The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 13th April 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download

Data for better education, a brighter future for students
Why in News?
In the last two decades, discussions related to schooling and basic education in India have resulted in significant policy and priority changes. Recently, the ASER 2023: Beyond Basics report was executed in 28 districts across 26 states, involving 34,745 individuals aged 14-18. Concentrating on adolescents, the report introduces innovative strategies to enhance educational outcomes for young Indians and capitalize on the nation's demographic dividend.
What is the Annual Status of Education Report (ASER 2023: Beyond Basics)?
- The ASER 2023 report focuses on evaluating the educational status of young individuals in India.
- It was conducted in 28 districts spread over 26 states, engaging 34,745 youths aged between 14 and 18.
- The report concentrates on adolescents, offering insights to enhance learning results and leverage India's demographic dividend.
- Over the past two decades, discussions on schooling and basic education have led to significant policy shifts in India.
- The ASER 2023 report aims to suggest new ideas for improving education outcomes among young people in India.
- One of the key objectives is to make the most of the demographic dividend that India possesses.
Overview of ASER Survey
- About: ASER is a nationwide citizen-led household survey conducted by the NGO Pratham Education Foundation. It offers insights into the educational status of children in rural India.
- Initiation: The 'basic' ASER survey, which began in 2005, focuses on children aged 3 to 16. It evaluates their foundational reading and arithmetic skills through one-on-one assessments.
- Scheduling: Originally an annual endeavor, the survey transitioned to a biennial cycle starting in 2016.
Objectives of the 2023 ASER Survey
- Focus: The 2023 survey targeted 14-to-18-year-olds in rural India, emphasizing their practical application of reading and math skills in daily scenarios, along with their ambitions.
- Purpose: The primary aim was to gather data on various aspects of youth development in rural India. This data could be utilized by stakeholders across different sectors to shape policies and practices.
Key Domains Explored in the 2023 ASER Survey
- Activity: Understanding the current engagements of Indian youth.
- Ability: Assessing their fundamental and applied reading and math proficiencies.
- Digital Literacy: Investigating smartphone accessibility, usage patterns, and competency in performing basic tasks on smartphones.
- Aspirations: Exploring the career aspirations of the youth and identifying their role models.
What are the Key Findings of the Report?
- The youth in rural India are actively involved in a variety of activities.
- They exhibit varying levels of proficiency in both basic and applied reading and math skills.
- Access to smartphones is prevalent among these young individuals. They utilize smartphones for diverse purposes and can perform basic tasks on these devices.
- As for aspirations, the youth have diverse career goals and look up to specific individuals as their role models.
Enrollment and Vocational Training
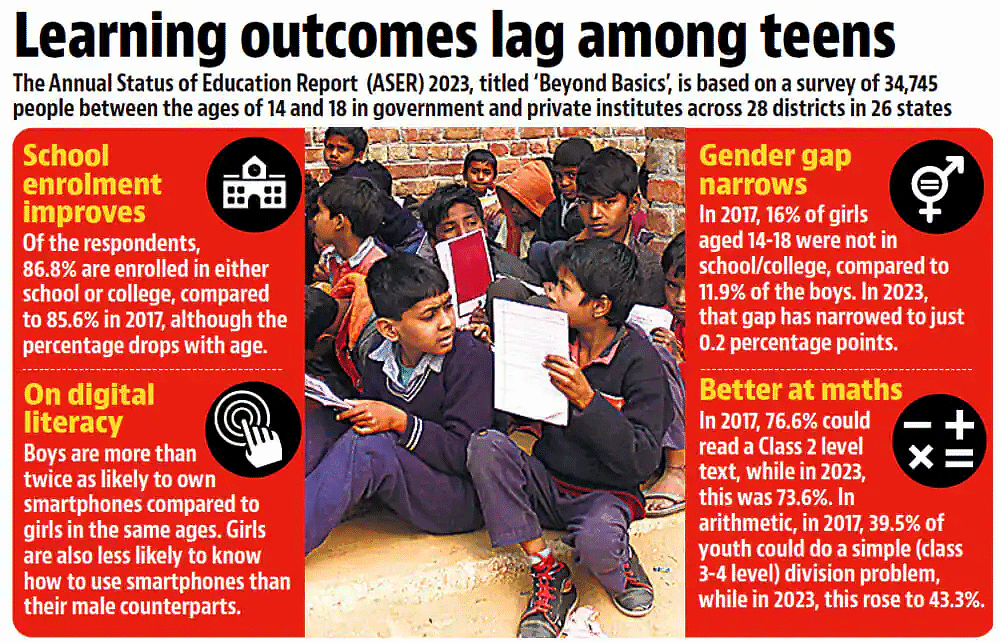
- Enrollment Statistics: Among 14-18-year-olds, 86.8% are currently enrolled in educational institutions. Notably, the enrollment rate differs significantly between age groups, with 3.9% of 14-year-olds not enrolled compared to 32.6% of 18-year-olds.
- Vocational Training Focus: At the college level, 16.2% of youths are engaged in vocational training. The majority opt for short-duration courses, typically lasting six months or less.
Foundational Skills and Everyday Applications
- Literacy and Numeracy: Approximately a quarter of 14-18-year-olds struggle to read fluently at a standard II level in their regional language. Additionally, more than half encounter challenges with division problems. Specifically, only 43.3% can solve 3-digit by 1-digit division correctly.
- Numerical Proficiency: While nearly 85% can measure length with precision from a 0 cm starting point, this ability drops to 39% when the starting point varies. Around 50% excel at other common calculations.
- Practical Applications: Among those who can read at least a standard I level text, roughly two-thirds can successfully respond to questions based on written instructions. In financial realms, over 60% can manage budgets, about 37% can apply discounts, but merely 10% can calculate repayments accurately. Notably, females generally perform less proficiently than males across these tasks.
Digital Literacy and Skills
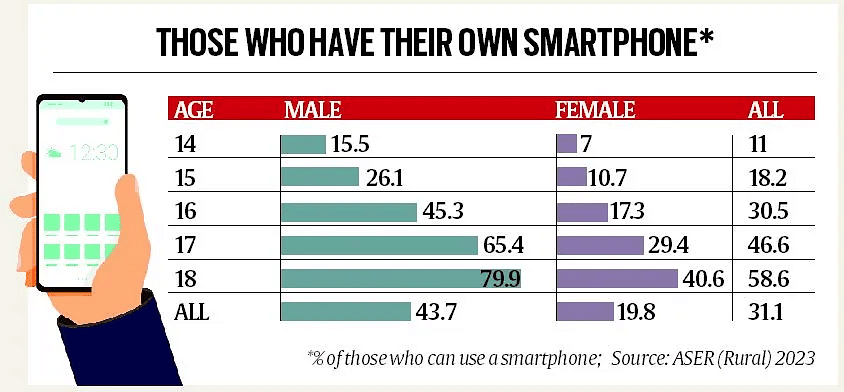
- Digital Access: Close to 90% of youths have access to smartphones at home and possess the necessary skills to operate them. However, females exhibit lower rates of proficiency in using smartphones and computers compared to males.
- Online Proficiency: While around 50% of social media users are familiar with online safety settings, a considerable portion remains unaware. Tasks such as browsing for information, setting alarms, and using Google Maps for directions are performed by varying proportions of youths, with males generally outperforming females in digital tasks.
What are the Key Concerns Highlighted in the Report?
Challenges Posed by Limited Academic Success:
- Low levels of Foundational Numeracy: The report highlights inadequate levels of foundational numeracy which may significantly hinder the ability of young individuals to handle day-to-day calculations.
- Flat Learning Trajectories: Over the time, there hasn't been significant improvement in the academic progress of students.
Challenges Posed by Curriculum Constraints:
- Acute Academic Competition: Parents in India often harbor overambitious aspirations for their children. These aspirations of parents translate into acute academic competition, widespread coaching, and heavy expenditure by families.
- All of these add to examination pressures often accompanied by severe disappointments for the student and the family if exam results are poor.
- Overambitious Curriculum: The Indian education system has an “over-ambitious” curriculum which does not take into account that many students have large learning deficits and are unable to cope with the grade level curriculum.
- For instance, in 2009, the only year when two states in India participated in PISA (Programme for International Student Assessment), the results were second last, just above Kyrgyzstan.
Challenges Posed by Ambiguous Aspirations:
- Not Motivated to Study: In the survey findings, a larger proportion of boys than girls reported not wanting to study after class 12. During the discussion, girls discussed wanting to study at least to undergraduate level, while boys talked about earning money.
- Not surprisingly, the proportion of youth who are currently not enrolled in school or college rises with age from 3.9% of 14-year-olds to 10.9% of 16-year-olds and 32.6% of 18-year-olds.
- The Dearth of Clarity: There is a lack of clear guidance for students when it comes to making decisions about their future. Many students are unsure about what to study, how much more education they need, and what kinds of jobs they should be aiming for.
- One out of every five youths were unable to name any type of work or job that they aspired to,” mentions the ASER report.
- No Role Model: From the figures shared in the ASER report, of the students surveyed, 42.5% of males and 48.3% of females did not have a role model for their aspired work.
Challenges posed by Digital Deprivation:
- Less Technical inclination: Most of the young people in this age group were enrolled in the Arts/Humanities stream. In Std XI or higher, more than half are enrolled in the Arts/Humanities stream (55.7%), followed by STEM (31.7%) and Commerce (9.4%).
- Females are less likely to be enrolled in the STEM stream (28.1%) than males (36.3%).
- Surface Layer Use of Digital Component: Close to 80% of the youth report having used their smartphone to do an entertainment-related activity, such as watching a movie or listening to music, during the reference week.
- The digital component is interesting because, at one level, it shows that everybody knows how to use the basic things. But they’re not using it in depth; they’re using the surface layer, say, mainly engaging with social media
- Gender gap in Tech Access: Males are more than twice as likely to own their own smartphone than females, and therefore were likely spending far more time using the device and using it for a wider variety of tasks.
What Should be the Way Forward ?
- Ease Out Early Childhood Struggles:
- Provide financial aid and grants to economically disadvantaged students as many of these students need to earn and support their families financially during this age group and it's a vicious cycle.
- Among girls, shifting social norms with regard to the appropriate age of marriage emerged as a key driver of young women's ability to study further.
- Comprehensive Strategy for Learning Improvement:
- Develop a comprehensive strategy for enhancing learning outcomes that caters to diverse learning needs and styles of students.
- Implement personalized learning approaches that consider individual student strengths and weaknesses to maximize educational growth.
- Utilize technology effectively to create interactive learning experiences that engage students and facilitate better understanding of complex concepts.
- Encourage collaborative learning environments that promote peer-to-peer interaction and knowledge sharing among students.
- Flexible Education System
- Embracing flexibility involves utilizing technology to support remote learning, online resources, and interactive platforms, ultimately enhancing the educational journey. Students should have the option to enroll in diverse learning and skill-building opportunities.
- Reform Assessments
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 emphasizes achieving 100% secondary school enrollment by meticulously monitoring student enrollment, attendance, and academic progress. This approach ensures that students receive appropriate support to either rejoin school or bridge learning gaps.
- One way to alleviate examination pressure is by reevaluating the structure and timing of assessments.
- Pathway Linking
- Integrating concepts from secondary school reforms with initiatives like NIPUN is vital for translating theoretical reform ideas into practical implementations. Continuous monitoring of outcomes is crucial for progress and eventual success.
- Establishing a clear connection between educational reform strategies and tangible outcomes is essential for driving improvements and ensuring successful outcomes.
Conclusion
It is imperative for emerging economies to empower the youth with essential knowledge, skills, and opportunities to drive their own progress and that of their families and communities. Realizing the full potential of India's anticipated "demographic dividend" and "digital dividend" hinges on the comprehensive execution of these strategies.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
FAQs on The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 13th April 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. क्या शिक्षा के लिए डेटा का उपयोग छात्रों के भविष्य को उज्ज्वल बनाने में मददगार है? |  |
| 2. कैसे शिक्षा के क्षेत्र में डेटा का उपयोग बेहतर भविष्य के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है? |  |
| 3. कैसे डेटा के उपयोग से छात्रों को शिक्षा के क्षेत्र में अधिक सक्षम किया जा सकता है? |  |
| 4. क्या छात्रों के शिक्षा में डेटा का उपयोग उनके भविष्य को सुधारने में मददगार हो सकता है? |  |
| 5. कैसे डेटा शिक्षा के क्षेत्र में नए और अद्वितीय शिक्षा सुविधाओं की विकसिति में मदद कर सकता है? |  |




















