are planes.
- All planes are ducks.
- Some ducks are lanterns.
Conclusions
I. Some lanterns are planes.
II. Some ducks are rooms.
III. Some rooms are glasses.
IV. Some ducks are glasses.
(a) I and II follow
(b) II and III follow
(c) I, II and III follo
(d) All I, II, III and IV follow
Ans: (b)
Sol: 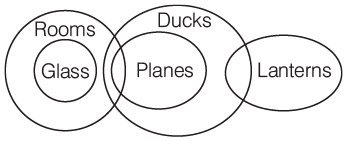
Hence, II and III follow.
Q10: Statements
- Some sweets are almonds.
- Some almonds are cashews.
- All cashews are pistachios.
Conclusions
I. All almonds are pistachios.
II. Some pistachios are sweets.
III. Some sweets are cashews.
IV. All almonds are either sweets or cashews.
(a) None follows
(b) II and III follow
(c) Only IV follows
(d) Either I or IV follows
Ans: (a)
Sol: 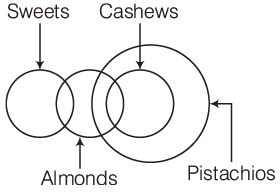
Hence, none follows.
Directions: In each question, a set of six statements is given, followed by four answer choices. Each of the answer choices has a combination of three statements from the given set of six statements. You are required to identify the answer choice in which the statements are logically related.
Q11: A. All synopses are poets.
B. Some synopses are mentors.
C. Some X are not mentors.
D. All X are poets.
E. All synopses are mentors.
F. All synopses are X.
(a) ACB
(b) AEC
(c) FEC
(d) DFA
Ans: (d)
Sol: The logically related statements are all synopses are poets, all X are poets and all synopses are X.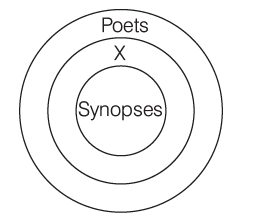
Hence, option (d) is correct.
Q12: A. Apples are not sweets.
B. Some apples are sweets.
C. All sweets are tasty.
D. Some apples are not tasty.
E. No apple is tasty.
F. Apples are sweets.
(a) CBD
(b) BDC
(c) CEA
(d) EAC
Ans: (c)
Sol: The logically related statements are, apples are not sweets, all sweets are tasty and no apple is tasty.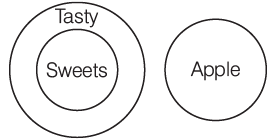
Hence, options (c) is correct
Q13: Consider the statements and find which two statements can be related to each other?
A. All P are Q.
B. Some P are not Q.
C. Some but not all, P are Q.
D. No P is Q.
(a) A and D
(b) A and C
(c) B and C
(d) A and B
Ans: (c)
Sol: The logically related statements are some P are not Q, so some but not all P are Q.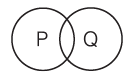
Q14: Consider the following three statements
I. Only students can participate in the race.
II. Some participants in the race are girls.
III. All girl participants in the race are invited for coaching.
Which one of the following conclusions can be drawn from the above statements?
(a) All participants in the race are invited for coaching
(b) All students are invited for coaching
(c) All participants in the race are students
(d) None of the statements follows
Ans: (c)
Sol: Here, make the consolidated Venn diagram and see which of the conclusion follows.
The three premises can be represented as shown below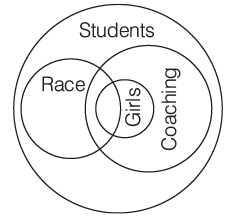
It can be seen from the diagram that only the girl participants in the race are invited for coaching. Thus, options (a) and (b) do not follow. Also, since only students can participate in the race, all participants in the race are students. Thus, option (c) follows.
Q15: ‘Every man is handsome.’ ‘All girls except a few are beautiful.’ If both these statements are true, then which of the following conclusions is definitely true?
Conclusions
I. Few girls are not beautiful.
II. All men are handsome.
III. Some handsome are beautiful.
IV. Girls are more beautiful than men.
(a) Only Conclusion III follows
(b) Conclusions III and IV follow
(c) Conclusion II follows
(d) Both Conclusions I and II follow
Ans: (d)
Sol: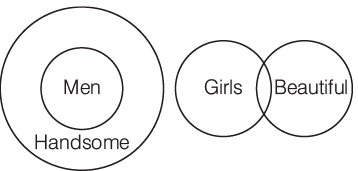
Hence, from above, we can conclude that some girls are not beautiful and all men are handsome.
|
205 videos|264 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Syllogism Based Questions - CSAT Preparation - UPSC
| 1. What is a syllogism and how is it used in logical reasoning? |  |
| 2. What are the common types of syllogisms used in logical reasoning? |  |
| 3. How can syllogisms be applied in UPSC exam preparation? |  |
| 4. What are some tips for solving syllogism questions effectively in exams? |  |
| 5. Are there any common mistakes to avoid while solving syllogism questions in exams? |  |
















